简介
Lombok 是一款好用顺手的工具,就像 Google Guava 一样。可用来帮助开发人员消除 Java 的冗长代码,尤其是对于简单的 Java 对象(POJO)。它通过注释实现这一目的。
通过在开发环境中实现 Lombok,开发人员可以节省构建诸如hashCode()和equals()这样的方法以及以往用来分类各种 accessor 和 mutator 的大量时间。
IntelliJ 安装 Lombok
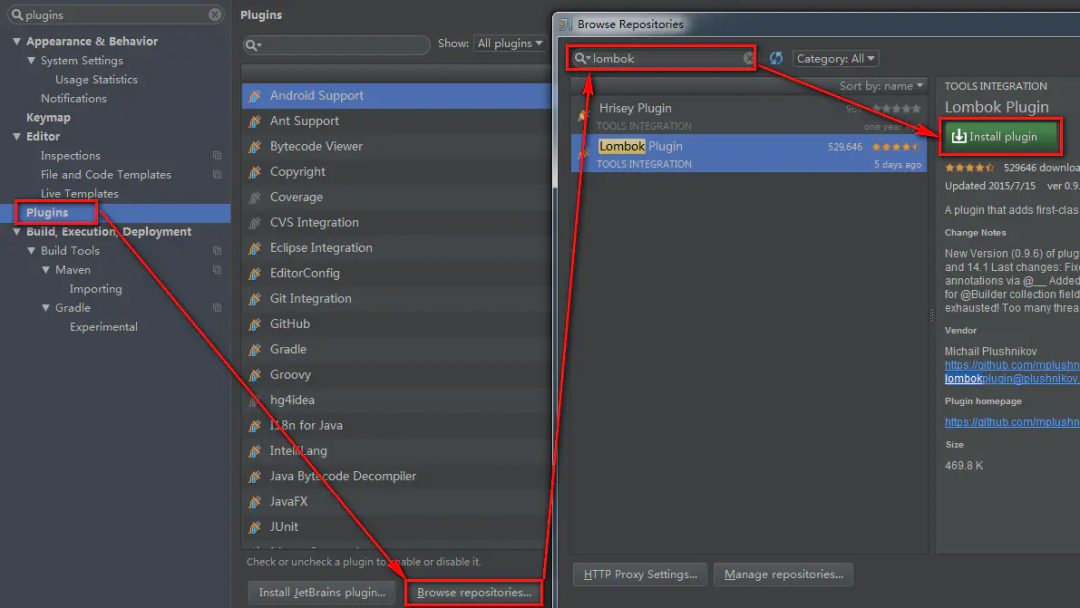
- 通过 IntelliJ 的插件中心安装
- Install Plugin
- 导入 lombok 包
<dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>1.16.8</version></dependency>
Lombok 注解大全说明
val:用在局部变量前面,相当于将变量声明为 final@NonNull:给方法参数增加这个注解,会自动在方法内对该参数进行是否为空的校验,如果为空,则抛出 NPE(NullPointerException)@Cleanup:自动管理资源,用在局部变量之前,在当前变量范围内即将执行完毕退出之前会自动清理资源,自动生成 try-finally 这样的代码来关闭流@Getter/@Setter:用在属性上,再也不用自己手写 setter 和 getter 方法了,还可以指定访问范围@ToString:用在类上,可以自动覆写 toString 方法,当然还可以加其他参数,例如@ToString(exclude=”id”)排除 id 属性,或者@ToString(callSuper=true, includeFieldNames=true)调用父类的 toString 方法,包含所有属性@EqualsAndHashCode:用在类上,自动生成 equals 方法和 hashCode 方法@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @AllArgsConstructor:用在类上,自动生成无参构造和使用所有参数的构造函数以及把所有@NonNull 属性作为参数的构造函数,如果指定 staticName = “of”参数,同时还会生成一个返回类对象的静态工厂方法,比使用构造函数方便很多@Data:注解在类上,相当于同时使用了@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCod- e、@Getter、@Setter 和@RequiredArgsConstrutor 这些注解,对于 POJO 类十分有用@Value:用在类上,是@Data 的不可变形式,相当于为属性添加 final 声明,只提供 getter 方法,而不提供 setter 方法@Builder:用在类、构造器、方法上,为你提供复杂的 builder APIs,让你可以像如下方式一样调用 Person.builder().name(“Adam Savage”).city(“San Francisco”).job(“Mythbusters”).job(“Unchained Reaction”).build();更多说明参考 Builder@SneakyThrows:自动抛受检异常,而无需显式在方法上使用 throws 语句@Synchronized:用在方法上,将方法声明为同步的,并自动加锁,而锁对象是一个私有的属性 或LOCK,而 java 中的 synchronized 关键字锁对象是 this,锁在 this 或者自己的类对象上存在副作用,就是你不能阻止非受控代码去锁 this 或者类对象,这可能会导致竞争条件或者其它线程错误@Getter(lazy=true):可以替代经典的 Double Check Lock 样板代码@Log:根据不同的注解生成不同类型的 log 对象,但是实例名称都是 log,有六种可选实现类@CommonsLogCreates log = org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory.getLog(LogExample.class);@LogCreates log = java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class.getName());@Log4jCreates log = org.apache.log4j.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class);@Log4j2Creates log = org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(LogExample.class);@Slf4jCreates log = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogExample.class);@XSlf4jCreates log = org.slf4j.ext.XLoggerFactory.getXLogger(LogExample.class);
Lombok 代码示例
val 示例
public static void main(String[] args) {val sets = new HashSet<String>();val lists = new ArrayList<String>();val maps = new HashMap<String, String>();//=>相当于如下final Set<String> sets2 = new HashSet<>();final List<String> lists2 = new ArrayList<>();final Map<String, String> maps2 = new HashMap<>();}
@NonNull 示例
public void notNullExample(@NonNull String string) {string.length();}//=>相当于public void notNullExample(String string) {if (string != null) {string.length();} else {throw new NullPointerException("null");}}
@Cleanup 示例
public static void main(String[] args) {try {@Cleanup InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(args[0]);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//=>相当于InputStream inputStream = null;try {inputStream = new FileInputStream(args[0]);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (inputStream != null) {try {inputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
@Getter/@Setter 示例
@Setter(AccessLevel.PUBLIC)@Getter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)private int id;private String shap;
@ToString 示例
@ToString(exclude = "id", callSuper = true, includeFieldNames = true)public class LombokDemo {private int id;private String name;private int age;public static void main(String[] args) {//输出LombokDemo(super=LombokDemo@48524010, name=null, age=0)System.out.println(new LombokDemo());}}
@EqualsAndHashCode 示例
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"id", "shape"}, callSuper = false)public class LombokDemo {private int id;private String shap;}
@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor ,@AllArgsConstructor 示例
@NoArgsConstructor@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")@AllArgsConstructorpublic class LombokDemo {@NonNullprivate int id;@NonNullprivate String shap;private int age;public static void main(String[] args) {new LombokDemo(1, "circle");//使用静态工厂方法LombokDemo.of(2, "circle");//无参构造new LombokDemo();//包含所有参数new LombokDemo(1, "circle", 2);}}
@Data 示例
import lombok.Data;@Datapublic class Menu {private String shopId;private String skuMenuId;private String skuName;private String normalizeSkuName;private String dishMenuId;private String dishName;private String dishNum;//默认阈值private float thresHold = 0;//新阈值private float newThresHold = 0;//总得分private float totalScore = 0;}
@Value 示例
@Valuepublic class LombokDemo {@NonNullprivate int id;@NonNullprivate String shap;private int age;//相当于private final int id;public int getId() {return this.id;}...}
@Builder 示例
@Builderpublic class BuilderExample {private String name;private int age;@Singularprivate Set<String> occupations;public static void main(String[] args) {BuilderExample test = BuilderExample.builder().age(11).name("test").build();}}
@SneakyThrows 示例
import lombok.SneakyThrows;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;public class Test {@SneakyThrows()public void read() {InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("");}@SneakyThrowspublic void write() {throw new UnsupportedEncodingException();}//相当于public void read() throws FileNotFoundException {InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("");}public void write() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {throw new UnsupportedEncodingException();}}
@Synchronized 示例
public class SynchronizedDemo {@Synchronizedpublic static void hello() {System.out.println("world");}//相当于private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];public static void hello() {synchronized ($LOCK) {System.out.println("world");}}}
@Getter(lazy = true)
public class GetterLazyExample {@Getter(lazy = true)private final double[] cached = expensive();private double[] expensive() {double[] result = new double[1000000];for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {result[i] = Math.asin(i);}return result;}}// 相当于如下所示:import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;public class GetterLazyExample {private final AtomicReference<java.lang.Object> cached = new AtomicReference<>();public double[] getCached() {java.lang.Object value = this.cached.get();if (value == null) {synchronized (this.cached) {value = this.cached.get();if (value == null) {final double[] actualValue = expensive();value = actualValue == null ? this.cached : actualValue;this.cached.set(value);}}}return (double[]) (value == this.cached ? null : value);}private double[] expensive() {double[] result = new double[1000000];for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {result[i] = Math.asin(i);}return result;}}

