CPU有L1、L2、L3,但是在CPU和一级缓存中间还有一个缓冲区, 也就是说,CPU往L1中写数据时不会一个字节写一次,而且先往一个缓冲区写,等缓冲区满了之后再一次性写入L1,这个缓冲区由于特别贵,所以很小,只有4个字节。
程序证明:
public final class WriteCombining {//循环次数private static final int ITERATIONS = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//数组长度private static final int ITEMS = 1 << 24;//混淆值,保证写入数据随机private static final int MASK = ITEMS - 1;//创建6个字节数组,数组长度为 ITEMSprivate static final byte[] arrayA = new byte[ITEMS];private static final byte[] arrayB = new byte[ITEMS];private static final byte[] arrayC = new byte[ITEMS];private static final byte[] arrayD = new byte[ITEMS];private static final byte[] arrayE = new byte[ITEMS];private static final byte[] arrayF = new byte[ITEMS];/*** 一次循环写入3个字节, 循环3次* @return*/public static long runCaseOne() {long start = System.nanoTime(); //计时开始int i = ITERATIONS;//一个循环写3个字节while (--i != 0) {int slot = i & MASK;byte b = (byte) i; //占用一个字节写入arrayA[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayB[slot] = b; //写入一个字节}//一个循环写3个字节while (--i != 0) {int slot = i & MASK;byte b = (byte) i; //占用一个字节写入arrayC[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayD[slot] = b; //写入一个字节}//一个循环写3个字节while (--i != 0) {int slot = i & MASK;byte b = (byte) i; //占用一个字节写入arrayE[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayF[slot] = b; //写入一个字节}return System.nanoTime() - start;}/*** 一个循环写4个字节, 循环2次* @return*/public static long runCaseTwo() {long start = System.nanoTime(); //计时开始int i = ITERATIONS;//一个循环写4个字节while (--i != 0) {int slot = i & MASK;byte b = (byte) i; //占用一个字节写入arrayA[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayB[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayC[slot] = b; //写入一个字节}//再来一个循环写4个字节i = ITERATIONS;while (--i != 0) {int slot = i & MASK;byte b = (byte) i; //占用一个字节写入arrayD[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayE[slot] = b; //写入一个字节arrayF[slot] = b; //写入一个字节}return System.nanoTime() - start;}public static void main(final String[] args) {//测试3次看结果for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {System.out.println(i + " write three bytes one loop duration (ns) = " + runCaseOne());System.out.println(i + " write four bytes one loop duration (ns) = " + runCaseTwo());}}}
结果: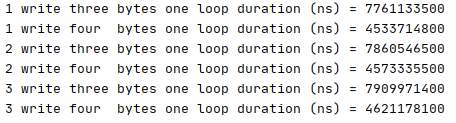
按照一般来讲两个方法的性能应该是差不多的。因为循环的次数是一样多的。但是从结果看runCaseTwo要比runCaseOne快很多, 这是因为runCaseTwo利用了CPU的合并写的缓冲区,每次循环正好填满一次缓冲区的4个字节。 而runCaseOne每次循环只往缓冲区写了3个字节,这时缓冲区还要等待下次循环写入一个字节才能刷新缓冲区。因此runCaseTwo要比runCaseOne快很多

