下边的程序在端口 8088 上启动了一个网页服务器;SimpleServer 会处理 /test1 url 使它在浏览器输出 hello world。FormServer 会处理 /test2 url:如果 url 最初由浏览器请求,那么它就是一个 GET 请求,并且返回一个 form 常量,包含了简单的 input 表单,这个表单里有一个文本框和一个提交按钮。当在文本框输入一些东西并点击提交按钮的时候,会发起一个 POST 请求。FormServer 中的代码用到了 switch 来区分两种情况。在 POST 情况下,使用 request.FormValue("inp") 通过文本框的 name 属性 inp 来获取内容,并写回浏览器页面。在控制台启动程序并在浏览器中打开 url http://localhost:8088/test2 来测试这个程序:
示例 15.10 simple_webserver.go
package mainimport ("io""net/http")const form = `<html><body><form action="#" method="post" name="bar"><input type="text" name="in" /><input type="submit" value="submit"/></form></body></html>`/* handle a simple get request */func SimpleServer(w http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {io.WriteString(w, "<h1>hello, world</h1>")}func FormServer(w http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html")switch request.Method {case "GET":/* display the form to the user */io.WriteString(w, form)case "POST":/* handle the form data, note that ParseForm mustbe called before we can extract form data *///request.ParseForm();//io.WriteString(w, request.Form["in"][0])io.WriteString(w, request.FormValue("in"))}}func main() {http.HandleFunc("/test1", SimpleServer)http.HandleFunc("/test2", FormServer)if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8088", nil); err != nil {panic(err)}}
注:当使用字符串常量表示 html 文本的时候,包含 <html><body></body></html> 对于让浏览器识别它收到了一个 html 非常重要。
更安全的做法是在处理器中使用 w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html") 在写入返回之前将 header 的 content-type 设置为 text/html
content-type 会让浏览器认为它可以使用函数 http.DetectContentType([]byte(form)) 来处理收到的数据
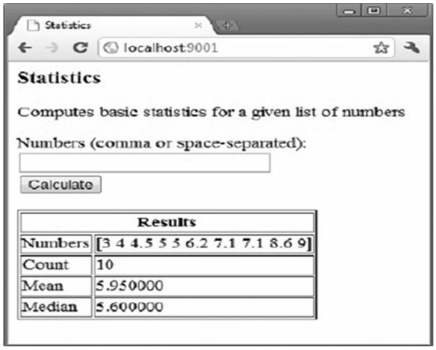
练习 15.6 [statistics.go]
编写一个网页程序,可以让用户输入一连串的数字,然后将它们打印出来,计算出这些数字的均值和中值,就像下边这张截图一样: