习题6.2
写出Logistic回归模型学习的梯度下降算法。
解答:
对于Logistic模型:
对数似然函数为:
似然函数求偏导,可得
梯度函数为:
Logistic回归模型学习的梯度下降算法:
(1) 取初始值,置 k=0
(2) 计算
(3) 计算梯度,当
时,停止迭代,令
;否则,求
,使得
(4) 置,计算
,当
或
时,停止迭代,令
(5) 否则,置 k=k+1,转(3)
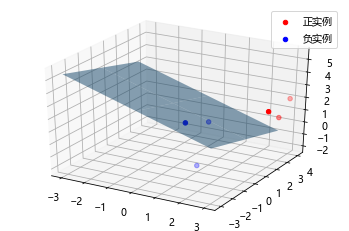
%matplotlib inlineimport numpy as npimport timeimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dfrom pylab import mpl# 图像显示中文mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']class LogisticRegression:def __init__(self, learn_rate=0.1, max_iter=10000, tol=1e-2):self.learn_rate = learn_rate # 学习率self.max_iter = max_iter # 迭代次数self.tol = tol # 迭代停止阈值self.w = None # 权重def preprocessing(self, X):"""将原始X末尾加上一列,该列数值全部为1"""row = X.shape[0]y = np.ones(row).reshape(row, 1)X_prepro = np.hstack((X, y))return X_preprodef sigmod(self, x):return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))def fit(self, X_train, y_train):X = self.preprocessing(X_train)y = y_train.T# 初始化权重wself.w = np.array([[0] * X.shape[1]], dtype=np.float)k = 0for loop in range(self.max_iter):# 计算梯度z = np.dot(X, self.w.T)grad = X * (y - self.sigmod(z))grad = grad.sum(axis=0)# 利用梯度的绝对值作为迭代中止的条件if (np.abs(grad) <= self.tol).all():breakelse:# 更新权重w 梯度上升——求极大值self.w += self.learn_rate * gradk += 1print("迭代次数:{}次".format(k))print("最终梯度:{}".format(grad))print("最终权重:{}".format(self.w[0]))def predict(self, x):p = self.sigmod(np.dot(self.preprocessing(x), self.w.T))print("Y=1的概率被估计为:{:.2%}".format(p[0][0])) # 调用score时,注释掉p[np.where(p > 0.5)] = 1p[np.where(p < 0.5)] = 0return pdef score(self, X, y):y_c = self.predict(X)error_rate = np.sum(np.abs(y_c - y.T)) / y_c.shape[0]return 1 - error_ratedef draw(self, X, y):# 分离正负实例点y = y[0]X_po = X[np.where(y == 1)]X_ne = X[np.where(y == 0)]# 绘制数据集散点图ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')x_1 = X_po[0, :]y_1 = X_po[1, :]z_1 = X_po[2, :]x_2 = X_ne[0, :]y_2 = X_ne[1, :]z_2 = X_ne[2, :]ax.scatter(x_1, y_1, z_1, c="r", label="正实例")ax.scatter(x_2, y_2, z_2, c="b", label="负实例")ax.legend(loc='best')# 绘制p=0.5的区分平面x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)y = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)x_3, y_3 = np.meshgrid(x, y)a, b, c, d = self.w[0]z_3 = -(a * x_3 + b * y_3 + d) / cax.plot_surface(x_3, y_3, z_3, alpha=0.5) # 调节透明度plt.show()# 训练数据集X_train = np.array([[3, 3, 3], [4, 3, 2], [2, 1, 2], [1, 1, 1], [-1, 0, 1],[2, -2, 1]])y_train = np.array([[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]])# 构建实例,进行训练clf = LogisticRegression()clf.fit(X_train, y_train)clf.draw(X_train, y_train)迭代次数:3232次最终梯度:[ 0.00144779 0.00046133 0.00490279 -0.00999848]最终权重:[ 2.96908597 1.60115396 5.04477438 -13.43744079]
**