continue语句用于循环。当在循环内遇到 continue语句时,控制流跳转到循环的开头以进行下一次迭代,跳过当前迭代循环体内语句的执行。
C - continue语句
语法:
continue;
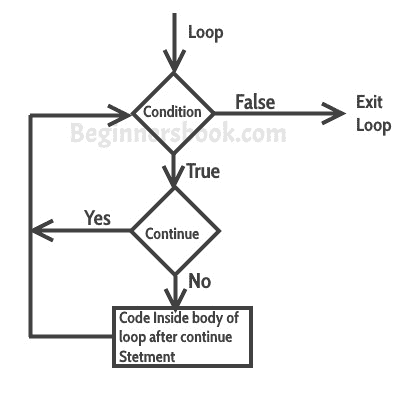
continue语句的流程图
示例:for循环中的continue语句
#include <stdio.h>int main(){for (int j=0; j<=8; j++){if (j==4){/* The continue statement is encountered when* the value of j is equal to 4.*/continue;}/* This print statement would not execute for the* loop iteration where j ==4 because in that case* this statement would be skipped.*/printf("%d ", j);}return 0;}
输出:
0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8
输出中缺少值 4,为什么?当变量j的值为 4 时,程序遇到一个continue语句,它使控制流跳转到for循环的开头以进行下一次迭代,跳过当前迭代的语句(这就是printf在j等于 4 时没有执行的原因)。
示例:在while循环中使用continue
在这个例子中,我们在while循环中使用continue。当使用while或do-while循环时,需要在continue上方放置一个递增或递减语句,以便在下一次迭代时更改计数器值。例如,如果我们不在if的正文中放置语句,那么counter的值将无限期地保持为 7。
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int counter=10;while (counter >=0){if (counter==7){counter--;continue;}printf("%d ", counter);counter--;}return 0;}
输出:
10 9 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
当计数器值为 7 时,将跳过print语句。
do-While循环的continue的另一个例子
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int j=0;do{if (j==7){j++;continue;}printf("%d ", j);j++;}while(j<10);return 0;}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9

