JLRoutes是一个调用极少代码 , 可以很方便的处理不同URL schemes以及解析它们的参数,并通过回调block来处理URL对应的操作 , 可以用于处理复杂跳转逻辑的三方库.
原理
JLRoutes本质可以理解为:保存一个全局的Map,scheme为Key,JLRoutes为Value,Value是对应存放block的数组,url和block都会常驻在内存中,当打开一个URL时,JLRoutes就可以遍历 , 这个全局的map,通过url来执行对应的block。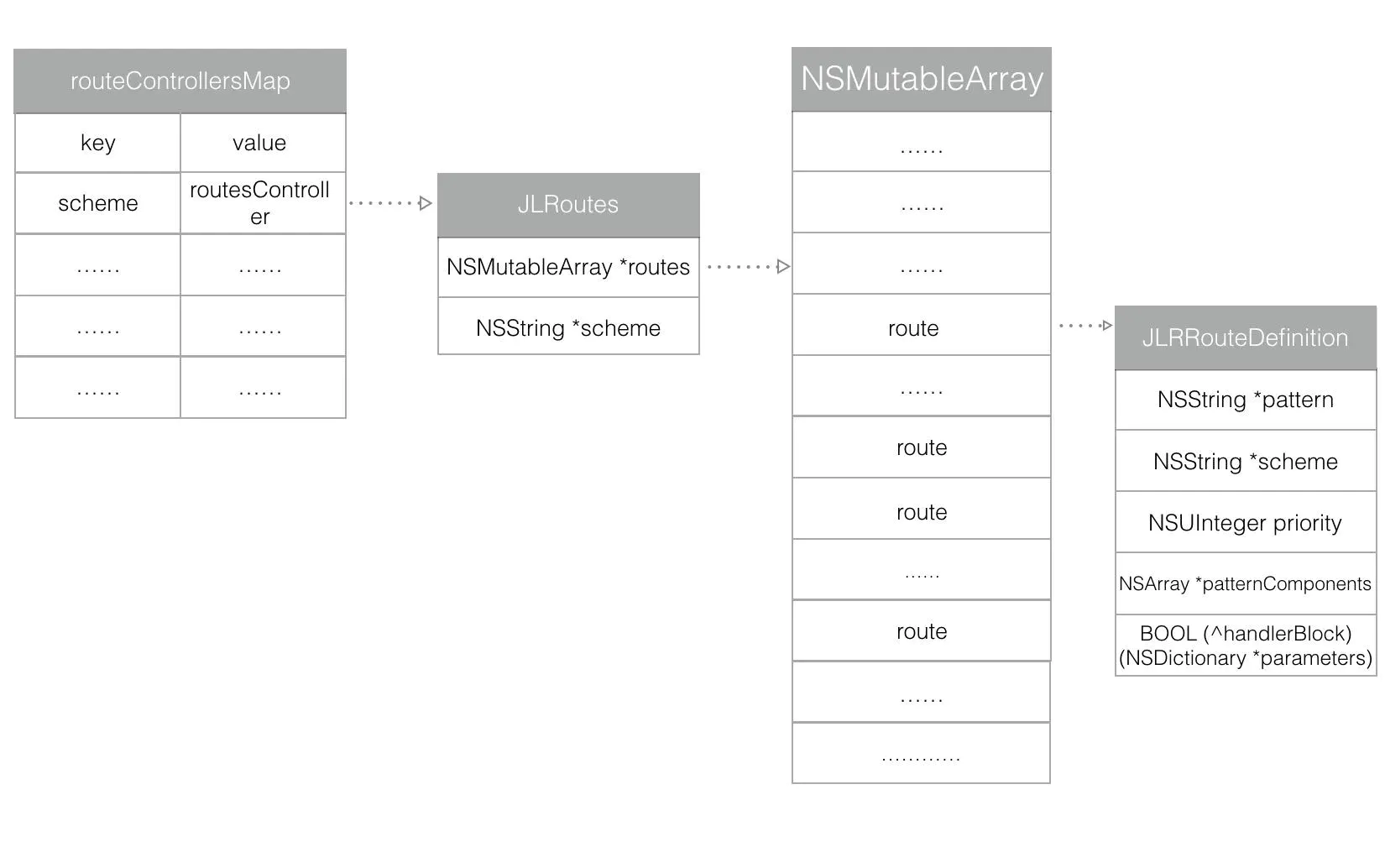
- routeControllersMap 是全局的单例字典 , 你可以想象成一个大的盒子 .
2 . 这个盒子里装了很多的字典 , 而字典的key值对应 一个标识 , 源码中称之为 scheme ,为了不混淆 , 咱们就叫其为JLRoutes对象标识 . 这个标识对应的value值 为JLRoutes类的对象 .
3. JLRoutes对象有很多属性 , 常用的有两个 , 一个是 scheme 也就是是上述所说的JLRoutes对象标识 , 也就是说 , 此value值记录了自己的key值 . 另外一个属性为 routes数组 , 此数组中存放了 JLRRouteDefinition 对象 .
4. JLRRouteDefinition对象为最终的具体模型 , 也就是说 你注册的跳转逻辑的所有信息 , 都存在于这个模型中 ,包括要实施操作的block代码块 , JLRoutes对象标识 , 取url内容值的标识
在每个JLRoutes的数组里面,会按照路由的优先级进行排列,优先级高的排列在前面。
- (void)_registerRoute:(NSString *)routePattern priority:(NSUInteger)priority handler:(BOOL (^)(NSDictionary *parameters))handlerBlock{JLRRouteDefinition *route = [[JLRRouteDefinition alloc] initWithScheme:self.scheme pattern:routePattern priority:priority handlerBlock:handlerBlock];if (priority == 0 || self.routes.count == 0) {[self.routes addObject:route];} else {NSUInteger index = 0;BOOL addedRoute = NO;// 找到当前已经存在的一条优先级比当前待插入的路由低的路由for (JLRRouteDefinition *existingRoute in [self.routes copy]) {if (existingRoute.priority < priority) {// 如果找到,就插入数组[self.routes insertObject:route atIndex:index];addedRoute = YES;break;}index++;}// 如果没有找到任何一条路由比当前待插入的路由低的路由,或者最后一条路由优先级和当前路由一样,那么就只能插入到最后。if (!addedRoute) {[self.routes addObject:route];}}}
由于这个数组里面的路由是一个单调队列,所以查找优先级的时候只用从高往低遍历即可。
具体查找路由的过程如下: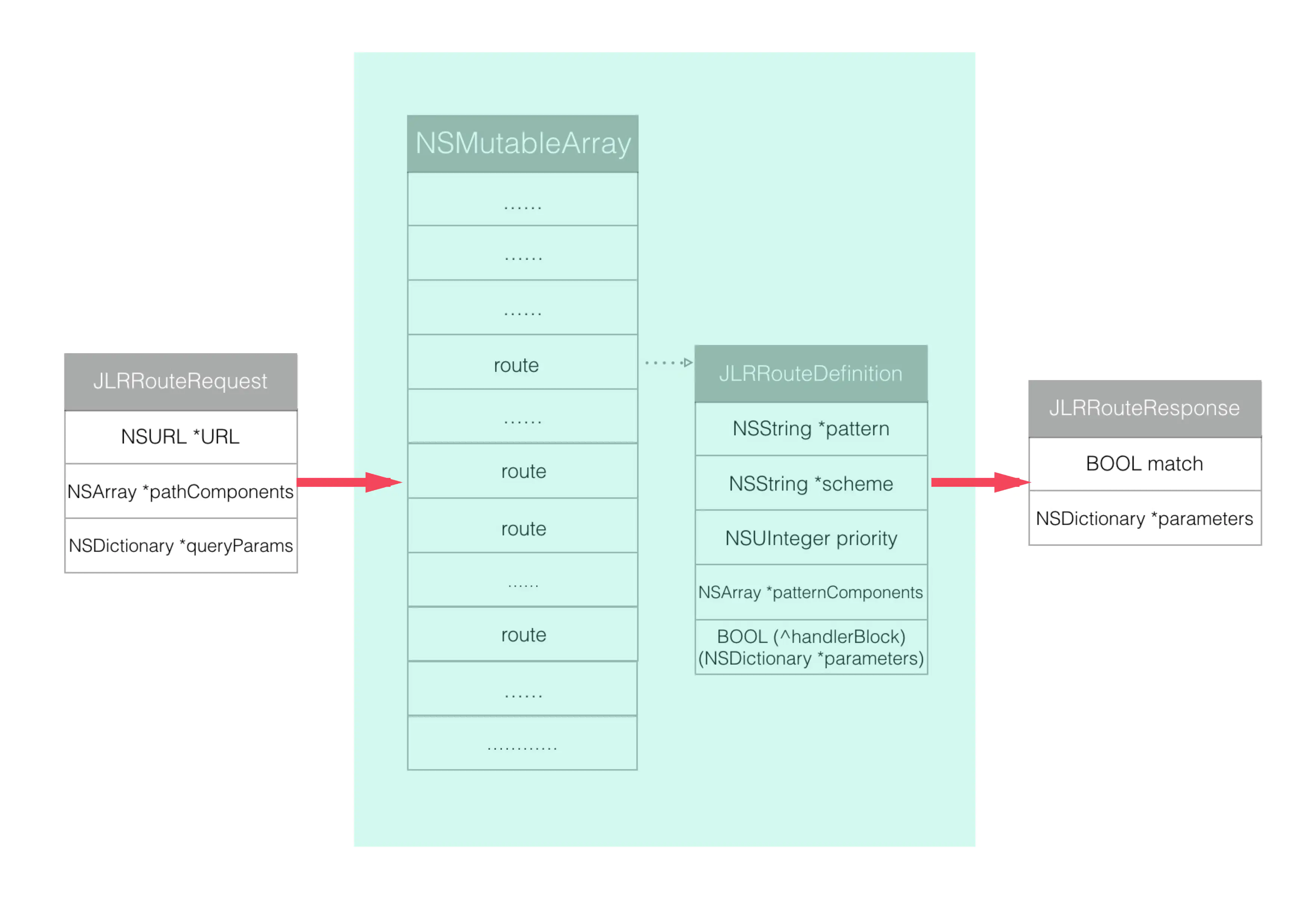
首先根据外部传进来的URL初始化一个JLRRouteRequest,然后用这个JLRRouteRequest在当前的路由数组里面依次request,每个规则都会生成一个response,但是只有符合条件的response才会match,最后取出匹配的JLRRouteResponse拿出其字典parameters里面对应的参数就可以了。查找和匹配过程中重要的代码如下:
- (BOOL)_routeURL:(NSURL *)URL withParameters:(NSDictionary *)parameters executeRouteBlock:(BOOL)executeRouteBlock{if (!URL) {return NO;}[self _verboseLog:@"Trying to route URL %@", URL];BOOL didRoute = NO;JLRRouteRequest *request = [[JLRRouteRequest alloc] initWithURL:URL];for (JLRRouteDefinition *route in [self.routes copy]) {// 检查每一个route,生成对应的responseJLRRouteResponse *response = [route routeResponseForRequest:request decodePlusSymbols:shouldDecodePlusSymbols];if (!response.isMatch) {continue;}[self _verboseLog:@"Successfully matched %@", route];if (!executeRouteBlock) {// 如果我们被要求不允许执行,但是又找了匹配的路由response。return YES;}// 装配最后的参数NSMutableDictionary *finalParameters = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];[finalParameters addEntriesFromDictionary:response.parameters];[finalParameters addEntriesFromDictionary:parameters];[self _verboseLog:@"Final parameters are %@", finalParameters];didRoute = [route callHandlerBlockWithParameters:finalParameters];if (didRoute) {// 调用Handler成功break;}}if (!didRoute) {[self _verboseLog:@"Could not find a matching route"];}// 如果在当前路由规则里面没有找到匹配的路由,当前路由不是global 的,并且允许降级到global里面去查找,那么我们继续在global的路由规则里面去查找。if (!didRoute && self.shouldFallbackToGlobalRoutes && ![self _isGlobalRoutesController]) {[self _verboseLog:@"Falling back to global routes..."];didRoute = [[JLRoutes globalRoutes] _routeURL:URL withParameters:parameters executeRouteBlock:executeRouteBlock];}// 最后,依旧没有找到任何能匹配的,如果有unmatched URL handler,调用这个闭包进行最后的处理。if, after everything, we did not route anything and we have an unmatched URL handler, then call itif (!didRoute && executeRouteBlock && self.unmatchedURLHandler) {[self _verboseLog:@"Falling back to the unmatched URL handler"];self.unmatchedURLHandler(self, URL, parameters);}return didRoute;}
举例
注册
[[JLRoutes globalRoutes] addRoute:@"/:object/:action" handler:^BOOL(NSDictionary *parameters) {NSString *object = parameters[@"object"];NSString *action = parameters[@"action"];// stuffreturn YES;}];// 1. 参数传递需要进行一一对应[[JLRoutes routesForScheme:@"JLRoutesOne"]addRoute:@"/:ViewController/:userID/:pass"handler:^BOOL(NSDictionary * _Nonnull parameters){Class class = NSClassFromString(parameters[@"ViewController"]);NSLog(@"-----------userID : %@",parameters[@"userID"]);NSLog(@"-----------pass : %@",parameters[@"pass"]);[navVc pushViewController:[[class alloc]init] animated:YES];return YES;}];
跳转点击
- (void)touch{//中文传输需要进行转义NSString*url = @"JLRoutesOne://OneNextViewController/我是userID/我是pwd";//中文传输需要进行转义url = [url stringByAddingPercentEncodingWithAllowedCharacters:[NSCharacterSet URLQueryAllowedCharacterSet]];[[UIApplication sharedApplication]openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:url] options:nil completionHandler:nil];}
匹配成功之后,我们会得到下面这样一个字典:
{"object": "post","action": "halfrost","debug": "true","foo": "bar","JLRouteURL": "ele://post/halfrost?debug=true&foo=bar","JLRoutePattern": "/:object/:action","JLRouteScheme": "JLRoutesGlobalRoutesScheme"}
把上述过程图解出来,见下图: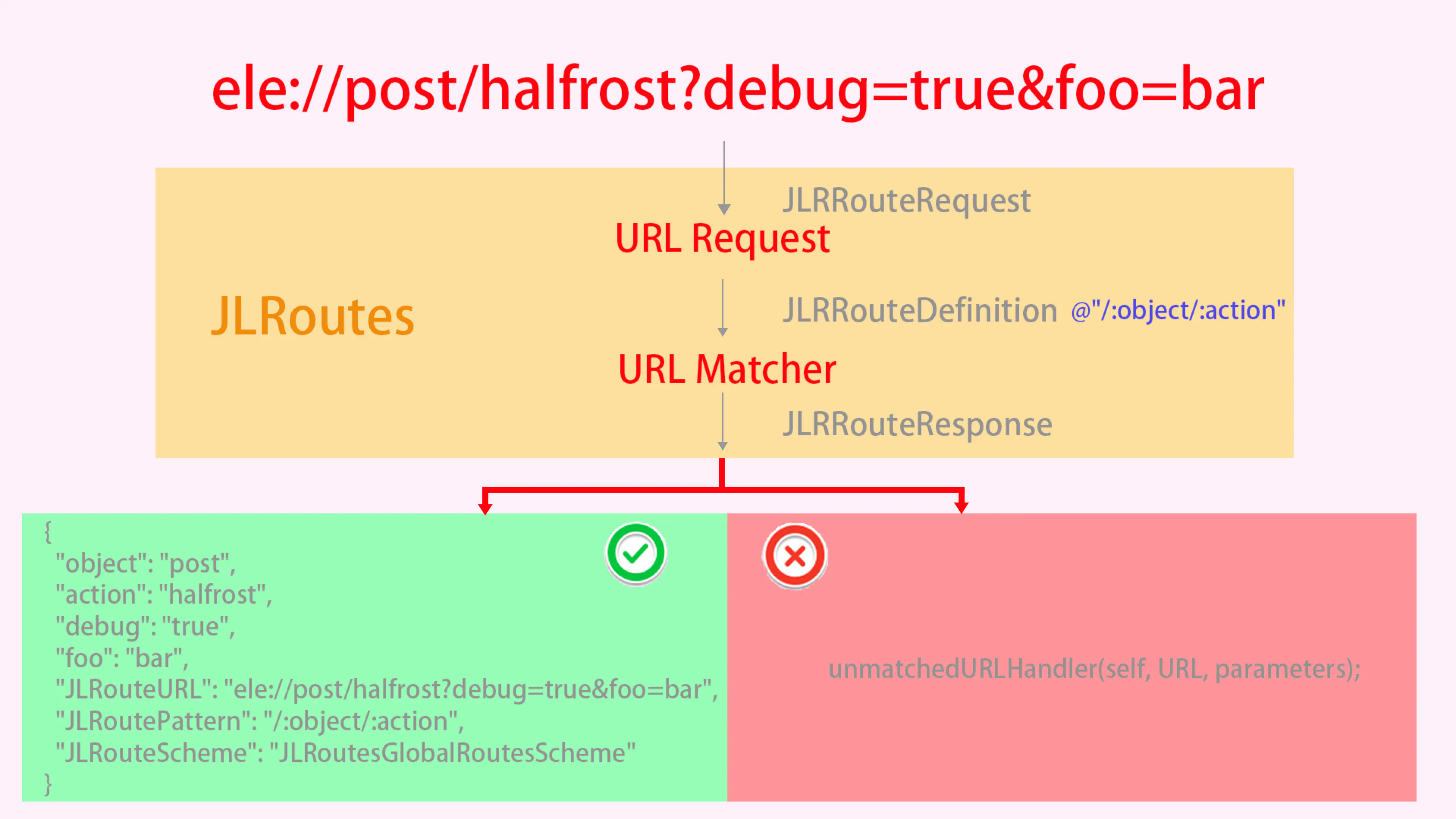
JLRoutes还可以支持Optional的路由规则,假如定义一条路由规则:
/the(/foo/:a)(/bar/:b)
JLRoutes 会帮我们默认注册如下4条路由规则:
/the/foo/:a/bar/:b/the/foo/:a/the/bar/:b/the

