前置了解
Environment
本身是一个PropertyResolver,但是提供了Profile特性,即可以根据环境得到相应数据(即激活不同的Profile,可以得到不同的属性数据,用于多环境场景的配置。我们分析Spring Boot的启动流程,以创建StandardServletEnvironment为例: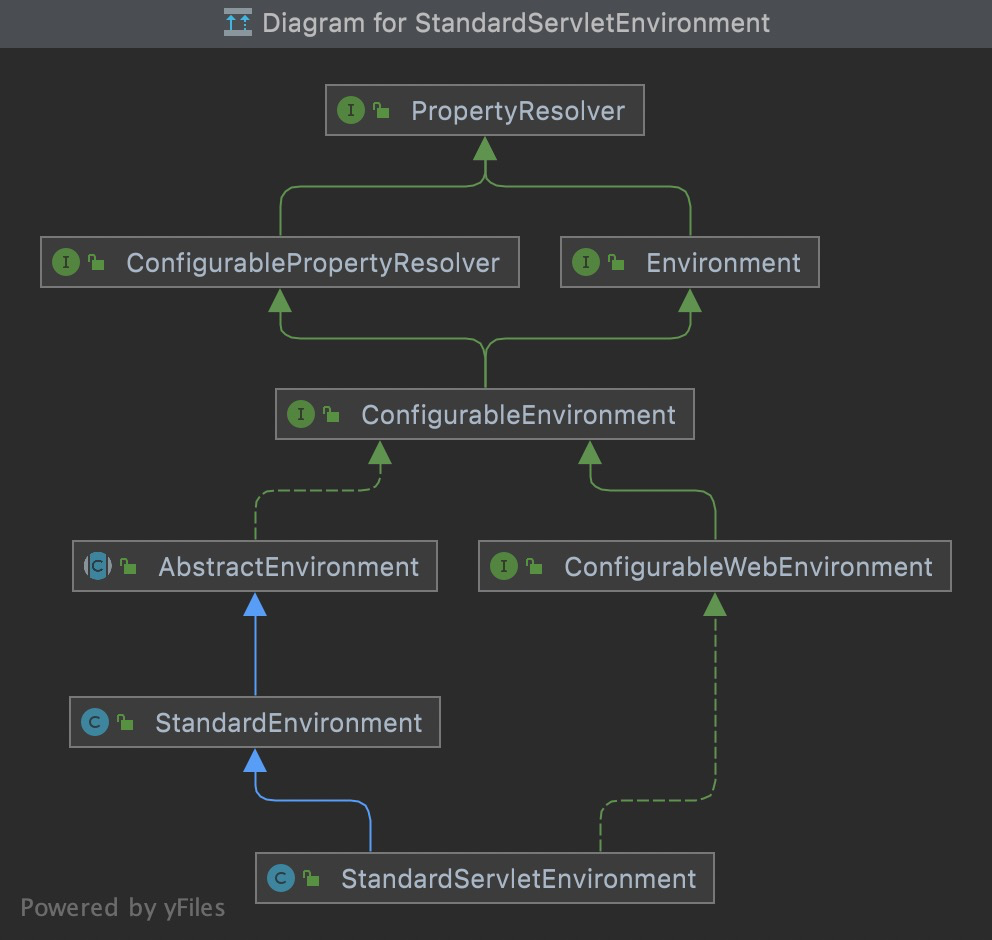
PropertySource
属性源,key-value属性对抽象,比如用于配置数据。 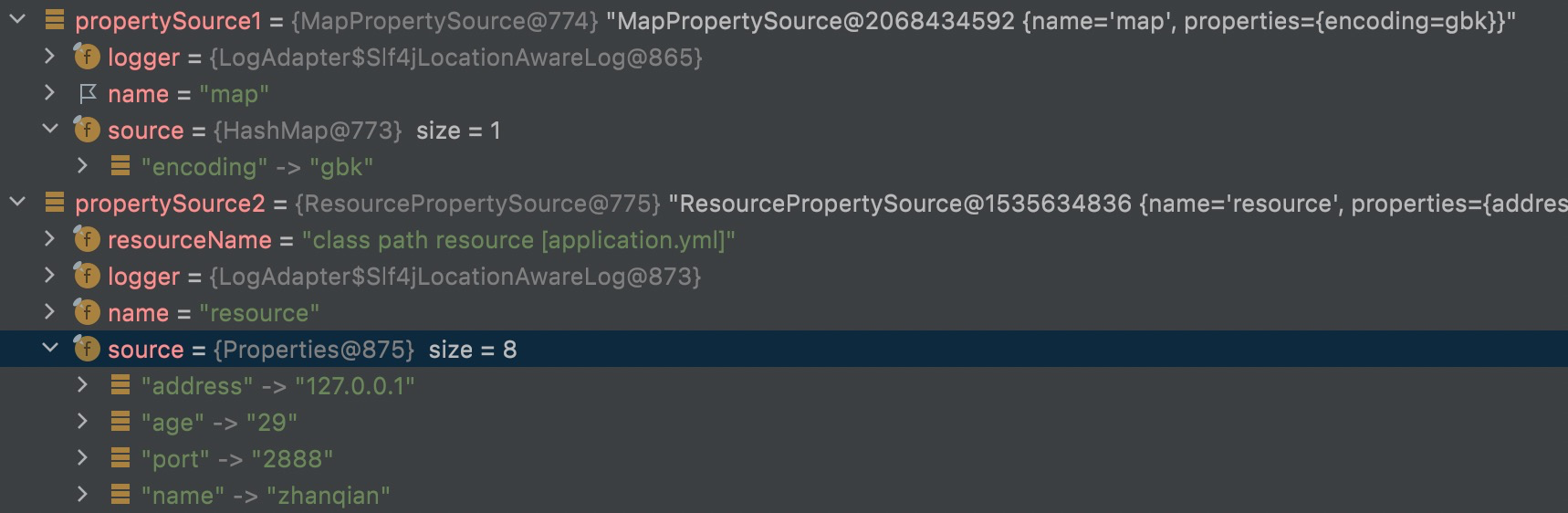
PropertyResolver
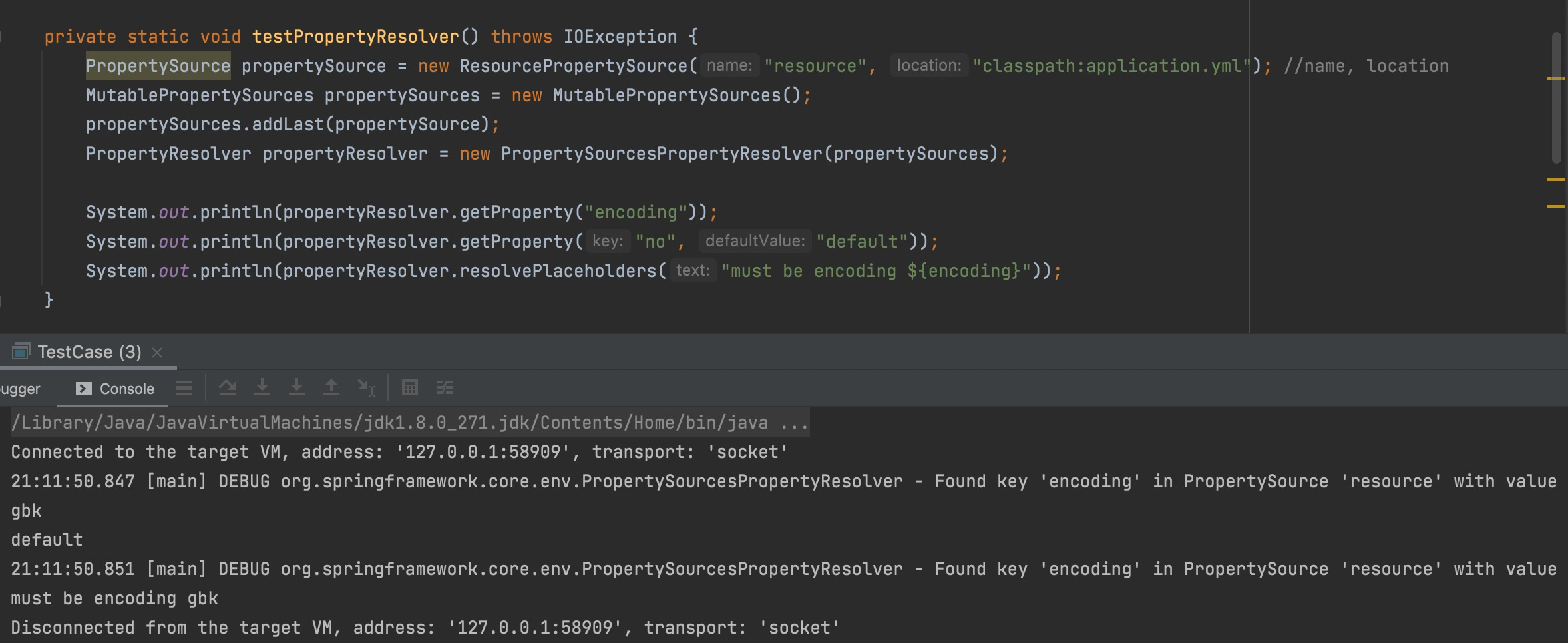
属性解析器,用于解析相应key的value。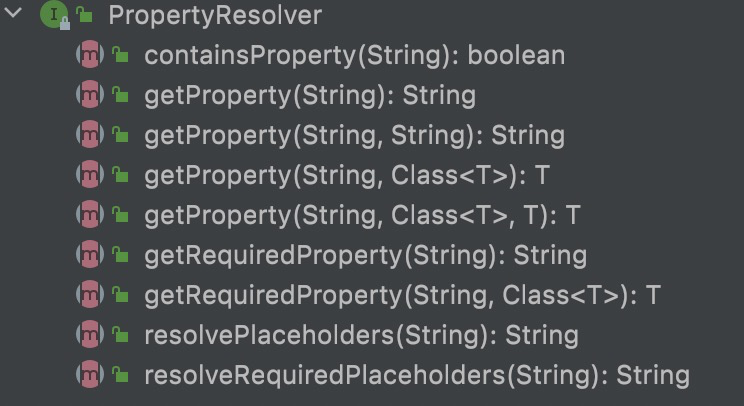
Profile
剖面,只有激活的剖面的组件/配置才会注册到Spring容器
Context
上下文,这个上下文由多种数据结构组成,可以提供我们运行时需要的一些数据和保存运行时的一些数据,context 可以理解对一个程序运行时所需要的一些数据结构的抽象表达。
Spring Boot的启动流程中申明创建了ConfigurableApplicationContext(实际的类型为AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext)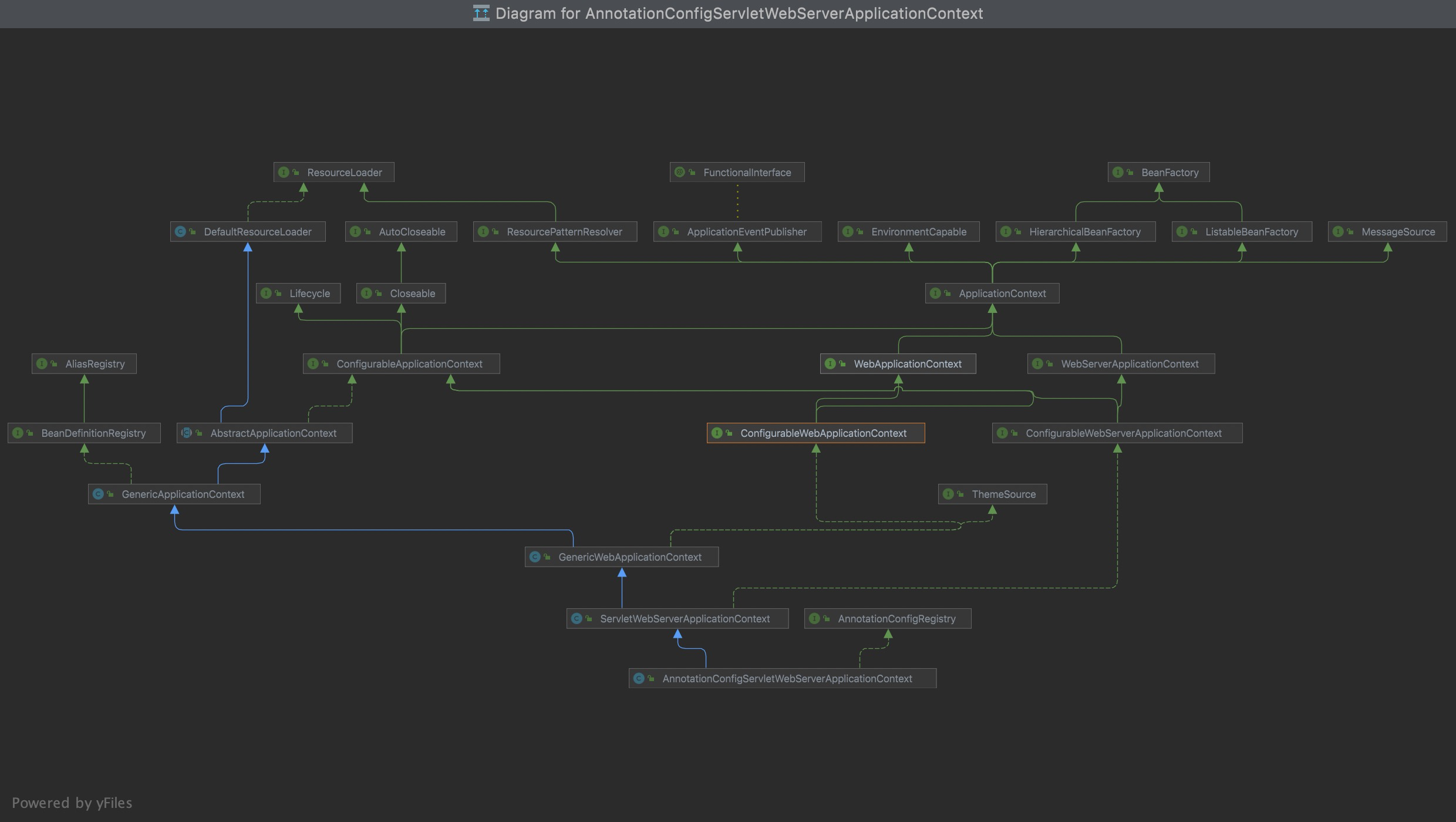
组成
- environment:所属
AbstractApplicationContext,是将上一步的prepareEnvironment()中的environment赋值给Context中变量。
主流程
我将SpringApplication#run()主流程分为#getRunListeners、#prepareEnvironment、#prepareContext、#refreshContext、#afterRefresh这5部分,本篇讲解的Spring加载配置,与Environment和Context两个类关联紧密,主要讲解#prepareEnvironment、#prepareContext
1. #getRunListeners
获取EventPublishingRunListener,该Listener对象内包含成员变量SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,用于广播后续流程中的事件。
2. #prepareEnvironment
#prepareEnvironment方法内分为#getOrCreateEnvironment、#configureEnvironment、listeners#environmentPrepared3个部分。
2.1 #getOrCreateEnvironment
根据webApplicationType生成环境类new StandardServletEnvironment()。在构造方法中会封装成员变量propertySources和propertyResolver。封装的propertySources为systemEnvironment�、systemProperties�、servletConfigInitParams、servletContextInitParams
2.2 #configureEnvironment
封装环境信息分为
configurePropertySources,添加、删除、重排PropertySourceconfigureProfiles,配置activeProfiles2.3 listeners#environmentPrepared
EventPublishingRunListener通过initialMulticaster
�发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,然后通过event和eventType获取监听的listeners,listener基于同步的方式处理事件,此处是ConfigFileApplicationListener处理该事件。ConfigFileApplicationListener中包含数个EnvironmentPostProcessor环境准备完的后置处理。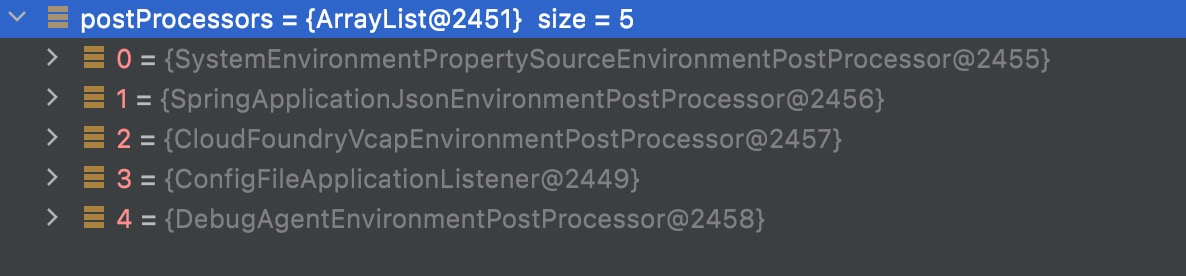
3. #prepareContext
3.1 context.setEnvironment(environment)
将createApplicationContext()创建的context的变量environment赋值。�3.2 postProcessApplicationContext(context)
� 后置处理ApplicationContext,设置context的类型转换ConversionService,context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(xxx),
�
�
其他细节
监听器部分使用了观察者模式,回调的实现是在ApplicationEventMulticaster在广播时候(调用multicastEvent�方法)�中实现的,以子类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster为例,最终调用#doInvokeListener代码如下:
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {try {listener.onApplicationEvent(event);}catch (ClassCastException ex) {String msg = ex.getMessage();if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);}}else {throw ex;}}}
�
参考
【1】:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48030077
【2】:https://www.cnblogs.com/yourbatman/p/14061177.html
【3】:https://blog.csdn.net/dkyaoyao/article/details/84819519


