一、Hadoop 序列化
为什么进行序列化?
- 序列化 主要是我们通过 网络通信传输数据 时或者 把对象持久化到文件,需要把对象序列化成 二进制的结构
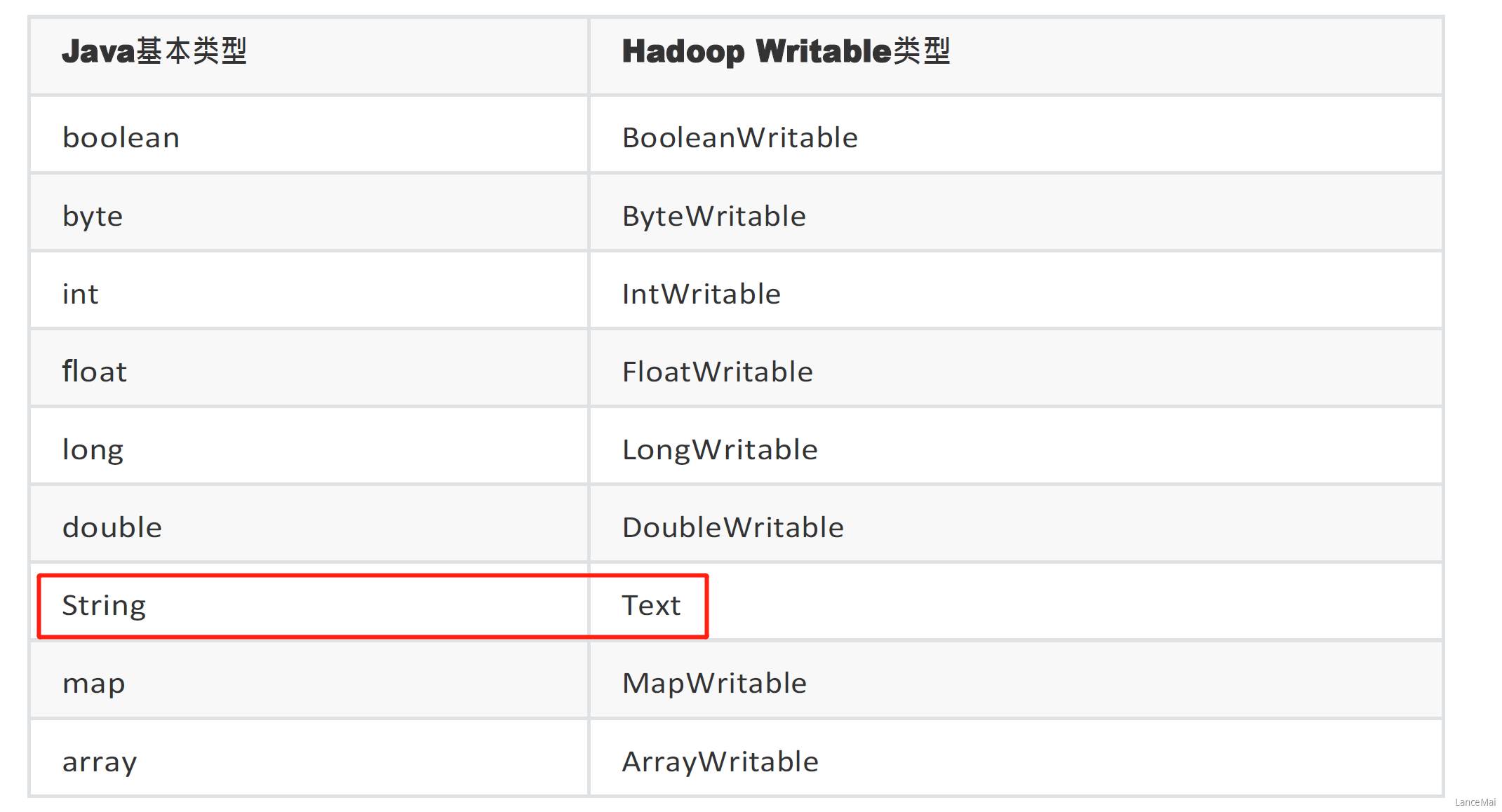
观察源码时发现自定义 Mapper类 与自定义 Reducer类 都有 泛型类型约束,比如自定义 Mapper 有四个形参类型,但是形参类型并不是常见的 java 基本类型
序列化在 分布式程序 中非常重要,在 Hadoop 中,集群中多个节点的进程间的通信是通过 RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用)实现;RPC将消息序列化成二进制流发送到远程节点,远程节点再将接收到的二进制数据反序列化为原始的消息,因此 RPC 往往追求如下特点(也是与 java序列号的区别)
- 紧凑:数据更紧凑,能充分利用网络带宽资源
- 快速:序列化和反序列化的性能开销更低
一个对象使用 Serializable 序列化后,会携带很多额外信息比如校验信息、Header、继承体系等。Hadoop 使用的是自己的序列化格式 Writable,它比 java 的序列化 Serialization 更紧凑、速度更快
Java基本类型与Hadoop序列化类型
二、Writable 序列化接口
基本序列化类型 往往不能满足所有需求,比如在 Hadoop 框架内部传递一个自定义 bean 对象,那么该对象就需要实现 Writable 序列化接口
必须实现 Writable 接口
反序列化时,需要反射调用空参构造函数,所以 必须有空参构造
public CustomBean() {super();}
重写序列化方法
@Overridepublic void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {....}
重写反序列化方法
@Overridepublic void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {....}
反序列化的字段顺序和序列化字段的 顺序必须完全一致
为了方便展示结果数据,需要重写 bean对象的 toString() 方法,可以自定义分隔符
如果自定义 Bean 对象需要放在 Mapper 输出 KV 中的 K,则该对象还需实现 Comparable 接口,因为 MapReduce 框架中的 Shuffle 过程要求对 key 必须能排序!!
- 需求
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException;
// 1 实现 writable 接⼝ public class SpeakBean implements Writable {
private Long selfDuration;private Long thirdPartDuration;private String deviceId;private Long sumDuration;// 2 反序列化时,需要反射调用空参构造函数,所以必须有public SpeakBean() {}public SpeakBean(Long selfDuration, Long thirdPartDuration, String deviceId) {this.selfDuration = selfDuration;this.thirdPartDuration = thirdPartDuration;this.deviceId = deviceId;this.sumDuration = selfDuration + thirdPartDuration;}//3 序列化方法@Overridepublic void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {dataOutput.writeLong(selfDuration);dataOutput.writeLong(thirdPartDuration);dataOutput.writeUTF(deviceId);dataOutput.writeLong(sumDuration);}//4 反序列化方法// 反序列化方法读顺序 必须和 序列化方法的写顺序 一致@Overridepublic void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {this.selfDuration = dataInput.readLong();this.thirdPartDuration = dataInput.readLong();this.deviceId = dataInput.readUTF();this.sumDuration = dataInput.readLong();}public Long getSelfDuration() {return selfDuration;}public void setSelfDuration(Long selfDuration) {this.selfDuration = selfDuration;}public Long getThirdPartDuration() {return thirdPartDuration;}public void setThirdPartDuration(Long thirdPartDuration) {this.thirdPartDuration = thirdPartDuration;}public String getDeviceId() {return deviceId;}public void setDeviceId(String deviceId) {this.deviceId = deviceId;}public Long getSumDuration() {return sumDuration;}public void setSumDuration(Long sumDuration) {this.sumDuration = sumDuration;}//6 编写 toString 方法,方便后续打印到文本@Overridepublic String toString() {return selfDuration +"\t" + thirdPartDuration +"\t" + sumDuration;}
}
<a name="ZQNBm"></a>
#### ② 编写 Mapper 类
```java
package com.lagou.speak;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SpeakMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, SpeakBean> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 1 获取一行
String line = value.toString();
// 2 切割字段
String[] strings = line.split("\t");
// 3 封装对象
// 取出设备id
String deviceId = strings[1];
//取出自有时长数据和第三方时长数据
String selfDuration = strings[strings.length - 3];
String thirdPartDuration = strings[strings.length - 2];
//4 封装对象
SpeakBean bean = new SpeakBean(Long.parseLong(selfDuration), Long.parseLong(thirdPartDuration), deviceId);
// 5 写出
context.write(new Text(deviceId), bean);
}
}
③ 编写 Reducer 类
package com.lagou.speak;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SpeakReducer extends Reducer<Text, SpeakBean, Text, SpeakBean> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<SpeakBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Long sumSelfDuration = 0L;
Long sumThirdPartDuration = 0L;
// 1 遍历所用 bean,将其中的自有,第三方时长分别累加
for (SpeakBean bean : values) {
Long selfDuration = bean.getSelfDuration();
Long thirdPartDuration = bean.getThirdPartDuration();
sumSelfDuration += selfDuration;
sumThirdPartDuration += thirdPartDuration;
}
// 2 封装对象
SpeakBean bean = new SpeakBean(sumSelfDuration, sumThirdPartDuration, key.toString());
// 3 写出
context.write(key, bean);
}
}
④ 编写驱动类 Driver
package com.lagou.speak;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SpeakDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
// 输入输出路径需要根据自己电脑上实际的输入输出路径设置
args = new String[] { "d:/speak/input", "e:/speak/output" };
// 1 获取配置信息,或者job对象实例
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "SpeakDriver");
// 2 指定本程序的jar包所在的本地路径
job.setJarByClass(SpeakDriver.class);
// 3 指定本业务job要使用的mapper/Reducer业务类
job.setMapperClass(SpeakMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SpeakReducer.class);
// 4 指定mapper输出数据的kv类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(SpeakBean.class);
// 5 指定最终输出的数据的kv类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(SpeakBean.class);
// 6 指定job的输⼊原始文件所在目录,以及输出结果的目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
// 7 将job中配置的相关参数,以及job所用的java类所在的jar包,提交给 yarn去运行
boolean success = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(success ? 0 : 1);
}
}
MR 编程技巧总结
- 结合业务设计 Map 输出的 key 和 value,利用 key相同则去往同一个reduce 的特点!!
- map() 方法中获取到只是一行文本数据,尽量不做聚合运算
- reduce() 方法的参数要清楚含义