- 一、概述">一、概述
- 五、Helm Chart 详解">五、Helm Chart 详解
- 六、Templates and Values">六、Templates and Values
- 七、Helm 资源安装顺序">七、Helm 资源安装顺序
- 八、Helm 安装 Chart 包的三种方式">八、Helm 安装 Chart 包的三种方式
- 九、Helm 基础语法">九、Helm 基础语法
- 1)变量">1)变量
- 2)内置对象">2)内置对象
- 3)常用的内置函数">3)常用的内置函数
- 1、quote and squote">1、quote and squote
- 2、default">2、default
- 3、print">3、print
- 4、println">4、println
- 5、printf">5、printf
- 6、trim">6、trim
- 7、trimAll">7、trimAll
- 8、lower">8、lower
- 9、upper">9、upper
- 10、title">10、title
- 11、substr">11、substr
- 12、abbrev">12、abbrev
- 13、contains">13、contains
- 14、cat">14、cat
- 15、indent">15、indent
- 16、nindent">16、nindent
- 17、replace">17、replace
- 18、date">18、date
- 5)正则表达式(Regular Expressions)">5)正则表达式(Regular Expressions)
- 6)编码和解码函数">6)编码和解码函数
- 7)Dictionaries and Dict Functions">7)Dictionaries and Dict Functions
- 1、创建字典(dict)">1、创建字典(dict)
- 2、获取值(get)">2、获取值(get)
- 3、添加键值对(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">set</font>)">3、添加键值对(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">set</font>) - 4、删除(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">unset</font>)">4、删除(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">unset</font>) - 5、判断 key(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">hasKey</font>)">5、判断 key(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">hasKey</font>) - 6、pluck">6、pluck
- 7、合并 dict(merge, mustMerge)">7、合并 dict(merge, mustMerge)
- 8、获取所有 keys">8、获取所有 keys
- 9、获取所有 values">9、获取所有 values
- 8)Lists and List Functions">8)Lists and List Functions
- 1、创建列表">1、创建列表
- 2、获取列表第一项(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">first</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustFirst</font>)">2、获取列表第一项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">first</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustFirst</font>) - 3、获取列表的尾部内容(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">rest</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustRest</font>)">3、获取列表的尾部内容(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">rest</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustRest</font>) - 4、获取列表的最后一项(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">last</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustLast</font>)">4、获取列表的最后一项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">last</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustLast</font>) - 5、获取列表所有内容(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">initial</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustInitial</font>)">5、获取列表所有内容(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">initial</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustInitial</font>) - 6、末尾添加元素(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">append</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustAppend</font>)">6、末尾添加元素(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">append</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustAppend</font>) - 7、前面添加元素(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">prepend</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustPrepend</font>)">7、前面添加元素(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">prepend</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustPrepend</font>) - 8、多列表连接(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">concat</font>)">8、多列表连接(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">concat</font>) - 9、反转(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">reverse</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustReverse</font>)">9、反转(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">reverse</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustReverse</font>) - 10、去重(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">uniq</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustUniq</font>)">10、去重(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">uniq</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustUniq</font>) - 11、过滤(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">without</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustWithout</font>)">11、过滤(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">without</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustWithout</font>) - 12、判断元素是否存在(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">has</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustHas</font>)">12、判断元素是否存在(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">has</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustHas</font>) - 13、删除空项(
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">compact</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustCompact</font>)">13、删除空项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">compact</font>,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustCompact</font>) - 14、index">14、index
- 15、获取部分元素(slice, mustSlice)">15、获取部分元素(slice, mustSlice)
- 16、构建一个整数列表(until)">16、构建一个整数列表(until)
- 17、seq">17、seq
- 9)数学函数(Math Functions)">9)数学函数(Math Functions)
- 10)条件语句">10)条件语句
- 11)变更作用域 with">11)变更作用域 with
- 12)rang 循环语句">12)rang 循环语句
- 13)命名模板">13)命名模板
- 14)NOTES.txt 文件">14)NOTES.txt 文件
- 15)模板调试">15)模板调试
一、概述
可以将 Helm 看作 Kubernetes 下的 apt-get/yum。Helm 是 kubernetes 的包管理器,helm 仓库里面只有配置清单文件,而没有镜像,镜像还是由镜像仓库来提供,比如 hub.docker.com、私有仓库。 官方文档:https://v3.helm.sh/zh/docs/ ## 二、Helm 架构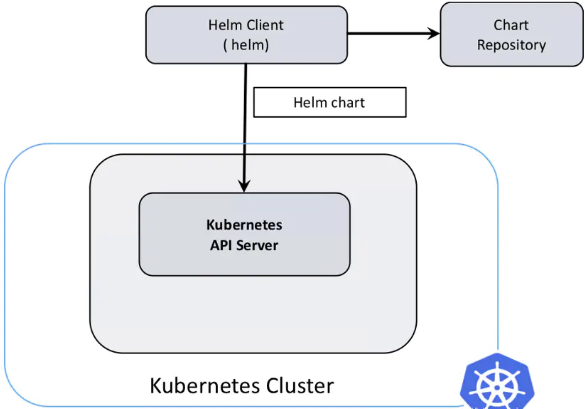 ## 三、Helm 安装
下载地址:https://github.com/helm/helm/releases
## 三、Helm 安装
下载地址:https://github.com/helm/helm/releases
bash
# 下载包
$ wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.9.4-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 解压压缩包
$ tar -xf helm-v3.9.4-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 制作软连接
$ ln -s /opt/helm/linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
# 验证
$ helm version
$ helm help
## 四、Helm 组件及相关术语
+ Helm——Helm 是一个命令行下的客户端工具。主要用于 Kubernetes 应用程序 Chart 的创建、打包、发布以及创建和管理本地和远程的 Chart 仓库。
+ Chart——Chart 代表着 Helm 包。它包含在 Kubernetes 集群内部运行应用程序,工具或服务所需的所有资源定义。可以把它看作是 Homebrew formula,Apt dpkg,或 Yum RPM 在 Kubernetes 中的等价物。
+ Release——Release 是运行在 Kubernetes 集群中的 chart 的实例。一个 chart 通常可以在同一个集群中安装多次。每一次安装都会创建一个新的 release。
+ Repoistory——Repository(仓库) 是用来存放和共享 charts 的地方。它就像 Perl 的 CPAN 档案库网络 或是 Fedora 的 软件包仓库,只不过它是供 Kubernetes 包所使用的。
五、Helm Chart 详解
1)Chart 目录结构
# 通过helm create命令创建一个新的chart包helm create nginxtree nginx
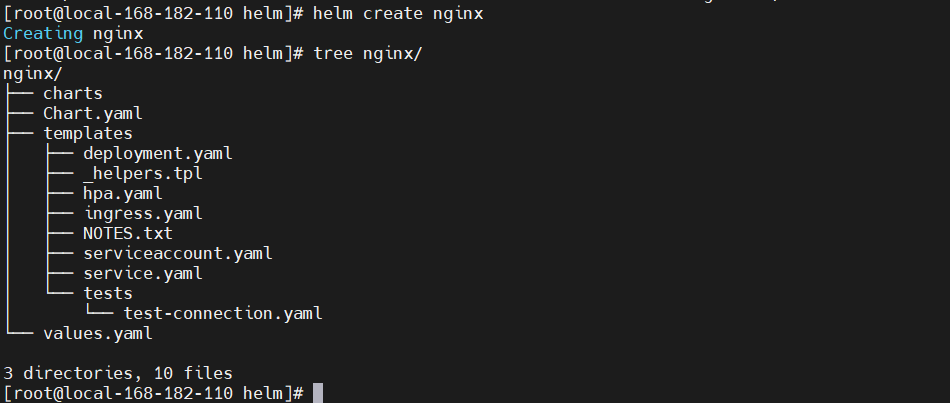
可能有写包还会有以下几个目录:
nginx/├── charts #依赖其他包的charts文件├── Chart.yaml # 该chart的描述文件,包括ico地址,版本信息等├── templates # #存放k8s模板文件目录│ ├── deployment.yaml # 创建k8s资源的yaml 模板│ ├── _helpers.tpl # 下划线开头的文件,可以被其他模板引用│ ├── hpa.yaml # 弹性扩缩容,配置服务资源CPU 内存│ ├── ingress.yaml # ingress 配合service域名访问的配置│ ├── NOTES.txt # 说明文件,helm install之后展示给用户看的内容│ ├── serviceaccount.yaml # 服务账号配置│ ├── service.yaml # kubernetes Serivce yaml 模板│ └── tests # 测试模块│ └── test-connection.yaml└── values.yaml # 给模板文件使用的变量
wordpress/...LICENSE # 可选: 包含chart许可证的纯文本文件README.md # 可选: 可读的README文件values.schema.json # 可选: 一个使用JSON结构的values.yaml文件charts/ # 包含chart依赖的其他chartcrds/ # 自定义资源的定义...
2)Chart.yaml 文件
apiVersion: chart API 版本 (必需)name: chart名称 (必需)version: chart 版本,语义化2 版本(必需)kubeVersion: 兼容Kubernetes版本的语义化版本(可选)description: 一句话对这个项目的描述(可选)type: chart类型 (可选)keywords:- 关于项目的一组关键字(可选)home: 项目home页面的URL (可选)sources:- 项目源码的URL列表(可选)dependencies: # chart 必要条件列表 (可选)- name: chart名称 (nginx)version: chart版本 ("1.2.3")repository: (可选)仓库URL ("https://example.com/charts") 或别名 ("@repo-name")condition: (可选) 解析为布尔值的yaml路径,用于启用/禁用chart (e.g. subchart1.enabled )tags: # (可选)- 用于一次启用/禁用 一组chart的tagimport-values: # (可选)- ImportValue 保存源值到导入父键的映射。每项可以是字符串或者一对子/父列表项alias: (可选) chart中使用的别名。当你要多次添加相同的chart时会很有用maintainers: # (可选)- name: 维护者名字 (每个维护者都需要)email: 维护者邮箱 (每个维护者可选)url: 维护者URL (每个维护者可选)icon: 用做icon的SVG或PNG图片URL (可选)appVersion: 包含的应用版本(可选)。不需要是语义化,建议使用引号deprecated: 不被推荐的chart (可选,布尔值)annotations:example: 按名称输入的批注列表 (可选).
- 从 v3.3.2,不再允许额外的字段。推荐的方法是在 annotations 中添加自定义元数据。
- 每个 chart 都必须有个版本号(version)。版本必须遵循 语义化版本 2 标准。不像经典 Helm, Helm v2 以及后续版本会使用版本号作为发布标记。仓库中的包通过名称加版本号标识。
【温馨提示】appVersion字段与version字段并不相关。这是指定应用版本的一种方式。比如,这个 drupal chart 可能有一个 appVersion: “8.2.1”,表示包含在 chart(默认)的 Drupal 的版本是 8.2.1。
nginx-1.2.3.tgz
3)Chart 依赖管理(dependencies)
当前 chart 依赖的其他 chart 会在 dependencies 字段定义为一个列表。
dependencies:- name: apacheversion: 1.2.3repository: https://example.com/charts- name: mysqlversion: 3.2.1repository: https://another.example.com/charts
- name 字段是需要的 chart 的名称
- version 字段是需要的 chart 的版本
- repository 字段是 chart 仓库的完整 URL。注意必须使用
<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">helm repo add</font>在本地添加仓库 - 可以使用仓库的名称代替 URL
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnamihelm pull bitnami/wordpresstar -xf wordpresscat wordpress/Chart.yaml
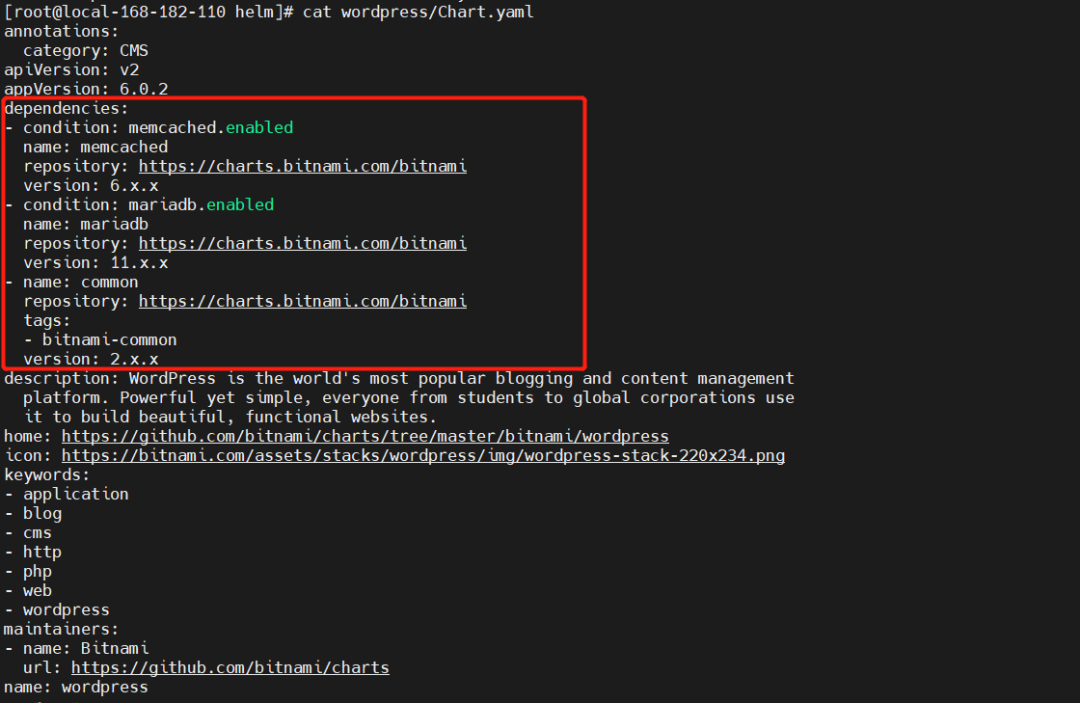
一旦定义好了依赖,运行 <font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm dependency update</font> 就会使用依赖文件下载所有指定的 chart 到 charts/目录。
当
helm dependency update ./wordpress
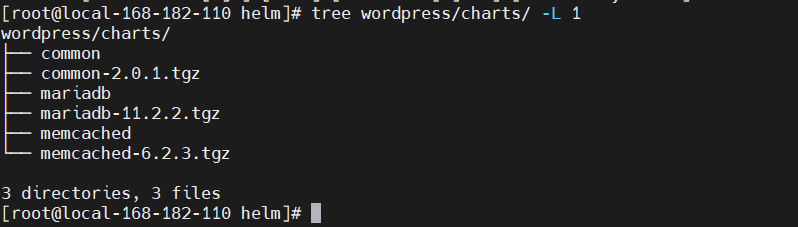
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">helm dependency update</font> 拉取 chart 时,会在 charts/目录中形成一个 chart 包。因此对于上面的示例,会在 chart 目录中期望看到以下文件:
wordpress/charts/├── common├── common-2.0.1.tgz├── mariadb├── mariadb-11.2.2.tgz├── memcached└── memcached-6.2.3.tgz
依赖中的 tag 和条件字段
除了上面的其他字段外,每个需求项可以包含可选字段 tags 和 condition。所有的 chart 会默认加载。如果存在 tags 或者 condition 字段,它们将被评估并用于控制它们应用的 chart 的加载。- Condition ——条件字段field 包含一个或多个 YAML 路径(用逗号分隔)。如果这个路径在上层 values 中已存在并解析为布尔值,chart 会基于布尔值启用或禁用 chart。只会使用列表中找到的第一个有效路径,如果路径为未找到则条件无效。
- Tags ——tag字段是与 chart 关联的 YAML 格式的标签列表。在顶层 value 中,通过指定 tag 和布尔值,可以启用或禁用所有的带 tag 的 chart。
# parentchart/Chart.yamldependencies:- name: subchart1repository: http://localhost:10191version: 0.1.0condition: subchart1.enabled, global.subchart1.enabledtags:- front-end- subchart1- name: subchart2repository: http://localhost:10191version: 0.1.0condition: subchart2.enabled,global.subchart2.enabledtags:- back-end- subchart2# parentchart/values.yamlsubchart1:enabled: truetags:front-end: falseback-end: true
- 在上面的例子中,所有带 front-end tag 的 chart 都会被禁用,但只要上层的 value 中
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">subchart1.enabled</font>路径被设置为<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">'true'</font>,该条件会覆盖 front-end 标签且 subchart1 会被启用。 - 一旦 subchart2 使用了 back-end 标签并被设置为了 true,subchart2 就会被启用。也要注意尽管 subchart2 指定了一个条件字段, 但是上层 value 没有相应的路径和 value,因此这个条件不会生效。
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--set</font> 参数可以用来设置标签和条件值。
标签和条件的解析:
helm install --set tags.front-end=true --set subchart2.enabled=false
- 条件 (当设置在 value 中时)总是会覆盖标签 第一个 chart 条件路径存在时会忽略后面的路径。
- 标签被定义为 ‘如果任意的 chart 标签是 true,chart 就可以启用’。
- 标签和条件值必须被设置在顶层 value 中。
- value 中的 tags:键必须是顶层键。
4)通过依赖导入子 Value
- 在某些情况下,允许子 chart 的值作为公共默认传递到父 chart 中是值得的。使用
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">exports</font>格式的额外好处是它可是将来的工具可以自检用户可设置的值。 - 被导入的包含值的 key 可以在父 chart 的 dependencies 中的
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">import-values</font>字段以 YAML 列表形式指定。列表中的每一项是从子 chart 中 exports 字段导入的 key。 - 导入 exports key 中未包含的值,使用 子-父格式。两种格式的示例如下所述。
如果子 chart 的 values.yaml 文件中在根节点包含了 exports 字段,它的内容可以通过指定的可以被直接导入到父 chart 的 value 中, 如下所示:
# parent's Chart.yaml filedependencies:- name: subchartrepository: http://localhost:10191version: 0.1.0import-values:- data
只要再导入列表中指定了键 data,Helm 就会在子 chart 的 exports 字段查找 data 键并导入它的内容。 最终的父级 value 会包含导出字段:
# child's values.yaml fileexports:data:myint: 99
【注意】父级键 data 没有包含在父级最终的 value 中,如果想指定这个父级键,要使用‘子-父’ 格式。 下面示例中的
# parent's valuesmyint: 99
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">import-values</font> 指示 Helm 去拿到能再 child:路径中找到的任何值,并拷贝到 parent:的指定路径。
上面的例子中,在 subchart1 里面找到的 default.data 的值会被导入到父 chart 的 myimports 键中,细节如下:
# parent's Chart.yaml filedependencies:- name: subchart1repository: http://localhost:10191version: 0.1.0...import-values:- child: default.dataparent: myimports
父 chart 的结果值将会是这样:
# parent's values.yaml filemyimports:myint: 0mybool: falsemystring: "helm rocks!"# subchart1's values.yaml filedefault:data:myint: 999mybool: true
# parent's final valuesmyimports:myint: 999mybool: truemystring: "helm rocks!"
六、Templates and Values
1)Templates and Values 简介
- Helm Chart 模板是按照 Go 模板语言书写, 增加了 50 个左右的附加模板函数 来自 Sprig 库 和一些其他 指定的函数。
- 所有模板文件存储在 chart 的 templates/ 文件夹。当 Helm 渲染 chart 时,它会通过模板引擎遍历目录中的每个文件。
- Chart 开发者可以在 chart 中提供一个命名为 values.yaml 的文件。这个文件包含了默认值。
- Chart 用户可以提供一个包含了 value 的 YAML 文件。可以在命令行使用
<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">helm install</font>命令时通过<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">-f</font>指定 value 文件。
上面的例子,松散地基于:https://github.com/deis/charts 是一个 Kubernetes 副本控制器的模板。可以使用下面四种模板值(一般被定义在 values.yaml 文件):
apiVersion: v1kind: ReplicationControllermetadata:name: deis-databasenamespace: deislabels:app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: deisspec:replicas: 1selector:app.kubernetes.io/name: deis-databasetemplate:metadata:labels:app.kubernetes.io/name: deis-databasespec:serviceAccount: deis-databasecontainers:- name: deis-databaseimage: {{ .Values.imageRegistry }}/postgres:{{ .Values.dockerTag }}imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.pullPolicy }}ports:- containerPort: 5432env:- name: DATABASE_STORAGEvalue: {{ default "minio" .Values.storage }}
<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">imageRegistry</font>: Docker 镜像的源注册表<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">dockerTag</font>: Docker 镜像的 tag<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">pullPolicy</font>: Kubernetes 的拉取策略<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">storage</font>: 后台存储,默认设置为”minio”
2)预定义的 Values
Values 通过模板中.Values 对象可访问的 values.yaml 文件(或者通过<font style="color:rgb(89, 89, 89);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--set</font> 参数)提供, 但可以模板中访问其他预定义的数据片段。
以下值是预定义的,对每个模板都有效,并且可以被覆盖。和所有值一样,名称 区分大小写。
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Name</font>: 版本名称(非 chart 的)<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Namespace</font>: 发布的 chart 版本的命名空间<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Service</font>: 组织版本的服务<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.IsUpgrade</font>: 如果当前操作是升级或回滚,设置为 true<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.IsInstall</font>: 如果当前操作是安装,设置为 true<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Chart</font>: Chart.yaml的内容。因此,chart 的版本可以从<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">Chart.Version</font>获得, 并且维护者在 Chart.Maintainers 里。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Files</font>: chart 中的包含了非特殊文件的类图对象。这将不允许您访问模板, 但是可以访问现有的其他文件(除非被.helmignore 排除在外)。使用<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{ index .Files "file.name" }}</font>可以访问文件或者使用<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{.Files.Get name }}</font>功能。也可以使用<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{ .Files.GetBytes }}</font>作为[]byte 访问文件内容。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Capabilities</font>: 包含了 Kubernetes 版本信息的类图对象。(<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{ .Capabilities.KubeVersion }}</font>) 和支持的 Kubernetes API 版本(<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{ .Capabilities.APIVersions.Has "batch/v1" }}</font>)
values 文件被定义为 YAML 格式。chart 会包含一个默认的 values.yaml 文件。Helm 安装命令允许用户使用附加的 YAML values 覆盖这个 values:
imageRegistry: "quay.io/deis"dockerTag: "latest"pullPolicy: "Always"storage: "s3"
helm install --generate-name --values=myvals.yaml wordpress
3)范围,依赖和值
Values 文件可以声明顶级 chart 的值,以及charts/目录中包含的其他任意 chart。或者换个说法,values 文件可以为 chart 及其任何依赖项提供值。比如,上面示范的 WordPress chart 同时有 mysql 和 apache 作为依赖。values 文件可以为以下所有这些组件提供依赖:
更高阶的 chart 可以访问下面定义的所有变量。因此WordPress chart 可以用
title: "My WordPress Site" # Sent to the WordPress templatemysql:max_connections: 100 # Sent to MySQLpassword: "secret"apache:port: 8080 # Passed to Apache
**<font style="color:black;">.Values.mysql.password</font>** 访问 MySQL 密码。但是低阶的 chart 不能访问父级 chart,所以 MySQL 无法访问 title 属性。同样也无法访问 apache.port。
4)全局 Values
从 2.0.0-Alpha.2 开始,Helm 支持特殊的”global”值。设想一下前面的示例中的修改版本:面添加了 global 部分和一个值 app: MyWordPress。这个值以
title: "My WordPress Site" # Sent to the WordPress templateglobal:app: MyWordPressmysql:max_connections: 100 # Sent to MySQLpassword: "secret"apache:port: 8080 # Passed to Apache
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">.Values.global.app</font>在 所有 chart 中有效。
比如,mysql 模板可以以<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">{{.Values.global.app}}</font>访问 app,同样 apache chart 也可以访问。实际上,上面的 values 文件会重新生成为这样:
title: "My WordPress Site" # Sent to the WordPress templateglobal:app: MyWordPressmysql:global:app: MyWordPressmax_connections: 100 # Sent to MySQLpassword: "secret"apache:global:app: MyWordPressport: 8080 # Passed to Apache
七、Helm 资源安装顺序
- Namespace
- NetworkPolicy
- ResourceQuota
- LimitRange
- PodSecurityPolicy
- PodDisruptionBudget
- ServiceAccount
- Secret
- SecretList
- ConfigMap
- StorageClass
- PersistentVolume
- PersistentVolumeClaim
- CustomResourceDefinition
- ClusterRole
- ClusterRoleList
- ClusterRoleBinding
- ClusterRoleBindingList
- Role
- RoleList
- RoleBinding
- RoleBindingList
- Service
- DaemonSet
- Pod
- ReplicationController
- ReplicaSet
- Deployment
- HorizontalPodAutoscaler
- StatefulSet
- Job
- CronJob
- Ingress
- APIService
八、Helm 安装 Chart 包的三种方式
Helm 自带一个强大的搜索命令,可以用来从两种来源中进行搜索:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm search hub</font>从 Artifact Hub https://artifacthub.io/ 中查找并列出 helm charts。Artifact Hub 中存放了大量不同的仓库。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm search repo</font>从添加(使用<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm repo add</font>)到本地 helm 客户端中的仓库中进行查找。该命令基于本地数据进行搜索,无需连接互联网。
# 添加bitnami仓库源helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami# 从bitnami源查找所有chart包,不指定具体源的话,会查找本地添加的所有源地址的所有chart包helm search repo bitnami
1)values 传参
安装过程中有两种方式传递配置数据:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--values (或 -f)</font>:使用 YAML 文件覆盖配置。可以指定多次,优先使用最右边的文件。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--set</font>:通过命令行的方式对指定项进行覆盖。
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">--set</font> 中的值会被合并到 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">--values</font> 中,但是 <font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--set</font> 中的值优先级更高。在<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">--set</font> 中覆盖的内容会被被保存在 ConfigMap 中。可以通过 <font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm get values <release-name></font> 来查看指定 release 中 **<font style="color:black;">--set</font>** 设置的值。也可以通过运行 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">helm upgrade</font> 并指定 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">--reset-values</font> 字段来清除 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">--set</font> 中设置的值。示例如下:
echo '{mariadb.auth.database: user0db, mariadb.auth.username: user0}' > values.yamlhelm install -f values.yaml bitnami/wordpress --generate-name
2)【第一种方式】直接在线 安装不需要先下载包到本地
helm install mysql bitnami/mysqlhelm list
3)【第二种方式】离线安装 直接通过安装包安装
# 先删除helm uninstall mysql# 拉包到本地helm pull bitnami/mysql# 不解压直接安装helm install mysql ./mysql-9.3.1.tgzhelm list
4)【第三种方式】离线安装 解压包再安装
# 拉包到本地helm pull bitnami/mysql# 解压安装tar -xf mysql-9.3.1.tgz# 开始安装helm install mysql ./mysql \--namespace=mysql \--create-namespace \--set image.registry=myharbor.com \--set image.repository=bigdata/mysql \--set image.tag=8.0.30 \--set primary.service.type=NodePort \--set service.nodePorts.mysql=30306# 查看在运行的Releasehelm list# 卸载helm uninstall mysql -n mysql
九、Helm 基础语法
1)变量
模板(templates/)中的变量都放在<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">{{}}</font>中,比如:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">{{ .Values.images }}</font> 表示 Values 对象下的 images 字段。Values 来源于values.yaml文件或者<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">-f</font>指定的 yaml 文件,或者<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--set</font>设置的变量。
【温馨提示】使用<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">-</font>删除空格和换行符,要想删除那行其他的空格和换行符可以用<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">{{-</font><font style="color:rgb(89, 89, 89);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">或者-}}</font>,一个是删除左边的空格和换行符,一个是删除右边的空格和换行符。
2)内置对象
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release</font>:Release 对象描述了版本发布本身。包含了以下对象:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Name</font>:release 名称;<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Namespace</font>:版本中包含的命名空间(如果 manifest 没有覆盖的话);<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.IsUpgrade</font>:如果当前操作是升级或回滚的话,该值将被设置为 true<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.IsInstall</font>:如果当前操作是安装的话,该值将被设置为 true<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Revision</font>:此次修订的版本号。安装时是 1,每次升级或回滚都会自增;<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Service</font>:该 service 用来渲染当前模板。Helm 里始终 Helm。
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Values</font>:Values 对象是从values.yaml文件和用户提供的文件传进模板的。默认为空<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Chart</font>:Chart.yaml文件内容。Chart.yaml 里的所有数据在这里都可以可访问的。比如<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}</font>会打印出 mychart-0.1.0。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Template</font>:包含当前被执行的当前模板信息<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Template.Name</font>: 当前模板的命名空间文件路径 (e.g. mychart/templates/mytemplate.yaml);<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Template.BasePath</font>: 当前 chart 模板目录的路径 (e.g. mychart/templates)。
3)常用的内置函数
1、quote and squote
该函数将值转换成字符串用双引号(**<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">quote</font>**) 或者单引号(<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">squote</font>)括起来。示例如下:
倒置命令是模板中的常见做法。可以经常看到
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmapdata:myvalue: "Hello World"drink: {{ .Values.favorite.drink | quote }}food: {{ .Values.favorite.food | upper | quote }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">.val | quote</font> 而不是 <font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">quote .val</font>。实际上两种操作都是可以的。
2、default
这个函数允许在模板中指定一个默认值,以防这个值被忽略。“空”定义取决于以下类型:
# 如果.Values.favorite.drink是非空值,则使用它,否则会返回tea。drink: {{ .Values.favorite.drink | default "tea" | quote }}# 还可以这样写,如果.Bar是非空值,则使用它,否则会返回foo。default "foo" .Bar
整型: 0字符串: ""列表: []字典: {}布尔: false以及所有的nil (或 null)
3、print
返回各部分组合的字符串,非字符串类型会被转换成字符串。【温馨提示】当相邻两个参数不是字符串时会在它们之间添加一个空格。
print "Matt has " .Dogs " dogs"
4、println
和 print 效果一样,但会在末尾新添加一行。5、printf
返回参数按顺序传递的格式化字符串。更多占位符的使用,可以参考官方文档:
printf "%s has %d dogs." .Name .NumberDogs{{- printf "%d" (.Values.externalCache.port | int ) -}}{{- printf "%s" .Values.existingSecret -}}{{- printf "%v" .context.Values.redis.enabled -}}# %s 字符串占位符,未解析的二进制字符串或切片# %d 数字占位符,十进制# %v 默认格式的值,当打印字典时,加号参数(%+v)可以添加字段名称
https://helm.sh/zh/docs/chart_template_guide/function_list/
6、trim
trim 行数移除字符串两边的空格:
trim " hello "
7、trimAll
从字符串中移除给定的字符:上述结果为:5.00 (作为一个字符串)。
trimAll "$" "$5.00"
8、lower
将整个字符串转换成小写:上述结果为:hello
lower "HELLO"
9、upper
将整个字符串转换成大写:上述结果为:HELLO
upper "hello"
10、title
首字母转换成大写:上述结果为:Hello World
title "hello world"
11、substr
获取字符串的子串,有三个参数:<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">start (int)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">end (int)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">string (string)</font>
上述结果为:hello
substr 0 5 "hello world"
12、abbrev
用省略号截断字符串 (<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">...</font>)
上述结果为:he…, 因为将省略号算进了长度中。
abbrev 5 "hello world"# 第一个参数:最大长度# 第二个参数:字符串
13、contains
测试字符串是否包含在另一个字符串中:
contains "cat" "catch"
14、cat
cat 函数将多个字符串合并成一个,用空格分隔:上述结果为:hello beautiful world
cat "hello" "beautiful" "world"
15、indent
indent 以指定长度缩进给定字符串所在行,在对齐多行字符串时很有用:上述结果会将每行缩进 4 个空格。
indent 4 $lots_of_text
16、nindent
nindent 函数和 indent 函数一样,但可以在字符串开头添加新行。上述结果会在字符串所在行缩进 4 个字符,并且在开头新添加一行。
nindent 4 $lots_of_text
17、replace
执行简单的字符串替换。上述结果为:I-Am-Henry-VIII
# 下面两行等价replace " " "-" "I Am Henry VIII""I Am Henry VIII" | replace " " "-"# 参数1:待替换字符串# 参数2:要替换字符串# 参数3:源字符串
18、date
date 函数格式化日期,日期格式化为 YEAR-MONTH-DAY:想了解更多内置函数,可以参考官方文档:https://helm.sh/zh/docs/chart_template_guide/function_list/ ### 4)类型转换函数 Helm 提供了以下类型转换函数:
now | date "2006-01-02"
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">atoi</font>: 字符串转换成整型。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">float64</font>: 转换成 float64。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">int</font>: 按系统整型宽度转换成 int。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">int64</font>: 转换成 int64。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toDecimal</font>: 将 unix 八进制转换成 int64。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toString</font>: 转换成字符串。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toStrings</font>: 将列表、切片或数组转换成字符串列表。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toJson (mustToJson)</font>: 将列表、切片、数组、字典或对象转换成 JSON。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toPrettyJson (mustToPrettyJson)</font>: 将列表、切片、数组、字典或对象转换成格式化 JSON。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">toRawJson (mustToRawJson)</font>: 将列表、切片、数组、字典或对象转换成 HTML 字符未转义的 JSON。
5)正则表达式(Regular Expressions)
Helm 包含以下正则表达式函数<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexFind(mustRegexFind)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexFindAll(mustRegexFindAll)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexMatch (mustRegexMatch)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexReplaceAll (mustRegexReplaceAll)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexReplaceAllLiteral(mustRegexReplaceAllLiteral)</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">regexSplit (mustRegexSplit)</font>
6)编码和解码函数
Helm 有以下编码和解码函数:- b64enc/b64dec: 编码或解码 Base64
- b32enc/b32dec: 编码或解码 Base32
7)Dictionaries and Dict Functions
Helm 提供了一个 key/value 存储类型称为 dict(”dictionary”的简称,Python 中也有)。dict 是无序类型。字典的 key 必须是字符串。但值可以是任意类型,甚至是另一个 dict 或 list。1、创建字典(dict)
下面是创建三个键值对的字典:
$myDict := dict "name1" "value1" "name2" "value2" "name3" "value 3"
2、获取值(get)
给定一个映射和一个键,从映射中获取值。上述结果为:”value1” 注意如果没有找到,会简单返回””。不会生成 error。
get $myDict "name1"
3、添加键值对(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">set</font>)
使用 set 给字典添加一个键值对。
注意 set 返回字典 (Go 模板函数的一个要求),因此可能需要像上面那样使用使用
$_ := set $myDict "name4" "value4"
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$_</font>赋值来获取值。
4、删除(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">unset</font>)
给定一个映射和 key,从映射中删除这个 key。
和 set 一样,需要返回字典。
$_ := unset $myDict "name4"
5、判断 key(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">hasKey</font>)
hasKey 函数会在给定字典中包含了给定 key 时返回 true。
如果 key 没找到,会返回 false。
hasKey $myDict "name1"
6、pluck
pluck 函数给定一个键和多个映射,并获得所有匹配项的列表:上述会返回的 list 包含了每个找到的值(
pluck "name1" $myDict $myOtherDict
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">[value1 otherValue1]</font>)。
7、合并 dict(merge, mustMerge)
将两个或多个字典合并为一个, 目标字典优先:
$newdict := merge $dest $source1 $source2
8、获取所有 keys
keys 函数会返回一个或多个 dict 类型中所有的 key 的 list。由于字典是 无序的,key 不会有可预料的顺序。可以使用 sortAlpha 存储。当提供了多个词典时,key 会被串联起来。使用
keys $myDict | sortAlpha
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">uniq</font>函数和<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">sortAlpha</font>获取一个唯一有序的键列表。
keys $myDict $myOtherDict | uniq | sortAlpha
9、获取所有 values
values 函数类似于 keys,返回一个新的 list 包含源字典中所有的 value(只支持一个字典)。上述结果为:
$vals := values $myDict
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">list["value1", "value2", "value 3"]</font>。
注意 values 不能保证结果的顺序;如果需要顺序, 请使用sortAlpha。
8)Lists and List Functions
Helm 提供了一个简单的 list 类型,包含任意顺序的列表。类似于数组或切片,但列表是被设计用于不可变数据类型。1、创建列表
上述会生成一个列表 [1 2 3 4 5]。
$myList := list 1 2 3 4 5
2、获取列表第一项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">first</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustFirst</font>)
获取列表中的第一项,使用 first。
first 有问题时会出错,mustFirst 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
first $myList# 返回 1
3、获取列表的尾部内容(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">rest</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustRest</font>)
获取列表的尾部内容(除了第一项外的所有内容),使用 rest。
rest 有问题时会出错,mustRest 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
rest $myList# 返回 [2 3 4 5]
4、获取列表的最后一项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">last</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustLast</font>)
使用 last 获取列表的最后一项:
last $myList# 返回 5。这大致类似于反转列表然后调用first。
5、获取列表所有内容(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">initial</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustInitial</font>)
通过返回所有元素 但 除了最后一个元素。
initial 有问题时会出错,但是 mustInitial 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
initial $myList# 返回 [1 2 3 4]。
6、末尾添加元素(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">append</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustAppend</font>)
在已有列表中追加一项,创建一个新的列表。
上述语句会设置 myList 会保持不变。 append 有问题时会出错,但 mustAppend 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
$new = append $myList 6
7、前面添加元素(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">prepend</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustPrepend</font>)
将元素添加到列表的前面,生成一个新的列表。
上述语句会生成
prepend $myList 0
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">[0 1 2 3 4 5]</font>。<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">$myList</font> 会保持不变。
<font style="color:rgb(89, 89, 89);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">prepend</font> 有问题时会出错,但 <font style="color:rgb(89, 89, 89);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">mustPrepend</font> 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
8、多列表连接(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">concat</font>)
将任意数量的列表串联成一个。
上述语句会生成
concat $myList ( list 6 7 ) ( list 8 )
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]</font>。<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">$myList</font> 会保持不变。
9、反转(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">reverse</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustReverse</font>)
反转给定的列表生成一个新列表。
上述语句会生成一个列表:[5 4 3 2 1]。 reverse 有问题时会出错,但 mustReverse 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
reverse $myList
10、去重(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">uniq</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustUniq</font>)
生成一个移除重复项的列表。
上述语句会生成 [1 2] uniq 有问题时会出错,但 mustUniq 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
list 1 1 1 2 | uniq
11、过滤(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">without</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustWithout</font>)
without 函数从列表中过滤内容。
一个过滤器可以过滤多个元素:
without $myList 3# 上述语句会生成 [1 2 4 5]
without 有问题时会出错,但 mustWithout 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
without $myList 1 3 5# 这样会得到: [2 4]
12、判断元素是否存在(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">has</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustHas</font>)
验证列表是否有特定元素。
上述语句会返回 true,但 has “hello” $myList 就会返回 false。 has 有问题时会出错,但 mustHas 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
has 4 $myList
13、删除空项(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">compact</font>, <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mustCompact</font>)
接收一个列表并删除空值项。
compact 会返回一个移除了空值(比如, “”)的新列表。 compact 有问题时会出错,但 mustCompact 有问题时会向模板引擎返回错误。
$list := list 1 "a" "foo" ""$copy := compact $list
14、index
使用<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">index list [n]</font>获取列表的第 n 个元素。使用 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">index list [n] [m] ...</font>获取多位列表元素。
<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">index $myList 0</font>返回 1,同<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[0]</font><font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">index $myList 0 1</font>同<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[0][1]</font>
15、获取部分元素(slice, mustSlice)
从列表中获取部分元素,使用<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">slice list [n] [m]</font>。等同于 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">list[n:m]</font>.
<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">slice $myList</font>返回<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">[1 2 3 4 5]</font>。等同于<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[:]</font>。<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">slice $myList 3</font>返回<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">[4 5]</font>等同于<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[3:]</font>。<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">slice $myList 1 3</font>返回<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">[2 3]</font>等同于<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[1:3]</font>。<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">slice $myList 0 3</font>返回<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">[1 2 3]</font>等同于<font style="color:rgb(1, 1, 1);">myList[:3]</font>。
16、构建一个整数列表(until)
until 函数构建一个整数范围。上述语句会生成一个列表:
until 5
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]</font>。
对循环语句很有用:<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">range e := until 5</font>。
17、seq
seq 5 => 1 2 3 4 5seq -3 => 1 0 -1 -2 -3seq 0 2 => 0 1 2seq 2 -2 => 2 1 0 -1 -2seq 0 2 10 => 0 2 4 6 8 10seq 0 -2 -5 => 0 -2 -4
9)数学函数(Math Functions)
1、求和(add)
使用 add 求和。接受两个或多个输入。
add 1 2 3
2、自加 1(add1)
自增加 1,使用 add1。3、相减(sub)
相减使用 sub。4、除(div)
整除使用 div。5、取模(mod)
取模使用 mod。6、相乘(mul)
相乘使用 mul。接受两个或多个输入。
mul 1 2 3
7、获取最大值(max)
返回一组整数中最大的整数。
max 1 2 3# 返回 3
8、获取最小值(min)
返回一组数中最小的数。
min 1 2 3# 会返回 1。
9、获取长度(len)
以整数返回参数的长度。
len .Arg
10)Network Functions
Helm 提供了几个网络函数:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">getHostByName</font>接收一个域名返回 IP 地址。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">getHostByName</font>“www.google.com”会返回对应的 www.google.com 的地址。
10)条件语句
运算符:
eq: 等于(equal to)ne: 不等于(not equal to)lt: 小于(less than)le: 小于等于(less than or equal to)gt: 大于(greater than)ge: 大于等于(greater than or equal to)
if/else 用法:
如果是以下值时,管道会被设置为 false:
{{if 命令}}…{{else if 命令}}…{{else}}…{{end}}
【示例】
布尔false数字0空字符串nil (空或null)空集合(map, slice, tuple, dict, array)
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmapdata:myvalue: "Hello World"drink: {{ .Values.favorite.drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .Values.favorite.food | upper | quote }}{{ if eq .Values.favorite.drink "coffee" }}mug: "true"{{ end }}
11)变更作用域 with
下一个控制结构是with操作。这个用来控制变量范围。回想一下,.是对 当前作用域 的引用。因此 .Values就是告诉模板在当前作用域查找 Values 对象。 with 的语法与 if 语句类似:作用域可以被改变。with 允许为特定对象设定当前作用域(
{{ with PIPELINE }}# restricted scope{{ end }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">.</font>)。比如,已经在使用<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">.Values.favorite</font>。修改配置映射中的.的作用域指向<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">.Values.favorite</font>:
但是这里有个注意事项,在限定的作用域内,无法使用.访问父作用域的对象。错误示例如下:
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmapdata:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}{{- end }}
这样会报错因为
{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}release: {{ .Release.Name }}{{- end }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">Release.Name</font>不在**<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">.</font>**限定的作用域内。但是如果对调最后两行就是正常的, 因为在<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">{{ end }}</font>之后作用域被重置了。
或者,可以使用
{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}{{- end }}release: {{ .Release.Name }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$</font>从父作用域中访问 Release.Name 对象。当模板开始执行后<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$</font>会被映射到根作用域,且执行过程中不会更改。下面这种方式也可以正常工作:
也可以在外边定义变量,遵循
{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}release: {{ $.Release.Name }}{{- end }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$name变量</font>的格式且指定了一个特殊的赋值运算符:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">:=</font>。可以使用针对 <font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">Release.Name</font> 的变量重写上述内容。
注意在 with 块开始之前,赋值
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmapdata:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- $relname := .Release.Name -}}{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}release: {{ $relname }}{{- end }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$relname := .Release.Name</font>。现在在 with 块中,<font style="color:rgb(89, 89, 89);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">$relname</font> 变量仍会执行版本名称。
12)rang 循环语句
很多编程语言支持使用 for 循环,foreach 循环,或者类似的方法机制。在 Helm 的模板语言中,在一个集合中迭代的方式是使用range操作符。 定义 values现在有了一个 pizzaToppings 列表(模板中称为切片)。修改模板把这个列表打印到配置映射中:
favorite:drink: coffeefood: pizzapizzaToppings:- mushrooms- cheese- peppers- onions
有时能在模板中快速创建列表然后迭代很有用,Helm 模板的 tuple 可以很容易实现该功能。在计算机科学中, 元组表示一个有固定大小的类似列表的集合,但可以是任意数据类型。这大致表达了
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmapdata:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- with .Values.favorite }}drink: {{ .drink | default "tea" | quote }}food: {{ .food | upper | quote }}{{- end }}toppings: |-{{- range .Values.pizzaToppings }}- {{ . | title | quote }}{{- end }}
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">tuple</font>的用法。
上述模板会生成以下内容:
sizes: |-{{- range tuple "small" "medium" "large" }}- {{ . }}{{- end }}
sizes: |-- small- medium- large
13)命名模板
此时需要越过模板,开始创建其他内容了。该部分会看到如何在一个文件中定义 命名模板,并在其他地方使用。命名模板 (有时称作一个 部分 或一个 子模板)仅仅是在文件内部定义的模板,并使用了一个名字。有两种创建方式和几种不同的使用方法。- 三种声明和管理模板的方法:define,template,和block,在这部分,将使用这三种操作并介绍一种特殊用途的 include方法,类似于 template 操作。
- 命名模板时要记住一个重要细节:模板名称是全局的。如果您想声明两个相同名称的模板,哪个最后加载就使用哪个。因为在子 chart 中的模板和顶层模板一起编译,命名时要注意 chart 特定名称。
- 一个常见的命名惯例是用 chart 名称作为模板前缀:{{ define “mychart.labels” }}。使用特定 chart 名称作为前缀可以避免可能因为 两个不同 chart 使用了相同名称的模板而引起的冲突。
- templates/中的大多数文件被视为包含 Kubernetes 清单
- NOTES.txt 是个例外
- 命名以下划线(
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">_</font>)开始的文件则假定 没有 包含清单内容。这些文件不会渲染为 Kubernetes 对象定义,但在其他 chart 模板中都可用。
1、用 define 和 template 声明和使用模板
define 操作允许在模板文件中创建一个命名模板,语法如下:比如可以定义一个模板封装 Kubernetes 的标签:
{{- define "MY.NAME" }}# body of template here{{- end }}
现在将模板嵌入到了已有的配置映射中,然后使用template包含进来:
{{- define "mychart.labels" }}labels:generator: helmdate: {{ now | htmlDate }}{{- end }}
当模板引擎读取该文件时,它会存储 mychart.labels 的引用直到 template “mychart.labels”被调用。然后会按行渲染模板,因此结果类似这样:
{{- define "mychart.labels" }}labels:generator: helmdate: {{ now | htmlDate }}{{- end }}apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmap{{- template "mychart.labels" }}data:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- range $key, $val := .Values.favorite }}{{ $key }}: {{ $val | quote }}{{- end }}
注意:define 不会有输出,除非像本示例一样用模板调用它。 按照惯例,Helm chart 将这些模板放置在局部文件中,一般是_helpers.tpl。把这个方法移到那里:
# Source: mychart/templates/configmap.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: running-panda-configmaplabels:generator: helmdate: 2022-09-04data:myvalue: "Hello World"drink: "coffee"food: "pizza"
{{/* Generate basic labels */}}{{- define "mychart.labels" }}labels:generator: helmdate: {{ now | htmlDate }}{{- end }}
2、设置模板范围
在上面定义的模板中,没有使用任何对象,仅仅使用了方法。修改定义好的模板让其包含 chart 名称和版本号:
{{/* Generate basic labels */}}{{- define "mychart.labels" }}labels:generator: helmdate: {{ now | htmlDate }}chart: {{ .Chart.Name }}version: {{ .Chart.Version }}{{- end }}
3、<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">include</font> 方法
假设定义了一个简单模板如下:
现在假设想把这个插入到模板的 labels:部分和 data:部分:
{{- define "mychart.app" -}}app_name: {{ .Chart.Name }}app_version: "{{ .Chart.Version }}"{{- end -}}
如果渲染这个,会得到以下错误:
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmaplabels:{{ template "mychart.app" . }}data:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- range $key, $val := .Values.favorite }}{{ $key }}: {{ $val | quote }}{{- end }}{{ template "mychart.app" . }}
要查看渲染了什么,可以用
$ helm install --dry-run measly-whippet ./mychartError: unable to build kubernetes objects from release manifest: error validating "": error validating data: [ValidationError(ConfigMap): unknown field "app_name" in io.k8s.api.core.v1.ConfigMap, ValidationError(ConfigMap): unknown field "app_version" in io.k8s.api.core.v1.ConfigMap]
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">--disable-openapi-validation</font>参数重新执行:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm install --dry-run --disable-openapi-validation measly-whippet ./mychart</font>。输入不是想要的:
注意两处的app_version 缩进都不对,为啥?因为被替换的模板中文本是左对齐的。由于template是一个行为,不是方法,无法将 **template**调用的输出传给其他方法,数据只是简单地按行插入。 为了处理这个问题,Helm 提供了一个include,可以将模板内容导入当前管道,然后传递给管道中的其他方法。下面这个示例,使用indent正确地缩进了 mychart.app 模板:
# Source: mychart/templates/configmap.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: measly-whippet-configmaplabels:app_name: mychartapp_version: "0.1.0"data:myvalue: "Hello World"drink: "coffee"food: "pizza"app_name: mychartapp_version: "0.1.0"
现在生成的 YAML 每一部分都可以正确缩进了:
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: {{ .Release.Name }}-configmaplabels:{{ include "mychart.app" . | indent 4 }}data:myvalue: "Hello World"{{- range $key, $val := .Values.favorite }}{{ $key }}: {{ $val | quote }}{{- end }}{{ include "mychart.app" . | indent 2 }}
include 相较于使用 template,在 helm 中使用 include 被认为是更好的方式 只是为了更好地处理 YAML 文档的输出格式。
# Source: mychart/templates/configmap.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: edgy-mole-configmaplabels:app_name: mychartapp_version: "0.1.0"data:myvalue: "Hello World"drink: "coffee"food: "pizza"app_name: mychartapp_version: "0.1.0"
14)NOTES.txt 文件
该部分会介绍为 chart 用户提供说明的 Helm 工具。在 helm install 或 helm upgrade 命令的最后,Helm 会打印出对用户有用的信息。使用模板可以高度自定义这部分信息。 要在 chart 添加安装说明,只需创建templates/NOTES.txt文件即可。该文件是纯文本,但会像模板一样处理, 所有正常的模板函数和对象都是可用的。创建一个简单的 NOTES.txt 文件:现在如果执行
Thank you for installing {{ .Chart.Name }}.Your release is named {{ .Release.Name }}.To learn more about the release, try:$ helm status {{ .Release.Name }}$ helm get all {{ .Release.Name }}
<font style="color:rgb(58, 58, 58);">helm install rude-cardinal ./mychart</font> 会在底部看到:
使用 NOTES.txt 这种方式是给用户提供关于如何使用新安装的 chart 细节信息的好方法。尽管并不是必需的,强烈建议创建一个**NOTES.txt**文件。
RESOURCES:==> v1/SecretNAME TYPE DATA AGErude-cardinal-secret Opaque 1 0s==> v1/ConfigMapNAME DATA AGErude-cardinal-configmap 3 0sNOTES:Thank you for installing mychart.Your release is named rude-cardinal.To learn more about the release, try:$ helm status rude-cardinal$ helm get all rude-cardinal
15)模板调试
调试模板可能很棘手,因为渲染后的模板发送给了 Kubernetes API server,可能会以格式化以外的原因拒绝 YAML 文件。以下命令有助于调试:<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm lint</font>是验证 chart 是否遵循最佳实践的首选工具<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm install --dry-run --debug</font>或<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm template --debug</font>:已经看过这个技巧了, 这是让服务器渲染模板的好方法,然后返回生成的清单文件。<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm get manifest</font>:这是查看安装在服务器上的模板的好方法。
<font style="color:rgb(155, 110, 35);background-color:rgb(255, 245, 227);">helm install --dry-run --debug</font>:
以上内容会被渲染同时返回完整的注释:
apiVersion: v2# some: problem section# {{ .Values.foo | quote }}
其实这里主要是正对官方文档进行整理,列出了常见的使用语法,想了解更多,可以参考官方文档,官方文档讲解的很细致。
apiVersion: v2# some: problem section# "bar"

