Open Graph Benchmark (OGB) datasets
OGB是一个真实的、大规模的、不同的基准数据集的集合,用于在图上进行机器学习。
ref1: https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/notes/create_gnn.html#implementing-the-gcn-layer
ref2: https://blog.csdn.net/Jenny_oxaza/article/details/107561125
ref3: https://blog.csdn.net/Jenny_oxaza/rss/list?spm=1001.2014.3001.5494
消息传递图神经网络: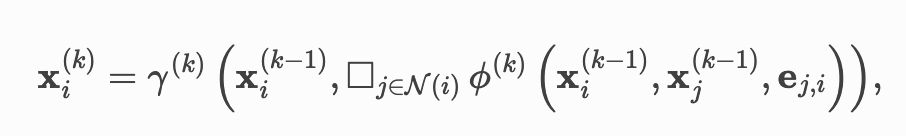
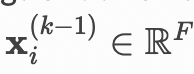 表示节点
表示节点在
层的节点特征
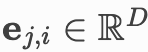 表示从节点
表示从节点到节点
的边特征
表示一个可微的置换不变函数,如sum、mean、max
和
表示可微函数,如MLPs(Multi Layer Perceptions)
message()
update()
- MessagePassing(aggr=”add”, flow=”source_to_target”, node_dim=-2): 定义聚合使用”add”, “mean”, “max”,消息传递的流方向要么”source_to_target”要么”target_to_source”,node_dim指示沿着哪个轴传播
- MessagePassing.propagate(edge_index, size=None, kwargs): 开始传播消息的初始调用。接收边索引和所有用于构造消息和点嵌入的附加数据。propagate() **不仅限于 [N, N] 的方形邻接矩阵中交换消息,还可通过传递size=(N, M) 作为附加参数,在(N, M)的一般稀疏分配矩阵中交换信息,如二分图。若设为None,则赋值矩阵为方阵。对于具有两个独立的节点和索引集的二分图,且每个集合拥有自己的信息,这种分割可通过将信息传递为元组来标记,如x=(x_N, x_M)
- MessagePassing.message(…): 类似于
,构造节点
的消息,若flow=”source_to_target”,则每个边
;若flow=”target_to_source”,则每个边
。可接受最初传给propagate(…)的任何参数。此外,传递给propagate(…)的张量可通过将 _i 或 _j 附加到变量名,从而映射到各自节点
或
,例如x_i和x_j。通常将
称为聚集信息的中心点,将
称为邻近节点,因为这是最常用的表示方法。
- MessagePassing.update(aggr_out, …): 对每个节点
,进行类似于
的节点嵌入更新。接收聚合的输出作为第一个参数,以及最初传递给propagate(…)的任何参数。
GCN层的数学定义: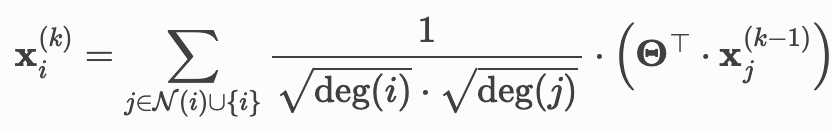
相邻节点特征首先通过权重矩阵进行变换,按其度进行归一化,最后加和。
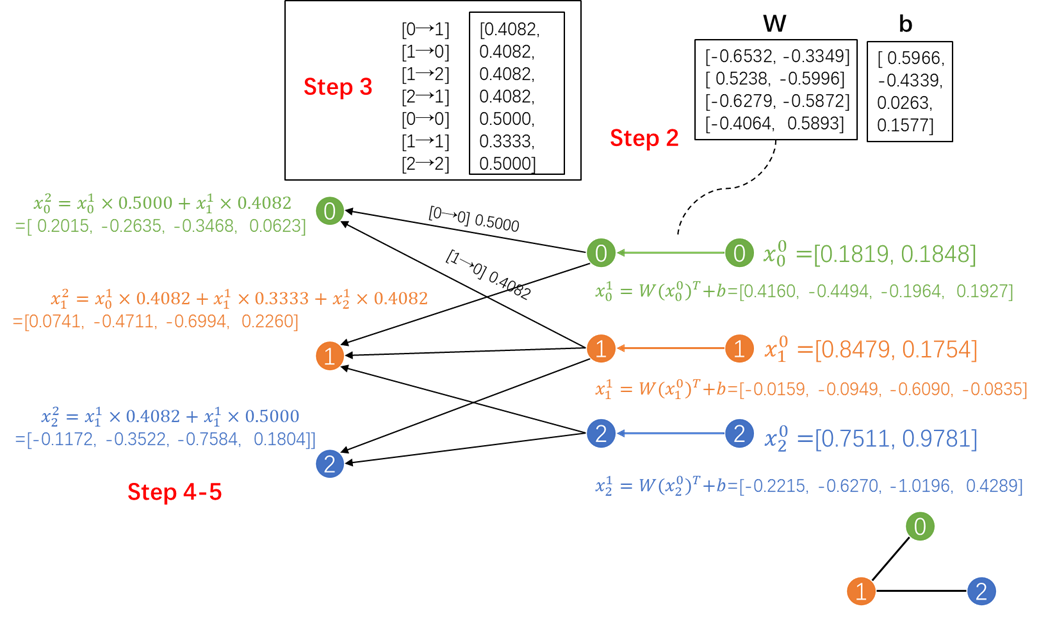
- step1. 在邻接矩阵中加入self-loops。add_self_loops最终返回两个值——“edge_index, edge_weight”。
 ```python
import torch
from torch_geometric.utils import add_self_loops, degree
```python
import torch
from torch_geometric.utils import add_self_loops, degree
x = torch.tensor([[-1], [0], [1]], dtype=torch.float) edge_index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2], [1, 0, 2, 1]], dtype=torch.long) print(‘original edge_index’) print(edge_index)
tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1]])
edgeindex, = add_self_loops(edge_index, num_nodes=x.size(0)) print(‘new edge_index’) print(edge_index)
tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2]])
row, col = edge_index
tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2]])
deg = degree(row, x.size(0), dtype=x.dtype) print(deg) # tensor([2., 3., 2.]) deg_inv_sqrt = deg.pow(-0.5) print(deg_inv_sqrt) # tensor([0.7071, 0.5774, 0.7071]) print(deg_inv_sqrt[row]) # tensor([0.7071, 0.5774, 0.5774, 0.7071, 0.7071, 0.5774, 0.7071]) print(deg_inv_sqrt[col]) # tensor([0.5774, 0.7071, 0.7071, 0.5774, 0.7071, 0.5774, 0.7071])
- step2. 线性变换节点特征矩阵。通过一个线性层torch.nn.Linear实现。- step3. 计算归一化系数。节点的度可以通过torch_geometric.utils.degree实现。- step4. 在中归一化节点特征。- step5. 加和邻居节点特征("add"聚合)。step1~step3常在消息传递之前进行计算,可使用**MessagePassing**基类轻松处理step4~step5.```pythonimport torchfrom torch_geometric.nn import MessagePassingfrom torch_geometric.utils import add_self_loops, degreeclass GCNConv(MessagePassing):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):super(GCNConv, self).__init__(aggr='add') # "Add" aggregation (Step 5).self.lin = torch.nn.Linear(in_channels, out_channels)def forward(self, x, edge_index):# x has shape [N, in_channels]# edge_index has shape [2, E]# Step 1: Add self-loops to the adjacency matrix.edge_index, _ = add_self_loops(edge_index, num_nodes=x.size(0))# Step 2: Linearly transform node feature matrix.x = self.lin(x)# Step 3: Compute normalization.row, col = edge_indexdeg = degree(col, x.size(0), dtype=x.dtype)deg_inv_sqrt = deg.pow(-0.5)norm = deg_inv_sqrt[row] * deg_inv_sqrt[col]# Step 4-5: Start propagating messages.return self.propagate(edge_index, x=x, norm=norm)def message(self, x_j, norm):# x_j has shape [E, out_channels]# Step 4: Normalize node features.return norm.view(-1, 1) * x_j
x = torch.tensor(torch.rand(3,2), dtype=torch.float)
edge_index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1]], dtype=torch.long)
conv = GCNConv(2, 4)
x is
tensor([[0.1819, 0.1848],
[0.8479, 0.1754],
[0.7511, 0.9781]])
----Step 1: Add self-loops to the adjacency matrix.----
tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2]])
----Step 2: Linearly transform node feature matrix.----
linear weight is
Parameter containing:
tensor([[-0.6532, -0.3349],
[ 0.5238, -0.5996],
[-0.6279, -0.5872],
[-0.4064, 0.5893]], requires_grad=True)
linear bias is
Parameter containing:
tensor([ 0.5966, -0.4339, 0.0263, 0.1577], requires_grad=True)
transformed x is
tensor([[ 0.4160, -0.4494, -0.1964, 0.1927],
[-0.0159, -0.0949, -0.6090, -0.0835],
[-0.2215, -0.6270, -1.0196, 0.4289]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
----Step 3: Compute normalization.----
tensor([0.4082, 0.4082, 0.4082, 0.4082, 0.5000, 0.3333, 0.5000])
----Step 4-5: Start propagating messages.----
tensor([[ 0.2015, -0.2635, -0.3468, 0.0623],
[ 0.0741, -0.4711, -0.6994, 0.2260],
[-0.1172, -0.3522, -0.7584, 0.1804]], grad_fn=<ScatterAddBackward>)
边卷积层 edge convolutional layer 的数学定义: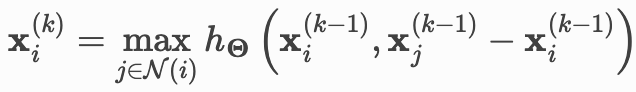
为MLP,类似于GCN,边卷积层同样继承于基础类MessagePassing,不同在于采用max函数作为
函数。
边卷积层的主要理论来自于论文Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds,这篇文章提出一种边卷积(EdgeConv)操作,来完成点云中点与点之间关系的建模,使得网络能够更好地学习局部和全局特征。具体可以看这两篇博客:【深度学习——点云】DGCNN(EdgeConv)和论文笔记:DGCNN(EdgeConv)。
import torch
from torch.nn import Sequential as Seq, Linear, ReLU
from torch_geometric.nn import MessagePassing
class EdgeConv(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(EdgeConv, self).__init__(aggr='max')
self.mlp = Seq(Linear(2*in_channels, out_channels),
ReLU(),
Linear(out_channels, out_channels))
def forward(self, x, edge_index):
# x has shape [N, in_channels]
# edge_index has shape [2, E]
return self.propagate(edge_index, x=x)
def message(self, x_i, x_j):
# x_i has shape [E, in_channels]
# x_j has shape [E, in_channels]
tmp = torch.cat([x_i, x_j - x_i], dim=1) # tmp has shape [E, 2*in_channels]
return self.mlp(tmp)
econv = EdgeConv(2, 4)
econv(x, edge_index)
# 边卷积实际上是一个动态卷积,它使用特征空间内的最近邻重新计算每一层的图
# PyTorch geometry附带一个GPU加速的批处理k-NN图形生成方法 —— torch_geometric.nn.knn_graph
from torch_geometric.nn import knn_graph
class DynamicEdgeConv(EdgeConv):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, k=6):
super(DynamicEdgeConv, self).__init__(in_channels, out_channels)
self.k = k
def forward(self, x, batch=None):
edge_index = knn_graph(x, self.k, batch, loop=False, flow=self.flow)
return super(DynamicEdgeConv, self).forward(x, edge_index)
deconv = DynamicEdgeConv(2, 3)
deconv(x, edge_index)

