资料链接
Union Type
说明
type UnionType = number | string;let x: UnionType;x = 1;x = "1";// Literal Typeslet y: "abc";y = "abc";// 编译不通过 设置类型为一个值时只能使用这个值作为其内容// y = "bcd";// 例如:骰子的数值 可以利用union 取值的并let dicNum: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6;
类型判断
// UnionType存在一个问题 就是对于输入是union的,函数需要根据输入类型判断处理 方式大体分为三种// 1. 普通类型判断function getValueType(value: string | number) {if (typeof value === "string") {return 0;}if (typeof value === "number") {return 1;}}// 2. 多态的类型判断class Animal {name: string;constructor(name: string) {this.name = name;}eat() {console.log(`${this.name} whu chi`);}}class Cat extends Animal {meow() {console.log(`${this.name} Meow`);}}class Dog extends Animal {bark() {console.log(`${this.name} Wang Wang`);}}// 使用instanceof判断类型function getAnimalSound(animal: Cat | Dog) {if (animal instanceof Cat) {animal.meow();}if (animal instanceof Dog) {animal.bark();}}// 3. interface判断type Square = { size: number };type Rectangle = { width: number; height: number };type Shape = Square | Rectangle;// 需要找到差异 然后进行判断类型// 另外可以增加属性type 或者使用从基类继承的方式function area(geometry: Shape) {if ("size" in geometry) {return geometry.size * geometry.size;}if ("width" in geometry) {return geometry.width * geometry.height;}}
intersection types
说明
type User = {name?: string | null;email: number | string;};type Email = {name?: number | string;email: string;};type ContactDetails = User & Email;// 关于属性的复合 应该有一套特殊的复合关系生成 比如有交集且不为undefined和null 输出交集 否则输出never类型 标识不存在该类型let a: ContactDetails = { name: undefined, email: "aa" };a.name = "Sam";a.email = "111@qq.com";// console.log(a);// not-null assertionlet t!: { x: number };function initializeT() {// 可以让null check无效 因为这个声明表示它是一个非null的 原理应该是主动躲避编译器的检查t.x = 123;// 也可以写作t!.x = 123;}// 会报错// initializeT();// console.log(t.x);
interface和type的区别
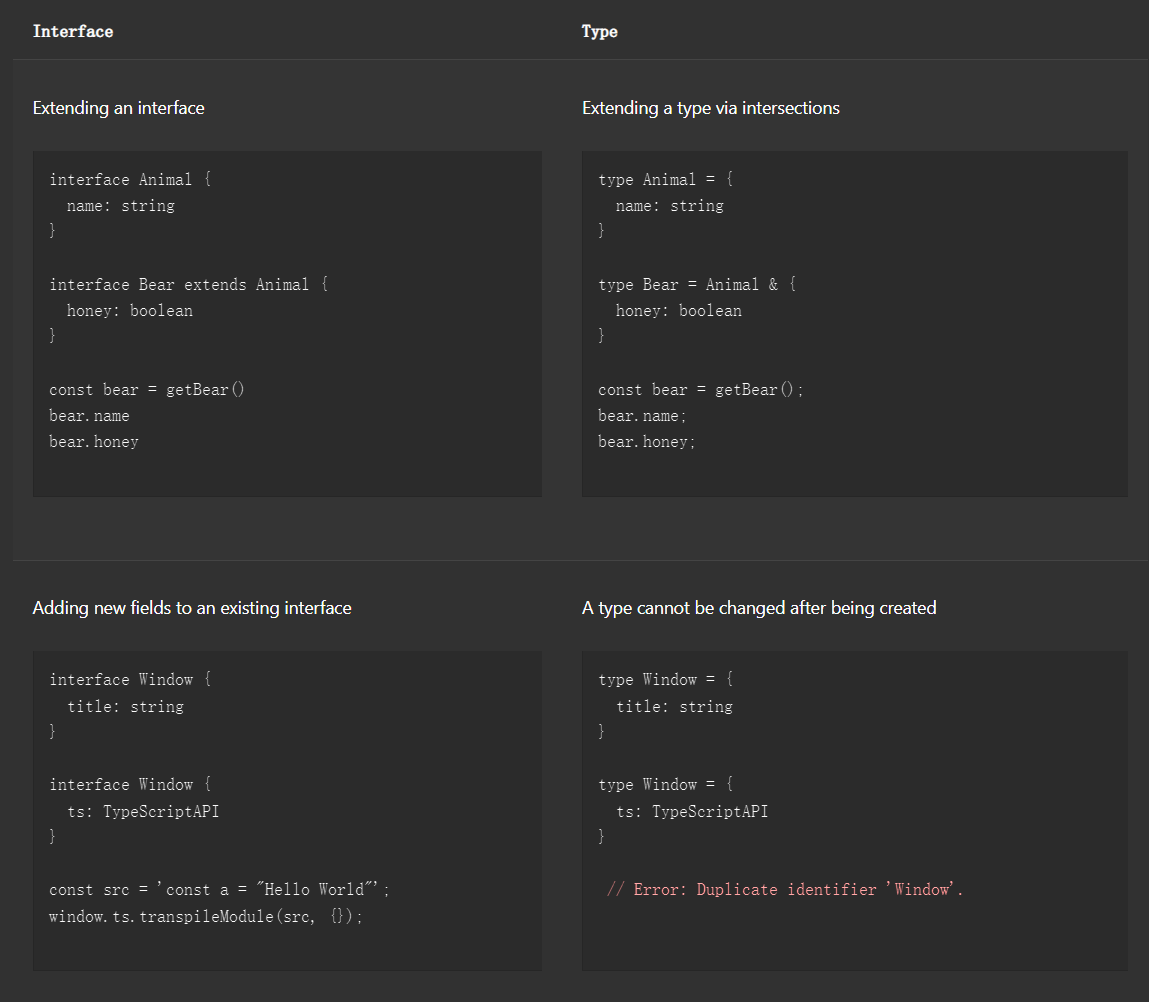
- type基本可以覆盖interface的一切功能,除了覆盖声明(上述的),以及interface的继承是extends符合其他的语言习惯
- type包含基本的类型 如string type可以union和intersection
- interface其实更倾向于C++的struct,或者是一个类的某种实现;而type倾向于反应某个属性的具体类型,它更倾向于这个属性属于某种基本类型,而不是一个结构类型(虽然是可以这样定义的)
never类型的使用
never 可以理解为 空 | 空 就是空,任何类型都可以extends never 但是never只能extends never
type Square2 = { type: "square"; size: number };type Rectangle2 = { type: "rectangle"; width: number; height: number };type Radius2 = { type: "radius"; radius: number };type Shape2 = Square2 | Rectangle2;// | Radius2;// 检验是否完成所有的casefunction area2(geometry: Shape2) {if (geometry.type === "square") {return geometry.size ** 2;}if (geometry.type === "rectangle") {return geometry.width * geometry.height;}// 测试下增加一种类型Radius2const _ensureAllCaseAreHandled: never = geometry;return _ensureAllCaseAreHandled;}
assert functions
如果typescript开启nullCheck,使用这种声明,可以减少不必要的判断(仅仅为了说明类型的状态,让编译器进行自动推断),可以用这样的声明
// assert functionstype Person = {name: string;dateOfBirth?: Date;};// 如果不满足条件则报错// 可以减少额外判断function assert(condition: unknown, message: string): asserts condition {if (!condition) throw new Error(message);}function assertDate(value: unknown): asserts value is Date {if (value instanceof Date) {return;} else {throw new TypeError("value is not a Date");}}
泛型和复杂类型
关于extends的说明
- 如果extends前面的类型能够赋值给extends后面的类型,那么表达式判断为真,否则为假;
- 对于object(结构,更倾向于interface),如果有extends关系;对于普通类型有包含关系 ‘string’|’number’ extends ‘string’,对于泛型,可以理解为一种特别的object 其extends关系和其生成的对象类型有直接关系
- exclude extract lowerCase这些基本都是作用在object的key上面 配合key使用
``typescript // generic constraints // 对于泛型的一些限制 type NameFields = { firstName: string; lastName: string }; // 需求 给定的类型包含名和姓 输出增加属性 fullName 其中fullName和姓名相关 function addFullName<T extends NameFields>(obj: T): T & { fullName: string } { return { ...obj, fullName:${obj.firstName} ${obj.lastName}`, }; } const john = addFullName({ email: “john@exaple.com”, firstName: “John”, lastName: “Doe”, }); // console.log(john);
// 学会使用 typeof type JohnFields = typeof john; const john2: JohnFields = { email: “john@exaple.com”, firstName: “John”, lastName: “Doe”, fullName: “”, };
// lookup types interface ComplexType { property1: boolean; property2: boolean; property3: { property1: boolean; property2: boolean; }; } // 可以使用接口里的属性作为类型输出 function getProperty3(): ComplexType[“property3”] { return { property1: true, property2: false, }; }
// keyof type type abc = keyof JohnFields; interface Student { name: string; age: number; grade: number; } const student: Student = { name: “sunwei”, age: 24, grade: 99, };
function propertyGet
function propertySet
// conditional type 条件类型 关于条件的三目运算
type IsNumber
export type TypeName
// infer type 类似于柯里化 然后代替被替换的元素 只能用于extends中
// 获取数组内的类型
type UnboxArray
type UnboxedStringArray = UnboxArray
// 获取函数的输出
type ReturnType
const numFunc = (x: number) => x.toString();
type RetType3 = ReturnType
// Map type
interface Point {
readonly x: number;
y?: number;
}
// +-标识对特性的增加或删除 删除有的 没有的不删除
type Mapped
// Partial
// 让object的所有key变为可选
type Partial
// Pick 选择部分属性 类似于filter
// type Pick

