golang提供了两个标准库用来处理模版text/template和html/template。我们使用html/template格式化html字符。
模版引擎
模版引擎很多,Python的jinja,nodejs的jade等都很好。所谓模版引擎,则将模版和数据进行渲染的输出格式化后的字符程序。对于go,执行这个流程大概需要三步:
创建模版对象
加载模版子串
执行渲染模版
其中最后一步就是把加载的字符和数据进行格式化。其过程可以总结下图:
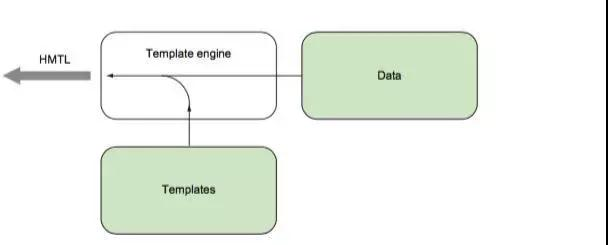
go提供的标准库html/template提供了很多处理模版的接口,我们的项目结构为:
templates文件夹有两个文件,分别为模版文件。layout.html文件如下:
!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}</body></html>
我们可以使用ParseFiles方法加载模版,该方法会返回一个模版对象和错误,接下来就可以使用模版对象执行模版,注入数据对象。go提供了一些模版标签,称之为action,.也是一种action。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html")fmt.Println(t.Name())t.Execute(w, "Hello world")}
我们打印了t模板对象的Name方法,实际上,每一个模板,都有一个名字,如果不显示指定这个名字,go将会把文件名(包括扩展名当成名字)本例则是layout.html。访问之后可以看见返回的html字串:
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:8000/HTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Fri, 09 Dec 2016 09:04:36 GMTContent-Length: 223Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: Hello world</body></html>
go不仅可以解析模版文件,也可以直接模版子串,这就是标准的处理,新建-加载-执行三部曲:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){tmpl := `<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Go Web Programming</title></head><body>{{ . }}</body></html>`t := template.New("layout.html")t, _ = t.Parse(tmpl)fmt.Println(t.Name())t.Execute(w, "Hello World")}
实际开发中,最终的页面很可能是多个模板文件的嵌套结果。go的ParseFiles也支持加载多个模板文件,不过模板对象的名字则是第一个模板文件的文件名。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html", "templates/index.html")fmt.Println(t.Name())t.Execute(w, "Hello world")}
可见打印的还是 layout.html的名字,执行的模板的时候,并没有index.html的模板内容。此外,还有ParseGlob方法,可以通过glob通配符加载模板。
模版命名与嵌套
模版命名
模版对象是有名字的,可以在创建模版对象的时候显示命名,也可以让go自动命名。go提供了ExecuteTemplate方法,用于执行指定名字的模版。例如加载layout.html模版的时候,可以指定layout.html
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html")fmt.Println(t.Name())t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", "Hello world")}
似乎和Execute方法没有太大的差别。下面修改一下layout.html文件:
{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}</body></html>{{ end }}
在模板文件中,使用了define这个action给模板文件命名了。虽然我们ParseFiles方法返回的模板对象t的名字还是layout.html, 但是ExecuteTemplate执行的模板却是html文件中定义的layout。
不仅可以通过define定义模板,还可以通过template action引入模板,类似jinja的include特性。修改 layout.html 和 index.html
{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}{{ template "index" }}</body></html>{{ end }}
{{ define "index" }}<div style="background: yellow">this is index.html</div>{{ end }}
go的代码也需要修改,使用ParseFiles加载需要渲染的模版文件:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html", "templates/index.html")t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", "Hello world")}
访问可以看到index被layout模版include了:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: Hello world<div style="background: yellow">this is index.html</div></body></html>
单文件嵌套
总而言之,创建模板对象后和加载多个模板文件,执行模板文件的时候需要指定base模板(layout),在base模板中可以include其他命名的模板。无论点.,define,template这些花括号包裹的东西都是go的action(模板标签)。
Action
action是go模版中用于动态执行一些逻辑和展示数据的形式。大致分为下面几种:
条件语句
迭代
封装
引用
条件判断
条件判断的语法很简单:
{{ if arg }}some content{{ end }}{{ if arg }}some content{{ else }}other content{{ end }}
arg可以是基本数据结构,也可以是表达式:if-end包裹的内容为条件为真的时候展示。和if语句一样,模版也可以有else语句。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html")rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", rand.Intn(10) > 5)}{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}{{ if . }}Number is greater than 5!{{ else }}Number is 5 or less!{{ end }}</body></html>{{ end }}
此时就能看见,当.的值为true的时候显示if的逻辑,否则显示else的逻辑。
迭代
对于一些数组,切片或者是map,可以使用迭代的action,与go的迭代类似,使用range进行处理:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {t := template.Must(template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html"))daysOfWeek := []string{"Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Ths", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"}t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", daysOfWeek)}{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}{{ range . }}<li>{{ . }}</li>{{ end }}</body></html>{{ end }}
可以看出输出了一堆li列表。迭代的时候,还可以使用$设置循环设置:
{{ range $key, $value := . }}<li>key: {{ $key }}, value: {{ $value }}</li>{{ else }}empty{{ end }}
可以看见和迭代切片很像。rang也可以使用else语句:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {t := template.Must(template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html"))daysOfWeek := []string{}t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", daysOfWeek)}{{ range . }}<li>{{ . }}</li>{{ else }}empty{{ end }}
当range的结构为空的时候,则会执行else分支的逻辑。
with封装
with语言在Python中可以开启一个上下文环境。对于go模板,with语句类似,其含义就是创建一个封闭的作用域,在其范围内,可以使用.action,而与外面的.无关,只与with的参数有关:
{{ with arg }}此时的点 . 就是arg{{ end }}{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: {{ . }}{{ with "world"}}Now the dot is set to {{ . }}{{ end }}</body></html>{{ end }}
访问结果如下:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: [Mon Tue Wed Ths Fri Sat Sun]Now the dot is set to world</body></html>
可见 with语句的.与其外面的.是两个不相关的对象。with语句也可以有else。else中的.则和with外面的.一样,毕竟只有with语句内才有封闭的上下文:
{{ with ""}}Now the dot is set to {{ . }}{{ else }}{{ . }}{{ end }}
访问效果为:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>template data: [Mon Tue Wed Ths Fri Sat Sun][Mon Tue Wed Ths Fri Sat Sun]</body></html>
引用
我们已经介绍了模板嵌套引用的技巧。引用除了模板的include,还包括参数的传递。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {t := template.Must(template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html", "templates/index.html"))daysOfWeek := []string{"Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Ths", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"}t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", daysOfWeek)}
修改 layout.html, layout中引用了 index模板:
{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>layout template data: ({{ . }}){{ template "index" }}</body></html>{{ end }}
index.html模板的内容也打印了 .:
{{ define "index" }}<div style="background: yellow">this is index.html ({{ . }})</div>{{ end }}
访问的效果如下,index.html 中的点并没有数据。
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>layout template data: ([Mon Tue Wed Ths Fri Sat Sun])<div style="background: yellow">this is index.html ()</div></body></html>
我们可以修改引用语句{{ template “index” . }},把参数传给子模板,再次访问,就能看见index.html模板也有数据啦。
<div style="background: yellow">this is index.html ([Mon Tue Wed Ths Fri Sat Sun])</div>
参数,变量和管道
模板的参数可以是go中的基本数据类型,如字串,数字,布尔值,数组切片或者一个结构体。在模板中设置变量可以使用 $variable := value。我们在range迭代的过程使用了设置变量的方式。
go还有一个特性就是模板的管道函数,熟悉django和jinja的开发者应该很熟悉这种手法。通过定义函数过滤器,实现模板的一些简单格式化处理。并且通过管道哲学,这样的处理方式可以连成一起。
{{ p1 | p2 | p3 }}
例如 模板内置了一些函数,比如格式化输出:
{{ 12.3456 | printf "%.2f" }}
函数
既然管道符可以成为模板中的过滤器,那么除了内建的函数,能够自定义函数可以扩展模板的功能。幸好go的模板提供了自定义模板函数的功能。
想要创建一个定义函数只需要两步:
创建一个FuncMap类型的map,key是模板函数的名字,value是其函数的定义。
将 FuncMap注入到模板中。
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {funcMap := template.FuncMap{"fdate": formDate}t := template.New("layout").Funcs(funcMap)t = template.Must(t.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html", "templates/index.html"))t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", time.Now())}
然后在模板中使用{{ . | fdate }},当然也可以不适用管道过滤器,而是使用正常的函数调用形式,{{ fdate . }}。
注意,函数的注入,必须要在parseFiles之前,因为解析模板的时候,需要先把函数编译注入。
智能上下文
go还提供了一个更有意思的特性。那就是根据上下文显示模板的内容。例如字符的转义,会根据所显示的上下文环境而智能变化。比如同样的html标签,在Js和html环境中,其转义的内容是不一样的:
func templateHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request){t, _ :=template.ParseFiles("templates/layout.html")content := `I asked: <i>What's up?</i>`t.ExecuteTemplate(w, "layout", content)}
模板文件:
{{ define "layout" }}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><title>layout</title></head><body><h3>This is layout</h3>layout template data: ({{ . }})<div><a href="/{{ . }}">Path</a></div><div><a href="/?q={{ . }}">Query</a></div><div><a onclick="f('{{ . }}')">Onclick</a></div></body></html>{{ end }}
访问结果
layout template data: (I asked: <i>What's up?</i>)<div><a href="/I%20asked:%20%3ci%3eWhat%27s%20up?%3c/i%3e">Path</a></div><div><a href="/?q=I%20asked%3a%20%3ci%3eWhat%27s%20up%3f%3c%2fi%3e">Query</a></div><div><a onclick="f('I asked: \x3ci\x3eWhat\x27s up?\x3c\/i\x3e')">Onclick</a></div>
可以看见go会自动为我们处理html标签的转义。这对web安全具有重要作用。避免了一些XSS攻击。


