Swing 是 Java 基础类(JFC)的一部分,JFC 的其他部分是 java2D 和抽象 window 工具包(AWT)。 AWT,Swing 和 Java 2D 用于在 java 中构建图形用户界面(GUI)。在本教程中,我们将主要讨论用于在 AWT 顶部构建 GUI 的 Swing API,与 AWT 相比,它更轻量级。
一个简单的例子
在下面的示例中,我们将使用您在本教程中到目前为止尚未学习的几个 swing 组件。我们将在即将到来的摇摆教程中详细讨论每一个和所有内容。
下面的 swing 程序会创建一个登录界面。
import javax.swing.JButton;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JLabel;import javax.swing.JPanel;import javax.swing.JPasswordField;import javax.swing.JTextField;public class SwingFirstExample {public static void main(String[] args) {// Creating instance of JFrameJFrame frame = new JFrame("My First Swing Example");// Setting the width and height of frameframe.setSize(350, 200);frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);/* Creating panel. This is same as a div tag in HTML* We can create several panels and add them to specific* positions in a JFrame. Inside panels we can add text* fields, buttons and other components.*/JPanel panel = new JPanel();// adding panel to frameframe.add(panel);/* calling user defined method for adding components* to the panel.*/placeComponents(panel);// Setting the frame visibility to trueframe.setVisible(true);}private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) {/* We will discuss about layouts in the later sections* of this tutorial. For now we are setting the layout* to null*/panel.setLayout(null);// Creating JLabelJLabel userLabel = new JLabel("User");/* This method specifies the location and size* of component. setBounds(x, y, width, height)* here (x,y) are cordinates from the top left* corner and remaining two arguments are the width* and height of the component.*/userLabel.setBounds(10,20,80,25);panel.add(userLabel);/* Creating text field where user is supposed to* enter user name.*/JTextField userText = new JTextField(20);userText.setBounds(100,20,165,25);panel.add(userText);// Same process for password label and text field.JLabel passwordLabel = new JLabel("Password");passwordLabel.setBounds(10,50,80,25);panel.add(passwordLabel);/*This is similar to text field but it hides the user* entered data and displays dots instead to protect* the password like we normally see on login screens.*/JPasswordField passwordText = new JPasswordField(20);passwordText.setBounds(100,50,165,25);panel.add(passwordText);// Creating login buttonJButton loginButton = new JButton("login");loginButton.setBounds(10, 80, 80, 25);panel.add(loginButton);}}
输出:
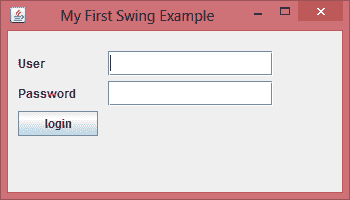
在上面的例子中,我们使用了几个组件。我们先讨论一下它们,然后我们将在下一个教程中详细讨论它们。
JFrame - 帧是JFrame的一个实例。框架是一个窗口,可以有标题,边框,菜单,按钮,文本字段和其他几个组件。 Swing 应用必须有一个框架才能添加组件。
JPanel - 面板是JPanel的一个实例。一个框架可以有多个面板,每个面板可以有几个组件。你也可以称它们为 Frame 的一部分。面板可用于对组件进行分组并将它们放置在框架中的适当位置。
JLabel - 标签是JLabel类的一个实例。标签是不可选择的文本和图像。如果要在框架上显示字符串或图像,可以使用标签。在上面的例子中,我们想要在文本字段之前显示文本"User"和"Password",我们通过创建标签并将其添加到适当的位置来实现此目的。
JTextField - 用于捕获用户输入,这些是用户输入数据的文本框。
JPasswordField - 与文本字段类似,但输入的数据被隐藏并在 GUI 上显示为点。
JButton - 一个按钮是JButton类的一个实例。在上面的例子中,我们有一个“登录”按钮。

