- 32.Shell函数与数组.html">32.Shell函数与数组.html
- 一 什么是函数
- 2.函数的作用
- 3.如何定义函数、调用函数
- 定义,两种方式
- 调用
- 3.函数的传参
- 调用
[root@bgx she11]# fun2 Linuxhel1o, Linux - sh funo3.sh 10 - 20
- 4.函数状态返回
- 5. 函数练习
- 二 数组-array(了解)
- 为数组进行赋值
hosts[0]=127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
hosts[1]=::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
hosts[2]=10.0.0.7 web01
hosts[3]=10.0.0.5 node.oldxu.com
hosts[4]=10.0.0.7 nginx.oldxu.com - 1.简单了
#2.性能比shell数组要高N倍
#3.没有关联数组,和普通数组的概念 - shell编程-综合练习
32.Shell函数与数组.html
一 什么是函数
函数就是一组命令的合集,通常用来编写特定的代码模块,供后续重复调用。
2.函数的作用
可以在脚本中调用该函数,不必重复编写。这样能减少代码冗余,可读性更强。
函数和变量类似,必须先定义才可以调用,如果定义不调用则不会被执行。
2函数基础语法
1.定义Shell函数,
可以通过如下两种方式进行定义。
3.如何定义函数、调用函数
定义,两种方式
F_Name() { command }
function F_Name_2 () { command }
调用
F_Name F_Name_2
[root@web01 shell-functions]# fun1() { echo “hello,Shell”; }
[root@web01 shell-functions]# fun1
hello,Shell
[root@web01 shell-functions]# fun1() { echo “hello,$1”; }
[root@web01 shell-functions]# fun1
hello,
[root@web01 shell-functions]# fun1 Linux #Linux就是第一个参数他会传递给函数中的$1
hello,Linux
3.函数的传参
在函数内部可以使用参数$1、$2I,调用函数function_name $1$2..
1.函数中传递参数
[root@bgx she11]# fun20 { echo “he11o,$1”;}
调用
[root@bgx she11]# fun2 Linuxhel1o, Linux
2.函数中接收多个参数
[root@bgx she11]# fun3 { echo he11o,”$1””$2””$3”;}[root@bgx she11]# fun3 hel1o,7inux Shel7 Python
linux She11 Python
3.函数中传递多个参数$,接收所有的参数传递
[root@bgx she11]# fun4O { echo “he11o,$“;}
( $1 脚本的位置传参 和 函数传参 不是一个意思 )
需求1:写一个脚本,该脚本可以实现计算器的功能,可以进行 +-*/ 四种计算。 例如: sh cal.sh 30 + 40 | sh cal.sh 30 - 40 | sh cal.sh 30 * 40 | sh cal.sh 30 / 40*
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat fun03.sh
#!/bin/bash############################################################### File Name: fun03.sh# Author: oldxu# Organization: 552408925@qq.com############################################################### 10 - 20cal() {case $2 in+)echo "$1 + $3 = $[ $1 + $3 ]";;-)echo "$1 - $3 = $[ $1 - $3 ]";;x)echo "$1 * $3 = $[ $1 * $3 ]";;/)echo "$1 / $3 = $[ $1 / $3 ]";;esac}cal $1 $2 $3
sh funo3.sh 10 - 20
需求2:写一个脚本,实现nginx服务的启动、停止、重启。
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat fun04.sh
#!/bin/bash############################################################### File Name: fun04.sh# Author: oldxu# Organization: 552408925@qq.com###############################################################1.先实现功能#2.将相同的重复内容抽象并封装到函数中#3.优化一下整体脚本ngx_is_status () {systemctl $1 nginx #3.接收函数传参if [ $? -eq 0 ];thenecho "Nginx Is $1 OK" #4.接收函数传参elseecho "Nginx Is $1 Err"fi}#1.脚本的位置参数case $1 instart)ngx_is_status $1 #2.将脚本的位置参数解析出来,传给函数;;stop)ngx_is_status $1;;*)echo "USAGE: $0 [ start | stop ]"esac
4.函数状态返回
Shell的函数返回值,也算是退出的状态。在shell中只有echo、return两种方式。
1.return返回值只能返回1-255的整数,函数使用return返回值,通常只是用来供其他地方调用获取状态,
因此通常仅返回0或1;
0表示成功,1表示失败。
2.echo返回值使用echo可以返回任何字符串结果,通常用于返回数据,比如一个字符串值或者列表值。
1.shell函数echo返回字符串结果示例
[root@web01 shell-functions]#cat fun05.sh
#!/bin/bashget_user () {users=$(cat /etc/passwd | awk -F ":" '{print $1}')echo $users #输出该变量的结果}index=1for i in $(get_user) #函数相当于是命令(所以在调用时要么直接执行,要么$() 执行 )doecho "This is Number $index: $i"index=$[ $index + 1 ] #或 let index++done
2. return 返回状态码示例
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat fun07.sh
#!/bin/bash#整数比较 (例子,不作为实际使用)cal () {if [ $1 -ge $2 ];thenreturn 100elseif [ $1 -lt $2 ];thenreturn 200elsereturn 300fifi}cal $1 $2rc=$?#任务if [ $rc -eq 100 ];thenecho "大于"elif [ $rc -eq 200 ];thenecho "小于"elif [ $rc -eq 300 ];thenecho "等于"fi
5. 函数练习
*跳板机脚本
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat fun08.sh
#!/bin/bash# 分析:# 1.本机要与其他主机是免密登录的# 2.打印菜单,提示可连接的主机# 3.不允许退出脚本,当登录这台主机时,自动执行这个脚本.meminfo () {cat <<-EOF-------------------------------| 1) db-10.0.0.51 || 2) nfs-10.0.0.31 || 3) web-10.0.0.8 || h) help |---------------------------------EOF}meminfo #打印菜单trap "" HUP INT QUIT TSTP #不让其执行ctrl+c、ctrl+zwhile truedoread -p "请输入你要连接的主机编号: " Actioncase $Action in3)ssh root@172.16.1.7;;4)ssh root@172.16.1.8;;h)clearmeminfocontinue;;exec)exit;;*)continueesacdone
脚本加入bashrc,新窗口强制执行
*LNMP多级菜单安装
( 函数、循环、case、if必用。(变量) )
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat fun09.sh
#!/bin/bashmem_info_1 () {cat <<-EOF-----------------------------1.Install Nginx2.Install PHP3.Install MySQL4.Quit-----------------------------EOF}mem_info_2 () {cat <<-EOF-----------------------------1.Install Nginx1.12.Install Nginx1.23.Install Nginx1.34.返回上一层页面-----------------------------EOF}#1.打印1级菜单mem_info_1while truedo#2.让用户选择是安装Nginx还是PHP、还是MySQLread -p "请根据编号输入对应的数字: " Action_1#根据用户选择来调用不同的预案case $Action_1 in1)#打印二级菜单,Nginx版本选择mem_info_2while truedoread -p "请根据编号选择你要安装的Nginx版本: " Action_2case $Action_2 in1)echo "Install Nginx 1.11 Done....";;2)echo "Install Nginx 1.12 Done....";;3)echo "Install Nginx 1.13 Done....";;4)clearmem_info_1break;;*)continueesacdone;;2);;3);;4)quit;;*)continueesacdone
二 数组-array(了解)
shell数组( awk数组 ) 必须先学习shell数组( 不是太好理解,用的比较少,所以了解 ),铺垫,再学习awk数组,非常的简单。
1.什么是数组
- 数组主要是用来存值,只不过可以存储多个值。
2.数组的分类
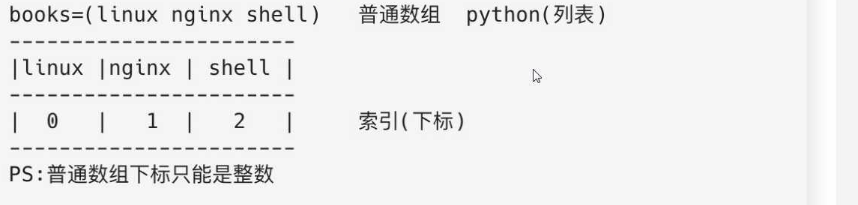
- 普通数组 : 当一个数组定义多个值,需要取值时,只能通过整数来取值 0 1 2 3 4 5
- 关联数组 :他可以自定义索引名称,当需要取值时,只需要通过 数组的名称[索引] —-> 值
- 作用: 统计 分析

普通数组
0 1 2 #普通数组的索引都是整数#普通赋值的两种方式#方式一[root@web01 shell-functions]# #books=(linux nginx shell)#方式二[root@web01 shell-functions]# array[0]=pear[root@web01 shell-functions]# array[1]=apple[root@web01 shell-functions]# array[2]=orange
关联数组
#1.必须先申明这是一个关联数组
[root@Shell ~]# declare -A info
[root@Shell ~]# declare -A info2
#2.方式一, 关联数组的赋值 (数组名[索引]=变量值 )
[root@Shell ~]# info[index1]=pear
[root@Shell ~]# info[index2]=apple
[root@Shell ~]# info[index3]=orange
#3.方式二, 关联数组的赋值 (数组名=([索引1]=变量值2 [索引2]=变量值2) )
[root@Shell ~]# info2=([index1]=linux [index2]=nginx [index3]=docker [index4]='bash shell')
3.数组如何赋值、如何取值
[root@web01 shell-functions]# books=(linux nginx shell)
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${books[0]}
linux
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${books[1]}
nginx
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${books[2]}
shell
#问题 我想取出所有的数据怎么做? **( 普通数组还是关联数组 方法都一样)
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${info_2[@]}
oldxu 18 m
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${!info_2[@]} #取出索引
name age sex
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${books[@]}
linux nginx shell
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${!books[@]}
4. 数组的遍历与循环( 重要 )
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
10.0.0.7 web01
10.0.0.5 node.oldxu.com
10.0.0.7 nginx.oldxu.com
为数组进行赋值
hosts[0]=127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
hosts[1]=::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
hosts[2]=10.0.0.7 web01
hosts[3]=10.0.0.5 node.oldxu.com
hosts[4]=10.0.0.7 nginx.oldxu.com
[root@web01 shell-functions]# sh array01.sh
你的索引是: 0 该索引对应的值是: 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
你的索引是: 1 该索引对应的值是: ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
你的索引是: 2 该索引对应的值是:
你的索引是: 3 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.7 web01
你的索引是: 4 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.5 node.oldxu.com
你的索引是: 5 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.7 nginx.oldxu.com
🍭数组的赋值
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat array01.sh
#!/bin/bash
while read line
do
#批量赋值(让索引进行自增即可)
hosts[i++]=$line
#hosts[0]=127.0.0.1 localhost
#hosts[1]=::1 localhost localhost.localdomain
done</etc/hosts
🍭数组的遍历
(循环取出值)p
#/bin/bash
#批量取值
for item in ${!hosts[@]}
do
#索引 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ${hosts[0]} ${hosts[1]} ${hosts[2]}
echo "你的索引是: $item 该索引对应的值是: ${hosts[$item]}"
done
[root@web01 shell-functions]# sh array01.sh
你的索引是: 0 该索引对应的值是: 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
你的索引是: 1 该索引对应的值是: ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
你的索引是: 2 该索引对应的值是:
你的索引是: 3 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.7 web01
你的索引是: 4 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.5 node.oldxu.com
你的索引是: 5 该索引对应的值是: 10.0.0.7 nginx.oldxu.com
6.统计练习—-赋值-遍历:
6.1 命令行取值: 统计/etc/passwd文件中,shells类型分别出现了多少次。
[root@web01 shell-functions]#
awk -F ":" '{print $NF}' /etc/passwd | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
289 /bin/bash
33 /sbin/nologin
1 /sbin/shutdown
1 /sbin/halt
1 /bin/sync
1 /bin/sh
1 /bin/false
6.2 shell数组: 统计/etc/passwd文件中,shells类型分别出现了多少次。
Ps: 统计谁,就将谁作为索引,然后取出他出现的次数就行了。
[root@web01 shell-functions]# declare -A shells #关联数组才支持字符串
[root@web01 shell-functions]# shells[/bin/bash]=0
[root@web01 shell-functions]# shells[/bin/bash]=1
[root@web01 shell-functions]# shells[/sbin/nologin]=1
[root@web01 shell-functions]# let shells[/bin/bash]++
[root@web01 shell-functions]# let shells[/bin/bash]++
[root@web01 shell-functions]# let shells[/bin/bash]++
[root@web01 shell-functions]# let shells[/sbin/nologin]++
[root@web01 shell-functions]# let shells[/sbin/nologin]++
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${shells[/bin/bash]}
4
[root@web01 shell-functions]# echo ${shells[/sbin/nologin]}
3
[root@web01 shell-functions]#cat array02.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A shells #shell中声明是关联数组(必要)
while read line
do
types=$(echo $line | awk -F ":" '{print $NF}')
let shells[$types]++ #要统计谁,就将谁作为索引,然后让其自增: 统计效果
done</etc/passwd
for item in ${!shells[@]} #取出数组中的索引名称
do
echo "索引是: $item 他出现的次数是: ${shells[$item]}"
#打印索引名称为: 统计次数为:
done
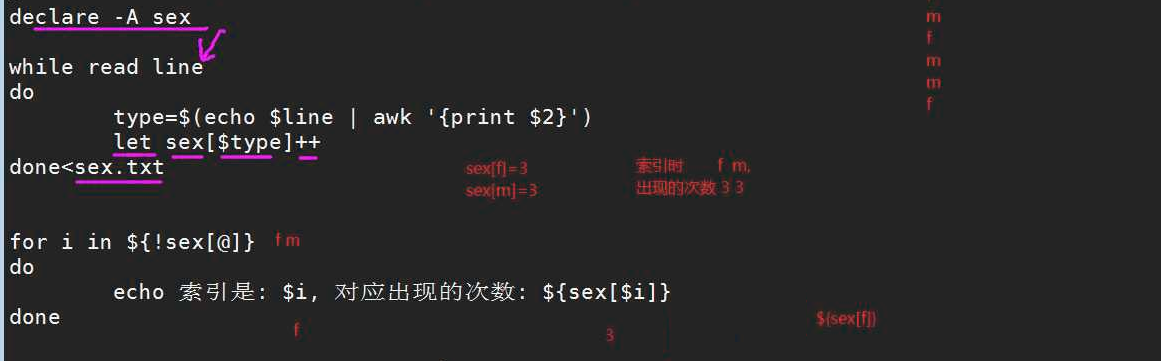
shell数组练习2
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat array03.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A Ops
while read line
do
types=$(echo $line | awk '{print $2}')
#要统计谁,就将谁作为其索引,然后让其自增。
let Ops[$types]++
done<sex.txt
for item in ${!Ops[@]}
do
echo "你的索引名称是: $item 你索引对应的值是: ${Ops[$item]}"
done
#拆解后的效果
[root@web01 shell-functions]# cat array03.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A Ops
#要统计谁,就将谁作为其索引,然后让其自增。
while read line
do
types=$(echo $line | awk '{print $2}')
let Ops[$types]++
#假设 m f m m f m 那么赋值之后的结果如下
# Ops[m]=4
# Ops[f]=2
done<sex.txt
# $[!Ops[@]] = m f #所以我们的循环要循环2次
for item in ${!Ops[@]}
do
# m 4
# f 2
echo "你的索引名称是: $item 你索引对应的值是: ${Ops[$item]}"
done
*6.3 统计一下nginx日志的TOP10的IP地址。
( Shell数组在统计1MB左右的文件时,效率非常低。)
shell数组
1.IP在文件中那一列 假设以 第一列为 IP
2.那么就可以将第一列的来源IP作为索引,然后让其自增。
3.遍历索引,取出对应的值(就是索引出现的次数。)

[root@web01 opt]# cat array_nginx.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A Ip
while read line
do
types=$(echo $line | awk '{print $1}')
let Ip[$types]++
done<access.log
#遍历
for item in ${!Ip[@]}
do
#ip #值(次数)
echo $item ${Ip[$item]}
done
awk数组:
1.简单了
#2.性能比shell数组要高N倍
#3.没有关联数组,和普通数组的概念
[root@web01 opt]#time awk '{Ip[$1]++} END { for (item in Ip) print Ip[item],item }' access.log_58
# 详解:
#赋值过程-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
Ip[$1]++ #要统计谁就将谁作为索引,然后让其自增
}
END
#遍历取值-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
for (item in Ip) #遍历数组(默认遍历的是索引名称)
print Ip[item],item
#item 是不是就是对应的IP地址信息,也就是存储在数组中的索引
#Ip[item] Ip[10.0.0.2] --->打印Ip数组中这个索引的值(也就是他的次数了)
}' access.log_58
6.4 使用Shell数组编写脚本,用来获取主机的所有端口,效果如下:
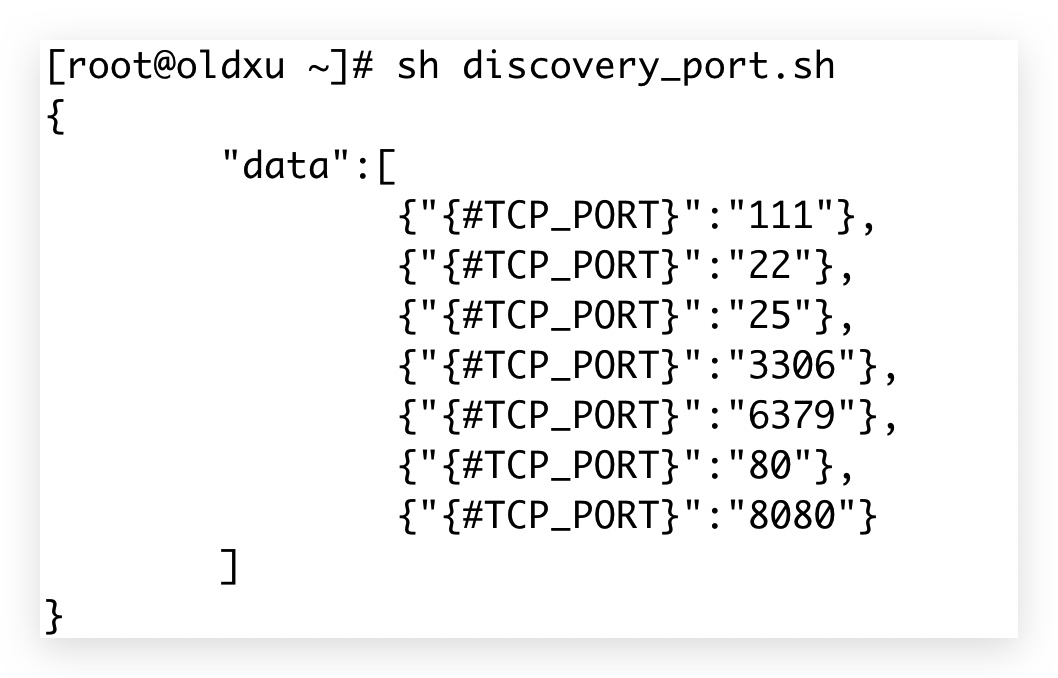
#!/bin/bash
port_all=($(netstat -lntp | awk '{print $4}' | awk -F ':' '{print $NF}' | egrep "^[0-9]+$" | sort | uniq))
# 数组的长度
port_length=${#port_all[@]}
printf "{ \n"
printf "\t \"data\":[ \n"
# 遍历数组
index=0
for port in ${port_all[@]}
do
index=$[ $index + 1 ]
if [ $port_length -eq $index ];then
printf "\t\t {\"{#TCP_PORT}\":\"${port}\"}\n"
else
printf "\t\t {\"{#TCP_PORT}\":\"${port}\"},\n"
fi
done
printf "\t ]\n"
printf "}\n"
shell编程-综合练习
1.网站监测脚本{xxx}
2.使用shell脚本实现跳板机的功能
3.使用shell脚本实现nginx的多版本安装,必须真的实现
1.nginx 1.18版本
2.nginx 1.19版本
在选择1.18时,需要清理环境,确保完整能安装.
在选择1.19时,需要清理环境,确保完整能安装.
4.根据业务需求,现要求开发一个货币兑换的服务系统,具体要求如下: ( Shell的普通数组 )
(1)实现人民币兑换美元的功能
(2)实现美元兑换人民币的功能
(3)实现人民币兑换欧元的功能
货币兑换利率:1美元 = 7.14人民币、1元=0.12欧元
5.使用awk统计Nginx日志 TOP10的IP访问次数
6.使用awk统计当前TCP状态的次数 (netstat -an | awk '{print $NF}' ) <---state 这一列
7.使用shell脚本完成 mysql备份 , 需要每天凌晨 04:00 运行.
0.只能管理员执行
1.加锁
2.判断文件备份成功或失败
3.定时运行.
8.使用Shell编写同步脚本 Rsync
9.使用Shell脚本编写 Sersync 的服务启停脚本 [ start | stop | restart | status (pid) ]
10.使用shell脚本编写批量创建用户, 批量删除用户 [ add | del ]
1.使用函数
add
del
3.用户如果存在不允许创建,也不允许重置密码
4.仅root能执行,执行过程还需要加锁.
3-使用shell脚本实现nginx的多版本安装,必须真的实现
#!/bin/bash
. ./nginx_install.sh
meminfo () {
cat<<-EOF
------------------------
| 1) 安装nginx 1.18版本 |
| ---------------------- |
| 2) 安装nginx 1.19版本 |
| ---------------------- |
| 3) 打印菜单 |
| -----------------------|
| 4) 登出 |
------------------------
EOF
}
meminfo
trap "" HUP INT QUIT TSTP
while true
do
read -p "请输入你要执行的操作 " Num
case $Num in
1)
if [ ! $Num =~ ^[0-9]+$ ];then
continue
fi
nginx_depend_pakeages
download_1_18_5_nginx
install_nginx_pakeage
nginx_status
;;
2)
if [ ! $Num =~ ^[0-9]+$];then
continue
fi
nginx_depend_pakeages
download_1_19_5_nginx
install_nginx_pakeage
nginx_status
;;
3)
clear
meminfo
;;
4)
break
esac
done
4-根据业务需求,现要求开发一个货币兑换的服务系统,具体要求如下: (1)实现人民币兑换美元的功能 (2)实现美元兑换人民币的功能 (3)实现人民币兑换欧元的功能 货币兑换利率:1美元 = 7.14人民币、1元=0.12欧元

#!/usr/bin/bash
your_money=100
service_menu=(人民币转换美元 美元转换人民币 人明币转换欧元)
echo "******欢迎使用货币转换服务系统*******"
for service in ${!service_menu[@]}
do
if [ $service -eq 0 ];then
echo "=============================="
echo "1.欢迎使用 ${service_menu[service]} 服务"
echo "您需要转换的人民币为:$your_money 元"
new_money=$(awk -v your_money=$your_money 'BEGIN{printf "%.2f\n",your_money/7.14}')
echo "兑换成美元为: ${new_money}$"
echo "=============================="
elif [ $service -eq 1 ];then
echo "=============================="
echo "2.欢迎使用 ${service_menu[service]} 服务"
echo "您需要转换的美元为:$your_money 元"
new_money=$(($your_money * 7 ))
echo "兑换成人名币为: ${new_money}元"
echo "=============================="
elif [ $service -eq 2 ];then
echo "=============================="
echo "3.欢迎使用 ${service_menu[service]} 服务"
echo "您需要转换的人民币为:$your_money 元"
new_money=$(awk -v your_money=$your_money 'BEGIN{printf "%.2f\n",your_money*0.12}')
echo "兑换成欧元为: ${new_money}$"
echo "=============================="
fi
done