原文: https://beginnersbook.com/2018/05/java-9-anonymous-inner-classes-and-diamond-operator/
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论 Java SE 9 中引入的菱形运算符增强。
什么是菱形运算符?
菱形操作符是作为 java SE 7 中的新功能引入的。菱形操作符的目的是通过将泛型类型保留在表达式的右侧来避免冗余代码。
// This is before Java 7\. We have to explicitly mention generic type// in the right side as well.List<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>();// Since Java 7, no need to mention generic type in the right side// instead we can use diamond operator. Compiler can infer type.List<String> myList = new ArrayList<>();
使用匿名内部类时菱形运算符的问题
Java 7 允许我们在普通类中使用菱形运算符,但它不允许我们在匿名内部类中使用它们。让我们举一个例子:
abstract class MyClass<T>{abstract T add(T num, T num2);}public class JavaExample {public static void main(String[] args) {MyClass<Integer> obj = new MyClass<>() {Integer add(Integer x, Integer y) {return x+y;}};Integer sum = obj.add(100,101);System.out.println(sum);}}
输出:
$javac JavaExample.javaJavaExample.java:7: error: cannot infer type arguments for MyClassMyClass obj = new MyClass<>() {^reason: cannot use '<>' with anonymous inner classeswhere T is a type-variable:T extends Object declared in class MyClass1 error
当我们在 Java SE 8 中运行上面的代码时,我们遇到了编译错误。
Java 9 - 菱形运算符改进
Java 9 改进了菱形运算符的使用,并允许我们将菱形运算符与匿名内部类一起使用。让我们采用我们在上面看到的相同的例子。
在 Java SE 9 中运行此代码
abstract class MyClass<T>{abstract T add(T num, T num2);}public class JavaExample {public static void main(String[] args) {MyClass<Integer> obj = new MyClass<>() {Integer add(Integer x, Integer y) {return x+y;}};Integer sum = obj.add(100,101);System.out.println(sum);}}
输出:
201
Eclipse Oxygen 中使用 jdk 9
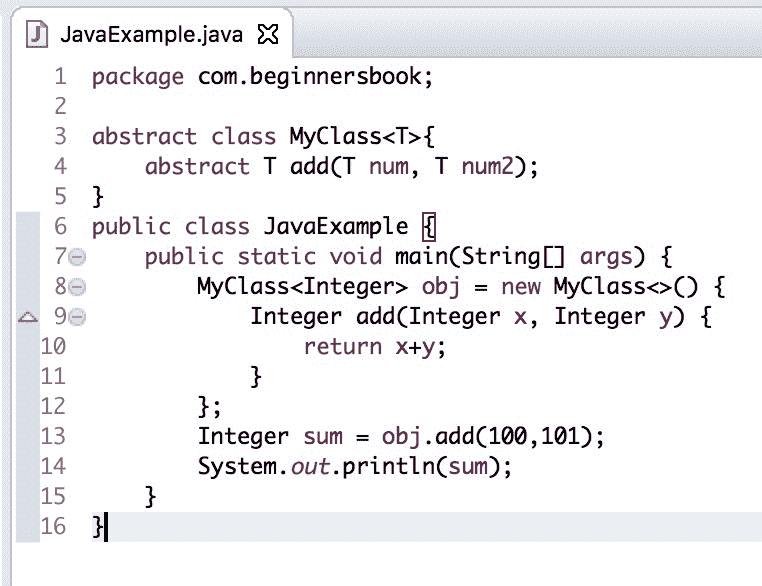 的上述代码的屏幕截图
的上述代码的屏幕截图

