分布式配置中心应用场景
引言
往往我们会使用配置文件管理一些配置信息,比如application.yml
单体应用架构:配置信息的管理、维护并不会显得特别麻烦,手动操作就可以,因为就一个工程。
微服务架构:因为我们的分布式集群环境可能有很多歌微服务,不可能一个个去修改配置然后重启生效。在一定场景下我们需要在运行期间动态调整配置信息。 比如根据各个微服务的负载情况,动态调整数据源连接大小,希望配置内容发生变化的时候,微服务也可以自动更新。
动态更新配置的场景
(1) 集中配置管理,一个微服务架构中可能有成百上千个微服务,所以集中配置管理是很重要的(一次修改,导出生效)。
(2)不同环境不同配置,比如数据源配置在不同环境(开发-dev,测试-test,生产-prod)中是不同的。
(3)运行期间可以动态调整。例如,可根据各个微服务的负载情况,动态调整数据源连接池大小等配置修改后可以自动更新。
(4)如果配置内容发生变化,微服务可以自动更新配置。
所以,需要对配置文件进行集中式管理,这也是分布式配置中心的作用。
Spring Cloud Config
Config 简介
Spring Cloud Config是一个分布式配置管理方案,包含了Server端和Client端两个部分。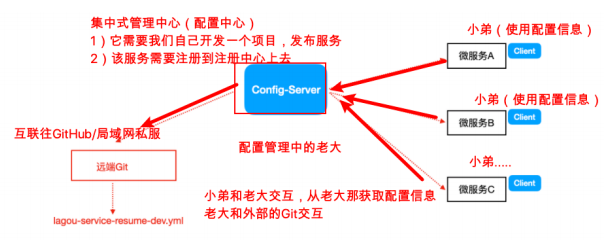
- Server端:提供配置文件的存储,以接口的形式将配置文件的内容提供出去。通过使用
@EnableConfigServer注解在Spring Boot应用非常简单地嵌入。 - Client端:通过接口获取配置数据并初始化自己的应用。
Config分布式配置应用
Config Server是集中式的配置服务,用于集中管理应用程序各个环境下的配置。默认使用Git存储配置文件内容。
针对微服务的application.yml进行管理(区分开发环境、测试环境、生产环境)。
(1)登录码云,创建项目 config-repo
(2)上传yml配置文件,命名规则: {application}-{profile}.yml 或 {application}-{profile}.properties 。 其中, application 为应用名称, profile 指的是环境。
(3)构建Config Server统一配置中心
新建Spring Boot工程,引入依赖坐标(需要注册到Eureka)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><parent><artifactId>lagou-parent</artifactId><groupId>com.lagou.edu</groupId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version></parent><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><artifactId>lagou-config1</artifactId><dependencies><!--eureka client 客户端依赖引⼊--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eurekaclient</artifactId></dependency><!--config配置中⼼服务端--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId></dependency></dependencies></project>
配置启动类,@EnableConfigServer开启配置中心功能
@SpringBootApplication@EnableDiscoveryClient@EnableConfigServer // 开启配置服务器功能public class ConfigApp9006 {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ConfigApp9003.class,args);}}
application.yml配置
server:port: 9006#注册到Eureka服务中⼼eureka:client:service-url:# 注册到集群,就把多个Eurekaserver地址使⽤逗号连接起来即可;# 注册到单实例(⾮集群模式),那就写⼀个就okdefaultZone: http://LagouCloudEurekaServerA:8761/eureka,http://LagouCloudEurekaServerB:8762/eurekainstance:prefer-ip-address: true #服务实例中显示ip,⽽不是显示主机名(兼容⽼的eureka版本)# 实例名称: 192.168.1.103:lagou-service-resume:8080,我们可以⾃定义它instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ipaddress}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:@project.version@spring:application:name: lagou-service-autodelivercloud:config:server:git:#配置git服务地址uri: https://github.com/5173098004/lagou-config-repo.gitusername: 517309804@qq.com #配置git⽤户名password: yingdian12341 #配置git密码search-paths:- config-repo# 读取分⽀label: master#针对的被调⽤⽅微服务名称,不加就是全局⽣效#service-resume:# ribbon:# NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule #负载策略调整# springboot中暴露健康检查等断点接⼝management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*"# 暴露健康接⼝的细节endpoint:health:show-details: always
(4)构建Client客户端
工程中添加依赖坐标
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-config-client</artifactId></dependency>
application.yml修改为bootstrap.yml配置文件
bootstrap.yml是系统级别的,优先级比application.yml高。应用启动时会检查这个配置文件,在这个配置文件中指定配置中心的服务地址,会自动拉取所有应用配置并且启用。
主要把与统一配置中心连接的配置信息放到 bootstrap.yml 。
bootstrap.yml
spring:application:name: service-resumecloud:# config客户端配置,和configServer通信,并告知configServer希望获取配置信息在哪个文件中config:name: service-resume # 配置文件名称profile: dev # 后缀名称label: master # 分支名称uri: http://localhost:9006 # configServer配置中心地址
Config配置手动刷新
不用重启微服务,只需要手动地做一些其他的操作(访问 http://localhost:port/actuator/refresh )刷新,之后再访问,此时,客户端就会取到配置中心的值。
此时,如果修改了GitHub上面的值,服务端(Config Server)能实时获取最新的值,但客户端(Config Client)读的是缓存,无法实时获取最新值。需要客户端使用post去触发refresh,获取最新数据。
(1)Client客户端添加依赖 springboot-start-actuator
(2)Client客户端bootstrap.yml中添加配置(暴露通信端点)
management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: refresh# 也可以暴露所有的端口management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*"
(3)Client客户端使用到配置信息的类添加 @RefreshScope
(4)手动向Client客户端发起POST请求, http://localhost:port/actuator/refresh 刷新配置信息。
Config配置自动更新
微服务架构中,微服务的实例是很多的。如果针对每个微服务都是用手动刷新的方式更新配置信息是不现实的。
两种方式实现自动更新
Zookeeper监听通知
Zookeeper特性是 存储 + 通知,zk中数据变更,可以通知到各个监听的客户端,客户端收到通知之后可以做相应的操作(内存级别的数据直接生效,对于数据库连接信息连接池等信息变化更新的,会在通知逻辑中处理)。
Spring Cloud Config + Spring Cloud Bus
在微服务架构中,可以结合消息总线(Bus)实现分布式配置的自动更新(Config + Spring Cloud Bus)
消息总线Bus
所谓的消息总线Bus,即使用MQ消息代理构建一个公用的Topic,通过这个Topic连接各个微服务实例,MQ广播的消息会被所有在注册中心的微服务实例监听和消费。换言之就是通过一个主题连接各个微服务,打通脉络。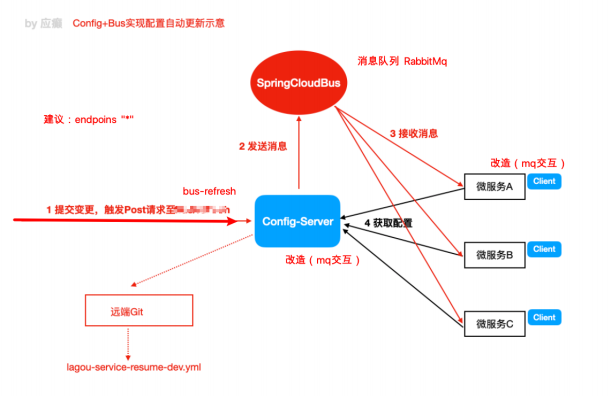
Spring Cloud Config + Spring Cloud Bus 实现自动刷新
选择使用RabbitMQ,并在Config Server和Config Client都添加消息总线的支持以及与RabbitMQ的连接信息。
1. Config Server服务端添加消息总线支持
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId></dependency>
2. Config Server添加配置
spring:rabbitmq:host: 127.0.0.1port: 5672username: guestpassword: guest
3. 微服务暴露端口
management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: bus-refresh# 建议暴露所有的端⼝management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*"
4. 重启各个服务,更改配置之后,向配置中心服务发送post请求
http://localhost:port/actuator/bus-refresh ,各个客户端配置即可自动刷新
定向更新微服务实例
在发起刷新请求的时候 http://localhost:port/actuator/bus-refresh/${service-name}:${service-port}
即在url最后面跟上要定向刷新的实例
服务名:端口号即可。
如果部署的服务存在多个实例(ID一样,端口一样,IP不一样),则上述url执行的定向刷新只会影响一个微服务实例的配置信息会被刷新。
解决办法是指定 spring.application.index=${random.long} 来生成随机的数字,用作微服务实例的标识。
刷新某个微服务的所有实例:使用 /actuator/bus-refresh/${service-name}:** 即可, service-name 指的就是应用的ID。

