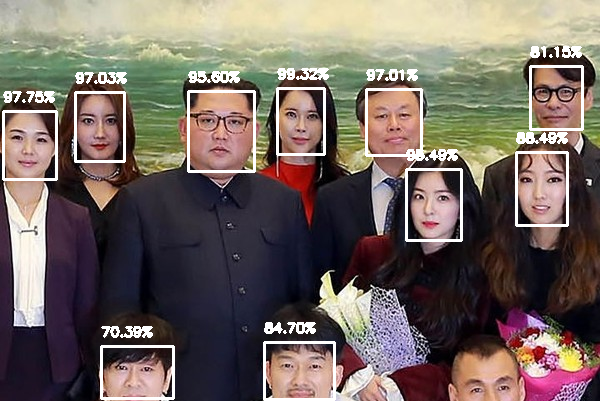
Face Detection
The more accurate OpenCV face detector is deep learning based, and in particular, utilizes the Single Shot Detector (SSD) framework with ResNet as the base network.
#!/usr/bin/env python# encoding: utf-8from imutils.video import VideoStreamimport numpy as npimport argparseimport cv2import imutilsimport timedef detected_draw(args, img, detections):(h, w) = img.shape[:2]# loop over the detectionsfor i in range(0, detections.shape[2]):# extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with the predictionconfidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]# filter out weak detections by ensuring the `confidence` is greater than the minimum confidenceif confidence > args["confidence"]:# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for the objectbox = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")# draw the bounding box of the face along with the associated probabilitytext = "{:.2f}%".format(confidence * 100)y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10cv2.rectangle(img, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (255, 255, 255), 2)cv2.putText(img, text, (startX, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (255, 255, 255), 2)passpassdef img_detect(args):# load our serialized model from diskprint("[INFO] loading model...")net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"])# load the input image and construct an input blob for the image# by resizing to a fixed 300x300 pixels and then normalizing itimage = cv2.imread(args["image"])blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(image, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0))# pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and predictionsprint("[INFO] computing object detections...")net.setInput(blob)detections = net.forward()detected_draw(args, image, detections)# show the output imagecv2.imshow("Output", image)cv2.waitKey(0)passdef cam_detect(args):# load our serialized model from diskprint("[INFO] loading model...")net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"])# initialize the video stream and allow the camera sensor to warm upprint("[INFO] starting video stream...")vs = VideoStream(src=0).start()#for Raspberry Pi camera#vs = VideoStream(usePiCamera=True).start()time.sleep(2.0)# loop over the frames from the video streamwhile True:# grab the frame from the threaded video stream and resize it# to have a maximum width of 400 pixelsframe = vs.read()frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=800)# grab the frame dimensions and convert it to a blobblob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0))# pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and predictionsnet.setInput(blob)detections = net.forward()detected_draw(args, frame, detections)# show the output framecv2.imshow("Frame", frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loopif key == ord("q"):breakpass# do a bit of cleanupcv2.destroyAllWindows()vs.stop()passif __name__ == '__main__':# construct the argument parse and parse the argumentsap = argparse.ArgumentParser()ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=False, default='', help="path to input image")ap.add_argument("-p", "--prototxt", required=False, default='deploy.prototxt', help="path to Caffe 'deploy' prototxt file")ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", required=False, default='res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000_fp16.caffemodel', help="path to Caffe pre-trained model")ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5, help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")args = vars(ap.parse_args())if len(args['image']) == 0:cam_detect(args)else:img_detect(args)pass
refs:
the Caffe prototxt file: deploy.prototxt
the Caffe weight file: res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000_fp16.caffemodel

