1. 内部结构
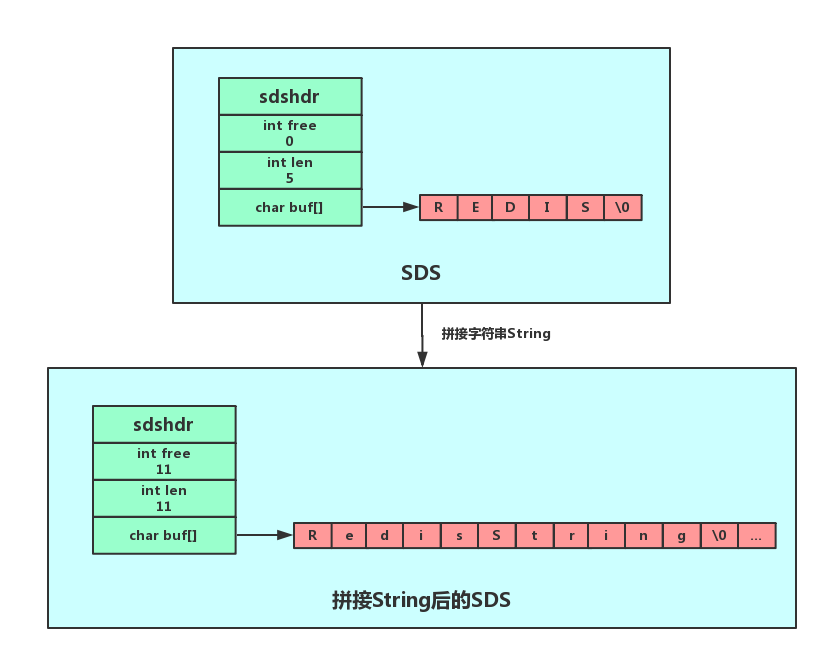
Redis 的字符串叫着「SDS」,也就是Simple Dynamic String。它的结构是一个带长度信息的字节数组。
typedef char *sds;/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */// __attribute__ ((__packed__)) 设置是告诉编译器取消字节对齐;gcc语法,取消编译内存对齐struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 { // 对应的字符串长度小于 1<<5unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 { // 对应的字符串长度小于 1<<8uint8_t len; /* used */ //目前字符串的长度uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ //已经分配的总长度unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ //flag用3bit来标明类型,类型后续解释,其余5bit目前没有使用char buf[];//柔性数组,以'\0'结尾};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {uint16_t len; /* used */uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {uint32_t len; /* used */uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {uint64_t len; /* used */uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};
1.1 数据结构
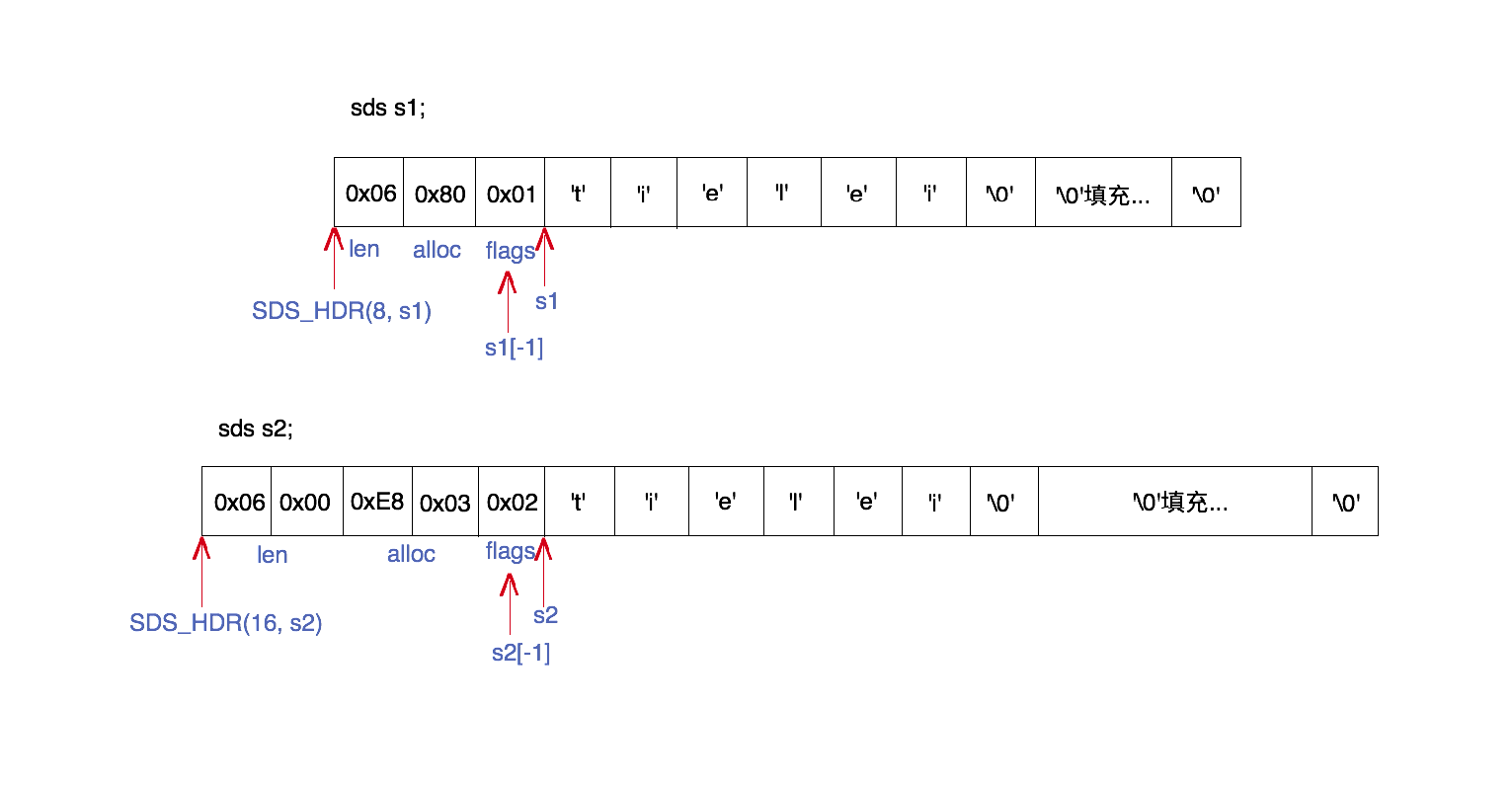
T len; /* used */ // 指存的长度T alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ //最大容量unsigned char flags;char buf[];
除了sdshdr5之外,其它4个header的结构都包含3个字段:
- len: 表示字符串的真正长度(不包含NULL结束符在内)。
- alloc: 表示字符串的最大容量(不包含最后多余的那个字节)。
- flags: 总是占用一个字节。其中的最低3个bit用来表示header的类型。header的类型共有5种,在sds.h中有常量定义。(一共5种类型,二进制位最大 101,所以用3个bit存)
标志位定义:
#define SDS_TYPE_5 0#define SDS_TYPE_8 1#define SDS_TYPE_16 2#define SDS_TYPE_32 3#define SDS_TYPE_64 4
static inline char sdsReqType(size_t string_size) {if (string_size < 1<<5)return SDS_TYPE_5;if (string_size < 1<<8)return SDS_TYPE_8;if (string_size < 1<<16)return SDS_TYPE_16;if (string_size < 1ll<<32)return SDS_TYPE_32;return SDS_TYPE_64;}
sds一共有5种类型的header。之所以有5种,是为了能让不同长度的字符串可以使用不同大小的header。这样,短字符串就能使用较小的header,从而节省内存。
通过sdsReqType的代码,很容易看到:
- 长度在0和2^5-1之间,选用SDS_TYPE_5类型的header。
- 长度在2^5和2^8-1之间,选用SDS_TYPE_8类型的header。
- 长度在2^8和2^16-1之间,选用SDS_TYPE_16类型的header。
- 长度在2^16和2^32-1之间,选用SDS_TYPE_32类型的header。
- 长度大于2^32的,选用SDS_TYPE_64类型的header。能表示的最大长度为2^64-1。
从这一点就能看到Redis 在内存存储上 精益求精,简直精湛。从而一定程度解释了Redis为啥单线程还那么快,因为他把操作内存的细节做得很精湛,没有浪费多余的操作时间和内存空间。
SDS如何在O(1)时间复杂度内获取长度
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {unsigned char flags = s[-1];switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {case SDS_TYPE_5:return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);case SDS_TYPE_8:return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;case SDS_TYPE_16:return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;case SDS_TYPE_32:return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;case SDS_TYPE_64:return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;}return 0;}根据指针直接找到这个sds 的header位置,获取len属性。
1.2 为什么要用SDS
1.2.1 时间复杂度
- SDS中有维护长度的len 获取长度时间复杂度为O(1) ,而 C 字符串获取字符串长度时间复杂度为O(N)
1.2.2 缓存区溢出
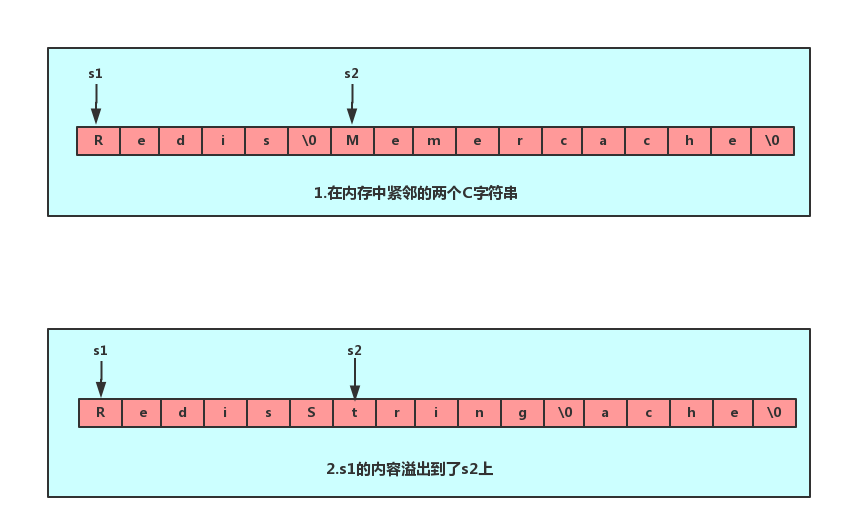
C字符串,如果程序员在字符串修改的时候如果忘记给字符串重新分配足够的空间,那么就会发生内存溢出,如上图所示,忘记给s1分配足够的内存空间, s1的数据就会溢出到s2的空间, 导致s2的内容被修改.。而Redis提供的SDS其内置的空间分配策略则可以完全杜绝这种事情的发生。
当API需要对SDS进行修改时, API会首先会检查SDS的空间是否满足条件, 如果不满足, API会自动对它动态扩展, 然后再进行修改。
1.2.3 二进制安全
C字符串中的字符必须符合某种编码(比如ASCII),并且除了字符串的末尾之外,字符串里面不能包含空字符,否则最先被程序读入的空字符将被误认为是字符串结尾,这些限制使得C字符串只能保存文本数据,而不能保存像图片、音频、视频、压缩文件这样的二进制数据。如果有一种使用空字符来分割多个单词的特殊数据格式,就不能用C字符串来表示,如”Redis\0String”,C字符串的函数会把’\0’当做结束符来处理,而忽略到后面的”String”。而SDS的buf字节数组不是在保存字符,而是一系列二进制数组,SDS API都会以二进制的方式来处理buf数组里的数据,使用len属性的值而不是空字符来判断字符串是否结束。
1.2.4 内存重分配
详情查看 3.内存分配
惰性空间释放 策略 缺点会造成一定的内存浪费,Redis SDS API 提供了 让我们在有需要的时候真正释放SDS的未使用空间。
2.存储方式
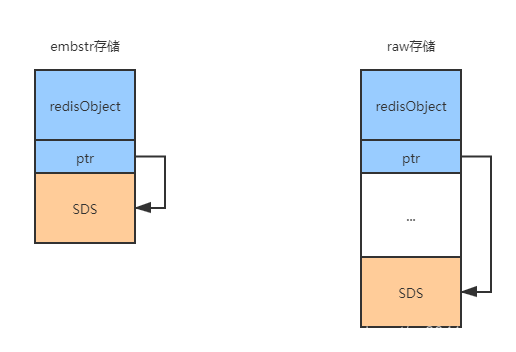
2.1 embstr 和 raw
所有redis结构都有这个头:server.htypedef struct redisObject {unsigned type:4;unsigned encoding:4;unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency* and most significant 16 bits access time). */int refcount;void *ptr; //指向 具体对象的指针} robj;
# 文件:object.c/* Create a string object with EMBSTR encoding if it is smaller than* OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT, otherwise the RAW encoding is* used.** The current limit of 44 is chosen so that the biggest string object* we allocate as EMBSTR will still fit into the 64 byte arena of jemalloc. */// 如果len小于44则使用embstr方式编码,否则使用raw方式编码#define OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT 44robj *createStringObject(const char *ptr, size_t len) {if (len <= OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT)return createEmbeddedStringObject(ptr,len);elsereturn createRawStringObject(ptr,len);}
当字符串的长度小于44字节使用embstr方式存储,否则使用raw方式存储,可以使用debug查看存储数据类型;
2.1.1 为什么是44字节
jemalloc/tcmalloc等内存分配器都可以2、4、8、16、32、64的单位分配内存大小,如果大小超过64字节则将被认为是大内存。RedisObject:16字节SDS header (len:uint_8 一个字节,alloc:uint_8 一个字节,flags:char 一个字节):3字节64字节 - 19字节 = 45字节(其中\0为redis字符串的结尾)
embstr字符串长度和cpu cache line保持一致可以更快加载、重用CPU缓存; (避免伪共享,从JMM角度分析)3.内存分配
3.1 空间预分配
(1)目前free空间足够,直接返回;
(2)free空间不够,预处理newlen=(len+addlen),即原大小+新增大小,如果 newlen小于1M,扩展空间newlen*2;
(3)新增newlen大于1M,newlen新空间+1M// 扩容的源码文件:sds.csds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {void *sh, *newsh;size_t avail = sdsavail(s); //计算剩余空间size_t len, newlen;char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;int hdrlen;/* Return ASAP if there is enough space left. */// s 目前的空余空间已经足够,无须再进行扩展,直接返回if (avail >= addlen) return s;// 获取 s 目前已占用空间的长度len = sdslen(s);sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);//// s 最少需要的长度newlen = (len+addlen);assert(newlen > len); /* Catch size_t overflow */// 根据新长度,为 s 分配新空间所需的大小if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)// 如果新长度小于 SDS_MAX_PREALLOC (如果当前大小小于1M,即扩容2倍)// 那么为它分配两倍于所需长度的空间newlen *= 2;else// 否则,分配长度为目前长度加上 1Mnewlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;type = sdsReqType(newlen);/* Don't use type 5: the user is appending to the string and type 5 is* not able to remember empty space, so sdsMakeRoomFor() must be called* at every appending operation. */if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);assert(hdrlen+newlen+1 > len); /* Catch size_t overflow */if (oldtype==type) {newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;} else {/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,* and can't use realloc */newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);s_free(sh);s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;s[-1] = type;sdssetlen(s, len);}sdssetalloc(s, newlen);return s;}
3.1.1 sdsavail
// 使用SDS中的 alloc 减去 len 就是空闲长度static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s) {unsigned char flags = s[-1];switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {case SDS_TYPE_5: {return 0;}case SDS_TYPE_8: {SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);return sh->alloc - sh->len;}
字符串长度小于1M使用加倍扩容方式,如果大小超过1M则扩容时以1M大小扩容。但是如果字符串总长度不能超过512M。
3.2 惰性空间释放
/* Remove the part of the string from left and from right composed just of* contiguous characters found in 'cset', that is a null terminted C string.** After the call, the modified sds string is no longer valid and all the* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call.** Example:** s = sdsnew("AA...AA.a.aa.aHelloWorld :::");* s = sdstrim(s,"Aa. :");* printf("%s\n", s);** Output will be just "HelloWorld".*/sds sdstrim(sds s, const char *cset) {char *start, *end, *sp, *ep;size_t len;sp = start = s;ep = end = s+sdslen(s)-1;while(sp <= end && strchr(cset, *sp)) sp++;while(ep > sp && strchr(cset, *ep)) ep--;len = (sp > ep) ? 0 : ((ep-sp)+1);if (s != sp) memmove(s, sp, len);s[len] = '\0';sdssetlen(s,len);return s;}
惰性空间释放指的是当对一个sds对象进行缩短操作时,其不会直接将buf数组缩短为目标数组的长度,而是只改变sds对象的len属性的值,数组中多余的部分则保存在free属性中,这样就可以保证后续可能的对该sds对象的增长操作不需要重新分配空间。