Lambda表达式是一种定义匿名函数对象的简便方法,在调用的位置或作为参数传递给函数的位置。Lambda通常用于封装传递给算法或异步方法的少量代码行。
原理:编译器会把一个lambda表达式生成一个匿名类的匿名对象,并在类中重载函数调用运算符。
auto print = []{cout << "zhangxiang" << endl; };//会被编译器翻译成为如下//用给定的lambda表达式生成相应的类class print_class{public:void operator()(void) const{cout << "zhangxiang" << endl;}};//用构造的类创建对象,print此时就是一个函数对象auto print = print_class();
auto add = [](int a, int b){return a + b; };
//会被编译器翻译成为如下形式
class add_class
{
public:
auto operator()(int a, int b) const
{
return a + b;
}
};
auto add = add_class();
值捕获
int year = 19900212;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
//采用值捕获,捕获所有的已定义的局部变量,如year,name
auto print = [=](){
cout << year << ends << name << endl;
};
//会被编译器翻译成为如下形式
int year = 19900212;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
class print_class
{
public:
//根据捕获列表来决定构造函数的参数列表形式
print_class(int year, char *name) :year(year), name(name)
{
}
void operator()(void) const
{
cout << year << ends << name << endl;
}
private:
int year;
char *name;
};
auto print = print_class(a, str);
引用捕获
int year = 19900212;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
auto print = [&](){
year++;
cout << year << ends << name << endl;
};
//会被编译器翻译成为如下形式
int year = 19900212;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
class print_class
{
public:
//由于是引用捕获,参数列表采用引用的方式
print_class(int &year, char *&name) :year(year), name(name)
{
}
void operator()(void) const
{
year++; //编译通过,const对引用类型无效
cout << year << ends << name << endl;
}
private:
int &year;
char *&name;
};
混合捕获
int year = 19900212;
int shoes = 42;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
auto show = [&, shoes]()mutable{
shoes++;
year++;
cout << year << ends << shoes << ends << name << endl;
};
//会被编译器翻译成为如下形式
int year = 19900212;
int shoes = 42;
char *name = "zhangxiang";
class show_class
{
private:
int &year;
mutable int shoes;
char *&name;
public:
show_class(int &year, int shoes, char *&name) :year(year), shoes(shoes), name(name)
{
}
void operator()(void)const
{
shoes++;
year++;
cout << year << ends << shoes << ends << name << endl;
}
};
auto show = show_class(year, shoes, name);
show();
默认情况下,经过值捕获的变量是不可以被修改的,除非在参数列表后加关键字mutable。
Lambda 表达式,实际上就是提供了一个类似匿名函数的特性, 而匿名函数则是在需要一个函数,但是又不想费力去命名一个函数的情况下去使用的。这样的场景其实有很多很多, 所以匿名函数几乎是现代编程语言的标配。
Syntax
[capture clause 捕获子句] (parameters参数列表 可有可无 也称为lambda声明符) mutable (可选) 异常属性-> return-type
{
definition of method
}
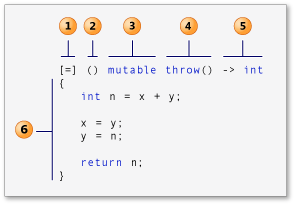
- 捕获子句 (也称为 c + + 规范中的 引导 。 )
- 参数列表 可有可无. (也称为 lambda 声明符)
- 可变规范 可有可无.
- 异常规范 可有可无.
- 尾随-返回类型 可有可无.
- lambda 体。
Generally return-type in lambda expression are evaluated by compiler itself and we don’t need to specify that explicitly and -> return-type part can be ignored but in some complex case as in conditional statement, compiler can’t make out the return type and we need to specify that.
Lambda 表达式的返回类型是由编译器本身来进行确定
// C++ program to demonstrate lambda expression in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print vector
void printVector(vector<int> v)
{
// lambda expression to print vector
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int i)
{
std::cout << i << " ";
});
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v {4, 1, 3, 5, 2, 3, 1, 7};
printVector(v);
// below snippet find first number greater than 4
// find_if searches for an element for which
// function(third argument) returns true
vector<int>:: iterator p = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int i)
{
return i > 4;
});
cout << "First number greater than 4 is : " << *p << endl;
// function to sort vector, lambda expression is for sorting in
// non-decreasing order Compiler can make out return type as
// bool, but shown here just for explanation
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const int& a, const int& b) -> bool
{
return a > b;
});
printVector(v);
// function to count numbers greater than or equal to 5
int count_5 = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int a)
{
return (a >= 5);
});
cout << "The number of elements greater than or equal to 5 is : "
<< count_5 << endl;
// function for removing duplicate element (after sorting all
// duplicate comes together)
p = unique(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int a, int b)
{
return a == b;
});
// resizing vector to make size equal to total different number
v.resize(distance(v.begin(), p));
printVector(v);
// accumulate function accumulate the container on the basis of
// function provided as third argument
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int f = accumulate(arr, arr + 10, 1, [](int i, int j)
{
return i * j;
});
cout << "Factorial of 10 is : " << f << endl;
// We can also access function by storing this into variable
auto square = [](int i)
{
return i * i;
};
cout << "Square of 5 is : " << square(5) << endl;
}
A lambda expression can have more power than an ordinary function by having access to variables from the enclosing scope.
Capture 子句
所谓捕获列表,其实可以理解为参数的一种类型,Lambda 表达式内部函数体在默认情况下是不能够使用函数体外部的变量的, 这时候捕获列表可以起到传递外部数据的作用。
空 capture 子句 [ ] 指示 lambda 表达式的主体不访问封闭范围中的变量。
[&total, factor]
[factor, &total]
[&, factor]
[factor, &]
[=, &total]
[&total, =]
值捕获
与参数传值类似,值捕获的前提是变量可以拷贝,不同之处则在于,被捕获的变量在 Lambda 表达式被创建时拷贝, 而非调用时才拷贝:
void lambda_value_capture() {
int value = 1;
auto copy_value = [value] {
return value;
};
value = 100;
auto stored_value = copy_value();
std::cout << "stored_value = " << stored_value << std::endl;
// 这时, stored_value == 1, 而 value == 100.
// 因为 copy_value 在创建时就保存了一份 value 的拷贝
}
引用捕获
与引用传参类似,引用捕获保存的是引用,值会发生变化。
void lambda_reference_capture() {
int value = 1;
auto copy_value = [&value] {
return value;
};
value = 100;
auto stored_value = copy_value();
std::cout << "stored_value = " << stored_value << std::endl;
// 这时, stored_value == 100, value == 100.
// 因为 copy_value 保存的是引用
}
隐式捕获
手动书写捕获列表有时候是非常复杂的,这种机械性的工作可以交给编译器来处理,这时候可以在捕获列表中写一个 & 或 = 向编译器声明采用引用捕获或者值捕获.
总结一下,捕获提供了 Lambda 表达式对外部值进行使用的功能,捕获列表的最常用的四种形式可以是:
- [] 空捕获列表
- [name1, name2, …] 捕获一系列变量
- [&] 引用捕获, 让编译器自行推导引用列表
- [=] 值捕获, 让编译器自行推导值捕获列表
表达式捕获
上面提到的值捕获、引用捕获都是已经在外层作用域声明的变量,因此这些捕获方式捕获的均为左值,而不能捕获右值。
C++14 给与了我们方便,允许捕获的成员用任意的表达式进行初始化,这就允许了右值的捕获, 被声明的捕获变量类型会根据表达式进行判断,判断方式与使用auto本质上是相同的: ```cppinclude
include
int main() {
auto important = std::make_unique
在上面的代码中,`important` 是一个独占指针,是不能够被捕获到的,这时候我们需要将其转移为右值, 在表达式中初始化。
<a name="Itgnf"></a>
## 以函数作为参数
```cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int add(int x, int y){return x+y;}
int sub(int x, int y){return x-y;}
int operation (int x, int y,int (*function)(int,int)){return function(x,y);}
int operation2(int x, int y,std::function<int(int, int)> function){return function(x,y);}
int main()
{
std::cout <<"Values 1 & 3. Pointer function: Add:"<<operation (1,3,&add)<<" Sub:"<<operation (1,3,&sub) << std::endl;
std::cout <<"Values 1 & 3. std::function : Add:"<<operation2(1,3,&add)<<" Sub:"<<operation2(1,3,&sub) << std::endl;
}
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangxiangdavaid/article/details/44064765

