概述
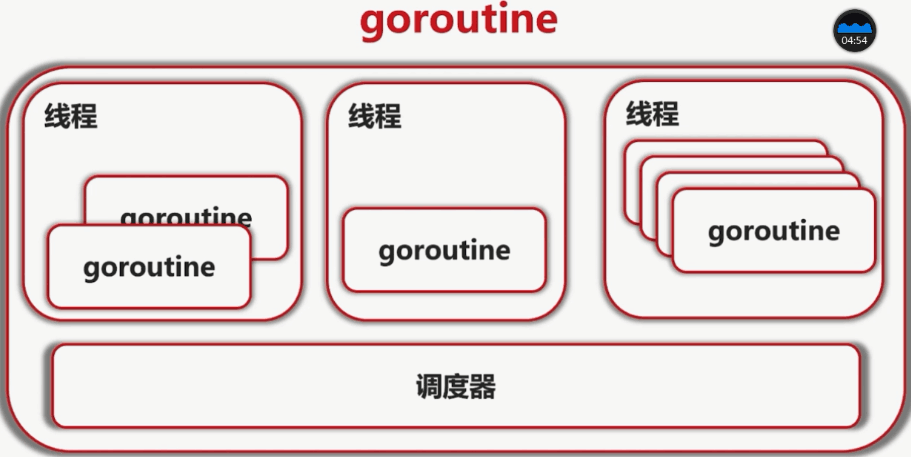
Go协程(Goroutine)是与其他函数或方法同时运行的函数或方法。可以认为Go协程是轻量级的线程。与创建线程相比,创建Go协程的成本很小。因此在Go中同时运行上千个协程是很常见的。
Go协程对比线程的优点
与线程相比,Go协程的开销非常小。Go协程的堆栈大小只有几kb,它可以根据应用程序的需要而增长和缩小,而线程必须指定堆栈的大小,并且堆栈的大小是固定的。
Go协程被多路复用到较少的OS线程。在一个程序中数千个Go协程可能只运行在一个线程中。如果该线程中的任何一个Go协程阻塞(比如等待用户输入),那么Go会创建一个新的OS线程并将其余的Go协程移动到这个新的OS线程。所有这些操作都是 runtime 来完成的,而我们程序员不必关心这些复杂的细节,只需要利用 Go 提供的简洁的 API 来处理并发就可以了。
Go 协程之间通过信道(channel)进行通信。信道可以防止多个协程访问共享内存时发生竟险(race condition)。信道可以想象成多个协程之间通信的管道。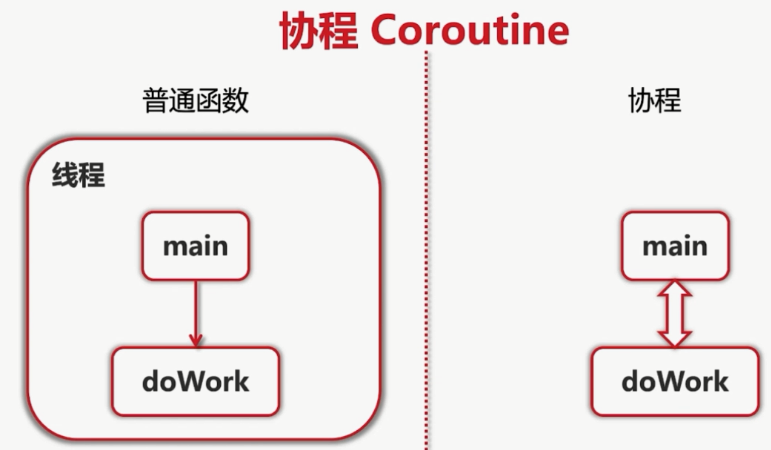
goroutine 可能切换的点
- 非强占式
- I/O ,select
- channel
- 等待锁
- 调用函数
- runtime.Gosched()
只是参考,不能保证切换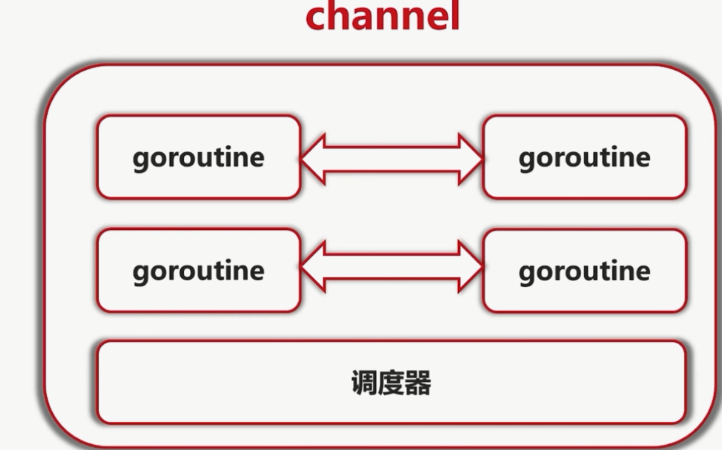
代码一
package mainimport ("fmt""time")func sample(message chan string) {message <- "hello goroutine!1"message <- "hello goroutine!2"message <- "hello goroutine!3"message <- "hello goroutine!4"}func sampleTwo(message chan string) {time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)str := <-messagestr = str + "I am goroutinetwo"message <- strclose(message)}func main() {/*** 队列为3的*/var message = make(chan string, 3)go sample(message)go sampleTwo(message)time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)str := <-messagefmt.Println(str)fmt.Println(<-message)for strTemp := range message {fmt.Println(strTemp)}}
代码二
select 多个队列的随机选择
package mainimport ("strconv""time""fmt")func sample(ch chan string) {for i := 0; i < 19; i++ {ch <- "I am sample num :" + strconv.Itoa(i)time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)}}func sampleTwo(ch chan int) {for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {ch <- itime.Sleep(2 * time.Second)}}func main() {/*** 队列为3的*/var ch1 = make(chan string, 3)var ch2 = make(chan int, 5)for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {go sample(ch1)go sampleTwo(ch2)}// select 多个队列的随机选择for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ {select {case str, ch1Check := <-ch1:if !ch1Check {fmt.Println("ch1Check false")}fmt.Println(str)case p, ch2Check := <-ch2:if !ch2Check {fmt.Println("ch2Check false")}fmt.Println(p)}}time.Sleep(60 * time.Second)}
加大两个sample的时间差
package mainimport ("strconv""time""fmt")func sample(ch chan string) {for i := 0; i < 19; i++ {ch <- "I am sample num :" + strconv.Itoa(i)time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)}}func sampleTwo(ch chan int) {for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {ch <- itime.Sleep(60 * time.Second)}}func main() {/*** 队列为3的*/var ch1 = make(chan string, 3)var ch2 = make(chan int, 5)for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {go sample(ch1)go sampleTwo(ch2)}// select 多个队列的随机选择for {select {case str, ch1Check := <-ch1:if !ch1Check {fmt.Println("ch1Check false")}fmt.Println(str)case p, ch2Check := <-ch2:if !ch2Check {fmt.Println("ch2Check false")}fmt.Println(p)}}}


