数据结构如下所示: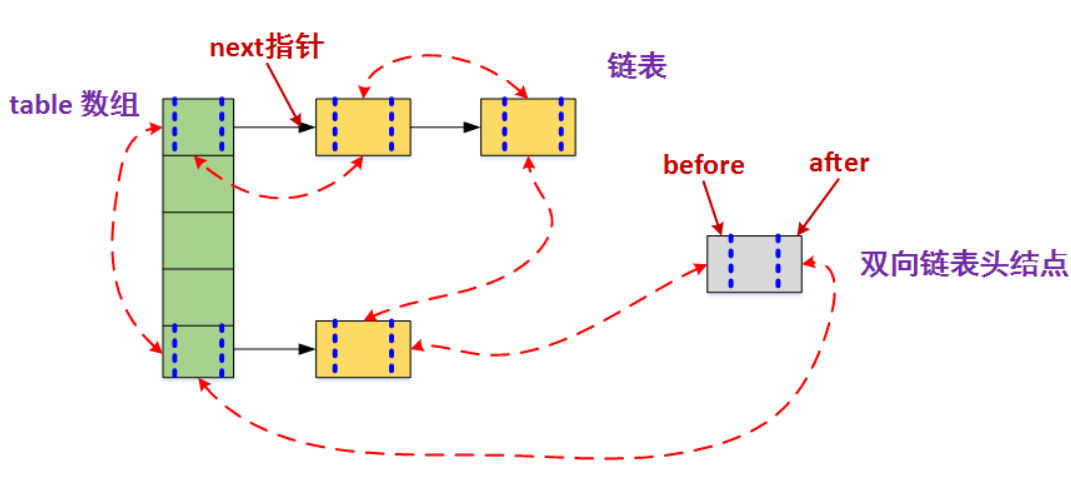

参考了https://blog.csdn.net/justloveyou_/article/details/71713781,发现和我看的源码(JDK1.8)有出入,找不到原文中的方法,发现1.6和1.8之间有做过修改。
基于1.6
- LinkedHashMap的Entry继承了HashMap中的Node,新增了before和after指针(实现双向链表),和Next不同,next是维护各个哈希桶中的Entry链。
LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的 put(Key,Value) 方法,只是对put(Key,Value)方法所调用的recordAccess方法和addEntry方法进行了重写;对于get(Key)方法而言,LinkedHashMap则直接对它进行了重写。
/*** Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old* value is replaced.** @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key* @return the previous value associated with key, or null if there was no mapping for key.* Note that a null return can also indicate that the map previously associated null with key.*/public V put(K key, V value) {//当key为null时,调用putForNullKey方法,并将该键值对保存到table的第一个位置if (key == null)return putForNullKey(value);//根据key的hashCode计算hash值int hash = hash(key.hashCode());//计算该键值对在数组中的存储位置(哪个桶)int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//在table的第i个桶上进行迭代,寻找 key 保存的位置for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {Object k;//判断该条链上是否存在hash值相同且key值相等的映射,若存在,则直接覆盖 value,并返回旧valueif (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {V oldValue = e.value;e.value = value;e.recordAccess(this); // LinkedHashMap重写了Entry中的recordAccess方法--- (1)return oldValue; // 返回旧值}}modCount++; //修改次数增加1,快速失败机制//原Map中无该映射,将该添加至该链的链头addEntry(hash, key, value, i); // LinkedHashMap重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法 ---- (2)return null;}
/*** This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.** LinkedHashMap中的addEntry方法*/void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {//创建新的Entry,并插入到LinkedHashMap中createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // 重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法//双向链表的第一个有效节点(header后的那个节点)为最近最少使用的节点,这是用来支持LRU算法的Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;//如果有必要,则删除掉该近期最少使用的节点,//这要看对removeEldestEntry的覆写,由于默认为false,因此默认是不做任何处理的。if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);} else {//扩容到原来的2倍if (size >= threshold)resize(2 * table.length);}}-------------------------------我是分割线------------------------------------/*** Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this* method to resize the table if appropriate.** Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.** HashMap中的addEntry方法*/void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {//获取bucketIndex处的EntryEntry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];//将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entrytable[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);//若HashMap中元素的个数超过极限了,则容量扩大两倍if (size++ >= threshold)resize(2 * table.length);}
基于1.8
1.8的LinkedHashMap的put()方法,基本继承了HashMap的,没有变动。但是LinkedHashMap重写了HashMap的三个回调方法:
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actionsvoid afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { } //设置按照访问顺序,accessOrder为true时void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
这三个回调方法(如上)在HashMap中均没有实现,是个空方法。但这三个方法都没有找到将节点插入到双向队列中的操作。都是维护插入后的节点信息的。
LinkedHashMap的newNode方法,该方法重写了HashMap的newNode方法。
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);linkNodeLast(p);return p;}// link at the end of listprivate void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) { //该方法会将节点放到双向链表的尾部,也就是最近访问的一个LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;tail = p;if (last == null)head = p;else {p.before = last;last.after = p;}}
这样就知道了在创建新节点的时候,把该节点放到了尾部。所以我们就清楚了当accessOrder设置为false时,会按照插入顺序进行排序,当accessOrder为true是,会按照访问顺序(afterNodeAccess()触发)(也就是插入和访问都会将当前节点放置到尾部,尾部代表的是最近访问的数据,这和JDK1.6是反过来的,jdk1.6头部是最近访问的)。
使用场景
本地缓存(LRU)
class LRULinkedHashMap<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K,V>{//定义缓存的容量private int capacity;private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;//带参数的构造器LRULinkedHashMap(int capacity){//调用LinkedHashMap的构造器,传入以下参数super(16,0.75f,true);//传入指定的缓存最大容量this.capacity=capacity;}//实现LRU的关键方法,如果map里面的元素个数大于了缓存最大容量,则删除链表的顶端元素@Overridepublic boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest){System.out.println(eldest.getKey() + "=" + eldest.getValue());return size()>capacity;}}

