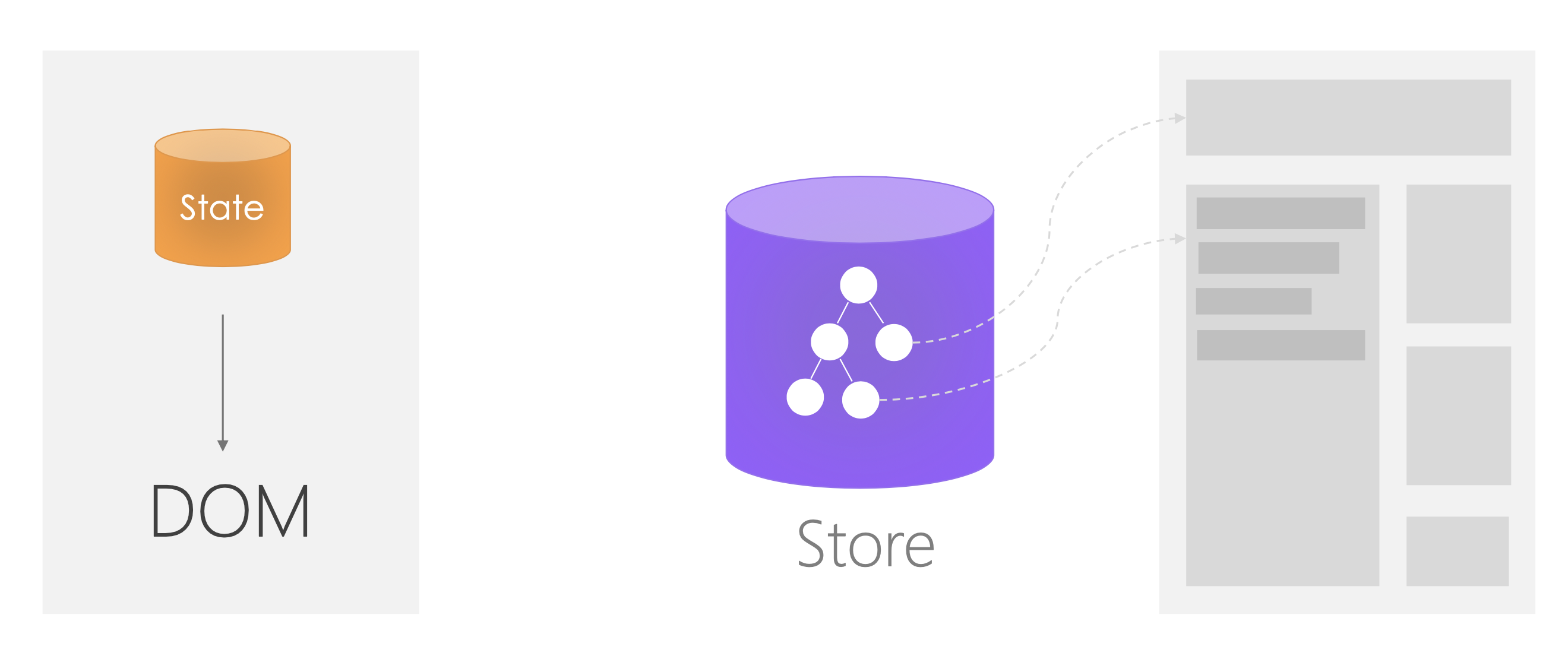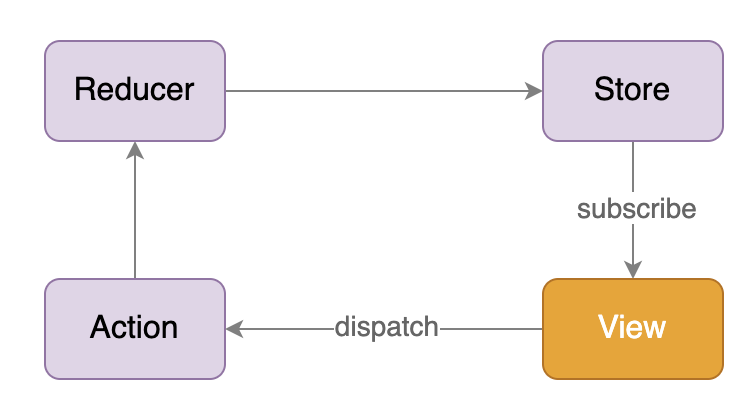
01|认识 React:如何创建你的第一个 React 应用?
- 组件
- 内置组件:映射到HTML的节点组件
- 自定义组件:自己创建的组件
- 状态
- state:管理组件内部状态
- props:组件外部传入的状态
- JSX
- 语法糖(JSX 不是一种新的概念,只是原生JS的另外一种写法)
```jsx
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
return (
); }
- 语法糖(JSX 不是一种新的概念,只是原生JS的另外一种写法)
```jsx
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
return (
React.createElement( “div”, null, React.createElement( “button”, { onClick: function onClick(){ return setCount(count + 1); } }, React.createElement(CountLabel, {count: count}) ) )
<a name="pcY3c"></a># 02|理解 Hooks:React 为什么要发明 Hooks?<a name="qHOKc"></a>### 类组件 VS 函数组件使用类组件的弊端(class的优势没有发挥的空间)- 组件之间不会相互集成- 组件的方法不会被外部调用函数组件<br />UI = render(state)<a name="GJo0e"></a>### Hooks> hooks解决的本质问题,就是跟纯函数组件提供状态管理的能力,通过提供外部的数据源,当数据发生变化时,组件渲染,但是在多次渲染期间,可以保持外部数据的状态如何实现HOOKS?<br />Hooks就是把某个 **目标结果(函数组件)**钩到可能变化的 **数据源或者事件源上(state、url、window size)**,那么当被钩到的数据源或者事件发生变化时,产生目标结果的代码会重新执行,产生更新后的结果(**view视图**)<br />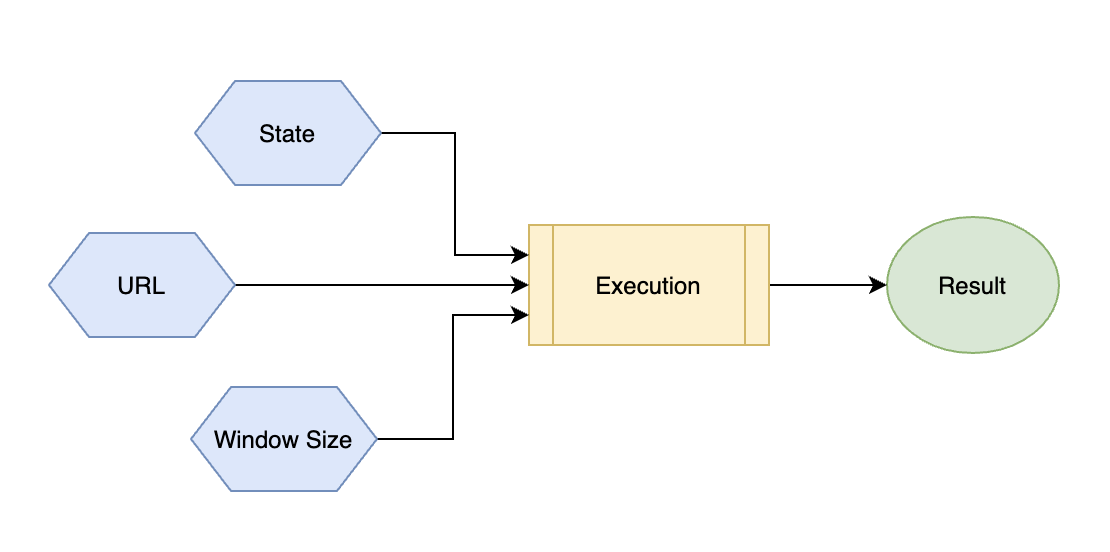Hooks的优势- 简化逻辑复用- HOC- render props- 有助于关注点分离<a name="ltUPS"></a># 03|内置 Hooks(1):如何保存组件状态和使用生命周期?<a name="hUmMd"></a># 04|内置 Hooks(2):为什么要避免重复定义回调函数?<a name="fcA1W"></a>### useState- 定义一个state,并提供一个修改的方法```javascriptconst [count, setCount] = useState(0)
注意事项
- state 不要存放能够通过计算得到的值
useEffect
用于执行一段副作用(一段和当前执行结果无关的代码)
在函数组件当次执行的过程中,useEffect中的代码的执行是不影响渲染出来的UI的
使用场景:
每次render后都执行(不提供第二个依赖项)
useEffect(()=>{// dosomething})
仅第一次render后执行(提供一个空的数组)
useEffect(()=>{// dosomething}, [])
第一次render后以及依赖项发生变化后执行(提供依赖数组)
useEffect(()=>{// dosomething}, [deps])
组件unmount后执行
useEffect(()=>{return ()=>{}},[])
useCallback
缓存回调函数
useCallback(fn, deps)
useMemo
缓存计算的结果
useMemo(fn, deps)
useRef
- 用于在多次渲染之间共享数据
- 活动元素的真实DOM(input 获得焦点)
const refContainer = useRef(initVal)
useContext
让react 函数组件具备了定义全局的响应式数据的能力
创建一个 context管理文件 并导出该上下文 CounterContext
import { createContext } from 'react';export const CounterContext = createContext();
父组件通过value提供传递下去的数据,并包裹子组件
<CounterContext.Provider value={{count, setCount}}><Counter/></CounterContext.Provider>
子组建消费父组件传递的数据
const value =useContext(CounterContext);
05|进一步认识 Hooks :如何正确理解函数组件的生命周期?
类组件 VS 函数组件
类组件:在某个生命周期我要做什么
函数组件:当某个状态发生变化时,我要做什么
构造函数 constructor
类组件:在其他代码执行之前的一次性初始化工作
函数组件:一次性的代码执行
import {useRef} from 'react';function useSingleton(callback){const called = useRef(false);if(called.current){return;}callback();called.current = true;}// demoimport useSingleton from './useSingleton';const MyComp = () => {// 使用自定义 HookuseSingleton(() => {console.log('这段代码只执行一次');});return (<div>My Component</div>);};
三种常用的生命周期方法
useEffect(() => {// componentDidMount + componentDidUpdateconsole.log('这里基本等价于 componentDidMount + componentDidUpdate');return () => {// componentWillUnmountconsole.log('这里基本等价于 componentWillUnmount');}}, [deps])
Class 组件中还有其它一些比较少用的方法,比如 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate, componentDidCatch, getDerivedStateFromError 目前在hooks还无法实现
06|自定义Hooks :四个典型的使用场景
抽取业务逻辑
import { useCallback, useState } from 'react';const useCounter = (step) =>{const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);// 加一const increment = useCallback(()=>{setCounter(counter + step);}, [counter, step])// 减一const reducer = useCallback(()=>{setCounter(counter - step);}, [counter, step])return {counter, increment, reducer}}export default useCounter;
import {useState} from 'react';import useCounter from './useCounter';const Counter = ()=>{const [setp, setStep] = useState(1);const {counter, increment, reducer} = useCounter(setp);return <div>{counter}<button onClick={increment}>add</button><button onClick={reducer}>reducer</button><button onClick={()=>{setStep(Math.floor(Math.random() * 10))}}>change setp {setp}</button></div>}export default Counter;
封装通用逻辑
利用了 Hooks 能够管理 React 组件状态的能力,将一个组件中的某一部分状态独立出来,从而实现了通用逻辑的重用
import { useCallback } from 'react';import {useState} from 'react';const useAsync = (execFun)=>{const [data, setData] = useState([]);const [error, setError] = useState(null);const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);const fetchFn = useCallback(()=>{setLoading(true);setError(null);return execFun().then((res)=>{setData(res);}).catch((err)=>{setError(err);}).finally(()=>{setLoading(false);})}, [execFun]);return {data, error, loading, fetchFn};}export default useAsync;
const fetchUsers = async ()=>{const res = await fetch("https://reqres.in/api/users/");const json = await res.json();return json.data;}const {data, error, loading, fetchFn} = useAsync(fetchUsers);
监听浏览器状态
可以让 React 的组件绑定在任何可能的数据源上。这样当数据源发生变化时,组件能够自动刷新
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';const getScrollPosition = ()=>{return {x: document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft,y: document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollLeft,}}const useScroll = ()=>{const [position, setPosition] = useState(getScrollPosition());useEffect(()=>{const handler = ()=>{setPosition(getScrollPosition(document));}document.addEventListener('scroll', handler)return ()=>{document.body.removeEventListener('scroll', handler)}}, [])return position;}export default useScroll;
拆分复杂组件
07|全局状态管理:如何在函数组件中使用 Redux?
redux的三个概念
- store
- reducer
- action
异步Action
使用模式,通过组合同步的Action,用一致的方案提供了处理异步逻辑的方案
Redux提供了一个middleware的机制实现异步的action
middleware 可以让你提供一个拦截器在 reducer 处理 action 之前被调用。在这个拦截器中,你可以自由处理获得的 action。无论是把这个 action 直接传递到 reducer,或者构建新的 action 发送到 reducer,都是可以的。
redux-thunk使用
Redux中的Action不仅可以是一个Object,也可以是一个函数;如果发现接受的action是函数的时候,那么不会传递给Reducer,而是先执行这个函数,并把dispatch作为参数传递给这个函数,从而在函数中可以自由的决定何时、如何的发送action
- 创建 Redux Store 时指定了 redux-thunk ```javascript mport { createStore, applyMiddleware } from ‘redux’ import thunkMiddleware from ‘redux-thunk’ import rootReducer from ‘./reducer’
const composedEnhancer = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware) const store = createStore(rootReducer, composedEnhancer)
2. dispatch action 时就可以 dispatch 一个函数用于来发送请求```javascriptfunction fetchData() {return dispatch => {dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_BEGIN' });fetch('/some-url').then(res => {dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS', data: res });}).catch(err => {dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_FAILURE', error: err });})}}
- dispatch action 时就可以 dispatch 一个函数用于来发送请求 ```javascript import fetchData from ‘./fetchData’;
function DataList() { const dispatch = useDispatch(); // dispatch 了一个函数由 redux-thunk 中间件去执行 dispatch(fetchData()); } ```