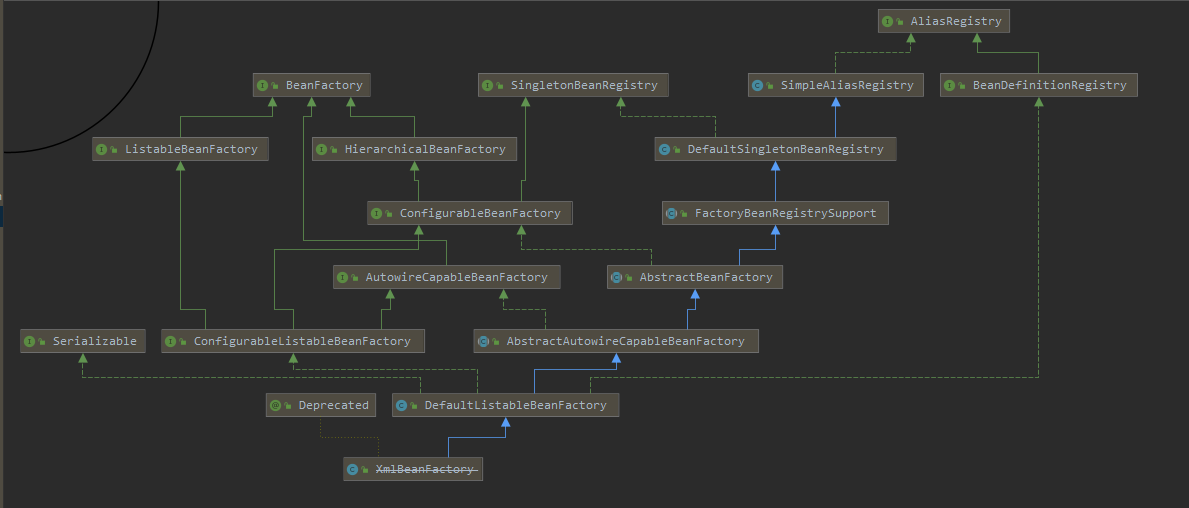
- XmlBeanFactory
- 类结构图
- 代码
- 源码解析
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);- doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())
- registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)
- documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource))
- doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root)
- parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
- parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
XmlBeanFactory
类结构图
代码
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;public class XmlBeanFactoryTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 资源加载ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml");// XmlBeanFactory 加载资源并解析注册beanBeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(classPathResource);// BeanFactory.getBean();UserBean userBean = (UserBean) beanFactory.getBean("userBean");System.out.println(userBean.getName());}}
源码解析
XmlBeanFactory解析Xml是使用了XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinition()方法
@Deprecated@SuppressWarnings({"serial", "all"})public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);/*** Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource,* which must be parsable using DOM.* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors*/public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {this(resource, null);}/*** Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream,* which must be parsable using DOM.* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors*/public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {super(parentBeanFactory);this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);}}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
/*** Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file* @return the number of bean definitions found* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors*/public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));}/*** Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file* @return the number of bean definitions found* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors*/public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());}// 通过属性来记录已经加载的资源Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();if (currentResources == null) {currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);}if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");}try {// 从encodedResource已经封装的Resource获取InputStreamInputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();try {//InputSource 并不是spring的,而是 org.xml.saxInputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);//如果encodedResource 中的 Encoding 不是 null 则同步设置 InputSource的 Encodingif (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());}//加载bean的Definitions 将xml中的信息加载到Definition中,并且在内存中注册的也是key+definitionsreturn doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());}finally {inputStream.close();}}catch (IOException ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);}finally {currentResources.remove(encodedResource);if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();}}}
上述源码可能看着比较长,但实际上这里并不是真正解析的地方,在这里做了如下: 1:从encodedResource已经封装的Resource获取InputStream; 2:如果encodedResource 中的 Encoding 不是 null 则同步设置 InputSource的 Encoding; 3:将解析动作委托给doLoadBeanDefinitions实现;
doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())
/*** Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file* @return the number of bean definitions found* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors*/protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {try {int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);//加载 DocumentDocument doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());//注册 beanreturn registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);}catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {throw ex;}catch (SAXParseException ex) {throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);}catch (SAXException ex) {throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);}catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);}catch (IOException ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);}}
当我们看着这个方法的时候,依旧不是真正的解析或注册的方法,在这里只是做了Document的加载,并将后续工作委托给了registerBeanDefinitions
registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)
/*** Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.* @param doc the DOM document* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)* @return the number of bean definitions found* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors* @see #loadBeanDefinitions* @see #setDocumentReaderClass* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions*/@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {//实例化 BeanDefinitionDocumentReaderBeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();documentReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());//获取之前的beanDefinition加载个数int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();//加载xml及注册beandocumentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));//记录本次加载个数return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;}
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource))
/*** This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD* (or DTD, historically).* <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings* specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions.*/public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {this.readerContext = readerContext;logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");//实例化 ReaderContextElement root = doc.getDocumentElement();//注册doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);}
registerBeanDefinitions并没有做什么,我们继续看doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root)
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);if (!getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {return;}}// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;this.delegate = createDelegate(this.readerContext, root, parent);//解析前处理, 内容null 留个子类实现preProcessXml(root);//解析parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);//解析后处理, 内容null 留个子类实现postProcessXml(root);this.delegate = parent;}
在doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法中验证xml的namespace,最重要的方法是parseBeanDefinitions,parseBeanDefinitions方法进行了解析操作;
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
/*** Parse the elements at the root level in the document:* "import", "alias", "bean".* @param root the DOM root element of the document*/protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {Node node = nl.item(i);if (node instanceof Element) {Element ele = (Element) node;if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {//对默认标签处理parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);}else {//对自定义标签处理delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);}}}}else {//对自定义标签处理delegate.parseCustomElement(root);}}
parseBeanDefinitions方法中已经开始对标签进行解析,区分默认标签和自定义标签,我们本次只对默认标签的源码进行解析,自定义标签自行DeBug
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {//解析import标签if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);}//解析alias标签并注册else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {processAliasRegistration(ele);}//解析bean标签并注册else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);}//解析beans标签else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {// recursedoRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);}}
到这里我们可以看到,spring对import/bean/alias/beans的解析过程,对于beans的解析无非就是解析beans中的bean标签,spring直接又重新调用了doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法,我们接下来进行对bean标签的解析
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
/*** Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition* and registering it with the registry.*/protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {//委托BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法进行元素解析并返回//BeanDefinitionHolder实例,BeanDefinitionHolder已经包含了配置文件中的各种属性BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);//当BeanDefinitionHolder返回不null的情况,弱存在默认标签下的子标签再有自定义的属性,还需要再次解析if (bdHolder != null) {//解析默认标签中的自定义标签bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);try {// Register the final decorated instance.// 进行实例注册注册操作是BeanDefinitionReaderUtisl.registerBeanDefinition进行处理BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());}catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);}// Send registration event.getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));}}
在processBeanDefinition方法中,spring做了两件事情: 1:委托BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法进行元素解析并返回BeanDefinitionHolder实例,BeanDefinitionHolder已经包含了配置文件中的各种属性 2:通过上获得的BeanDefinitionHolder进行bean的注册操作,通BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition方法;
delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
/*** Parses the supplied {@code <bean>} element. May return {@code null}* if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}.*/public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {//解析id属性String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);//解析name属性String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);//分割name属性List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));}String beanName = id;if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {beanName = aliases.remove(0);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");}}if (containingBean == null) {checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);}//将信息封装到 beanDefinition中AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);if (beanDefinition != null) {if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {try {//beanname不存在则使用默认规则创建if (containingBean != null) {beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);}else {beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();if (beanClassName != null &&beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {aliases.add(beanClassName);}}if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");}}catch (Exception ex) {error(ex.getMessage(), ele);return null;}}String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);}return null;}
在parseBeanDefinitionElement方法中做了三件事: 1:解析id/name; 2:检查name的唯一性; 3:将信息封装到 beanDefinition中,接下来直接看parseBeanDefinitionElement方法;
parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
/*** Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return* {@code null} if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition.*/public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));String className = null;//解析classname属性if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();}try {String parent = null;//解析parent属性if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);}//创建用于承载属性的AbstractBeanDefinition类型的AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);//解析bean的各种属性parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);//提取descriptionbd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));//解析meta (元数据)parseMetaElements(ele, bd);//解析Lookup-methodparseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());//解析replaced-methodparseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());//构造函数 参数//解析constructor-argparseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);//解析PropertyparsePropertyElements(ele, bd);//解析QualifierparseQualifierElements(ele, bd);bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));return bd;}catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);}catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);}catch (Throwable ex) {error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);}finally {this.parseState.pop();}return null;}
通过上述代码我们可以看到这里首先是实例化了一个AbstractBeanDefinition来承载各种xml属性,接下来通过parseBeanDefinitionAttributes方法解析了xml中的各种你属性值,然后在解析lookUp-method(方法注入),replaced-method(替换方法或方法返回值),构造函数参数constructor-arg,property属性,Qualifier属性等;上述方法的源码就不一一展示了,无非都是通过Element进行解析;
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
下面代码是上述代码块调用了registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()),真正具体实现如下(使用了DefaultListableBeanFactory类实现的方法)
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {try {//校验 MethodOverrides((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();}catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);}}BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");}else {if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +"': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");}}}else {// 增加beanDefinitionNamesthis.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);// 清除缓存this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;}// 仍处于启动注册阶段// 注册 beanDefinitionMap 新实例 beanName + beanDefinitiothis.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);}if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {resetBeanDefinition(beanName);}}
上述代码中首先验证了beanName和BeannDefinition不可为空,然后继续校验了MethodOverridesMethodOverrides在解析并组装beanDefinition时lookup-method和recpse-method的源码中有提到,继续判断beanDefinitionMap是否存在该bean,如果bean已经存在,通过allowBeanDefinitionOverriding属性判断是否可覆盖,反之则抛出异常;如果不存在则需要判断本次是否是第一次注册bean,如果是则初始化beanDefinitionMap后进行put操作,反之直接put beanDefinitionMap完成注册;