我们已经知道指针保存了同一类型的另一个变量的地址。当指针保存另一个指针的地址时,这种类型的指针称为指针的指针或双重指针。在本指南中,我们将学习什么是双重指针,如何声明它们以及如何在 C 编程中使用它们。要理解这个概念,你应该知道指针的基础知识。
如何在 C 中声明指针的指针(双重指针)?
int **pr;
这里pr是一个双重指针。在双重指针的声明中必须有两个*。
让我们借助图表来理解双重指针的概念:
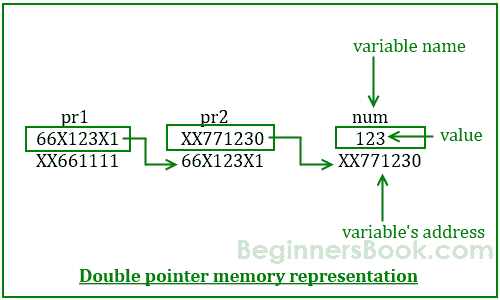
根据图表,pr2是一个普通指针,它保存整数变量num的地址。图中还有另一个指针pr1,它保存另一个指针pr2的地址,这里的指针pr1是一个指向指针的指针(或双重指针)。
上图中的数值:
Variable num has address: XX771230Address of Pointer pr1 is: XX661111Address of Pointer pr2 is: 66X123X1
双重指针示例
让我们根据上面看到的图表编写一个 C 程序。
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int num=123;//A normal pointer pr2int *pr2;//This pointer pr2 is a double pointerint **pr1;/* Assigning the address of variable num to the* pointer pr2*/pr2 = #/* Assigning the address of pointer pr2 to the* pointer-to-pointer pr1*/pr1 = &pr2;/* Possible ways to find value of variable num*/printf("\n Value of num is: %d", num);printf("\n Value of num using pr2 is: %d", *pr2);printf("\n Value of num using pr1 is: %d", **pr1);/*Possible ways to find address of num*/printf("\n Address of num is: %p", &num);printf("\n Address of num using pr2 is: %p", pr2);printf("\n Address of num using pr1 is: %p", *pr1);/*Find value of pointer*/printf("\n Value of Pointer pr2 is: %p", pr2);printf("\n Value of Pointer pr2 using pr1 is: %p", *pr1);/*Ways to find address of pointer*/printf("\n Address of Pointer pr2 is:%p",&pr2);printf("\n Address of Pointer pr2 using pr1 is:%p",pr1);/*Double pointer value and address*/printf("\n Value of Pointer pr1 is:%p",pr1);printf("\n Address of Pointer pr1 is:%p",&pr1);return 0;}
输出:
Value of num is: 123Value of num using pr2 is: 123Value of num using pr1 is: 123Address of num is: XX771230Address of num using pr2 is: XX771230Address of num using pr1 is: XX771230Value of Pointer pr2 is: XX771230Value of Pointer pr2 using pr1 is: XX771230Address of Pointer pr2 is: 66X123X1Address of Pointer pr2 using pr1 is: 66X123X1Value of Pointer pr1 is: 66X123X1Address of Pointer pr1 is: XX661111
关于此程序的输出存在一些混淆,当您运行此程序时,您将看到类似于此的地址:
0x7fff54da7c58。我以不同格式提供地址的原因,是我希望您将此程序与上图相关联。我已经使用了上图中的确切地址值,因此您可以轻松地将此程序的输出与上图相关联。
您还可以使用以下简单公式了解程序逻辑:
num == *pr2 == **pr1&num == pr2 == *pr1&pr2 == pr1

