一、字节打印输出流PrintStream
PrintStream 该流的作用是:将程序输出的内容,使用操作系统默认的编码集,进行字符处理 (好处:我们可以认识对应的文本内容)
package exercise;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintStream;public class MainEnter {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("D:\\introduce.txt");if(!file.exists()) {try {file.createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}FileOutputStream fos = null;PrintStream ps = null;try {fos = new FileOutputStream(file);ps = new PrintStream(fos);ps.println("我是梁雨");} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {ps.close();fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
二、对象流(ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream)
对象流,可以认为是对数据流的进一步的封装,让我们可以使用对象化的方式来读写数据
JavaBean 的编程规范: 要求JavaBean 实现Serializable ,其目的是:为了让对象提供序列化 和 反序列化的能力
序列化:通过对象流 将对象数据 转换为 字节数据 的过程
反序列化:通过对象流 将字节数据 转换为 对象数据的过程 (反序列化也是一种创建对象的方式)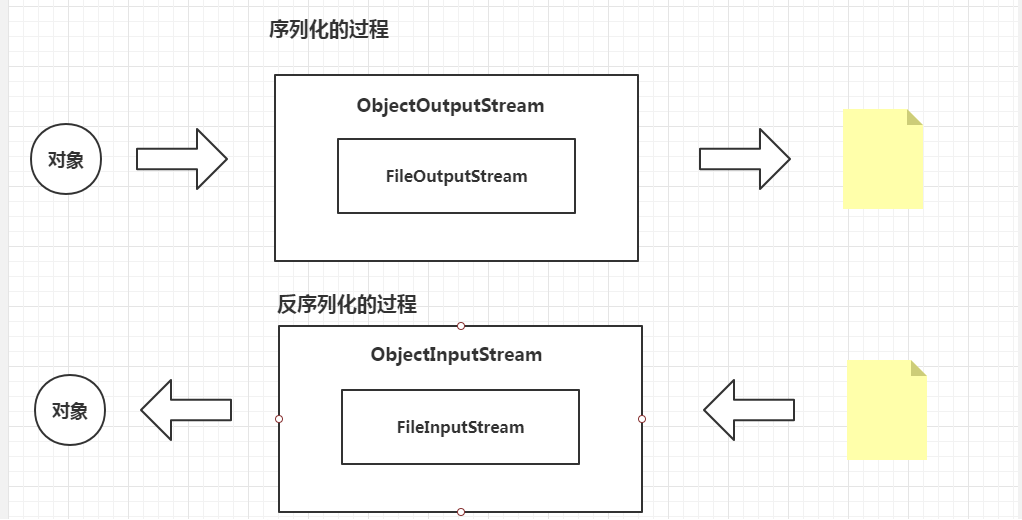
2.1 对象输出流 ObjectOutputStream 的使用
ObjectOutputStream : 将对象数据 转换为 字节数据
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class OrderBean implements Serializable{
/**
* 为啥要加序列化ID?
* 目的:是为保证 序列化和反序列过程中,对象的所对应的类 的版本 认为是一致的
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 315682470257319334L;
/**
* 商品的名称
*/
private String goodsName;
/**
* 数量
*/
private int nums;
private double price;
public OrderBean(String goodsName, int nums, double price) {
super();
this.goodsName = goodsName;
this.nums = nums;
this.price = price;
}
public OrderBean() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getGoodsName() {
return goodsName;
}
public void setGoodsName(String goodsName) {
this.goodsName = goodsName;
}
public int getNums() {
return nums;
}
public void setNums(int nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderBean [goodsName=" + goodsName + ", nums=" + nums + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectOutputStreamStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//定义多个对象
OrderBean order01 = new OrderBean("卫衣", 20, 200.0);
OrderBean order02 = new OrderBean("裙子", 31, 600.0);
//d:\\order.txt
File file = new File("D:\\order.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
if(!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
//创建流
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//操作流
oos.writeObject(order01);
oos.writeObject(order02);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭流
try {
oos.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.2 ObjectInputStream 对象输入流
ObjectInputStream:将 字节数据 转换为 对象数据
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
/**
* 对象输入流
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ObjectInputStreamStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File file = new File("D:\\order.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//操作流
while(true) {
Object obj = ois.readObject();
if(obj instanceof OrderBean) {
OrderBean order = (OrderBean)obj;
System.out.println(order);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
if(e instanceof EOFException) {
System.out.println("数据读取完毕!");
}else {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}finally {
try {
ois.close();
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.3 实现Serializable接口的目的
原因:(对象数据库的使用,网络数据传输过程)使用对象流传输数据时,要求:对象数据 可以和 字节数据 相互转换。
实现了Serializable接口的类可以被序列化输出,但并非该类的任何内容都能被序列化。在类中,属性(包括基本数据类型、数组、对其他对象的引用)以及类名可以被序列化,而static属性、方法、加了transient修饰符的属性则不能被序列化。
2.4 提供Serializable ID属性的目的
目的:是为保证 序列化和反序列过程中,对象的所对应的类的版本 认为是一致的
如果不加,那么每次修改类,编译器都会自动生成一个新的Serializable ID,这样反序列化时,就会出问题
2.5 transient 关键字
transient 表示某一个属性,无需参与序列化
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class OrderBean implements Serializable{
/**
* 为啥要加序列化ID?
* 目的:是为保证 序列化和反序列过程中,对象的所对应的类 的版本 认为是一致的
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 315682470257319334L;
/**
* 商品的名称
*/
private String goodsName;
/**
* 数量
*/
private int nums;
/**
* 单价
* transient 关键字(表示:该属性无需参与序列化)
*/
private transient double price;
public OrderBean(String goodsName, int nums, double price) {
super();
this.goodsName = goodsName;
this.nums = nums;
this.price = price;
}
public OrderBean() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getGoodsName() {
return goodsName;
}
public void setGoodsName(String goodsName) {
this.goodsName = goodsName;
}
public int getNums() {
return nums;
}
public void setNums(int nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderBean [goodsName=" + goodsName + ", nums=" + nums + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
三、字符流
字符流操作的以字符(2个字节)为单位进行 数据的读写
字符流用于处理文本文件。所有字符流都继承于抽象类Reader和Writer两个父类。
分类
3.1 低级字符流
操作文件的:FileReader FileWrite (*)
操作线程通讯的:PipedReader PipedWrite
操作内存字符串的:StringReader StringWriter
操作内存字符数组的:CharArrayReader CharArrayWrite
FileWrite 的使用
将程序中的数据,使用字符的方式 写入到外部文件中去
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.lower;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 文件输出字符流
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class FileWriteStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//定义文件对象
File file = new File("d:\\students.txt");
//创建流
FileWriter write = null;
try {
if(!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
//操作流(true 表示操作方式为:追加模式)
write = new FileWriter(file,true);
String str = "台湾是中国的!!!";
write.write(str);
String str02 = "钓鱼岛也是中国的!!!";
char[] arr = str02.toCharArray();
write.write(arr);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭流
try {
write.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileReader的使用
将外部文件的内容,使用字符的方式 读取到程序中来
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.lower;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class FileReaderStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//定义文件对象
File file = new File("d:\\students.txt");
FileReader reader = null;
try {
//实例化
reader = new FileReader(file);
char[] data = new char[1024];
//操作流
while(reader.read(data) != -1) {
//以字符数组的方式输出
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
//字符串的方式输出内容
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.2 高级字符流
3.2.1 分类
缓冲流:包括BufferedReader和BufferedWriter类,利用缓冲区来提高读写数据的效率。
转换流:用于字节数据到字符数据之间的转换,包括InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
打印输出流:包括PrintWriter类,允许将基本类型数据打印输出到字符串流中,PrintWriter带有带自动刷新(Flush)功能。
3.2.2 缓冲流 BufferedReader BufferedWriter
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class BufferedReaderStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File file = new File("D:\\index.txt");
BufferedReader reader = null;
//字节转换字符流
InputStreamReader isr = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//创建流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "GBK");
reader = new BufferedReader(isr);
String content = "";
//操作流
while((content = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class BufferedWriteStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File file = new File("D:\\user.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedWriter writer = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
if(!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
//建立流
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");
writer = new BufferedWriter(osw);
//操作流
writer.write("台湾是中国的!!!");
//换行
writer.newLine();
String str = "我是老婆的!!!";
char[] data = str.toCharArray();
writer.write(data);
//刷新流
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.3.3 字符打印输出流PrintWrite
前面讲过字节打印输出流 PrintStream (它的作用:将字节 按照操作系统默认的编码 进行数据的读写)
PrintWrite 和 PrintStream 在功能上是一样的。区别:在于PrintWrite 可以设置其他字符集
package com.woniuxy.java19.study.advance;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PrintWriterStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//先定义一个文件对象
File file = new File("d:\\movie\\lyf.txt");
PrintWriter writer = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//PrintWriter可以 借助OutputStreamWriter 进行编码集的设置
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");
writer = new PrintWriter(osw);
writer.println("花木兰");
writer.println("仙剑奇侠传");
writer.println("神雕侠侣");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
writer.close();
}
}
}
四、流的使用规则
1、如果数据源是文件,对于字节流,使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream;对于字符流,使用FileReader和 FileWriter。
2、如果数据源是字节数组byte[],则使用ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream。
3、如果数据源是字符数组Char[],则使用CharArrayReader和CharArrayWriter。
4、如果数据源是String对象,对于字节流,则使用StringBufferInputStream和StringBufferOuputStream;对于字符流,则使用StringReader和StringWriter。
5、如果数据源是网络数据流,对于字节流,使用InputStream和OutputStream;对于字符流,使用Reader和Writer。