os
os.path
os.path.normpath()
expanduser 把~替换成用户Home目录绝对路径。
os.path.expanduser(path)
os.path.dirname(file)
1. sys.exit(n) 退出程序引发SystemExit异常, 可以捕获异常执行些清理工作. n默认值为0, 表示正常退出. 其他都是非正常退出. 还可以sys.exit(“sorry, goodbye!”); 一般主程序中使用此退出.
2. os._exit(n), 直接退出, 不抛异常, 不执行相关清理工作. 常用在子进程的退出.
3. exit()/quit(), 跑出SystemExit异常. 一般在交互式shell中退出时使用.
multiprocessing
队列
队列是线程和进程安全的
def foo(name, q):q.put('hi: ' + name)queue = mp.Queue()p = mp.Process(target=foo, args=('gina', queue))p.start()p.join()r = queue.get()print(r)#输出#hi: gina
管道
管道是双工的,父子两头都可以读写。
import multiprocessing as mpdef foo(conn):conn.send('42')conn.close()p_conn, c_conn = mp.Pipe()p = mp.Process(target=foo, args=(c_conn, ))p.start()p.join()print(p_conn.recv())
共享内存
进程池
pool = multiprocessing.Pool()# 进程会阻塞pool.map()# 非阻塞pool.map_async()# 返回迭代器pool.imap()# 不保证返回和传入顺序一致pool.imap_unordered()
subprocess
Popen
shell
shell设置true将通过Shell执行args里的字符串。
在Linux下,shell=False时, Popen调用os.execvp()执行args指定的程序;shell=True时,如果args是字符串,Popen直接调用系统的Shell来执行args指定的程序,如果args是一个序列,则args的第一项是定义程序命令字符串,其它项是调用系统Shell时的附加参数。
Popen()返回Popen对象、run()返回CompletedProcess对象
preexec_fn=os.setsid
Popen.communicate()
使用这个函数与子进程通信,向子进程读写数据就要将子进程 stdin设置为PIPE、stdout、stderr设置PIPE
subprocess.Popen永远要考虑将参数close_fds设置为True。要不然多个子进程会持有其他进程的PIPE文件描述。主进程会以为某个子进程PIPE一直不关闭。
threading
两种方式实现多线程:绑定函数、继承基类。
绑定函数如下:
import threadingimport timedef job():time.sleep(0.1)print('exec job')t1 = threading.Thread(target=job, name='T1')t2 = threading.Thread(target=job, name='T2')t1.start()t2.start()t1.join()t2.join()print('all done')
继承基类实现init和run方法具体如下:
import threadingclass FooThread(threading.Thread):def __init__(self):passdef run(self):print('exec job')t1 = FooThread()t2 = FooThread()t1.start()t2.start()
functools
functools.partial
traceback
# 打印堆栈信息traceback.print_exc()# 返回traceback.format_exc()
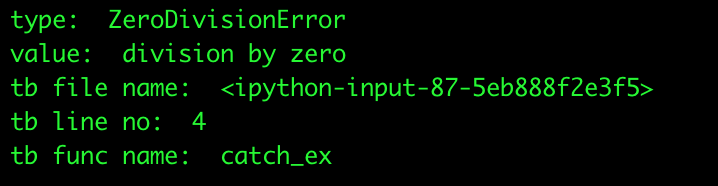
traceback信息是从sys.exc_info()里获取的
exc_info() 返回 type、value、traceback
asyncio
await
await 后面的函数返回值是特殊对象 协程、任务、Future
Future
pending -> DONE
模仿concurrent.futures.Future类
fileno() 返回文件描述符整型
re
import res = 'asdasdasd'r = re.match('asd', s)r2 = re.search('asd', s)r3 = re.finditer('asd', s)r4 = re.findall('asd', s)
fnctl
O_NONBLOCK使I/O变成非阻塞,在读不到数据或写缓冲区满时,直接return,不会阻塞等待。
fcntl.fcntl(fd, fcntl.F_SETFL, os.O_NONBLOCK)
fnmatch
import fnmatch
enum
from enum import Enum, unique#没有@unique 后面会变成第一个的别名class Color(Enum):red = 1red_alias = 1
socket
socket.gaierror gai是getaddrinfo的缩写
开发工具
unittest
test case, test suite, test runner, test fixture。
TestCase(测试用例): setUp()、run()、tearDown()。
TestSuite包含多个TestCase,也可嵌套TestSuite。
TestLoader加载TestCase到TestSuite中。
TestRunner执行用例。
1.Test fixture
- setUp():准备环境,执行每个测试用例的前置条件;
- tearDown():环境还原,执行每个测试用例的后置条件;
- setUpClass():必须使用@classmethod装饰器,所有case执行的前置条件,只运行一次;
- tearDownClass():必须使用@classmethod装饰器,所有case运行完后只运行一次;
2.TestCase
测试方法以test开头,不以test开头不会执行。 ```python import unittest
文件级别调用一次
def setUpModule():
pass
def tearDownModule():
pass
class Foo(unittest.TestCase):
# 测类所有方法只执行一次@classmethoddef setUpClass(cls):pass@classmethoddef tearDownClass(cls):pass# 每个测试用例方法会调用一次setUp和tearDowndef setUp(self):pass# setUp运行成功,无论测试方法是否成功都会执行tearDowndef tearDown(self):passdef test_bar(self):pass# 四种跳过测试@unittest.skip("skip this case")def test_foo_skip(self):pass@unittest.skipIf(True, "233")def test_foo_skip_if(self):pass@unittest.skipUnless(False, "233")def test_foo_skip_unless(self):passdef test_foo_skip_test(self):self.skipTest("skipTest() skip")
if “main“ == name:
#verbosity参数表示详细程度,2显示详细报告,默认是1,0则不输出任何结果。unittest.main(verbosity=2)
<a name="dx29i"></a>#### 3.TestSuite默认按照A-Z、a-z执行。自己控制顺序需要用TestSuite。```pythonif __name__ == "__main__":suite = unittest.TestSuite()# 定义list,按照list里的顺序执行测试用例tests=[TestFunc("test_add"),TestFunc("test_minus"),TestFunc("test_multi"),TestFunc("test_divide")]suite.addTests(tests)runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity=2)runner.run(suite)
TestSuite包含TestSuite
suite1 = module.TheTestSuite()suite2=module.TheTestSuite()alltests=unittest.TestSuite([suite1],[suite2])
TestLoader的一坨loadTestsFrom*()搜索TestCase创建实例,addTestSuite()。
unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(testCaseClass)unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule(module)unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromName(name,module=None)unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromNames(names,module=None)unittest.TestLoader().getTestCaseNames(testCaseclass)unittest.TestLoader().discover()
TextTestRunner执行测试用例
if __name__ == "__main__":runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity=2)runner.run(all_cases())
4.TestLoader
https://huilansame.github.io/huilansame.github.io/archivers/python-unittest
退出
os._exit() 会直接将python程序终止,之后的所有代码都不会执行。
sys.exit() 会抛出一个异常: SystemExit,如果这个异常没有被捕获,那么python解释器将会退出。如果有捕获该异常的代码,那么这些代码还是会执行。
参考
https://python-parallel-programmning-cookbook.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/index.html