在2019年9月之前,UiPath Cloud Orchestrator REST API的身份验证使用基本身份验证。但从2019年9月开始,UiPath Cloud Orchestrator REST API的身份验证已更改为OAuth。本文将使用postman解释调用步骤和操作,帮助读者理解操作过程,并且将为您部分python简单调用示范。 调用的范例使用 python 语言,读者也可以改成 php,go, c#, java, kotlin等语言。
基本概念¶
什么是API?¶
API是应用程序编程接口(Application Programming Interface)的首字母缩写,它是一种中介协议,允许两个应用程序相互通信。
API的示例?¶
当您安装和使用移动应用程序时,该移动应用程序将连接到Internet并将数据发送到服务器。然后,服务器检索该数据,对其进行解释,执行必要的操作,然后将其发送回手机。然后,应用程序将解释该数据,并以可读的方式为您提供所需的信息。这就是API,所有这些都是通过API进行的。
Orchestrator API的用途是什么?¶
Orchestrator API 可用于通过任何服务器、平板、手机的应用程序(甚至包括UiPath Studio /机器人)与Orchestrator进行交互。
通过API可以实现的基本功能是
- 开始/停止工作
- 检查机器人的状态
- 创建/修改资产
- 创建一个队列并将项目推入队列
- 检查作业状态
- 获取环境,流程,机器人,队列,作业详细信息等等…
到本文结尾您将学到什么?¶
您将能够:
- OAuth认证
- 从Orchestrator获取所有机器人数据
- 获取机器人的状态
- 从Orchestrator获取所有流程(Process)
- 从Orchestrator获取所有工作(Job)
- 从Orchestrator获取所有发行版(Release)
- 从Orchestrator开始作业(job)
- 停止Orchestrator的工作
- 从Orchestrator获取所有资产(Asset)
- 更新资产
- 创建队列(Queue)
- 添加队列元素(Item)
注意: 我们使用postman演示本文的调用步骤,并且给出对应的python调用示范
调用步骤¶
为了井井有条,我创建了一个json模板来存储安全信息。该JSON模板存储在一个文件名为settings.json。所有这些属性的含义,在阅读本文时,这一点将变得很清楚。 您的初始settings.json文件应类似于以下示例。 将本文中的json直接剪切并粘贴到记事本(Windows)或TextEdit(Mac)中,然后填写您的用户名和两个密码,然后保存文件。
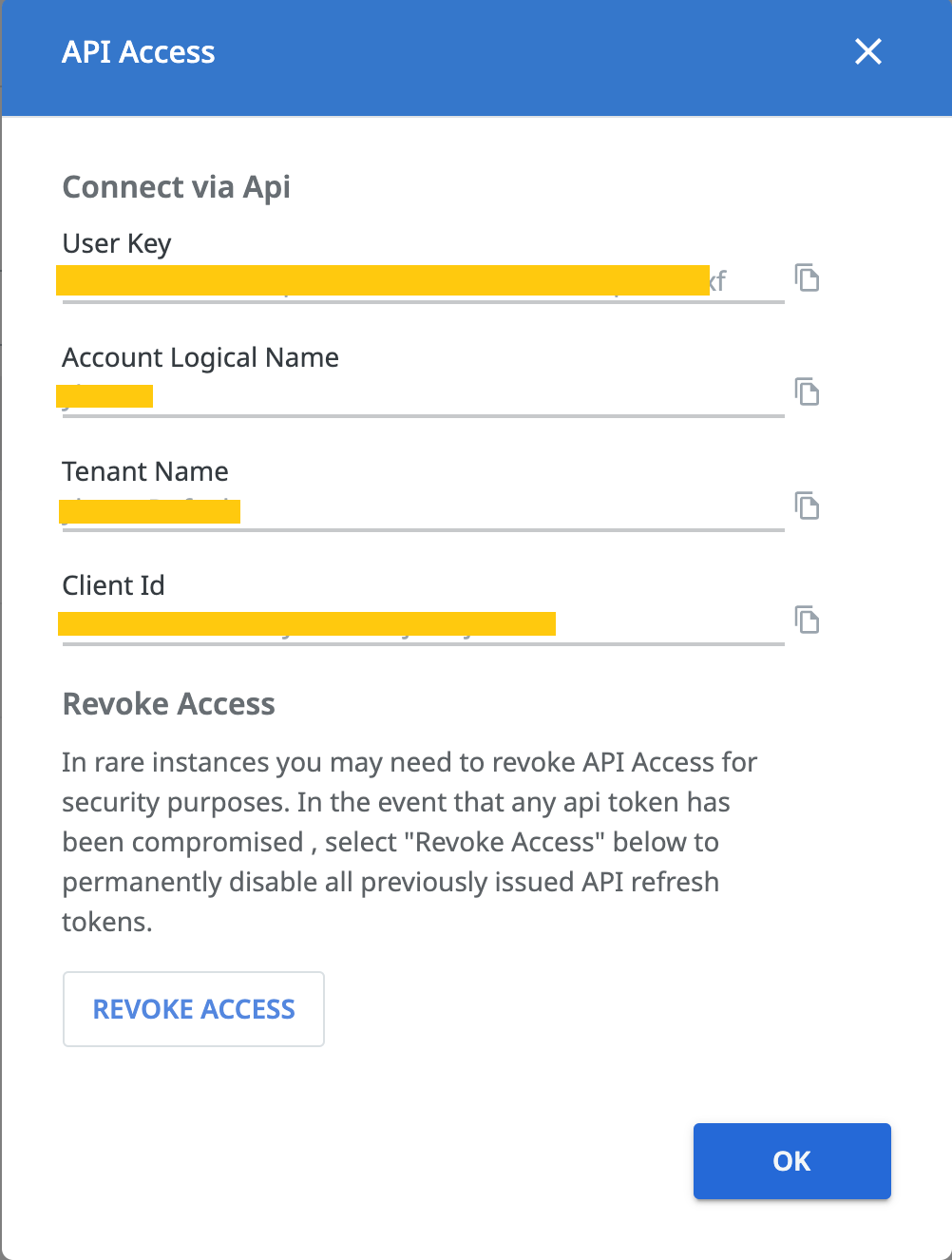
步骤一 从 Orchestrator 账户中获取 UserKey等 API OAuth 参数¶
登录进入你的 Orchestrator 账户,进入以下界面,复制参数 UserKey, AccountLogicName, TenantName, ClientId。 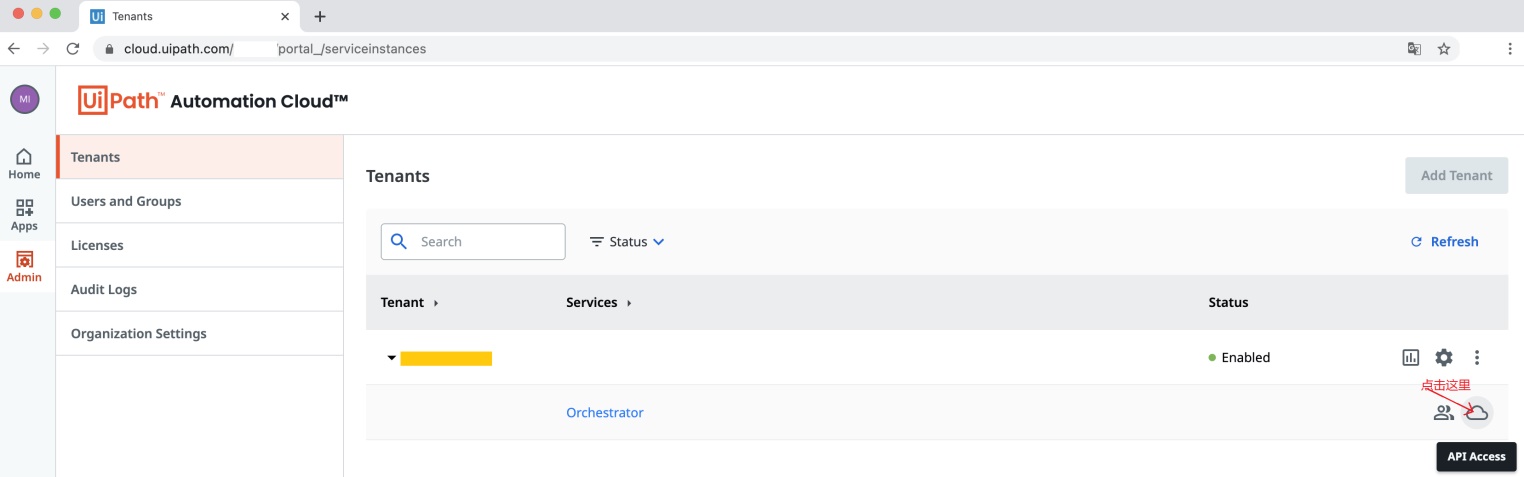
步骤二 Authenticate 认证¶
此过程的最终目标是拥有有效的OAuth访问令牌。该令牌将作为GET和POST请求标头中的Bearer令牌传递到UiPath Cloud Orchestrator REST API。
注意!
发出REST API请求时,请在每个会话开始时使用”刷新令牌”获取新的访问令牌,然后使用它来发出一个或多个REST API请求。令牌的有效期为24小时,每次运行时,可以使用储存的旧令牌。 请注意,请尽量减少重复生成新令牌,否则云端服务器可能会对你的api限速。
注意!
为方便多个get/post, 我们把各变量储存在postman的环境变量里,调用变量时,postman的形式是 {{变量名}} , 例如 {{access_token}}, {{AccountLogicName}}, {{TenantName}}等等。
Request (Post 访问)
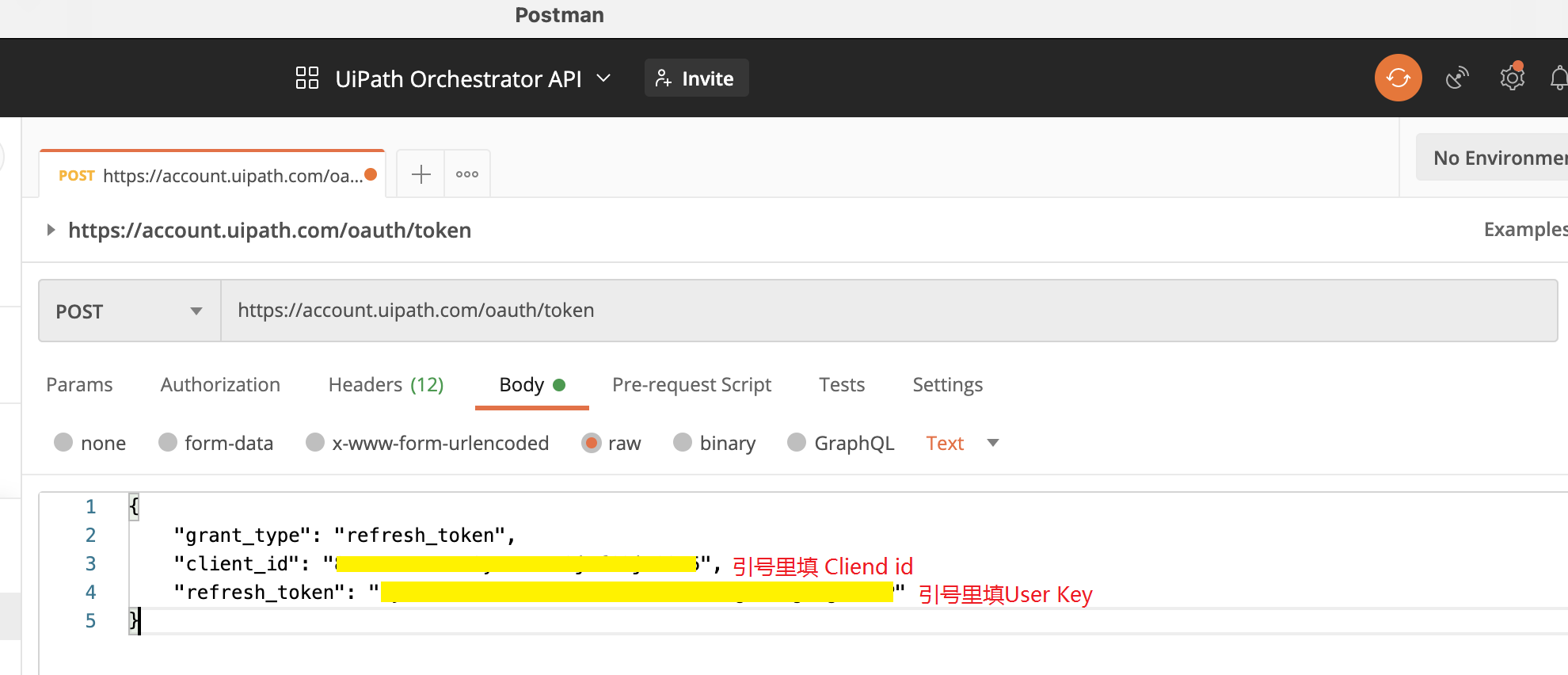
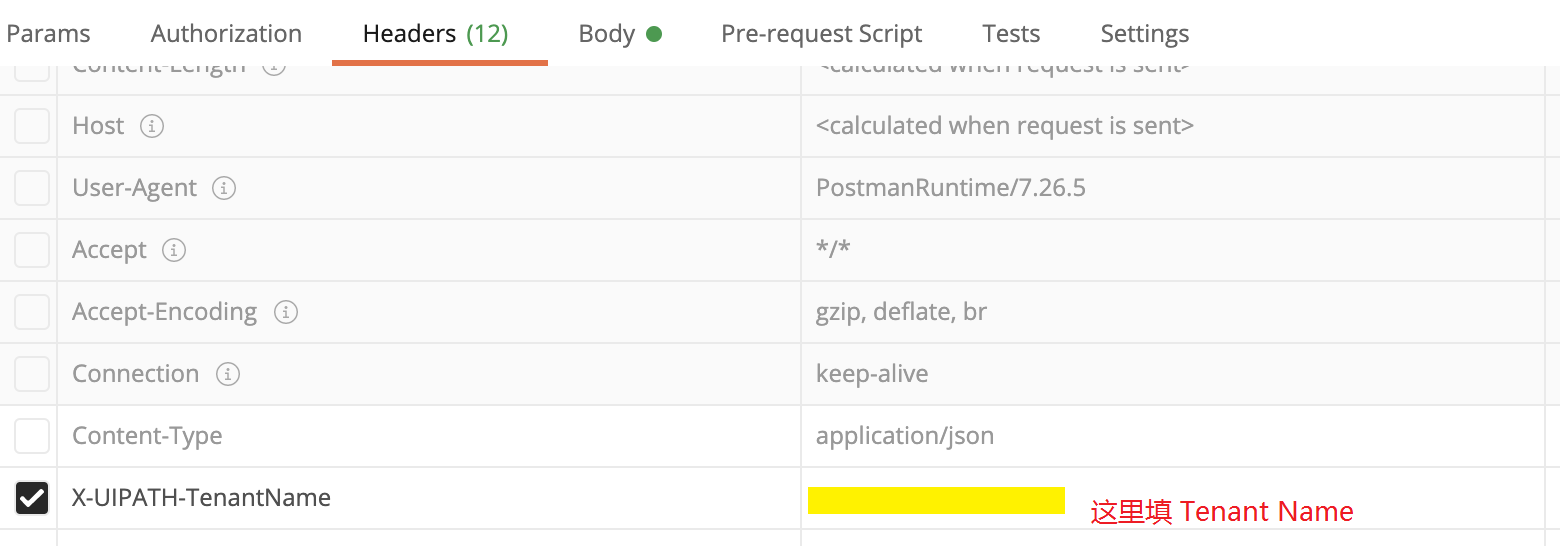
如图输入网址和相关参数,在Body里输入json, 值是ClientId和UserKey, 在Headers里输入键名 X-UIPATH-TenantName 和值 TenantName。
| {“grant_type”:”refresh_token”,”client_id”:”你的 ClientId”,”refresh_token”:”你的UserKey”} | |
|---|---|
Response (200 OK)
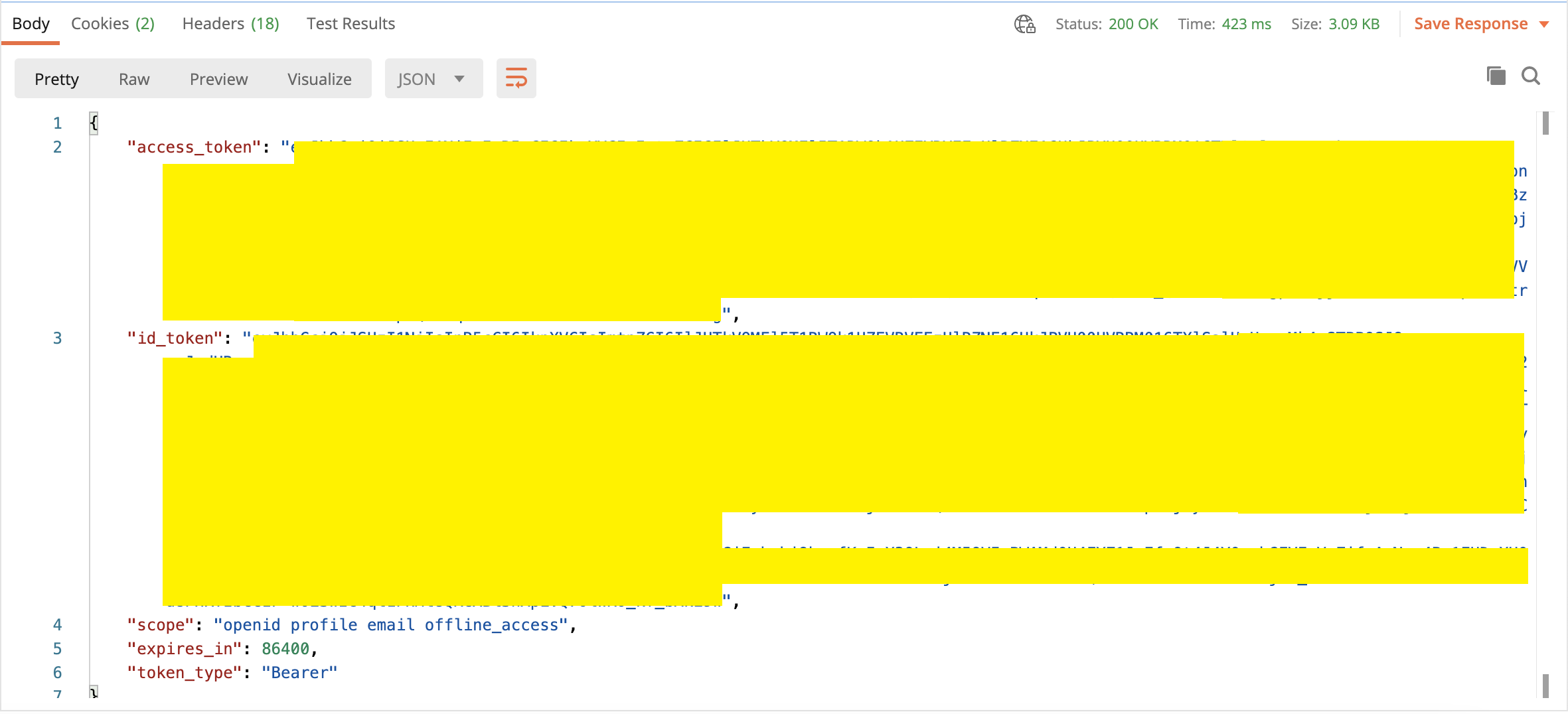
返回结果包括access_token, id_token等参数,我们要在后续的api访问里使用。
Python 代码片段
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91011121314151617181920212223 | asyncdefauthToken(self):”””OAuth 验证”””headers={‘content-type’:self.ContentType,’X-UIPATH-TenantName’:self.data[“TenantName”]}body_value={“grant_type”:self.GrantType,”client_id”:self.data[“ClientId”],”refresh_token”:self.data[“UserKey”]}payload=json.JSONEncoder().encode(body_value)try:ifcheck_expire(self.data[“expires_in”],self.data[“init_time”]):ret=awaitself.postdata(url=self.data[“OAuthUrl”],headers=headers,data=payload)ifretisNone:print(“请检查settings.json是否设置了api信息!”)os._exit(0)else:self.data[“access_token”]=ret.get(“access_token”)self.data[“id_token”]=ret.get(“id_token”)self.data[“scope”]=ret.get(“scope”)self.data[“expires_in”]=ret.get(“expires_in”,0)self.data[“token_type”]=ret.get(“token_type”)self.data[“init_time”]=int(time.time())exceptExceptionaserr:print(“OAuth Error: {0}”.format(err))raise |
|---|---|
步骤三 查询 Robot, Job, Process, Release信息¶
获取 License 信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Settings/UiPath.Server.Configuration.OData.GetLicense 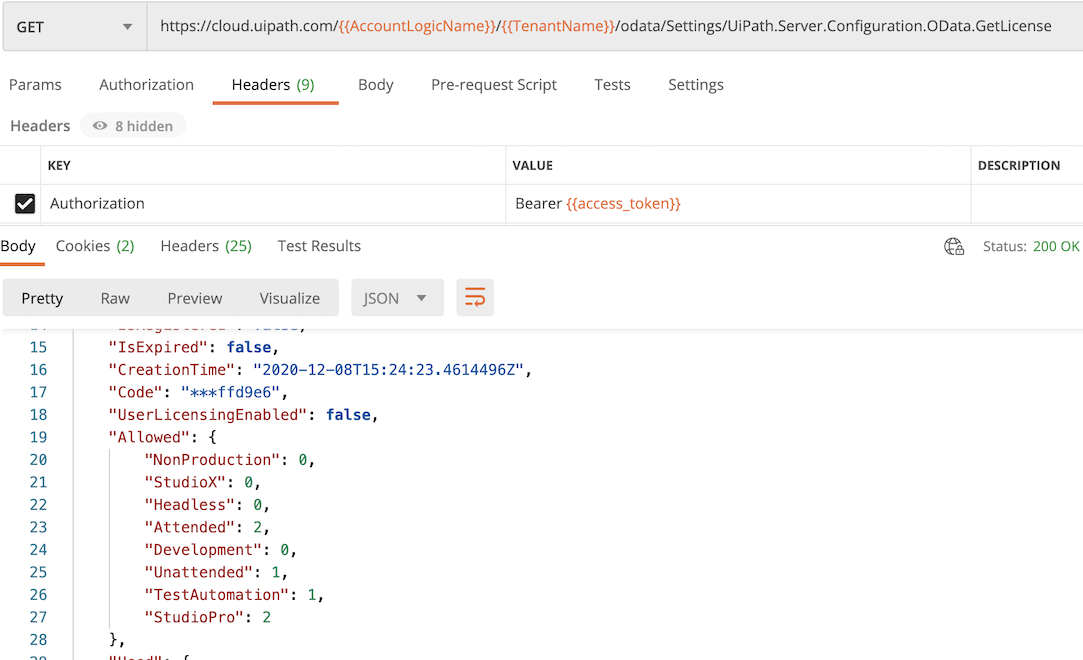
获取 Folder 信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/OrganizationUnits 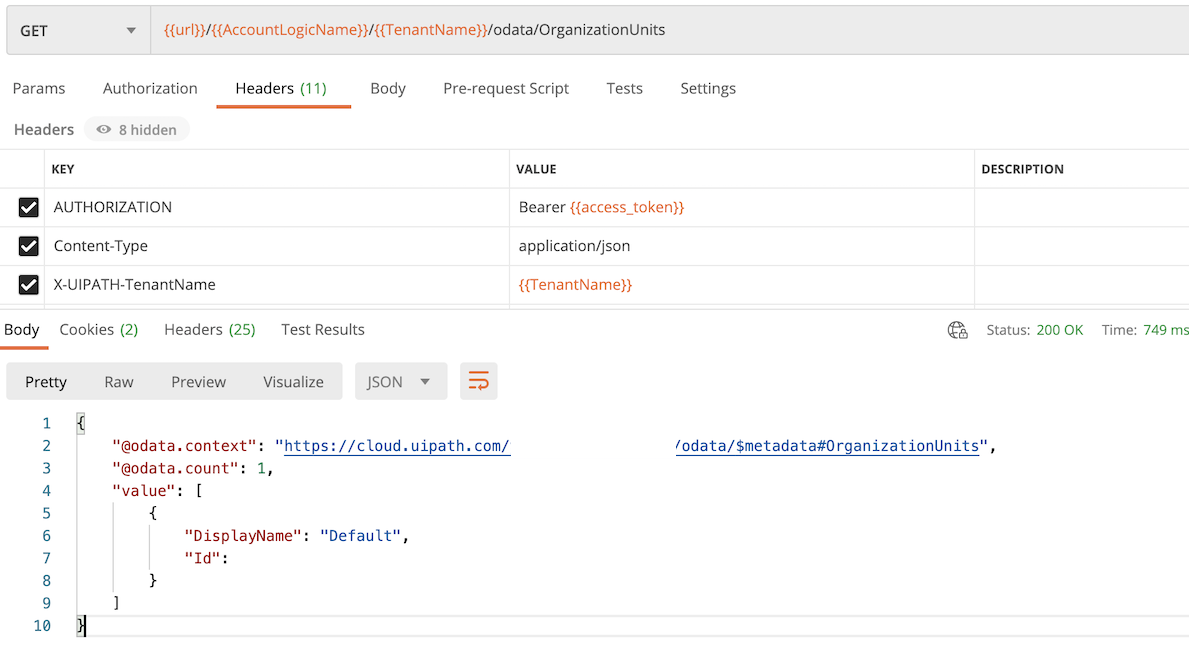
返回结果DisplayName参数,我们在后续的api里使用
Python 代码片段
| asyncdefgetFolder(self):”””获取 Folder 信息”””headers={“AUTHORIZATION”:self.data[“token_type”]+’ ‘+self.data[“access_token”],’content-type’:self.ContentType,’X-UIPATH-TenantName’:self.data[“TenantName”]}url=self._folder.format(self.data[“url”],self.data[“AccountLogicName”],self.data[“TenantName”])ret=awaitself.getdata(url,headers=headers)return[xforxinret.get(“value”,[])] | |
|---|---|
获取所有的 Robots 信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Robots 返回所有的 Robots 信息 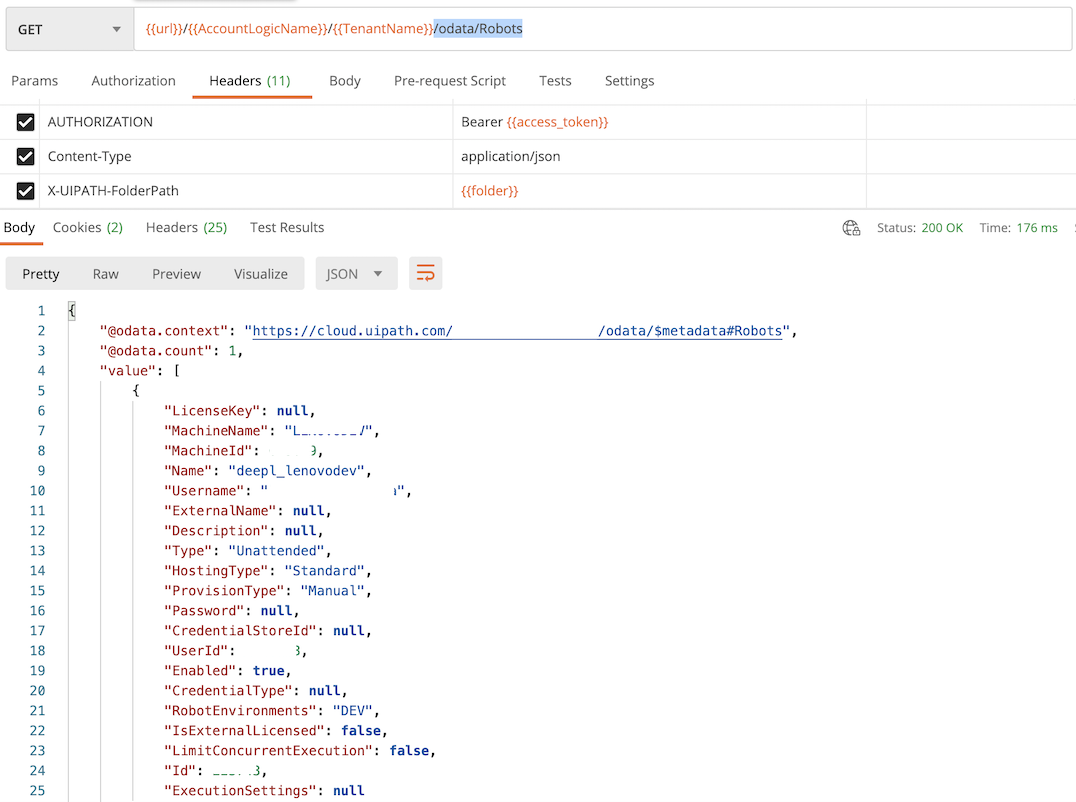
Headers 参数 AUTHORIZATION, Content-Type,X-UIPATH-FolderPath
Python 代码片段
| asyncdefgetRobots(self):”””获取全部 Robot 信息 “””headers={“AUTHORIZATION”:self.data[“token_type”]+’ ‘+self.data[“access_token”],’content-type’:self.ContentType,’X-UIPATH-FolderPath’:self.data[“DefaultFolder”]}url=self._getRobots.format(self.data[“url”],self.data[“AccountLogicName”],self.data[“TenantName”])ret=awaitself.getdata(url,headers=headers)return[xforxinret.get(“value”,[])] | |
|---|---|
获取指定的 Robot 状态
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Sessions?$top=1&$filter=Robot/Id eq (这里放robot id) &$select=State 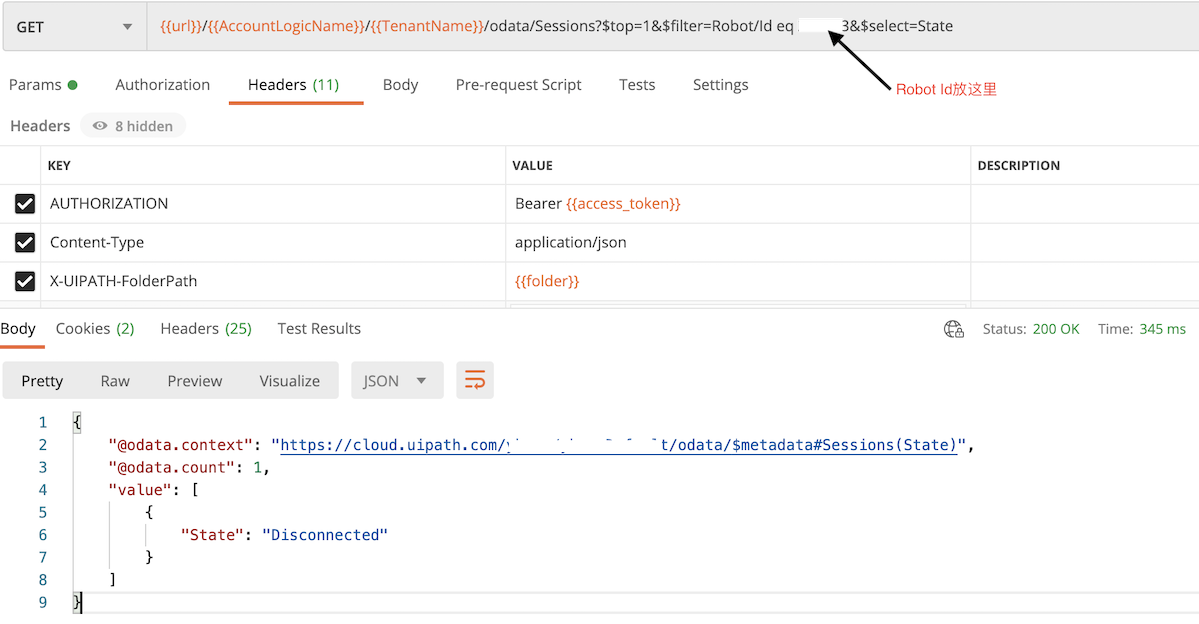
返回结果的可能状态包括: Available, Busy, Disconnected, Unresponsive, 我们在使用Robot执行作业时,需要先判断Robot是Available。
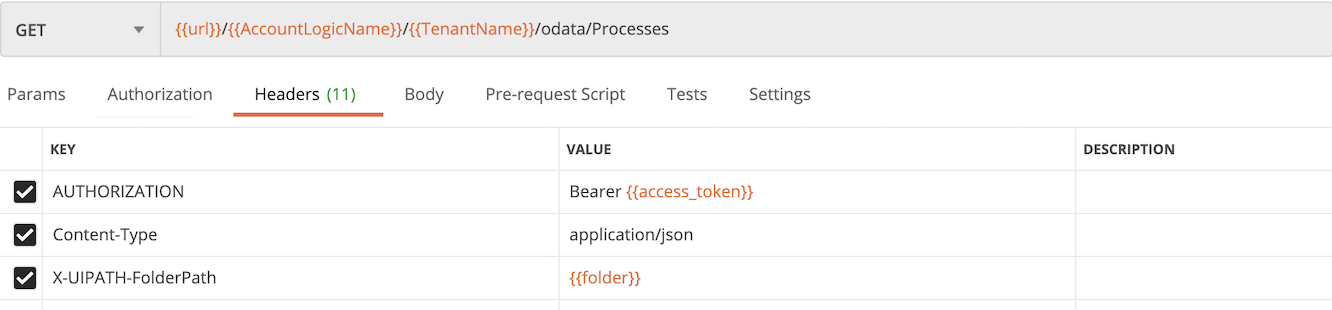
获取所有 Process 信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Processes 返回所有的 Process 信息 @odata.count 是Process总数
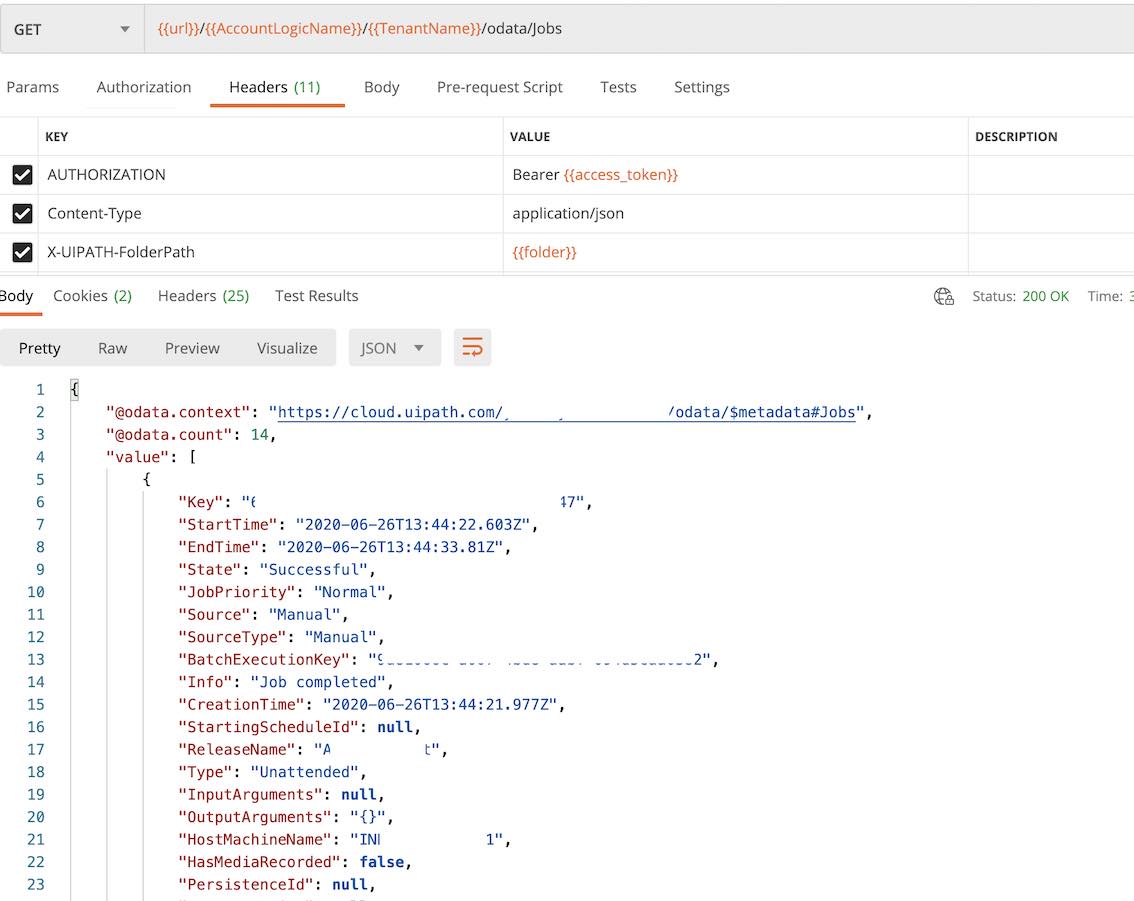
获取所有作业 Jobs 信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Jobs 返回所有的 Jobs 信息 @odata.count 是Jobs总数
获取所有 Releases信息
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Releases 返回所有的 Release 信息 @odata.count 是Release总数
执行 Job, 定义队列,添加队列,访问/修改 Asset¶
执行作业 Job
Post 访问endpoint: /odata/Jobs/UiPath.Server.Configuration.OData.StartJobs
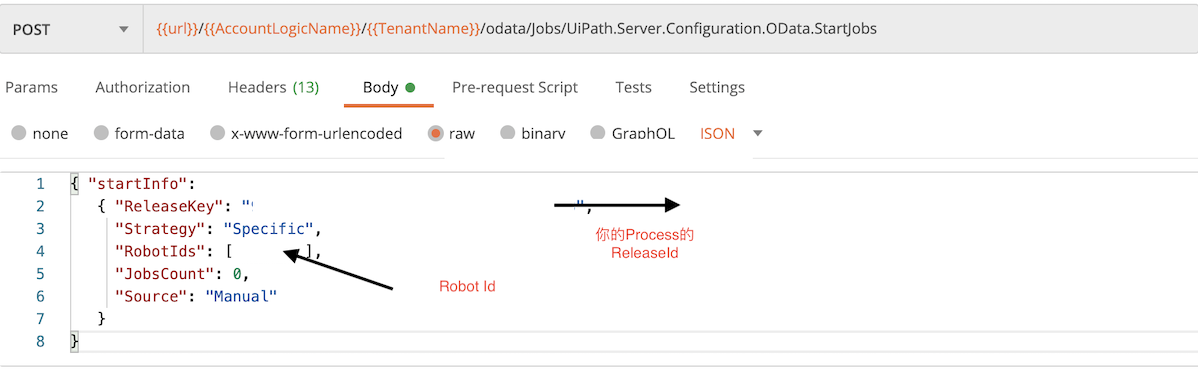
如图示,Body中需要添加如下的内容,具体参数含义,请参考UiPath Orchestrator 手册
| {“startInfo”:{“ReleaseKey”:”你的ReleaseId”,”Strategy”:”All”,”RobotIds”:[]}} | |
|---|---|
返回结果是 (HTTP 201 Created)
停止作业 Job
Post 访问endpoint: /odata/Jobs/UiPath.Server.Configuration.OData.StopJobs
| {“jobIds”:[141888,141889],”strategy”:”Kill”} | |
|---|---|
返回结果 (HTTP 200) 200 OK
列出所有 Assets
Get 访问endpoint: /odata/Assets
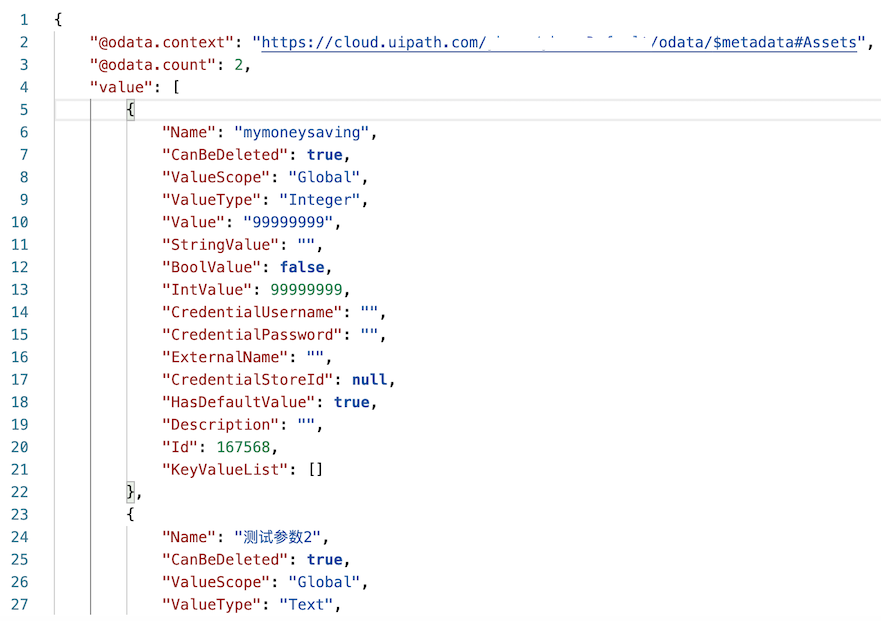
创建 Asset
Post 访问endpoint: /odata/Assets 设置Body为:
| {“Name”:”测试参数2”,”ValueScope”:”Global”,”ValueType”:”Text”,”StringValue”:”An asset added through an API call”} | |
|---|---|
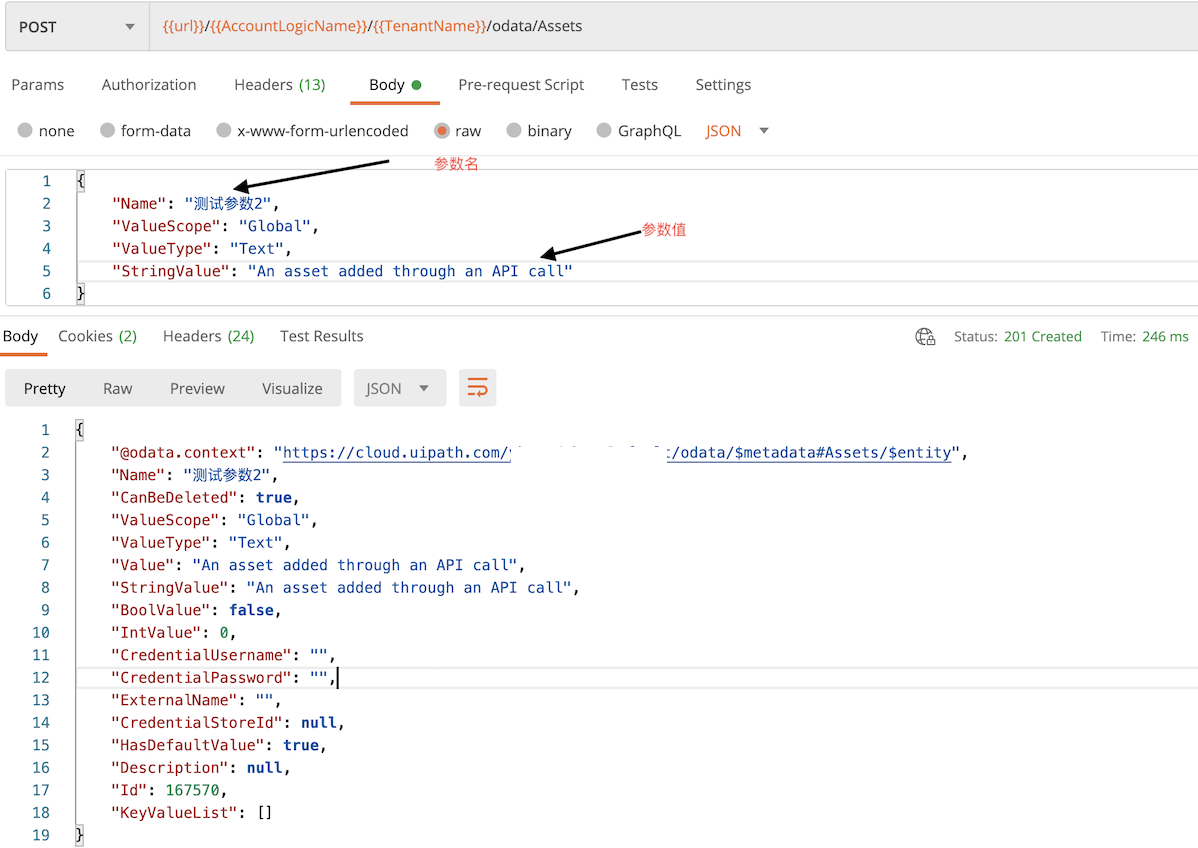
返回结果状态是 (HTTP 201), 返回内容如图示。
修改Asset
Put 访问endpoint: /odata/Assets(变量Id)
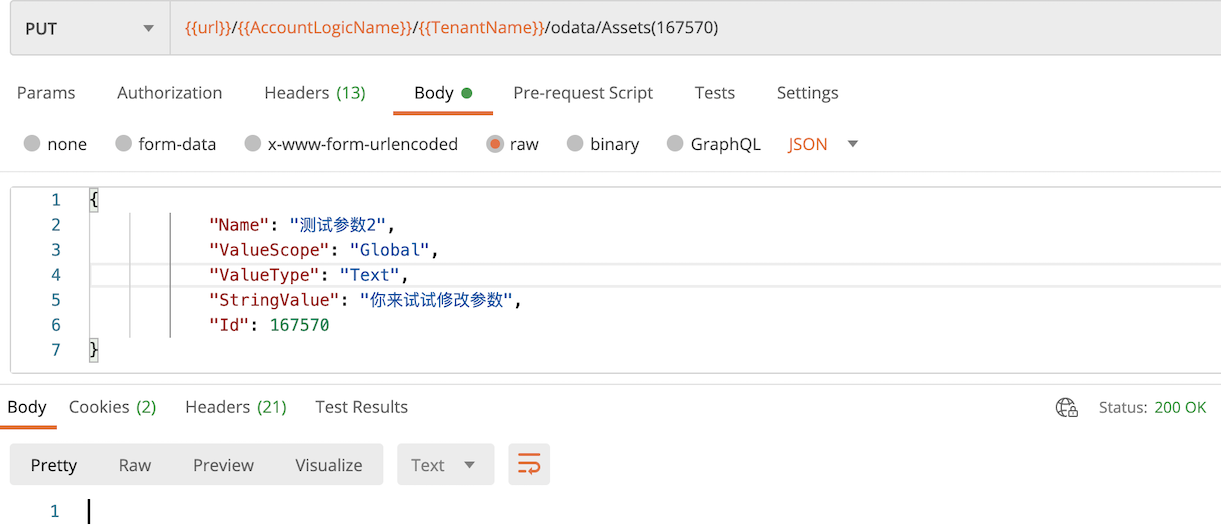
返回结果状态是 (HTTP 200)。
创建队列 Queue
Post 访问endpoint: /odata/QueueDefinitions
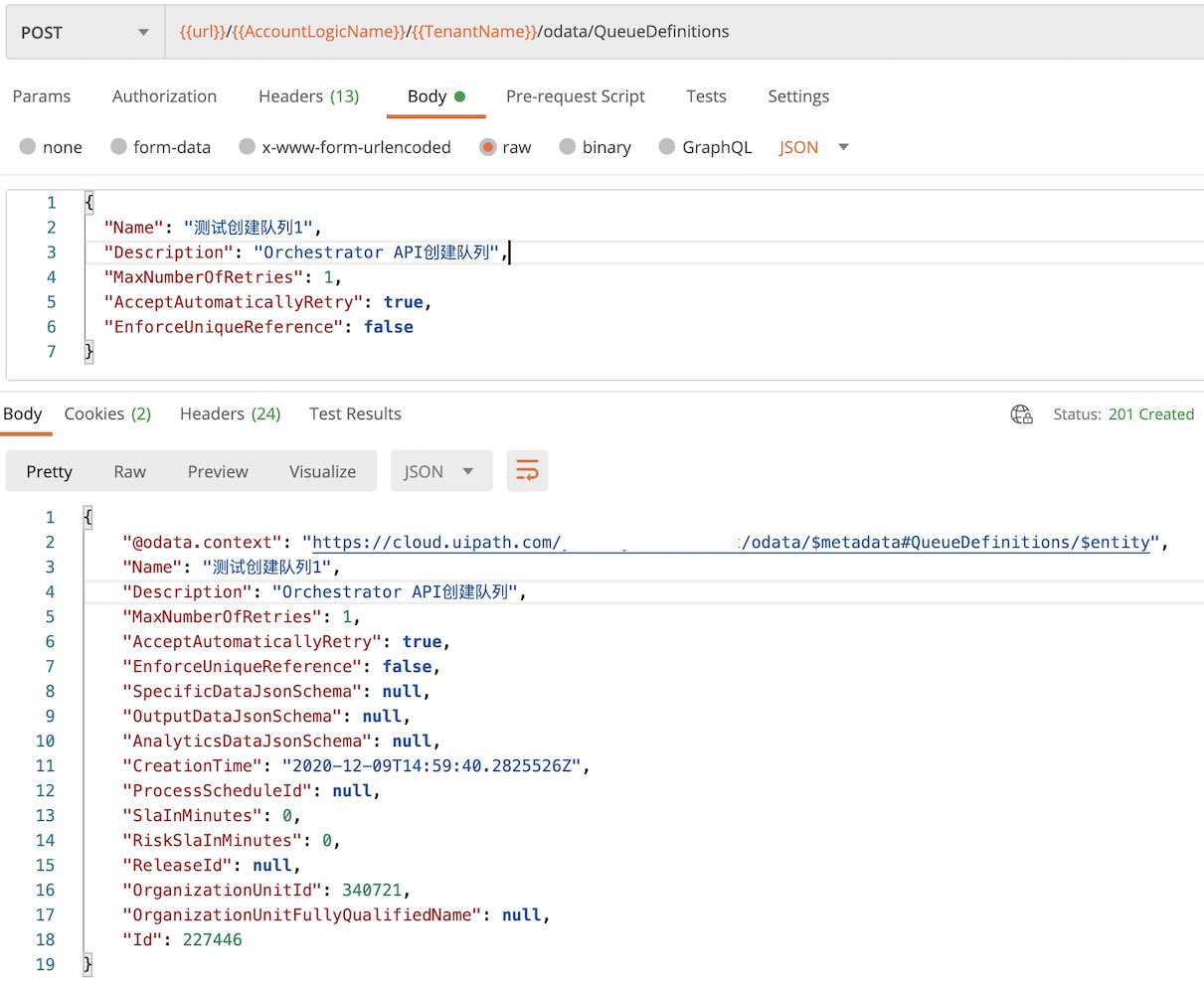
返回结果状态是 (HTTP 201 Created), 返回内容如图示。
添加队列元素
Post 访问endpoint: /odata/Queues/UiPathODataSvc.AddQueueItem
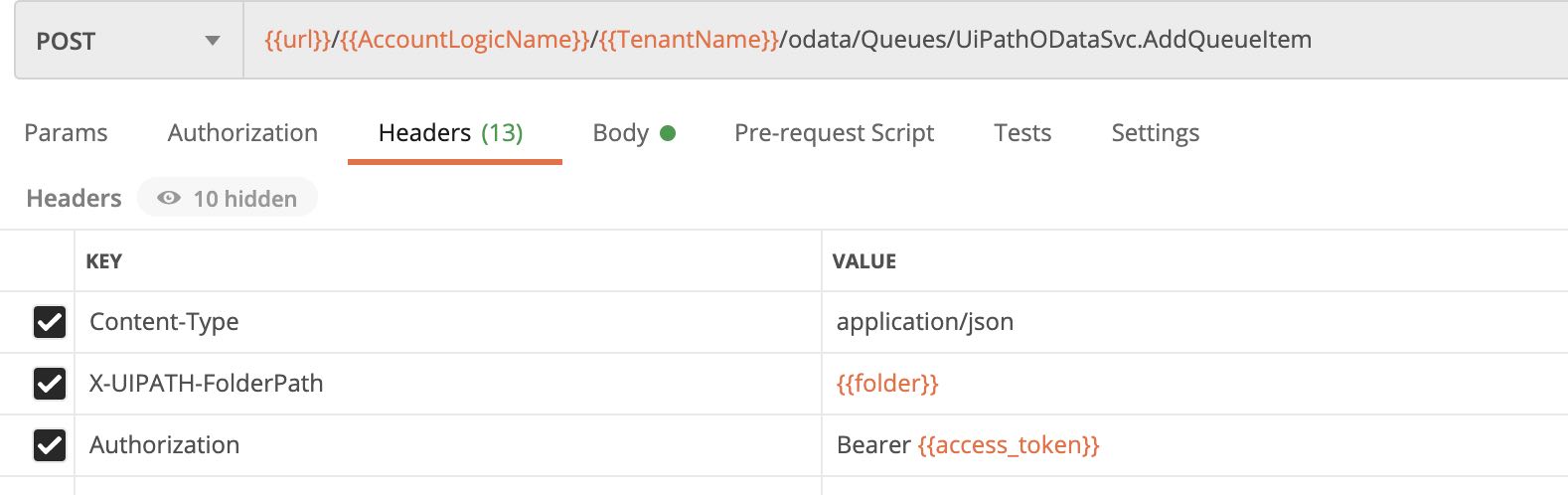
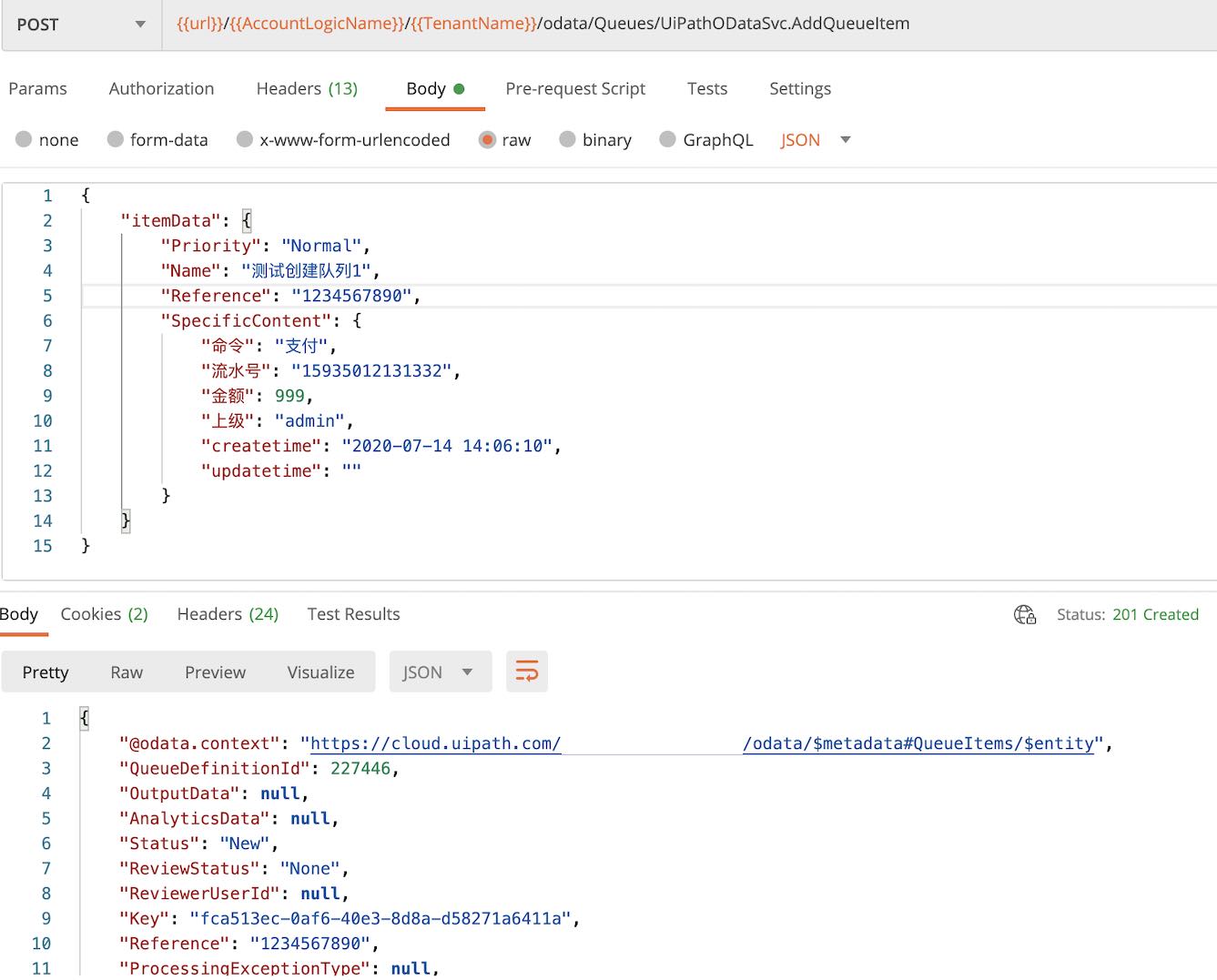
返回结果状态是 (HTTP 201 Created), 返回内容如图示。 如果进入Orchestrator的管理,队列管理界面,可以看到我们成功添加了新队列,队列元素。
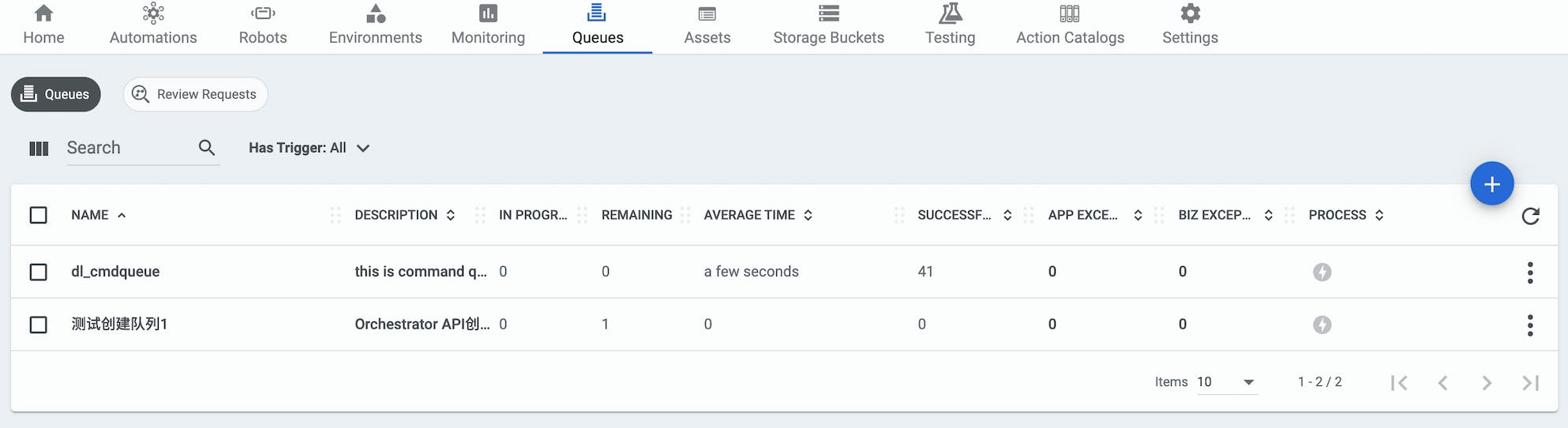
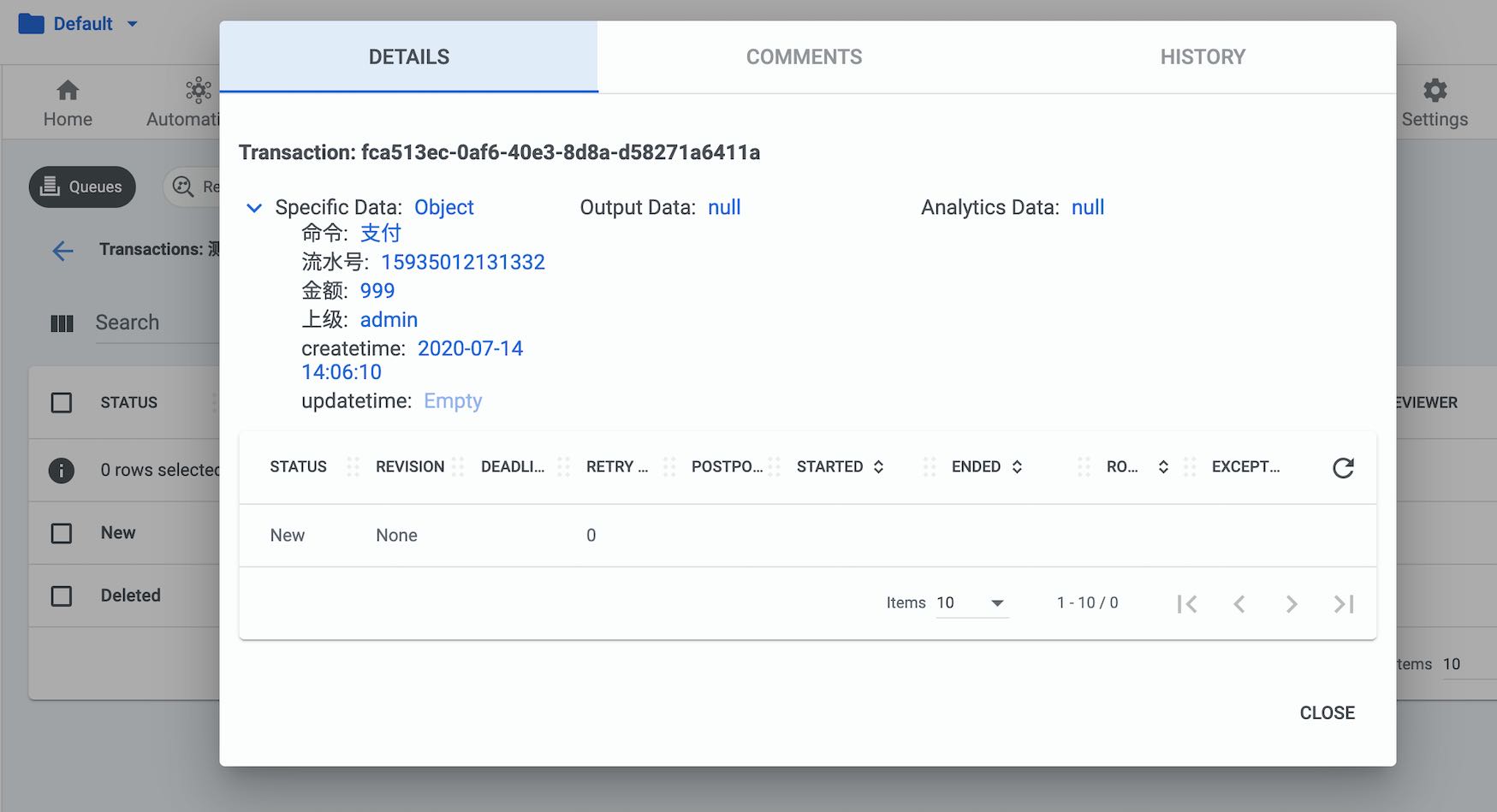
好了,到此我们就初步用Postman演示了如何调用Orchestrator 的API接口,使用这些接口,你可以很方便的创建手机,服务器和平板上的应用来驱动UiPath Robot,远程调用Robot的方式可以有三种:
- 队列异步驱动(设置队列一添加新元素,Robot就立即执行,应用的例子例如收到新邮件,或者银行事务)
- 定时驱动(设置按时间和执行频率,运行Robot)
- 用 StartJob 直接调用 Robot
Python 代码文件
orchestrator.py
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118 | # -- coding: utf-8 --“””This module holds class orchestrator of UiPath “””importasyncioimportaiohttpimportjsonimporttimeimportoscheck_expire = lambda expires_in,init_time: int(time.time()) > int(expires_in) + int(init_time) - 3600
class orchestrator():
def init(self, data):
“””初始化 Orchestrator 对象”””
self.data = data
self.ContentType = ‘application/json’
self.GrantType = ‘refresh_token’
self._folder = ‘{0}/{1}/{2}/odata/OrganizationUnits’
self._getRobots = ‘{0}/{1}/{2}/odata/Robots’
self._addQueue = ‘{0}/{1}/{2}/odata/Queues/UiPathODataSvc.AddQueueItem’
self._addQueueBulk = ‘{0}/{1}/{2}/odata/Queues/UiPathODataSvc.BulkAddQueueItems’
self._getRobotStatus = ‘{0}/odata/Sessions?filter=Robot/Id eq {1}&$select=State’
self._StartJob = ‘{0}/odata/Jobs/UiPath.Server.Configuration.OData.StartJobs’```
@staticmethod
async def postdata(url = None,headers = None, data = None):
ret = None
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(url,headers=headers,data = data, timeout=300, ssl=False) as r: #verify_ssl=False
if (r.status == 200) or (r.status == 201):
try:
ret = await r.json()
except Exception as err:
print(“post url {0} Exception error: {1}“.format(url, err))
raise
else:
print(“Post失败,code= %d %s“ % (r.status, await r.text()))
except aiohttp.ClientError as err:
print(“post url {0} error {1}“.format(url,err))
raise
return ret
@staticmethod async def getdata(url = None,headers = None, params = None): ret = None try: async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers=headers) as session: async with session.get(url,params=params,timeout=300,ssl=False) as r: #verify_ssl=False assert r.status == 200, r.status #401 Unauthorized raise AssertionError ret = await r.json() except aiohttp.ClientError as err: #traceback.print_exc() print(“Get url {0} error {1}“.format(url, err)) raise return ret
@staticmethod async def putdata(url = None,headers = None, data = None): ret = None try: async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: async with session.put(url,headers=headers,data = data, timeout=300, ssl=False) as r: #verify_ssl=False if (r.status == 200) or (r.status == 201): try: ret = await r.json() except Exception as err: print(“put url {0} Exception error: {1}“.format(url, err)) raise else: print(“Put失败,code= %d %s“ % (r.status, await r.text())) except aiohttp.ClientError as err: print(“put url {0} error {1}“.format(url,err)) raise return ret
async def authToken(self): “””OAuth 验证””” headers = {‘content-type’: self.ContentType, ‘X-UIPATH-TenantName’: self.data[“TenantName”]} body_value = {“grant_type”: self.GrantType, “client_id”: self.data[“ClientId”], “refresh_token”: self.data[“UserKey”]} payload = json.JSONEncoder().encode(body_value) try: if check_expire(self.data[“expires_in”], self.data[“init_time”]): ret = await self.postdata(url = self.data[“OAuthUrl”], headers = headers, data = payload) if ret is None: print(“请检查settings.json是否设置了api信息!”) os._exit(0) else: self.data[“access_token”] = ret.get(“access_token”) self.data[“id_token”] = ret.get(“id_token”) self.data[“scope”] = ret.get(“scope”) self.data[“expires_in”] = ret.get(“expires_in”, 0) self.data[“token_type”] = ret.get(“token_type”) self.data[“init_time”] = int(time.time()) except Exception as err: print(“OAuth Error: {0}“.format(err)) raise
async def getFolder(self): “””获取 Folder 信息””” headers = { “AUTHORIZATION”: self.data[“token_type”] + ‘ ‘ + self.data[“access_token”], ‘content-type’: self.ContentType, ‘X-UIPATH-TenantName’: self.data[“TenantName”]} url = self._folder.format(self.data[“url”], self.data[“AccountLogicName”],self.data[“TenantName”]) ret = await self.getdata(url, headers=headers) return [ x for x in ret.get(“value”, [])]
async def getRobots(self): “””获取全部 Robot 信息 “”” headers = { “AUTHORIZATION”: self.data[“token_type”] + ‘ ‘ + self.data[“access_token”], ‘content-type’: self.ContentType, ‘X-UIPATH-FolderPath’: self.data[“DefaultFolder”]} url = self._getRobots.format(self.data[“url”], self.data[“AccountLogicName”],self.data[“TenantName”]) ret = await self.getdata(url, headers=headers) return [ x for x in ret.get(“value”, [])]
|| --- | --- |`test_UiPathOC.py`| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-""" 单元测试组,测试 UiPath Orchestrator API的部分接口,提供调用API演示 """importunittestimporttimeimportasyncioimportjsonfromorchestratorimportorchestratorSETTINGS_FILE = "settings.json"<br />def print_test(method):<br />"""<br />输出测试单元,打印单元耗时,测试单元名和测试结果<br />"""<br />def run(*args, **kw):<br />ts = time.time()<br />print('\\t测试单元 %r' % method.**qualname**)<br />method(*args, **kw)<br />te = time.time()<br />print('\\t[测试通过] 耗时 %r %2.2f 秒' % (method.**qualname**, te - ts))<br />return run<br />def save_settings(data):<br />"""保存 settings.json"""<br /># 写入 JSON 数据<br />with open(SETTINGS_FILE, 'w') as f:<br />json.dump(data, f)<br />class OrchestratorTestCase(unittest.TestCase):<br />"""测试 Orchestrator API"""<br />def setUp(self):<br />"""执行单元测试前先执行"""<br /># 读取 settings.json 数据<br />with open(SETTINGS_FILE, 'r') as f:<br />data = json.load(f)<br />self.oc = orchestrator(data)<br />coroutine = self.oc.authToken()<br />loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()<br />loop.run_until_complete(coroutine)
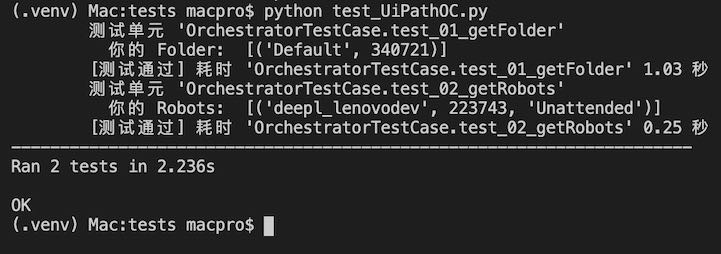
@print_test def test_01_getFolder(self): coroutine = self.oc.getFolder() loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() task = asyncio.ensure_future(coroutine) loop.run_until_complete(task) folders = task.result() self.assertTrue(isinstance(folders, list) and len(folders)>0) output = [] for folder in folders: output.append((folder[“DisplayName”],folder[“Id”])) print(“\t 你的 Folder: “, output)
@print_test def test_02_getRobots(self): coroutine = self.oc.getRobots() loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() task = asyncio.ensure_future(coroutine) loop.run_until_complete(task) robots = task.result() self.assertTrue(isinstance(robots, list) and len(robots)>0) output = [] for robot in robots: output.append((robot[“Name”],robot[“Id”],robot[“Type”])) print(“\t 你的 Robots: “, output)
if **name** == '**main**':<br />#执行单元测试<br />unittest.main(verbosity=0)<br />|| --- | --- |把如上的三个文件,`settings.json`, `orchestrator.py`, `test_UiPathOC.py` 放在同一目录,按步骤一从oc账户获取 API access 的参数填入 `settings.json`。在 `cmd` 窗口下, 输入:| |
pip install asyncio pip install aiohttp pip install unittest ``` | | —- | —- |
输入以下单元测试的命令,
结果:
总结: 通过在应用系统中远程异步调用Orchestrator API接口,可以实现手机、平板、服务器多平台应用驱动多个 UiPath Robot 并发处理任务,扩展了应用宽度和灵活性。

