5.3.1 PageRank 排名算法
5.3.1.1 算法概述
PageRank,即网页排名,又称网页级别、Google 左侧排名或佩奇排名。是 Google 创始人拉里 · 佩奇和谢尔盖 · 布林于 1997 年构建早期的搜索系统原型时提出的链接分析算法,在揉合了诸如 Title 标识和 Keywords 标识等所有其它因素之后,Google 通过 PageRank 来调整结果,使那些更具 “等级 / 重要性” 的网页在搜索结果中令网站排名获得提升,从而提高搜索结果的相关性和质量。
5.3.1.2 从入链数量到 PageRank
PageRank 的计算基于以下两个基本假设:
- 数量假设:在 Web 图模型中,如果一个页面节点接收到的其他网页指向的入链数量越多,那么这个页面越重要。
- 质量假设:指向页面 A 的入链质量不同,质量高的页面会通过链接向其他页面传递更多的权重。所以越是质量高的页面指向页面 A,则页面 A 越重要。
利用以上两个假设,PageRank 算法刚开始赋予每个网页相同的重要性得分,通过迭代递归计算来更新每个页面节点的 PageRank 得分,直到得分稳定为止。 PageRank 计算得出的结果是网页的重要性评价,这和用户输入的查询是没有任何关系的,即算法是主题无关的。
5.3.1.3 PageRank 算法原理
PageRank 的计算充分利用了两个假设:数量假设和质量假设。步骤如下:
- 在初始阶段:网页通过链接关系构建起 Web 图,每个页面设置相同的 PageRank 值,通过若干轮的计算,会得到每个页面所获得的最终 PageRank 值。随着每一轮的计算进行,网页当前的 PageRank 值会不断得到更新。
- 在一轮中更新页面 PageRank 得分的计算方法:在一轮更新页面 PageRank 得分的计算中,每个页面将其当前的 PageRank 值平均分配到本页面包含的出链上,这样每个链接即获得了相应的权值。而每个页面将所有指向本页面的入链所传入的权值求和,即可得到新的 PageRank 得分。当每个页面都获得了更新后的 PageRank 值,就完成了一轮 PageRank 计算。
基本思想
**
如果网页 T 存在一个指向网页 A 的连接,则表明 T 的所有者认为 A 比较重要,从而把 T 的一部分重要性得分赋予 A。这个重要性得分值为 。
说明:
- 其中 PR(T) 为 T 的 PageRank 值,L(T) 为 T 的出链数。
- 则 A 的 PageRank 值为一系列类似于 T 的页面重要性得分值的累加。
即一个页面的得票数由所有链向它的页面的重要性来决定,到一个页面的超链接相当于对该页投一票。一个页面的 PageRank 是由所有链向它的页面(链入页面)的重要性经过递归算法得到的。一个有较多链入的页面会有较高的等级,相反如果一个页面没有任何链入页面,那么它没有等级。
我们设向量 B 为第一、第二、…、第 N 个网页的网页排名:
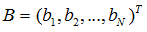
矩阵 A 代表网页之间的权重输出关系,其中 代表第 m 个网页向第 n 个网页的输出权重:
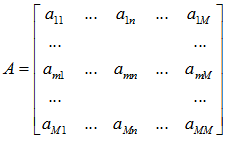
输出权重计算较为简单:假设 m 一共有 10 个出链,指向 n 的一共有 2 个,那么 m 向 n 输出的权重就为 2/10。
现在问题变为:A 是已知的,我们要通过计算得到 B。
假设 是第 i 次迭代的结果,那么:
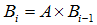
初始假设所有网页的排名都是 1/N (N 为网页总数量),即:
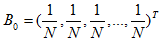
通过上述迭代计算,最终 会收敛,即
无限趋近于 B,此时
B = B × A。
具体示例
**
假设有网页 A、B、C、D,它们之间的链接关系如下图所示:
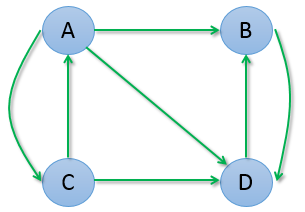
计算 如下:

不断迭代,计算结果如下:
第 1次迭代: 0.125, 0.333, 0.083, 0.458第 2次迭代: 0.042, 0.500, 0.042, 0.417第 3次迭代: 0.021, 0.431, 0.014, 0.535第 4次迭代: 0.007, 0.542, 0.007, 0.444第 5次迭代: 0.003, 0.447, 0.002, 0.547第 6次迭代: 0.001, 0.549, 0.001, 0.449第 7次迭代: 0.001, 0.449, 0.000, 0.550第 8次迭代: 0.000, 0.550, 0.000, 0.450第 9次迭代: 0.000, 0.450, 0.000, 0.550第10次迭代: 0.000, 0.550, 0.000, 0.450... ...
我们可以发现,A 和 C 的权重变为 0,而 B 和 D 的权重也趋于在 0.5 附近摆动。从图中也可以观察出:A 和 C 之间有互相链接,但它们又把权重输出给了 B 和 D,而 B 和 D 之间互相链接,并不向 A 或 C 输出任何权重,所以久而久之权重就都转移到 B 和 D 了。
PageRank 的改进
**
上面是最简单正常的情况,考虑一下两种特殊情况:
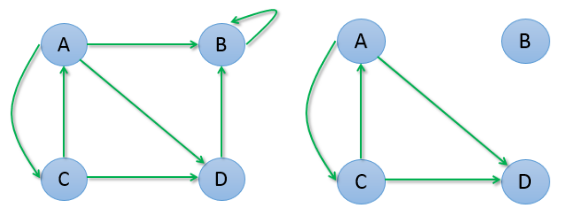
第一种情况是,B 存在导向自己的链接,迭代计算过程是:
第 1次迭代: 0.125, 0.583, 0.083, 0.208第 2次迭代: 0.042, 0.833, 0.042, 0.083第 3次迭代: 0.021, 0.931, 0.014, 0.035第 4次迭代: 0.007, 0.972, 0.007, 0.014第 5次迭代: 0.003, 0.988, 0.002, 0.006第 6次迭代: 0.001, 0.995, 0.001, 0.002第 7次迭代: 0.001, 0.998, 0.000, 0.001第 8次迭代: 0.000, 0.999, 0.000, 0.000第 9次迭代: 0.000, 1.000, 0.000, 0.000第10次迭代: 0.000, 1.000, 0.000, 0.000... ...
我们发现最终 B 权重变为 1,其它所有网页的权重都变为了 0。
第二种情况是 B 是孤立于其它网页的,既没有入链也没有出链,迭代计算过程是:
第 1次迭代: 0.125, 0.000, 0.125, 0.250第 2次迭代: 0.063, 0.000, 0.063, 0.125第 3次迭代: 0.031, 0.000, 0.031, 0.063第 4次迭代: 0.016, 0.000, 0.016, 0.031第 5次迭代: 0.008, 0.000, 0.008, 0.016第 6次迭代: 0.004, 0.000, 0.004, 0.008第 7次迭代: 0.002, 0.000, 0.002, 0.004第 8次迭代: 0.001, 0.000, 0.001, 0.002第 9次迭代: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.001第10次迭代: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000... ...
我们发现所有网页权重都变为了 0。
出现这种情况是因为上面的数学模型出现了问题,该模型认为上网者从一个网页浏览下一个网页都是通过页面的超链接。想象一下正常的上网情景,其实我们在看完一个网页后,可能直接在浏览器输入一个网址,而不通过上一个页面的超链接。
我们假设每个网页被用户通过直接访问方式的概率是相等的,即 1/N,N 为网页总数,设矩阵 e 如下:
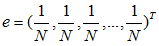
设用户通过页面超链接浏览下一网页的概率为 α,则直接访问的方式浏览下一个网页的概率为 1 - α,改进上一节的迭代公式为:
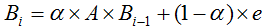
通常情况下设 α 为 0.8,上一节” 具体示例” 的计算变为如下:
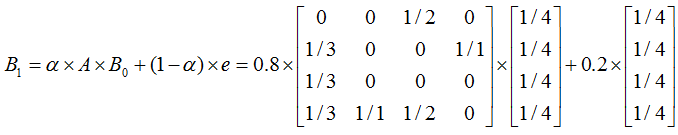
迭代过程如下:
第 1次迭代: 0.150, 0.317, 0.117, 0.417第 2次迭代: 0.097, 0.423, 0.090, 0.390第 3次迭代: 0.086, 0.388, 0.076, 0.450第 4次迭代: 0.080, 0.433, 0.073, 0.413第 5次迭代: 0.079, 0.402, 0.071, 0.447第 6次迭代: 0.079, 0.429, 0.071, 0.421第 7次迭代: 0.078, 0.408, 0.071, 0.443第 8次迭代: 0.078, 0.425, 0.071, 0.426第 9次迭代: 0.078, 0.412, 0.071, 0.439第10次迭代: 0.078, 0.422, 0.071, 0.428第11次迭代: 0.078, 0.414, 0.071, 0.437第12次迭代: 0.078, 0.421, 0.071, 0.430第13次迭代: 0.078, 0.415, 0.071, 0.436第14次迭代: 0.078, 0.419, 0.071, 0.431第15次迭代: 0.078, 0.416, 0.071, 0.435第16次迭代: 0.078, 0.419, 0.071, 0.432第17次迭代: 0.078, 0.416, 0.071, 0.434第18次迭代: 0.078, 0.418, 0.071, 0.432第19次迭代: 0.078, 0.417, 0.071, 0.434第20次迭代: 0.078, 0.418, 0.071, 0.433... ...
修正 PageRank 计算公式
由于存在一些出链为 0,也就是那些不链接任何其他网页的网,也称为孤立网页,使得很多网页能被访问到。因此需要对 PageRank 公式进行修正,即在简单公式的基础上增加了阻尼系数(damping factor)q, q 一般取值 q=0.85。其意义是,在任意时刻,用户到达某页面后并继续向后浏览的概率**。1- q= 0.15 就是用户停止点击,随机跳到新 URL 的概率)的算法被用到了所有页面上,估算页面可能被上网者放入书签的概率。
最后,即所有这些被换算为一个百分比再乘上一个系数 q。由于下面的算法,没有页面的 PageRank 会是 0。所以,Google 通过数学系统给了每个页面一个最小值。
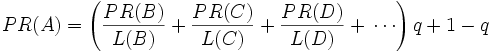
这个公式就是 S. Brin 和 L. Page 在《The Anatomy of a Large- scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine Computer Networks and ISDN Systems 》定义的公式。
所以一个页面的 PageRank 是由其他页面的 PageRank 计算得到。Google 不断的重复计算每个页面的 PageRank。如果给每个页面一个随机 PageRank 值(非 0),那么经过不断的重复计算,这些页面的 PR 值会趋向于正常和稳定。这就是搜索引擎使用它的原因。
首先求完整的公式

5.3.1.4 Spark GraphX 实现
import org.apache.spark.graphx.GraphLoader// Load the edges as a graphval graph = GraphLoader.edgeListFile(sc, "data/graphx/followers.txt")// Run PageRankval ranks = graph.pageRank(0.0001).vertices// Join the ranks with the usernamesval users = sc.textFile("data/graphx/users.txt").map { line =>val fields = line.split(",")(fields(0).toLong, fields(1))}val ranksByUsername = users.join(ranks).map {case (id, (username, rank)) => (username, rank)}// Print the resultprintln(ranksByUsername.collect().mkString("\n"))
5.3.2 广度优先遍历 (参考)
val graph = GraphLoader.edgeListFile(sc, "graphx/data/test_graph.txt")val root: VertexId = 1val initialGraph = graph.mapVertices((id, _) => if (id == root) 0.0 elseDouble.PositiveInfinity)val vprog = { (id: VertexId, attr: Double, msg: Double) => math.min(attr,msg) }val sendMessage = { (triplet: EdgeTriplet[Double, Int]) =>var iter:Iterator[(VertexId, Double)] = Iterator.emptyval isSrcMarked = triplet.srcAttr != Double.PositiveInfinityval isDstMarked = triplet.dstAttr != Double.PositiveInfinityif(!(isSrcMarked && isDstMarked)){if(isSrcMarked){iter = Iterator((triplet.dstId,triplet.srcAttr+1))}else{iter = Iterator((triplet.srcId,triplet.dstAttr+1))}}iter}val reduceMessage = { (a: Double, b: Double) => math.min(a,b) }val bfs = initialGraph.pregel(Double.PositiveInfinity, 20)(vprog, sendMessage, reduceMessage)println(bfs.vertices.collect.mkString("\n"))
5.3.3 单源最短路径 (参考)
import scala.reflect.ClassTagimport org.apache.spark.graphx._/*** Computes shortest paths to the given set of landmark vertices, returning a graph where each* vertex attribute is a map containing the shortest-path distance to each reachable landmark.*/object ShortestPaths {/** Stores a map from the vertex id of a landmark to the distance to that landmark. */type SPMap = Map[VertexId, Int]private def makeMap(x: (VertexId, Int)*) = Map(x: _*)private def incrementMap(spmap: SPMap): SPMap = spmap.map { case (v, d) => v -> (d + 1) }private def addMaps(spmap1: SPMap, spmap2: SPMap): SPMap =(spmap1.keySet ++ spmap2.keySet).map {k => k -> math.min(spmap1.getOrElse(k, Int.MaxValue), spmap2.getOrElse(k, Int.MaxValue))}.toMap/*** Computes shortest paths to the given set of landmark vertices.** @tparam ED the edge attribute type (not used in the computation)** @param graph the graph for which to compute the shortest paths* @param landmarks the list of landmark vertex ids. Shortest paths will be computed to each* landmark.** @return a graph where each vertex attribute is a map containing the shortest-path distance to* each reachable landmark vertex.*/def run[VD, ED: ClassTag](graph: Graph[VD, ED], landmarks: Seq[VertexId]): Graph[SPMap, ED] = {val spGraph = graph.mapVertices { (vid, attr) =>if (landmarks.contains(vid)) makeMap(vid -> 0) else makeMap()}val initialMessage = makeMap()def vertexProgram(id: VertexId, attr: SPMap, msg: SPMap): SPMap = {addMaps(attr, msg)}def sendMessage(edge: EdgeTriplet[SPMap, _]): Iterator[(VertexId, SPMap)] = {val newAttr = incrementMap(edge.dstAttr)if (edge.srcAttr != addMaps(newAttr, edge.srcAttr)) Iterator((edge.srcId, newAttr))else Iterator.empty}Pregel(spGraph, initialMessage)(vertexProgram, sendMessage, addMaps)}}
5.3.4 连通图 (参考)
import scala.reflect.ClassTagimport org.apache.spark.graphx._/** Connected components algorithm. */object ConnectedComponents {/*** Compute the connected component membership of each vertex and return a graph with the vertex* value containing the lowest vertex id in the connected component containing that vertex.** @tparam VD the vertex attribute type (discarded in the computation)* @tparam ED the edge attribute type (preserved in the computation)* @param graph the graph for which to compute the connected components* @param maxIterations the maximum number of iterations to run for* @return a graph with vertex attributes containing the smallest vertex in each* connected component*/def run[VD: ClassTag, ED: ClassTag](graph: Graph[VD, ED],maxIterations: Int): Graph[VertexId, ED] = {require(maxIterations > 0, s"Maximum of iterations must be greater than 0," +s" but got ${maxIterations}")val ccGraph = graph.mapVertices { case (vid, _) => vid }def sendMessage(edge: EdgeTriplet[VertexId, ED]): Iterator[(VertexId, VertexId)] = {if (edge.srcAttr < edge.dstAttr) {Iterator((edge.dstId, edge.srcAttr))} else if (edge.srcAttr > edge.dstAttr) {Iterator((edge.srcId, edge.dstAttr))} else {Iterator.empty}}val initialMessage = Long.MaxValueval pregelGraph = Pregel(ccGraph, initialMessage,maxIterations, EdgeDirection.Either)(vprog = (id, attr, msg) => math.min(attr, msg),sendMsg = sendMessage,mergeMsg = (a, b) => math.min(a, b))ccGraph.unpersist()pregelGraph} // end of connectedComponents/*** Compute the connected component membership of each vertex and return a graph with the vertex* value containing the lowest vertex id in the connected component containing that vertex.** @tparam VD the vertex attribute type (discarded in the computation)* @tparam ED the edge attribute type (preserved in the computation)* @param graph the graph for which to compute the connected components* @return a graph with vertex attributes containing the smallest vertex in each* connected component*/def run[VD: ClassTag, ED: ClassTag](graph: Graph[VD, ED]): Graph[VertexId, ED] = {run(graph, Int.MaxValue)}}
5.3.5 三角计数 (参考)
import scala.reflect.ClassTagimport org.apache.spark.graphx._/*** Compute the number of triangles passing through each vertex.** The algorithm is relatively straightforward and can be computed in three steps:** <ul>* <li> Compute the set of neighbors for each vertex</li>* <li> For each edge compute the intersection of the sets and send the count to both vertices.</li>* <li> Compute the sum at each vertex and divide by two since each triangle is counted twice.</li>* </ul>** There are two implementations. The default `TriangleCount.run` implementation first removes* self cycles and canonicalizes the graph to ensure that the following conditions hold:* <ul>* <li> There are no self edges</li>* <li> All edges are oriented src > dst</li>* <li> There are no duplicate edges</li>* </ul>* However, the canonicalization procedure is costly as it requires repartitioning the graph.* If the input data is already in "canonical form" with self cycles removed then the* `TriangleCount.runPreCanonicalized` should be used instead.** {{{* val canonicalGraph = graph.mapEdges(e => 1).removeSelfEdges().canonicalizeEdges()* val counts = TriangleCount.runPreCanonicalized(canonicalGraph).vertices* }}}**/object TriangleCount {def run[VD: ClassTag, ED: ClassTag](graph: Graph[VD, ED]): Graph[Int, ED] = {// Transform the edge data something cheap to shuffle and then canonicalizeval canonicalGraph = graph.mapEdges(e => true).removeSelfEdges().convertToCanonicalEdges()// Get the triangle countsval counters = runPreCanonicalized(canonicalGraph).vertices// Join them bath with the original graphgraph.outerJoinVertices(counters) { (vid, _, optCounter: Option[Int]) =>optCounter.getOrElse(0)}}def runPreCanonicalized[VD: ClassTag, ED: ClassTag](graph: Graph[VD, ED]): Graph[Int, ED] = {// Construct set representations of the neighborhoodsval nbrSets: VertexRDD[VertexSet] =graph.collectNeighborIds(EdgeDirection.Either).mapValues { (vid, nbrs) =>val set = new VertexSet(nbrs.length)var i = 0while (i < nbrs.length) {// prevent self cycleif (nbrs(i) != vid) {set.add(nbrs(i))}i += 1}set}// join the sets with the graphval setGraph: Graph[VertexSet, ED] = graph.outerJoinVertices(nbrSets) {(vid, _, optSet) => optSet.getOrElse(null)}// Edge function computes intersection of smaller vertex with larger vertexdef edgeFunc(ctx: EdgeContext[VertexSet, ED, Int]) {val (smallSet, largeSet) = if (ctx.srcAttr.size < ctx.dstAttr.size) {(ctx.srcAttr, ctx.dstAttr)} else {(ctx.dstAttr, ctx.srcAttr)}val iter = smallSet.iteratorvar counter: Int = 0while (iter.hasNext) {val vid = iter.next()if (vid != ctx.srcId && vid != ctx.dstId && largeSet.contains(vid)) {counter += 1}}ctx.sendToSrc(counter)ctx.sendToDst(counter)}// compute the intersection along edgesval counters: VertexRDD[Int] = setGraph.aggregateMessages(edgeFunc, _ + _)// Merge counters with the graph and divide by two since each triangle is counted twicegraph.outerJoinVertices(counters) { (_, _, optCounter: Option[Int]) =>val dblCount = optCounter.getOrElse(0)// This algorithm double counts each triangle so the final count should be evenrequire(dblCount % 2 == 0, "Triangle count resulted in an invalid number of triangles.")dblCount / 2}}}
5.3.6 PageRank 实例
采用的数据是 wiki 数据中含有 Berkeley 标题的网页之间连接关系,数据为两个文件:graphx-wiki-vertices.txt 和 graphx-wiki-edges.txt,可以分别用于图计算的顶点和边。
Step1:上传数据
$ pwd/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2$ bin/hdfs dfs -put /opt/software/graphx-wiki-edges.txt /$ bin/hdfs dfs -put /opt/software/graphx-wiki-vertices.txt /
Step2:RDD 加载数据转换 Edges
scala> val erdd = sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop102:9000/graphx-wiki-edges.txt")erdd: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/graphx-wiki-edges.txt MapPartitionsRDD[88] at textFile at <console>:26scala> val edges = erdd.map(x => { val para = x.split("\t"); Edge(para(0).trim.toLong, para(1).trim.toLong,0) })edges: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[org.apache.spark.graphx.Edge[Int]] = MapPartitionsRDD[89] at map at <console>:28
Step3:RDD 加载数据转换 vertices
scala> val vrdd = sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop102:9000/graphx-wiki-vertices.txt")vrdd: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/graphx-wiki-vertices.txt MapPartitionsRDD[91] at textFile at <console>:26scala> val vertices = vrdd.map(x => { val para = x.split("\t"); (para(0).trim.toLong, para(1).trim) })vertices: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(Long, String)] = MapPartitionsRDD[92] at map at <console>:28
Step4:构建 Graph
scala> val graph = Graph(vertices, edges)graph: org.apache.spark.graphx.Graph[String,Int] = org.apache.spark.graphx.impl.GraphImpl@a0ff17d
Step5:运行配置 RageRank
**
scala> val prGraph = graph.pageRank(0.001).cache() //0.001,以达到最终收敛的效果时才停止计算,返回图结果prGraph: org.apache.spark.graphx.Graph[Double,Double] = org.apache.spark.graphx.impl.GraphImpl@45e9b508
Step6:输出 RageRank 结果
scala> val titleAndPrGraph = graph.outerJoinVertices(prGraph.vertices) {(v, title, rank) => (rank.getOrElse(0.0), title)}titleAndPrGraph: org.apache.spark.graphx.Graph[(Double, String),Int] = org.apache.spark.graphx.impl.GraphImpl@6bb0284dscala> titleAndPrGraph.vertices.top(10) { Ordering.by((entry: (VertexId, (Double, String))) => entry._2._1) }.foreach(t => println(t._2._2 + ": " + t._2._1))University of California, Berkeley: 1321.1117543121227Berkeley, California: 664.8841977233989Uc berkeley: 162.5013274339786Berkeley Software Distribution: 90.47860388486127Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: 81.90404939642022George Berkeley: 81.85226118458043Busby Berkeley: 47.87199821801991Berkeley Hills: 44.76406979519929Xander Berkeley: 30.32407534728813Berkeley County, South Carolina: 28.908336483710315
示例代码如下:
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}import org.apache.spark.graphx._import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}object PageRank extends App {// 屏蔽日志Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR)Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.server").setLevel(Level.OFF)// 设定一个 SparkConfval conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SimpleGraphX").setMaster("local[4]")val sc = new SparkContext(conf)val erdd = sc.textFile("D:\\learn\\JetBrains\\workspace_idea\\spark\\doc\\graphx-wiki-edges.txt")val edges = erdd.map(x => {val para = x.split("\t");Edge(para(0).trim.toLong, para(1).trim.toLong, 0)})val vrdd = sc.textFile("D:\\learn\\JetBrains\\workspace_idea\\spark\\doc\\graphx-wiki-vertices.txt")val vertices = vrdd.map(x => {val para = x.split("\t");(para(0).trim.toLong, para(1).trim)})val graph = Graph(vertices, edges)println("**********************************************************")println("PageRank 计算,获取最有价值的数据")println("**********************************************************")val prGraph = graph.pageRank(0.001).cache()val titleAndPrGraph = graph.outerJoinVertices(prGraph.vertices) { (v, title, rank) => (rank.getOrElse(0.0), title) }titleAndPrGraph.vertices.top(10) {Ordering.by((entry: (VertexId, (Double, String))) => entry._2._1)}.foreach(t => println(t._2._2 + ": " + t._2._1))sc.stop()}
输出结果如下:
**********************************************************PageRank 计算,获取最有价值的数据**********************************************************University of California, Berkeley: 1321.1117543121227Berkeley, California: 664.8841977233989Uc berkeley: 162.5013274339786Berkeley Software Distribution: 90.47860388486127Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: 81.90404939642022George Berkeley: 81.85226118458043Busby Berkeley: 47.87199821801991Berkeley Hills: 44.76406979519929Xander Berkeley: 30.32407534728813Berkeley County, South Carolina: 28.908336483710315

