本章重点是motif搜索问题,19年发表一篇综述总结该类算法。
Problem 4.1两两距离
Write an algorithm that, given a set X, calculates the multiset ∆X.
:::info
If is a set of n points on a line segment in increasing order, then
denotes the multiset of all
pairwise distances between points in X:
. For example, if X={0,2,4,7,10}, then ∆X={2,2,3,3,4,5,6,7,8,10}
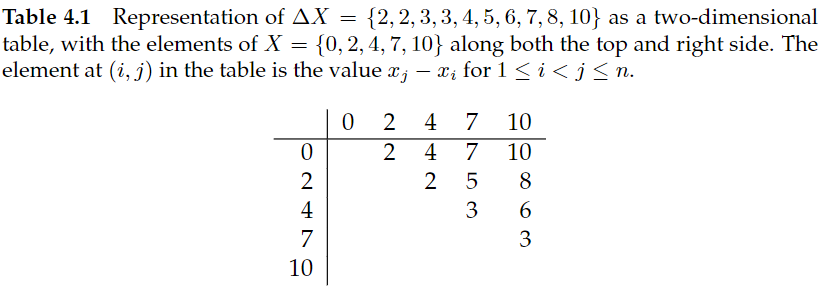 :::
:::
from typing import Listdef deltaX(X: List[int]) -> List[int]:return [X[j] - X[i] for i in range(len(X)) for j in range(i + 1, len(X))]print(deltaX([1, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9]))
Problem 4.2 Partial Digest problem
Consider partial digest L = {1,1,1,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,6,9,9,10,11,12,15}.Solve the Partial Digest problem for L (i.e., find X such that ∆X = L).
对书本当中几个算法进行总结下:
1、暴力算法:
from typing import Listdef bruteforcePDP(L: List[int], n: int) -> List[int]:"""通过ΔX=L构建切割位点集合:暴力枚举长度为n的集合输入:L[i] >= 0且任意i > 0有L[i] >= L[i-1]输出:List[int]"""M = max(L)X = [0]def backtrace(idx: int) -> None:"""使用回溯法枚举集合{0,Xi,..,M},枚举所有满足该集合内两两距离与L相同的集合"""if idx == n - 1:X.append(M)if sorted(X[j] - X[i] for i in range(n - 1) for j in range(i + 1, n)) == L:print(X)X.pop()returnfor Xi in range(1, M): # Xi ∈ [1,M]X.append(Xi)backtrace(idx + 1)X.pop()backtrace(1)bruteforcePDP([2,2,3,3,4,5,6,7,8,10], 5)# [0, 2, 4, 7, 10]# [0, 3, 6, 8, 10]
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:每个数字可在
[1, M-1]范围中选择,一个要选择n-2个数,时间复杂度为。
- 空间复杂度:
2、暴力剪枝:
Xi一定在L集合当中,当M特别大的时候这个prune(剪枝)非常有用!当输入L = {2, 998, 1000}时,此算法将比上面快很多。 ```python from typing import List
def anotherbruteforcePDP(L: List[int], n: int) -> List[int]: “””通过ΔX=L构建切割位点集合:优化枚举长度为n的集合 输入:L[i] >= 0且任意i > 0有L[i] >= L[i-1] 输出:List[int] “”” M = max(L) candidate = set(L) X = [0] def backtrace(idx: int) -> None: “””使用回溯法枚举集合{0,Xi,..,M},枚举所有满足该集合内两两距离与L相同的集合””” if idx == n - 1: X.append(M) if sorted(X[j] - X[i] for i in range(n - 1) for j in range(i + 1, n)) == L: print(X) X.pop() return for Xi in candidate: # Xi ∈ L X.append(Xi) backtrace(idx + 1) X.pop() backtrace(1)
anotherbruteforcePDP([2,2,3,3,4,5,6,7,8,10], 5)
**复杂度分析**:- **时间复杂度**:从集合`L`中选择`n-2`个数的方案数为 ,其中集合`L`最坏情况下全为不同数字,即长度为 ,因此总的时间复杂度为 。- **空间复杂度**:<a name="wg167"></a>## 3、从最长试探性构建由于python中没有multiset数据结构,同时也不需要复杂的集合操作,因此可以使用计数器字典数据结构替换。```pythonimport typingfrom collections import Counterdef delete(cnt: typing.Counter[int], element: int) -> None:"""从计数器集合cnt中删除element元素,删除操作都是合法"""cnt[element] -= 1if 0 == cnt[element]: # 出现次数为0则删除cnt.pop(element)def place(width: int, L: typing.Counter[int], X: typing.Counter[int]) -> None:"""每次从集合L中选出最大,分别尝试放在左侧或者右侧是否合法1、找到最大值width,它一定是两端点,从L中删除得到集合δ2、生成集合δ肯定也有最大值端点,因此选择k=max(δ),其有两种放置可能:放在k-0处(右)或 width-k(左)。分别检验放入后该集合内两两之间距离是否都在集合δ中"""if not L: # 证明到达终点,找到一个合法解print(sorted(X.elements()))returnfor p in [max(L), width - max(L)]:removeCnt = Counter() # 将删除操作都记录下来方便回溯时恢复原样for x in X:distance = abs(p - x)if distance in L:removeCnt[distance] += 1delete(L, distance)else:breakelse: # 两两距离都在L中X[p] += 1 # 选择 pplace(width, L, X)delete(X, p) # 撤销 pL += removeCnt # 撤销放在 p 处对L集合影响def PartialDigest(L: typing.Counter[int], n: int) -> typing.Counter[int]:"""从较长段开始枚举:输入:L[i] >= 0且任意i > 0有L[i] >= L[i-1]输出:List[int]"""width = max(L)delete(L, width)X = Counter([0, width])place(width, L, X)PartialDigest(Counter([2,2,3,3,4,5,6,7,8,10]), 5)
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:
,由公式
,一轮需要
检验当前选择位置之一是否合法(指数级)。
- 空间复杂度:
4、多项式算法:The chords’ problem
The chords’ problem.pdfProblem 4.3 枚举长度为m的子集(不可重复)
Write an algorithm that, given an n-element set, generates all m-element subsets of this set. For example, the set {1,2,3,4} has six two-element subsets {1,2}, {1,3}, {1,4}, {2,3}, {2,4}, and {3,4}. How long will your algorithm take to run? Can it be done faster?
暴力回溯:
组合
更好的答案可以参考下面链接:Problem 4.4 枚举长度为m的子集(可重复)
Write an algorithm that, given an n-element multiset, generates allm-element subsets of this set. For example, the set {1,2,2,3} has four two-element subsets {1,2}, {1,3}, {2,3}, and {2,2}. How long will your algorithm take to run? Can it be done faster?
出现重复原因:
- 可重集合无序性,例如
[2, 1, 2]和[1, 2, 2]相同,可以按有序枚举某个解集答案。 - 输入集合中有重复元素,选择时要避免重复,避免重复方式有两种。
子集
代码就是将上面枚举子集长度为k = 2记录下来。
Problem 4.5 证明两集合 homeometric
Prove that the sets and
are homometric for any two sets U and V.
:::info
In general, sets A and B are said to be homometric if
。
概念参照 Problem 4.1。
注意:书本正文写的是 是 multiset,而问题问是 set,在本题中 multiset 是 set 父集,因此我们假设是 multiset,这样解决办法对 set 也通用。
:::
假设可重集合
,标记
分布表示来自可重集合
集合
集合
那么对于两个 可重集合第
项,设
分布表示来自集合
,且有
,那么其与最后一项的距离都为
。因此同理可得之后
项到第
项距离都相同。综上可得
,因此两集合是 homeometric。
Problem 4.6
Given a multiset of integers A = {ai}, we call the polynomial the generating function for A. Verify that the generating function for
is
. Given generating functions for U and V , find generating functions for
and
. Compare generating functions for ∆A and ∆B. Are they the same?
Problem 4.7 PARTIALDIGEST 代码实现
Write pseudocode for the PARTIALDIGEST algorithm that has fewer lines than the one presented in the text.
书本上给的伪代码:
import typingfrom collections import Counterdef delete(cnt: typing.Counter[int], element: int) -> None:"""从计数器集合cnt中删除element元素,删除操作都是合法"""cnt[element] -= 1if 0 == cnt[element]: # 出现次数为0则删除cnt.pop(element)def place(width: int, L: typing.Counter[int], X: typing.Counter[int]) -> None:"""每次从集合L中选出最大,分别尝试放在左侧或者右侧是否合法1、找到最大值width,它一定是两端点,从L中删除得到集合δ2、生成集合δ肯定也有最大值端点,因此选择k=max(δ),其有两种放置可能:放在k-0处(右)或 width-k(左)。分别检验放入后该集合内两两之间距离是否都在集合δ中"""if not L: # 证明到达终点,找到一个合法解print(sorted(X.elements()))returnfor p in [max(L), width - max(L)]:removeCnt = Counter() # 将删除操作都记录下来方便回溯时恢复原样for x in X:distance = abs(p - x)if distance in L:removeCnt[distance] += 1delete(L, distance)else:breakelse: # 两两距离都在L中X[p] += 1 # 选择 pplace(width, L, X)delete(X, p) # 撤销 pL += removeCnt # 撤销放在 p 处对L集合影响def PartialDigest(L: typing.Counter[int], n: int) -> typing.Counter[int]:"""从较长段开始枚举:输入:L[i] >= 0且任意i > 0有L[i] >= L[i-1]输出:List[int]"""width = max(L)delete(L, width)X = Counter([0, width])place(width, L, X)PartialDigest(Counter([2,2,3,3,4,5,6,7,8,10]), 5)
Problem 4.8 求最短∆X:其来源X不止一个
Find a set ∆X with the smallest number of elements that could have arisen from more than one X, not counting shifts and reflections.
来自搜索引擎答案: CS431 homework 1
Page 87 of the textbook provides an example with a ∆X of size 36, so the sets from which it arises are of size 9. An example with ∆X of size 15 arises from X = {0, 1, 2, 5, 7, 9, 12} and X’ = {0, 1, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12}, where the ∆X = ∆X’ = {1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}. Here |X| = |X’| = 6. Now we will consider sets of size less than 6. A ∆X with a single element x has only one solution, X = {0, x}, if we ignore its shifts and reflections. The next possible size for ∆X is 3, since the size must be of the form, and
Let ∆X be {a, b, c}, where a ≤ b ≤ c. In any case, the first exit must be at distance 0 and the last exit at distance c. Therefore, for ∆X to be valid it must be true that c − b = a, and c − a = b, and the exits are also at those distances, so flipping the values of a and b result in the same output. This means that any ∆X of size 3 produces two turnpikes, each of which is the reflection of the other. Remaining possibilities for the size of ∆X is
and
. We are not sure if there are ∆X of size 6 or 10.

