RunLoop是通过内部维护的事件循环来对 事件、消息进行管理的一个对象
事件循环(EventLoop)
没有消息需要处理时,休眠以避免资源占用
有消息需要处理时,立刻被唤醒
用户态我们可以理解为我们日常开发的API接口都是面向我们用户态的。也就是程序员和开发者自行定义和开发的功能。内核态就是系统或者底层的内核方面的系统调用。
那么为什么main函数不会退出,我们可以看看工程里的main函数
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {@autoreleasepool {return UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]));}}
其实在main中存在的这个UIApplicationMain这个函数就是在内部启动了一个RunLoop从而不断的接收消息和休眠,从而导致main方法不会退出了。
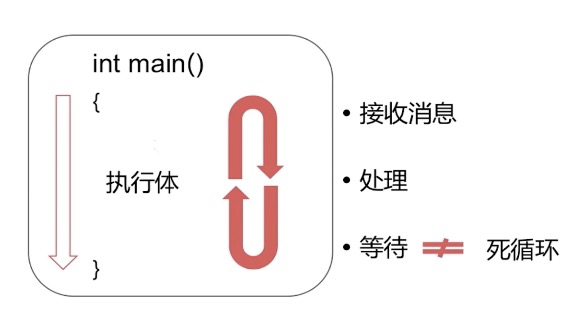

RunLoop对象
OS中有2套API来访问和使用RunLoop
- Foundation:NSRunLoop
- Core Foundation:CFRunLoopRef
NSRunLoop和CFRunLoopRef都代表着RunLoop对象
NSRunLoop是基于CFRunLoopRef的一层OC包装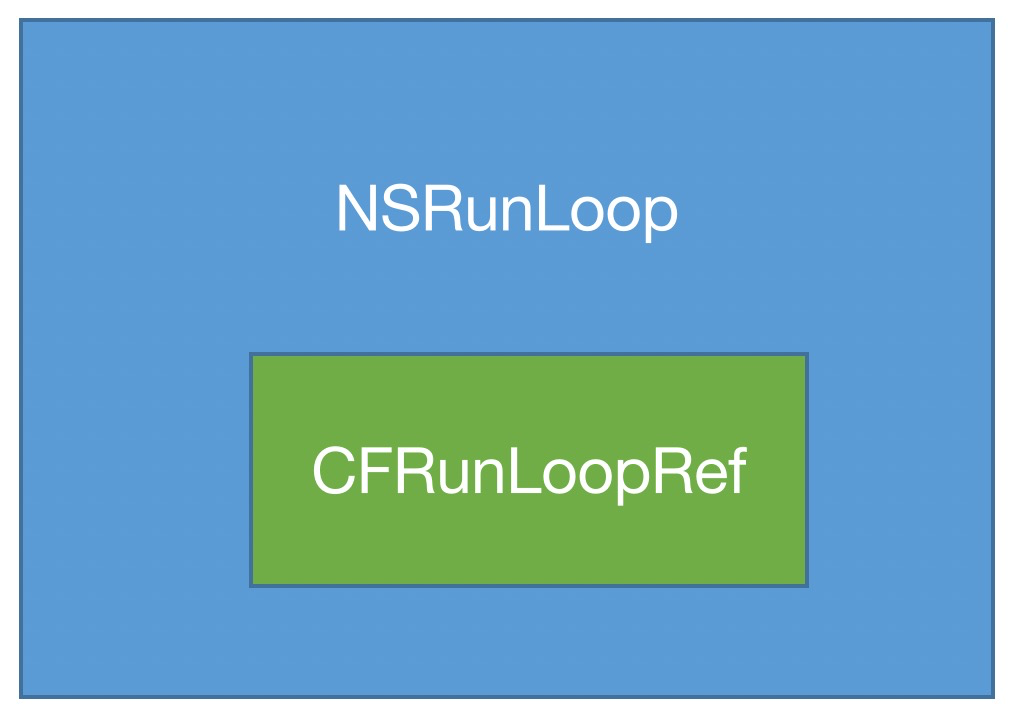
CFRunLoopRef是开源的 https://opensource.apple.com/tarballs/CF/ ```objectivec //Foundation [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]; // 获得当前线程的RunLoop对象 [NSRunLoop mainRunLoop]; // 获得主线程的RunLoop对象
//Core Foundation CFRunLoopGetCurrent(); // 获得当前线程的RunLoop对象 CFRunLoopGetMain(); // 获得主线程的RunLoop对象
//NSRunLoop <—> CFRunLoopRef 相互转化 NSLog(@”NSRunLoop <—> CFRunloop == %p—%p”,CFRunLoopGetMain() , [NSRunLoop mainRunLoop].getCFRunLoop);
【打印结果】:内存地址相同
0000-00-13 00:30:16.527 MultiThreading[57703:1217113] NSRunLoop <—> CFRunloop == 0x60000016a680—0x60000016a680
<a name="69fa3701"></a>## RunLoop的基本作用1. 保持程序的持续运行(如:程序一启动就会开启一个主线程(中的 runloop 是自动创建并运行),runloop 保证主线程不会被销毁,也就保证了程序的持续运行)。2. 处理App中的各种事件(如:touches 触摸事件、NSTimer 定时器事件、Selector事件(选择器 performSelector))。3. 节省CPU资源,提高程序性能(有事情就做事情,没事情就休息 (其资源释放))。4. 负责渲染屏幕上的所有UI。附:CFRunLoop.c 源码```c#【用DefaultMode启动,具体实现查看 CFRunLoopRunSpecific Line2704】#【RunLoop的主函数,是一个死循环 dowhile】void CFRunLoopRun(void) { /* DOES CALLOUT */int32_t result;do {/*参数一:CFRunLoopRunSpecific 具体处理runloop的运行情况参数二:CFRunLoopGetCurrent() 当前runloop对象参数三:kCFRunLoopDefaultMode runloop的运行模式的名称参数四:1.0e10 runloop默认的运行时间,即超时为10的九次方参数五:returnAfterSourceHandled 回调处理*/result = CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);CHECK_FOR_FORK();//【判断】:如果runloop没有停止 且 没有结束则继续循环,相反侧退出。} while (kCFRunLoopRunStopped != result && kCFRunLoopRunFinished != result);}#【直观表现】RunLoop 其实内部就是do-while循环,在这个循环内部不断地处理各种任务(`比如Source、Timer、Observer`),通过判断result的值实现的。所以 可以看成是一个死循环。如果没有RunLoop,UIApplicationMain 函数执行完毕之后将直接返回,就是说程序一启动然后就结束;
Runloop 开启&退出
验证 Runloop 是在UIApplicationMain 中开启。
# int 类型返回值UIKIT_EXTERN int UIApplicationMain(int argc, char *argv[], NSString * __nullable principalClassName, NSString * __nullable delegateClassName);int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {@autoreleasepool {NSLog(@"开始");int number = UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]));NSLog(@"结束");return number;}}#【验证结果】:只会打印开始,并不会打印结束。----#【Runloop 的退出条件】。App退出;线程关闭;设置最大时间到期;
【注解】:说明在UIApplicationMain函数内部开启了一个和主线程相关的RunLoop (保证主线程不会被销毁),导致 UIApplicationMain 不会返回,一直在运行中,也就保证了程序的持续运行。
Runloop和线程关系
- 每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的RunLoop对象
- RunLoop保存在一个全局的Dictionary里,线程作为key,RunLoop作为value
- 创建子线程RunLoop,通过
[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]在子线程内部获取,不获取则不会创建,方法调用时,会先查看字典,有则返回,没有则创建并存入字典中。 - 主线程的RunLoop已经自动获取(创建),子线程默认没有开启RunLoop
RunLoop在第一次获取时创建,在线程结束时销毁。
CFRunLoopRef源码
# 1. 主线程相关联的RunLoop创建// 创建字典CFMutableDictionaryRef dict = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, 0, NULL, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);// 创建主线程 根据传入的主线程创建主线程对应的RunLoopCFRunLoopRef mainLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(pthread_main_thread_np());// 保存主线程 将主线程-key和RunLoop-Value保存到字典中CFDictionarySetValue(dict, pthreadPointer(pthread_main_thread_np()), mainLoop);# 2. 创建与子线程相关联的RunLoop// 从字典中获取子线程的runloopCFRunLoopRef loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);if (!loop) {// 如果子线程的runloop不存在,那么就为该线程创建一个对应的runloopCFRunLoopRef newLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(t);__CFLock(&loopsLock);loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));// 把当前子线程和对应的runloop保存到字典中if (!loop) {CFDictionarySetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t), newLoop);loop = newLoop;}// don't release run loops inside the loopsLock, because CFRunLoopDeallocate may end up taking it__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);CFRelease(newLoop);}
RunLoop的运行逻辑
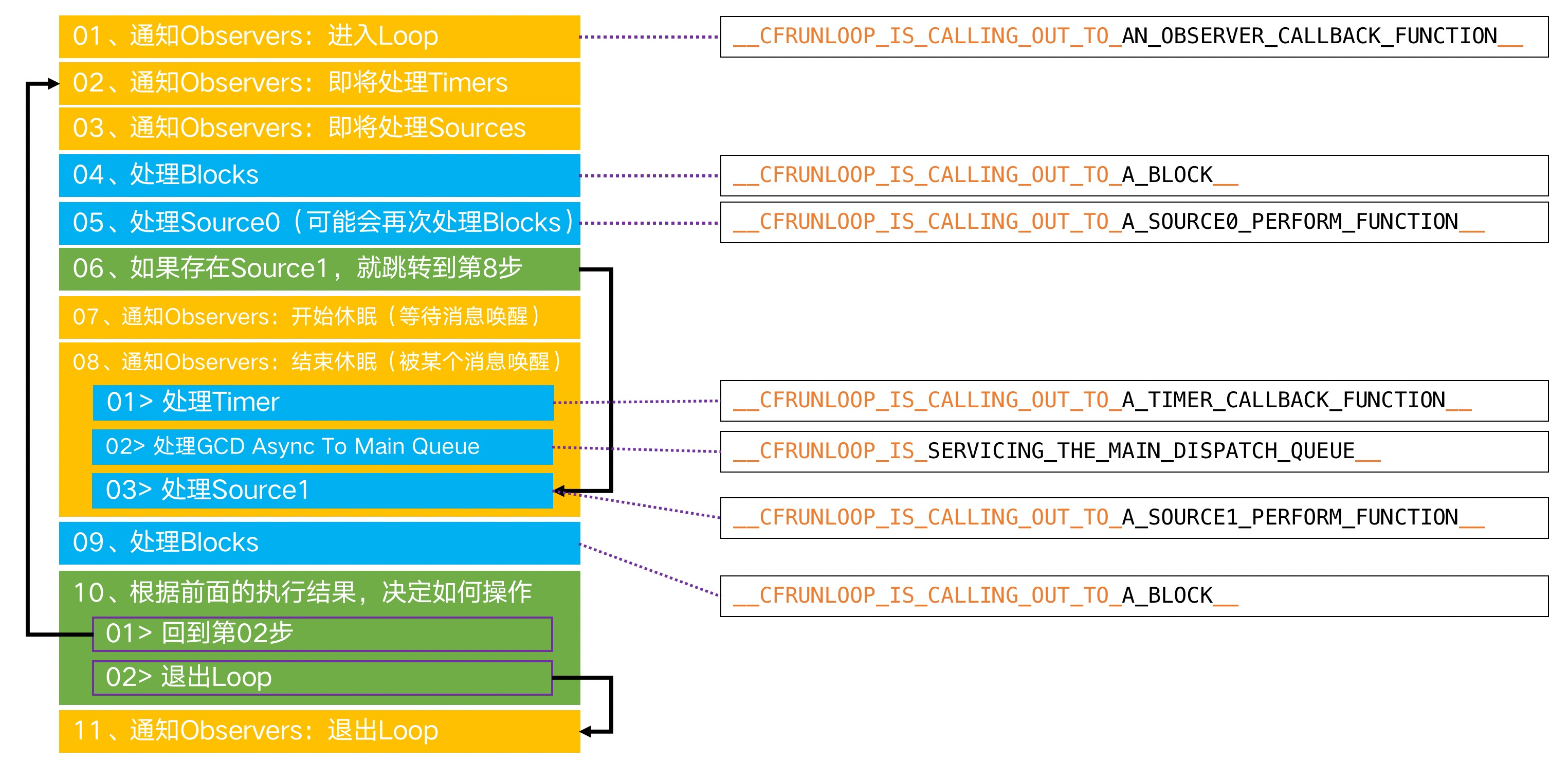
其内部代码整理如下 :
/// 用DefaultMode启动void CFRunLoopRun(void) {CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);}/// 用指定的Mode启动,允许设置RunLoop超时时间int CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle) {return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);}/// RunLoop的实现int CFRunLoopRunSpecific(runloop, modeName, seconds, stopAfterHandle) {/// 首先根据modeName找到对应modeCFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(runloop, modeName, false);/// 如果mode里没有source/timer/observer, 直接返回。if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(currentMode)) return;/// 1. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将进入 loop。__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);/// 内部函数,进入loop__CFRunLoopRun(runloop, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled) {Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = NO;int retVal = 0;do {/// 2. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Timer 回调。__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);/// 3. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);/// 执行被加入的block__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);/// 4. RunLoop 触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(runloop, currentMode, stopAfterHandle);/// 执行被加入的block__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);/// 5. 如果有 Source1 (基于port) 处于 ready 状态,直接处理这个 Source1 然后跳转去处理消息。if (__Source0DidDispatchPortLastTime) {Boolean hasMsg = __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg)if (hasMsg) goto handle_msg;}/// 通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程即将进入休眠(sleep)。if (!sourceHandledThisLoop) {__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);}/// 7. 调用 mach_msg 等待接受 mach_port 的消息。线程将进入休眠, 直到被下面某一个事件唤醒。/// 一个基于 port 的Source 的事件。/// 一个 Timer 到时间了/// RunLoop 自身的超时时间到了/// 被其他什么调用者手动唤醒__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort) {mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG, port); // thread wait for receive msg}/// 8. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程刚刚被唤醒了。__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);/// 收到消息,处理消息。handle_msg:/// 9.1 如果一个 Timer 到时间了,触发这个Timer的回调。if (msg_is_timer) {__CFRunLoopDoTimers(runloop, currentMode, mach_absolute_time())}/// 9.2 如果有dispatch到main_queue的block,执行block。else if (msg_is_dispatch) {__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);}/// 9.3 如果一个 Source1 (基于port) 发出事件了,处理这个事件else {CFRunLoopSourceRef source1 = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(runloop, currentMode, livePort);sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(runloop, currentMode, source1, msg);if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply);}}/// 执行加入到Loop的block__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {/// 进入loop时参数说处理完事件就返回。retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;} else if (timeout) {/// 超出传入参数标记的超时时间了retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(runloop)) {/// 被外部调用者强制停止了retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(runloop, currentMode)) {/// source/timer/observer一个都没有了retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;}/// 如果没超时,mode里没空,loop也没被停止,那继续loop。} while (retVal == 0);}/// 10. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将退出。__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);}
RunLoop休眠的实现原理
从上面代码第7步可以看到,RunLoop 的核心是基于mach port 的,其进入休眠时调用的函数是 mach_msg()。
/// 7. 调用 mach_msg 等待接受 mach_port 的消息。线程将进入休眠, 直到被下面某一个事件唤醒。/// 一个基于 port 的Source 的事件。/// 一个 Timer 到时间了/// RunLoop 自身的超时时间到了/// 被其他什么调用者手动唤醒__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort) {mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG, port); // thread wait for receive msg}
为了实现消息的发送和接收,mach_msg() 函数实际上是调用了一个 Mach 陷阱 (trap),即函数mach_msg_trap(),陷阱这个概念在 Mach 中等同于系统调用。当你在用户态调用 mach_msg_trap() 时会触发陷阱机制,切换到内核态;内核态中内核实现的 mach_msg() 函数会完成实际的工作,如下图: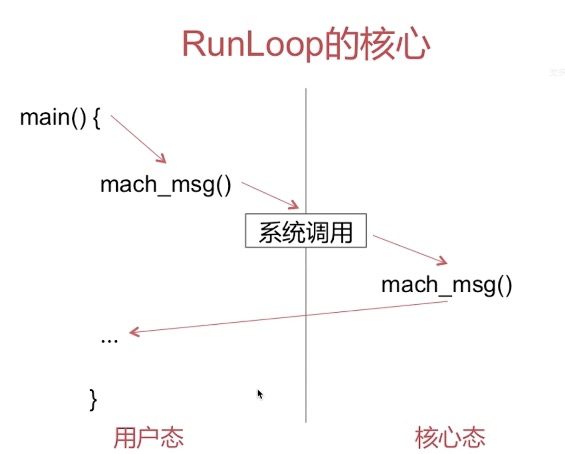

- 例如你在模拟器里跑起一个 iOS 的 App,然后在 App 静止时点击暂停,你会看到主线程调用栈是停留在
mach_msg_trap()这个地方
应用
运行循环与时钟
@interface ViewController ()@property (nonatomic, strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation ViewController- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(fire) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];}- (void)fire {static int num = 0;/// 耗时操作for (int i = 0; i < 1000 * 1000; ++i) {[NSString stringWithFormat:@"hello - %d", i];}NSLog(@"%d", num++);}@end
运行测试,会发现卡顿非常严重
- 将时钟添加到其他线程工作
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {self.thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(startTimer) object:nil];[self.thread start];}- (void)startTimer {@autoreleasepool {NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(fire) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];_timerRf = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();CFRunLoopRun();NSLog(@"come here");}}
注意:主线程的运行循环是默认启动的,但是子线程的运行循环是默认不工作的,这样能够保证线程执行完毕后,自动被销毁
- 停止运行循环
- (IBAction)stop {if (_timerRf == NULL) {return;}CFRunLoopStop(_timerRf);_timerRf = NULL;}

