张量排序
tf.sort
tf.sort函数可以对张量进行排序.
格式:
tf.sort(values, axis=-1, direction='ASCENDING', name=None)
参数:
values: 要进行排序的张量axis: 操作维度direction: 正序或者倒序name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序a = tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(10))print(a)# 从小到大b = tf.sort(a) # direction="ASCENDING"print(b)# 从大到小c = tf.sort(a, direction="DESCENDING")print(c)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([6 3 7 5 4 0 2 9 8 1], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.argsort
tf.argsort返回张量的索引排序, 沿给的轴排序.
格式:
tf.argsort(values, axis=-1, direction='ASCENDING', stable=False, name=None)
参数:
- 要进行排序的张量
axis: 操作维度direction: 正序或者倒序stable: 如果为 True, 则原始张量中的相等元素将不会按返回的顺序重新排序name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序a = tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(10))print(a)# 从小到大b = tf.argsort (a)print(b)# 从大到小c = tf.argsort (a, direction="DESCENDING")print(c)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([9 4 3 1 2 6 0 5 7 8], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([6 3 4 2 1 7 5 8 9 0], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([0 9 8 5 7 1 2 4 3 6], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
tf.math.top_k
tf.math.top_k可以查找最后一个维度的 k 个最大条目的值和索引.
格式:
tf.math.top_k(input, k=1, sorted=True, name=None)
参数:
input: 传入张量k=1: 前 k 位sorted: 是否排序name: 数据名称
例子:
# 创建张量0~9, 并打乱顺序, 形状为 3*3a = tf.reshape(tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(9)), [3, 3])print(a)# 取top2b = tf.math.top_k(a, 2)print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[2 1 4][5 7 0][8 6 3]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)TopKV2(values=<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=array([[4, 2],[7, 5],[8, 6]])>, indices=<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=array([[2, 0],[1, 0],[0, 1]])>)
填充与复制
tf.pad
tf.pad可以对一个 tensor 四周进行填充.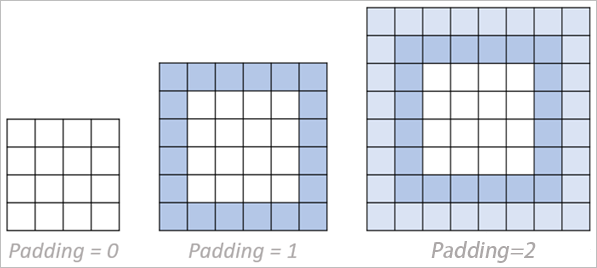
格式:
tf.pad(tensor, paddings, mode='CONSTANT', constant_values=0, name=None)
参数:
tensor: 传入的张量paddings: 要扩展的维度mode: 模式, 默认为 “CONSTANT”constant_value: 在 “CONSTANT” 模式下, 要使用的标量填充值 (必须与张量类型相同)name: 数据名称
例子:
# pada = tf.reshape(tf.range(9), [3, 3])print(a)# 上下左右填充一圈0b = tf.pad(a, [[1, 1], [1, 1]])print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[0 1 2][3 4 5][6 7 8]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([[0 0 0 0 0][0 0 1 2 0][0 3 4 5 0][0 6 7 8 0][0 0 0 0 0]], shape=(5, 5), dtype=int32)
tf.tile
tf.tile可以实现 tensor 的复制.
格式:
tf.tile(input, multiples, name=None)
参数:
input: 传入的张量multiples: 复制的次数name: 数据名称
例子:
# tilea = tf.reshape(tf.range(9), [3, 3])print(a)b = tf.tile(a, [2, 2])print(b)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[0 1 2][3 4 5][6 7 8]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([[0 1 2 0 1 2][3 4 5 3 4 5][6 7 8 6 7 8][0 1 2 0 1 2][3 4 5 3 4 5][6 7 8 6 7 8]], shape=(6, 6), dtype=int32)
查找与替换
tf.where (第一种)
返回元素为 True 的位置.
格式:
tf.where(condition, name=None)
参数:
condition: 判断条件name: 数据名称
例子:
# 第一种用法(单参数)mask = tf.constant([[True, True, True], [False, True, True], [True, False, False]])print(mask)indices = tf.where(mask)print(indices)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[ True True True][False True True][ True False False]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)tf.Tensor([[0 0][0 1][0 2][1 1][1 2][2 0]], shape=(6, 2), dtype=int64)
tf.where (第二种)
类似三元运算符的用法.
格式:
tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None)
参数:
condition: 判断条件x: 如果条件为 True 赋值y: 如果条件为 False 赋值name: 数据名称
例子:
# 第二种用法(三个参数)zeros = tf.zeros([3, 3])print(zeros)ones = tf.ones([3, 3])print(ones)mask = tf.constant([[True, True, True], [False, True, True], [True, False, False]])print(mask)result = tf.where(mask, zeros, ones)print(result)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[0. 0. 0.][0. 0. 0.][0. 0. 0.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)tf.Tensor([[1. 1. 1.][1. 1. 1.][1. 1. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)tf.Tensor([[ True True True][False True True][ True False False]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)tf.Tensor([[0. 0. 0.][1. 0. 0.][0. 1. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.scatter_nd
使用索引更新张量.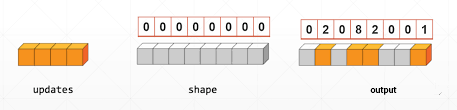
格式:
tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape, name=None)
参数:
indices: 索引updates: 更新的值shape: 形状name: 数据名称
例子:
# scatter_ndindices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [7]])print(indices)updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])print(updates)shape = tf.constant([8])print(shape)result = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)print(result)
输出结果:
tf.Tensor([[4][3][1][7]], shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([ 9 10 11 12], shape=(4,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([8], shape=(1,), dtype=int32)tf.Tensor([ 0 11 0 10 9 0 0 12], shape=(8,), dtype=int32)

