一、DML
1.1 新增
1.1.1 新增数据语法
insert into 表 (字段列表……) values (值列表……);
举例:
insert into goods_info (id,goods_name,goods_no,goods_price) values ('123sdsdfqwedfgwer','一条草绿色的秋裤!','9527','1000.0');
insert into goods_info (id,goods_name,goods_no,goods_price,goods_type) values ('123123','一条白色的秋裤!','9218','1000.0','1');
字段列表,哪些可以不写
1、允许为NULL的列,是可以不写的
2、主键如果自增的,可以不写
3、有默认值的列,也可以不写
create table user_info(id int primary key auto_increment,
user_name varchar(20) not null,
pwd varchar(32) default '123456');
insert into user_info (user_name) values ('李四');
1.1.2 简化写法(不推荐)
insert into 表 values (值列表……);
举例
insert into goods_info values ('wert34545','一条黑色的秋裤','1','1200','9568','这是一条非常好看,黑色的秋裤');
这种写法,value的列表,一定要对应着表中的 字段结构。不好记,也不好些!也不好维护!
1.1.3 批量新增语法(推荐)
insert into 表 (字段列表……) values (值列表……),(值列表……),(值列表……),(值列表……)……;
特点:values 后,有多少个() 就代表有几条数据!
举例:
insert into user_info (user_name) values ('张三'),('王五'),('赵六'),('田七'),('王八');
1.2 修改
1.2.1 修改数据语法
update 表的表名 set 字段名1=值1,字段名2=值2,字段名3=值3, …… where 条件筛选
举例:
update goods_info set goods_name = '白色的秋裤',goods_price = 1100 where id = 'wert34545';
效果是:修改表中id = ‘wert34545’这行数据,将他的名字,价格做调整
当然,where条件后,并不是只能跟 id,也可以是其他字段
update goods_info set goods_name = '黑色的秋裤',goods_price = 1200 where goods_type = '1';
1.2.2 and or 拼接
如果有多个条件,则采用and | or 来进行拼接
update goods_info set goods_name = '肉色的秋裤',goods_price = 1300 where goods_type = '1' and goods_no = '9218';
update goods_info set goods_name = '肉色的秋裤',goods_price = 1300 where goods_type = '1' or goods_no = '9218';
1.2.3 不加where的情况
update goods_info set goods_name = '白色的秋裤',goods_price = 1100;
效果是:修改表中的所有数据,将他们的名字,价格统一做调整
1.3 删除
1.3.1 删除数据的语法 - 全删
删除数据的语法(1)-全删
delete from 表的表名;
删除数据的语法(2)-全删
truncate user_info;
delete 与 truncate 全删表时的区别(面试题)
delete 是一行一行的删除,而且数据库会做相关的记录,如果删除了,DBA还可以找回来
truncate 是一次整体删除,并且数据库不会做删除的相关记录,也就说你删了,DBA都干不回来(所以慎重)
1.3.2 删除数据的语法 - 部分删
delete from 表的表名 where 条件筛选;
具体:
delete from goods_info where id = '123123';
二、DQL
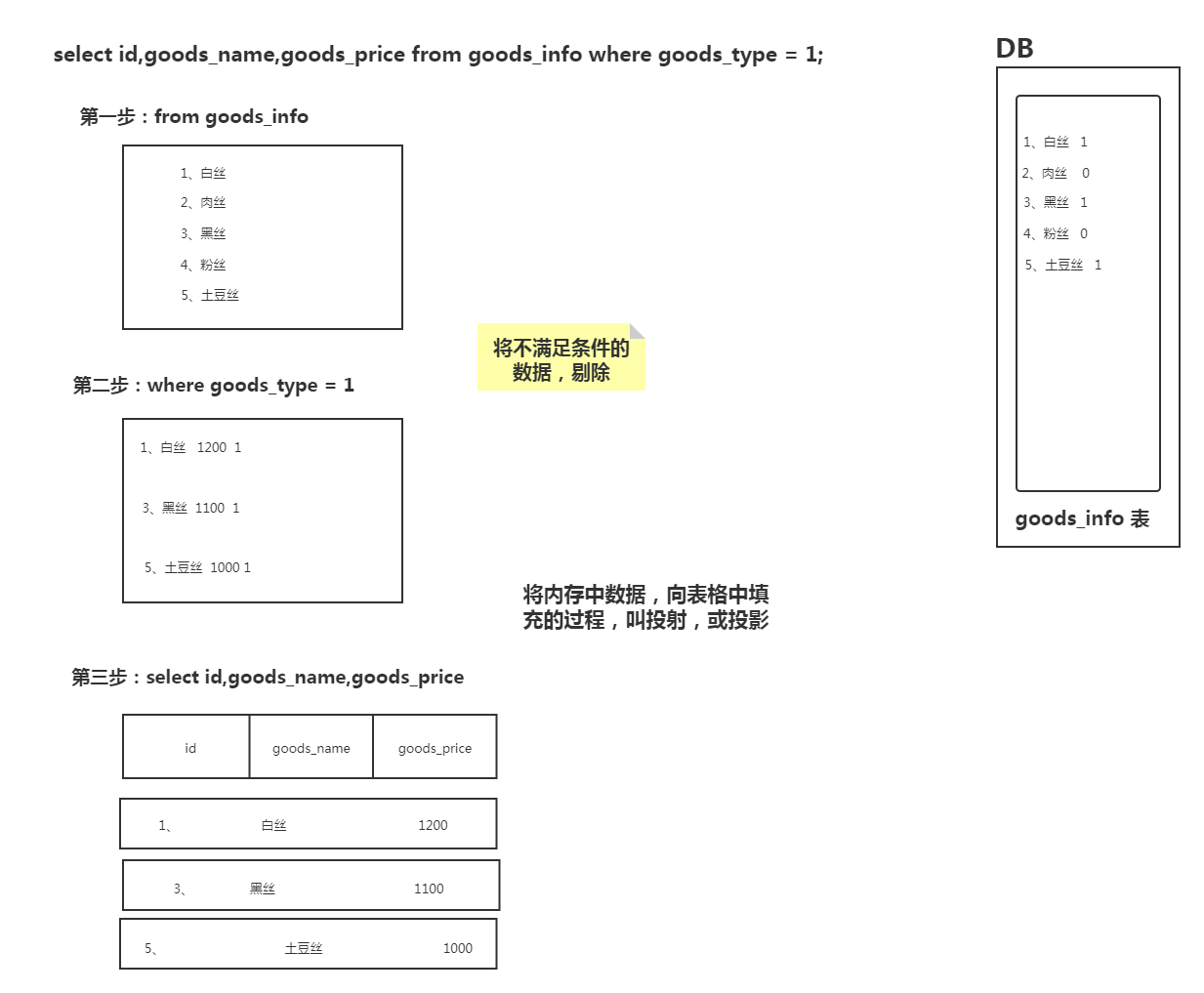
2.1 查询语句执行顺序
1、from子句组装来自不同数据源的数据;
2、where子句基于指定的条件对记录行进行筛选;
3、group by子句将数据划分为多个分组;
4、使用聚集函数进行计算;
5、使用having子句筛选分组;
6、计算所有的表达式;
7、select 的字段;
8、使用order by对结果集进行排序。
9、使用limit 完成分页显示
select 字段
from 表1 别名
连接类型 join 表2 别名
on 连接条件
where 条件1
group by 分组字段
having 条件2(一般是分组条件)
order by 排序字段 (desc/asc)
limit 索引,最大查询数量;
2.2 不加where条件的查询
例如:
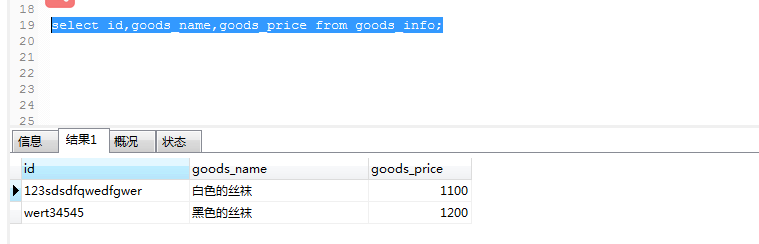
select id,goods_name,goods_price from goods_info;
2.3 加where条件的查询
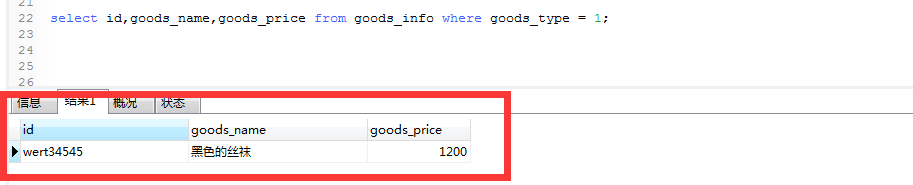
select id,goods_name,goods_price from goods_info where goods_type = 1;
2.4 查询所有列
select * from 表的表名 where 条件筛选 ……
举例:
select * from goods_info where goods_type = 1;
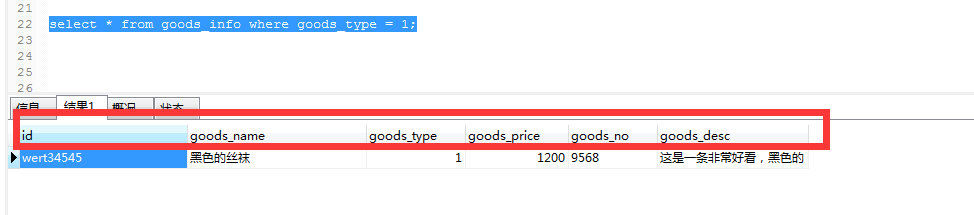
注意:如果你们以后在工作中,不是需要你显示所有的列,就不要用
**
2.5 给列取别名(常用)
select id as 'ID编号',goods_name as '商品名称',goods_price as '商品价格' from goods_info;
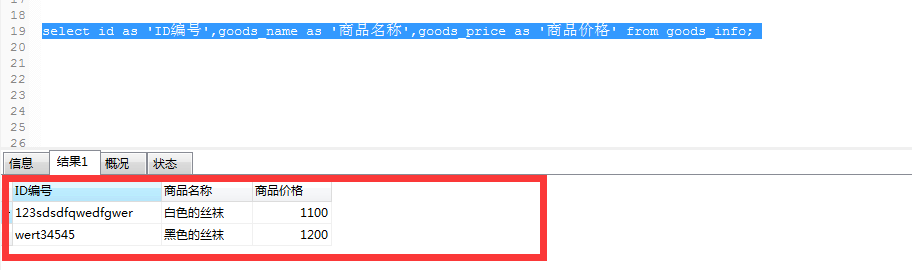
在投影时,给列取一个别名,其目的是为了:让列显示的更直观
2.6 针对查询出来的结果,做计算(了解)
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info;
2.7 精准查询 和 模糊查询(重点)
2.7.1 精准查询
精准查询,where 后的条件,使用 =
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name = '白色的秋裤';
2.7.2 模糊查询(1)-常用的
模糊查询,where 后的条件,使用 like ,并且配合% 来实现
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '白色%';
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '%秋裤';
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '%的%';
记住:
%秋裤 ,表示 以”秋裤”为基准,向前进行匹配元素
白色% ,表示 以”白色”为基准,向后进行匹配元素
%的% , 表示以 “的”为基准,向两边进行匹配元素
2.7.3 模糊查询(2)-不算常用
模糊查询,where 后的条件,使用 like ,并且配合 来实现
的模糊,只能匹配一个字符
%的模糊,可以匹配一串字符
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '白色_';
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '_白色';
select id,goods_name,goods_price + 500 as goods_price from goods_info where goods_name like '_白色_';
记住:
秋裤 ,表示 以”秋裤”为基准,向前进行匹配一个字符元素
白色 ,表示 以”白色”为基准,向后进行匹配一个字符元素
的, 表示以 “的”为基准,向两边分别进行匹配一个字符元素
2.7.4 distinct 去重
distinct 去重关键字!
语法是:
select distinct 字段列表 from 表的表名;
举例:
select distinct goods_name ,goods_price from goods_info;
2.7.5 数据复制
2.7.5.1 表的数据复制(要求目标表一定要存在)
insert into 目标表(字段列表) select 相同的字段列表 from 源表;
举例:
insert into user_info (user_name,pwd) select user_name,pwd from user_info;
2.7.5.2 表的数据复制(要求目标表一定不能存在)
create table 目标表 select * from 源表;
举例:
create table t_temp select * from user_info;
2.7.6 数据复制面试题(常问)
一个表中,可能存在大量的重复数据,现在需要你去重,你会怎么做?
-- 第一步:查询去重后的数据,并复制到临时表中
create table t_temp select distinct user_name,pwd from user_info;
-- 第二步:删除源表的所有数据
truncate user_info;
-- 第三步:将临时表的数据,复制到源表
insert into user_info(user_name,pwd) select user_name,pwd from t_temp;
-- 第四步:删除临时表
drop table t_temp;
2.8 limit 分页(重点)
所有的数据页面,90%以上都需要提供分页功能!!!!
MYSQL的分页关键字:limit
SQLServer的分页关键字:top
Oracle的分页关键字:rownumber
limit分页语法
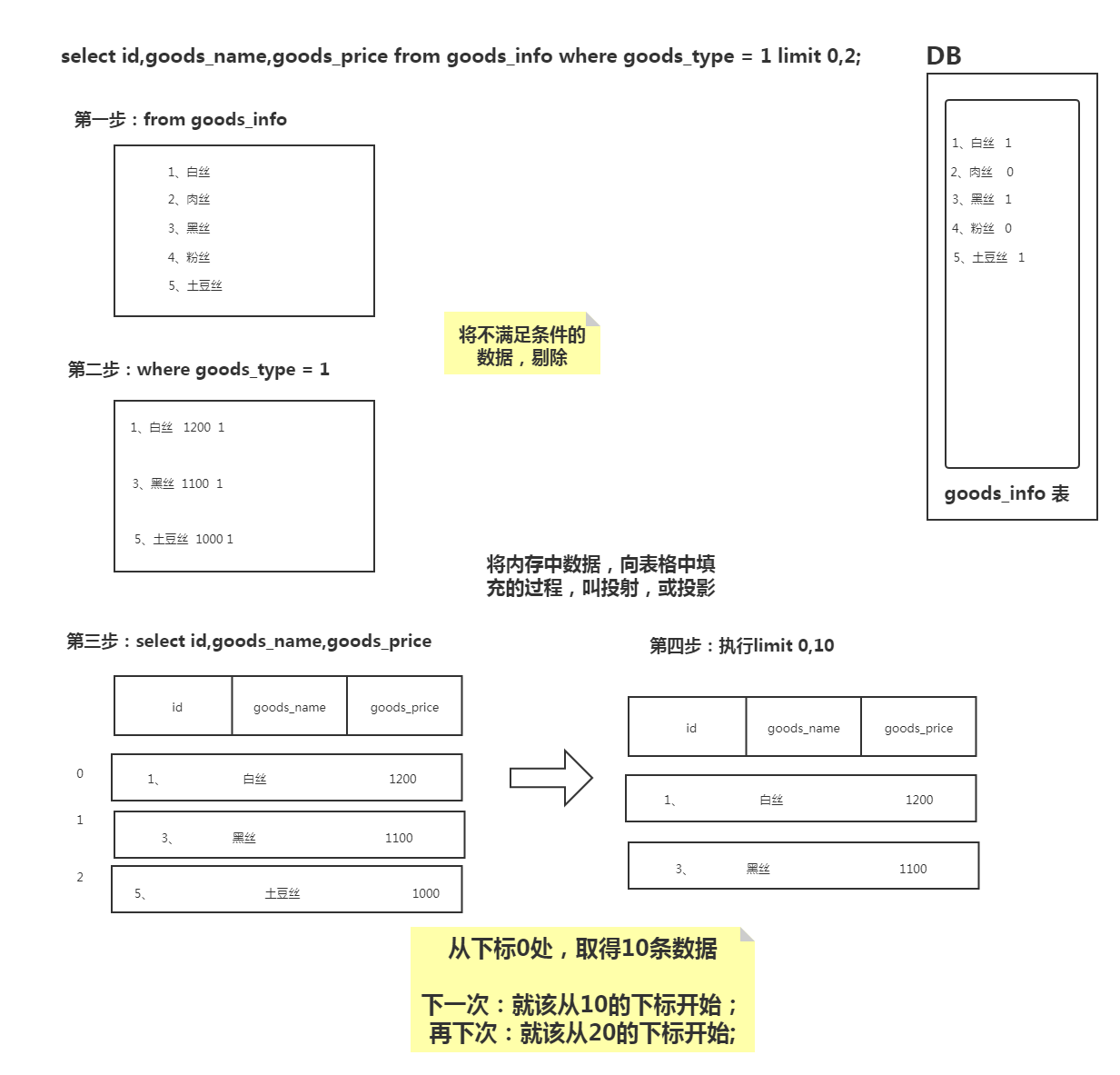
select * from user_info limit 0,10;
limit关键字后,有2个参数:
第1个参数指的是:从哪个位置开始获取数据
第2个参数指的是:每次获取多少条
**
2.9 where条件筛选
2.9.1 and or
如果有多个条件,要么用and ,要么用or来进行条件的连接
and 表示并且关系
or 表示或者关系
2.9.2 已经确定到某一个具体的内容 =
2.9.3 如果并确定到某一个具体的内容 like
2.9.4 如果比较的是个数值,而且筛选的数值的范围 > < >= <= != between and
例如:
where age >= 18;
where age >= 18 and age <= 60;
where age != 1;
where age between 18 and 60; === where age >= 18 and age <= 60;
举例:
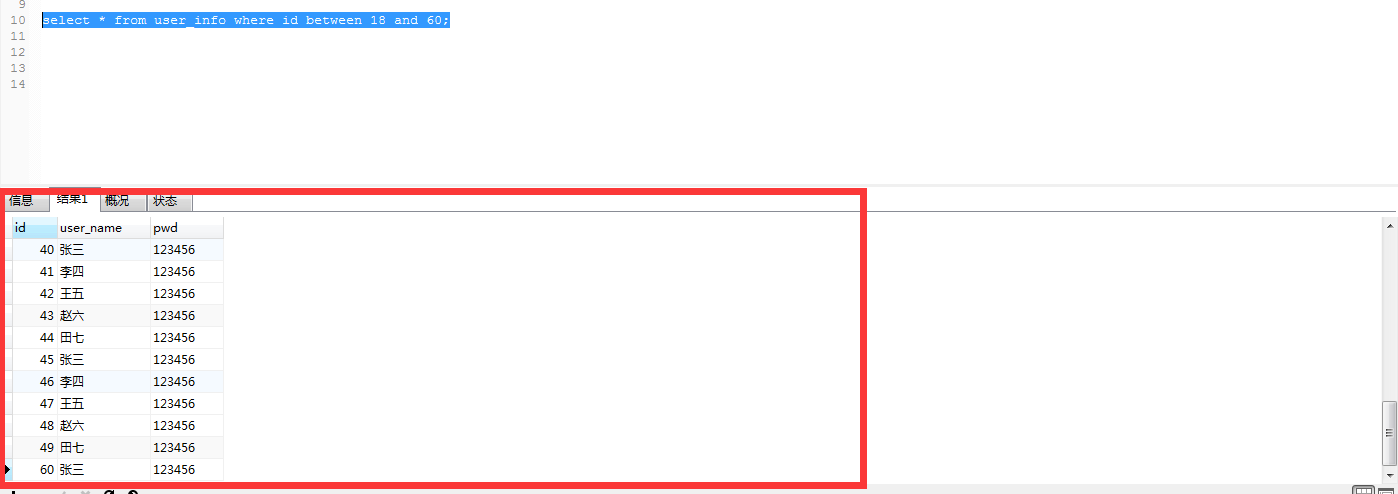
select * from user_info where id between 18 and 60;
2.9.5 如果筛选的值,不是一个范围,而是一些具体的值 则使用 in 和 not in
in
where id = 2 or id = 4 or id = 7;
此时,将上述的条件简写为:
where id in (2,4,7)
EG:
select * from user_info where id in (18,45,34,23);
等同于:
select * from user_info where id = 18 or id = 23 or id = 34 or id = 45;
not in
where id != 2 and id != 4 and id != 7;
此时,将上述的条件简写为:
where id not in (2,4,7);
EG:
select * from user_info where id != 18 and id != 23 and id != 34 and id != 45;
select * from user_info where id not in (18,23,34,45);
执行结果:将会剔除id 是18,23,34,45的数据
2.10 操作NULL值(面试)
语法:
select 字段列表 from 表的表名 where 某一个字段 IS NULL;
or
select 字段列表 from 表的表名 where 某一个字段 IS NOT NULL;
EG:
查出用户表中,所有用户描述信息是NULL的数据
select * from user_info where user_desc IS NULL;
查出用户表中,所有用户描述信息不是NULL的数据
select * from user_info where user_desc IS NOT NULL;
2.11 order by 排序
排序在数据库中有2种排序:升序asc,降序 desc
语法结构:
select 字段列表 from 表的表名 where 条件筛选 order by 某一个排序字段 asc | desc;
EG:
//升序
select * from goods_info where goods_desc IS NULL order by goods_price asc;
//降序
select * from goods_info where goods_desc IS NULL order by goods_price desc;
order by 执行在投影之后,但是在limit 执行之前!
三、日期函数
3.1 now()显示当前系统时间 (yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss)
select now();
or
select now() from dual;
同样适用于:新增,修改
insert into t_user(user_name,create_time,modify_time) values ('小苍',now(),null);
特别注明:dual 是一张不存在的虚拟表
3.2 curdate()显示当前系统时间(yyyy-MM-dd)
select curdate();
or
select curdate() from dual;
3.3 curtime()显示当前系统时间(hh:mm:ss)
select curtime();
or
select curtime() from dual;
3.4 date_format() 完成对日期进行格式化显示
select student_name,gender,age,date_format(birthday,'%Y年%m月%d日') as birthday from t_student;
or
select student_name,gender,age,date_format(birthday,'%y年%m月%d日') as birthday from t_student;
3.5 year() 返回日期的年份
select student_name,gender,age, year(birthday) as year from t_student;
3.6 month() 返回日期的月份
select student_name,gender,age, month(birthday) as month from t_student;
3.7 day() 返回日期的日
select student_name,gender,age, day(birthday) as day from t_student;
3.8 date()显示某个时间的yyyy-MM-dd的格式
select student_name,gender,age, DATE(create_time) as '创建时间' from t_student;
3.9 time()显示某个时间的hh:mm:ss的格式
select student_name,gender,age, time(create_time) as '创建时间' from t_student;
3.10 dayofweek()显示某个时间,是本周第几天
select student_name,gender,age, dayofweek(create_time) as '星期几' from t_student;
1-星期天
2-星期一
3-星期二
……
四、字符串函数
4.1 小写字母转大写字母 upper()
select upper(student_name) as student_name,gender,age from t_student;
4.2 大写字母转小写字母 lower()
select lower(student_name) as student_name,gender,age from t_student;
4.3 使用substring()截取字符串
//从下标5开始,向后截取
select substring(student_name,5) as student_name,gender,age from t_student;
//从下标2开始,截取到4结束
select substring(student_name,2,4) as student_name,gender,age from t_student;
4.4 rand() 随机函数
select rand() * 10 from dual;
4.5 round() 四舍五入
select round(rand() * 10) from dual;