原文: https://beginnersbook.com/2019/03/kotlin-recursion-and-tail-recursion/
如果函数调用自身,则该函数称为递归函数,此过程称为递归。
递归函数如何看起来像?
这里函数myfunction()调用自身,这是一个递归函数。
fun myfunction(){//some code....//myfunction() calling myfunction()myfunction()}
让我们举个例子来理解递归。
Kotlin 递归示例
这是阶乘的一个简单例子。这里我们定义了一个函数fact()来计算它作为参数传递给该函数的数字的阶乘。在函数体中我们再次调用此函数,此过程称为递归。
要求用户输入正整数,并根据输入,程序通过将输入数作为参数传递给用户定义函数fact()来查找输入数的阶乘。
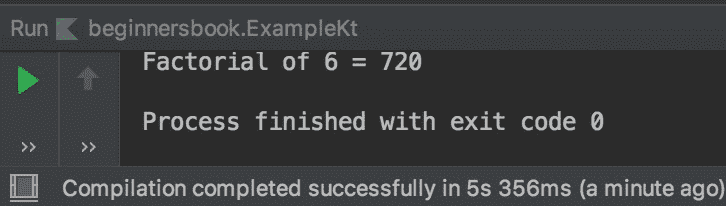
fun main(args: Array<String>) {print("Enter a positive integer number: ")val number: Int =Integer.valueOf(readLine())val factorial = fact(number)println("Factorial of $number = $factorial")}//recursive functionfun fact(num: Int): Int {return if(num == 1){num}else{//function fact() calling itselfnum*fact(num-1)}}
输出:
尾递归
在递归中,计算在递归调用之后完成,我们在上面看到的阶乘的例子是递归或头递归的一个例子,其中计算n的阶乘,我们需要n-1的阶乘。
在尾递归中,计算在递归调用之前的开始处完成。在尾递归中,递归函数的调用发生在函数的末尾。这意味着首先完成计算,然后传递给下一个递归调用。
让我们举一个尾递归的例子。
尾递归示例
要声明尾递归函数,我们在函数之前使用tailrec修饰符。
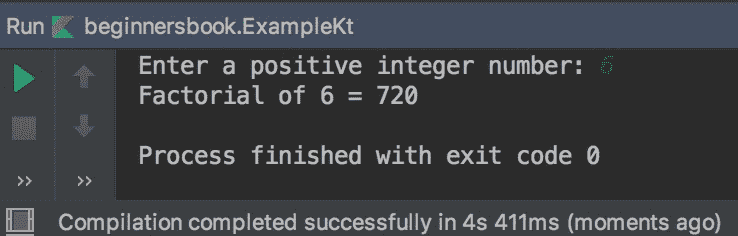
fun main(args: Array<String>) {val number = 6val factorial = fact(number)println("Factorial of $number = $factorial")}tailrec fun fact(n: Int, temp: Int = 1): Int {return if (n == 1){temp} else {fact(n-1, temp*n)}}
输出: