https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6Mmy4_d11P1iPFSgX7GOBw
先问一个问题,JavaScript有几种数据类型?
number、string、boolean、null、undefined、symbol、bigint、object
其中 bigint 是 ES2020 新增的数据类型,而早在 TS3.2 时便成为 TS 的标准,其实还有好多 ES+ 标准是 TS 率先提出的,可见 TS 在很多方面是走在了 ES 前列。
TypeScript又新增了多少种数据类型?
any、unknown、enum、void、never、tuple…
其实 TypeScript 更重要的是通过 interface 和 type 赋予了用户自定义数据类型的能力,使数据在流转的过程中始终能轻易被用户掌握。
接口智能提示
interface Seal {name: string;url: string;}interface API {"/user": { name: string; age: number; phone: string };"/seals": { seal: Seal[] };}const api = <URL extends keyof API>(url: URL): Promise<API[URL]> => {return fetch(url).then((res) => res.json());};
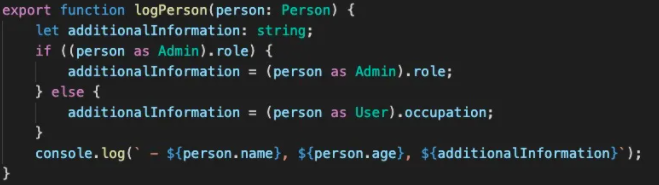
正确的使用类型收缩
使用类型断言
使用类型保护
使用 is,in,typeof,instanceof 等,使得 TypeScript 能够 get 到当前的类型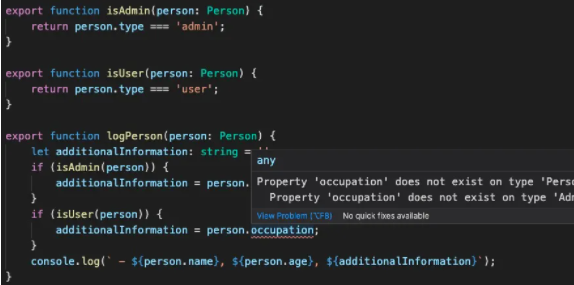
常用的高级类型
类型编程是对类型进行编程,可以利用 keyof 对属性做一些扩展,省的我们要重新定义一下接口,造成很多冗余代码
type Partial<T> = {[P in keyof T]?: T[P];};type Required<T> = {[P in keyof T]-?: T[P];};type Pick<T, K extends keyof T> = {[P in K]: T[P];};type Exclude<T, U> = T extends U ? never : T;// 相当于: type A = 'a'type A = Exclude<'x' | 'a', 'x' | 'y' | 'z'>type Omit<T, K extends keyof any> = Pick<T, Exclude<keyof T, K>>;type Record<K extends keyof any, T> = {[P in K]: T;};interface User {id: number;age: number;name: string;};// 相当于: type PartialUser = { id?: number; age?: number; name?: string; }type PartialUser = Partial<User>// 相当于: type PickUser = { id: number; age: number; }type PickUser = Pick<User, "id" | "age">// 相当于: type OmitUser = { age: number; name: string; }type OmitUser = Omit<User, "id">type AnimalType = 'cat' | 'dog' | 'frog';interface AnimalDescription { name: string, icon: string }const AnimalMap: Record<AnimalType, AnimalDescription> = {cat: { name: '猫', icon: ' '},dog: { name: '狗', icon: ' ' },forg: { name: '蛙', icon: ' ' }, // Hey!};