让我们首先导入作业过程中需要的所有包。
- numpy是Python科学计算的基本包。
- matplotlib是在Python中常用的绘制图形的库。
- dnn_utils 为此笔记本提供了一些必要的函数。
- testCases 提供了一些测试用例来评估函数的正确性
- np.random.seed(1)使所有随机函数调用保持一致。 这将有助于我们评估你的作业,请不要改变seed。 ```python import numpy as np import h5py import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from testCases_v2 import * from dnn_utils_v2 import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
%matplotlib inline plt.rcParams[‘figure.figsize’] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots plt.rcParams[‘image.interpolation’] = ‘nearest’ plt.rcParams[‘image.cmap’] = ‘gray’
%load_ext autoreload %autoreload 2
np.random.seed(1)
<a name="fGC5j"></a># 逐步构建深度神经网络<a name="GGJpo"></a>## 0 作业大纲1. 初始化神经网络的参数。2. 实现正向传播模块(在下图中以紫色显示)。- 完成模型正向传播步骤的LINEAR部分()。- 提供使用的ACTIVATION函数(relu / Sigmoid)。- 将前两个步骤合并为新的[LINEAR-> ACTIVATION]前向函数。- 堆叠[LINEAR-> RELU]正向函数L-1次(第1到L-1层),并在末尾添加[LINEAR-> SIGMOID](最后的层)。这合成了一个新的L_model_forward函数。3. 计算损失。4. 实现反向传播模块(在下图中以红色表示)。- 完成模型反向传播步骤的LINEAR部分。- 提供的ACTIVATE函数的梯度(relu_backward / sigmoid_backward)- 将前两个步骤组合成新的[LINEAR-> ACTIVATION]反向函数。- 将[LINEAR-> RELU]向后堆叠L-1次,并在新的L_model_backward函数中后向添加[LINEAR-> SIGMOID]5. 最后更新参数。<a name="VqT22"></a>## 1. L层初始化- 模型的结构为 _[LINEAR -> RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID_。也就是说,前层使用ReLU作为激活函数,最后一层采用sigmoid激活函数输出。- 随机初始化权重矩阵。使用`np.random.rand(shape)* 0.01`。- 零初始化偏差。使用`np.zeros(shape)`。- 我们将在不同的layer_dims变量中存储,即不同层中的神经元数。例如,上周“二维数据分类模型”的`layer_dims`为[2,4,1]:即有两个输入,一个隐藏层包含4个隐藏单元,一个输出层包含1个输出单元。因此,`W1`的维度为(4,2),`b1`的维度为(4,1),`W2`的维度为(1,4),而`b2`的维度为(1,1)。现在你将把它应用到层!```pythondef initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):np.random.seed(3)parameters = {}L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the networkfor l in range(1, L):parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) * 0.01parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))return parametersparameters = initialize_parameters_deep([5,4,3])
{'W1': array([[ 0.01788628, 0.0043651 , 0.00096497, -0.01863493, -0.00277388],[-0.00354759, -0.00082741, -0.00627001, -0.00043818, -0.00477218],[-0.01313865, 0.00884622, 0.00881318, 0.01709573, 0.00050034],[-0.00404677, -0.0054536 , -0.01546477, 0.00982367, -0.01101068]]),'b1': array([[0.],[0.],[0.],[0.]]),'W2': array([[-0.01185047, -0.0020565 , 0.01486148, 0.00236716],[-0.01023785, -0.00712993, 0.00625245, -0.00160513],[-0.00768836, -0.00230031, 0.00745056, 0.01976111]]),'b2': array([[0.],[0.],[0.]])}
2. 正向传播
2.1 线性正向
现在,你已经初始化了参数,接下来将执行正向传播模块。 首先实现一些基本函数,用于稍后的模型实现。按以下顺序完成三个函数:
- LINEAR
- LINEAR -> ACTIVATION,其中激活函数采用ReLU或Sigmoid。
- [LINEAR -> RELU]
(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID(整个模型)
线性正向模块(在所有数据中均进行向量化)的计算按照以下公式:
其中 .
练习:建立正向传播的线性部分。
提醒:
该单元的数学表示为 ,你可能会发现
np.dot()有用。 如果维度不匹配,则可以printW.shape查看修改。
- [LINEAR -> RELU]
(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID(整个模型)
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_forwarddef linear_forward(A, W, b):Z = np.dot(W, A) + bassert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))cache = (A, W, b)return Z, cacheA, W, b = linear_forward_test_case()Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A, W, b)
就是进行一个线性计算Z = np.dot(W, A) + b
2.2 正向线性激活
在此笔记本中,你将使用两个激活函数:
- Sigmoid:
%20%3D%20%5Csigma(W%20A%20%2B%20b)%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B%201%20%2B%20e%5E%7B-(W%20A%20%2B%20b)%7D%7D#card=math&code=%5Csigma%28Z%29%20%3D%20%5Csigma%28W%20A%20%2B%20b%29%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B%201%20%2B%20e%5E%7B-%28W%20A%20%2B%20b%29%7D%7D&id=KfiqS)。 我们为你提供了“ Sigmoid”函数。 该函数返回两项值:激活值”
a“和包含”Z“的”cache“(这是我们将馈入到相应的反向函数的内容)。 ReLU:ReLu的数学公式为
%20%3D%20max(0%2C%20Z)#card=math&code=A%20%3D%20RELU%28Z%29%20%3D%20max%280%2C%20Z%29&id=lnFll)。我们为你提供了
relu函数。 该函数返回两项值:激活值“A”和包含“Z”的“cache”(这是我们将馈入到相应的反向函数的内容)。 ```python def sigmoid(Z): A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z)) cache = Zreturn A, cache
def relu(Z): A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)cache = Zreturn A, cache
```python# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_activation_forwarddef linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):if activation == "sigmoid":# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev,W,b)A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)elif activation == "relu":# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev,W,b)A, activation_cache = relu(Z)assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)return A, cache
就是对线性计算套了一层非线性计算,可选relu或者 sigmoid。
4.3 L层模型
为了方便实现层神经网络,你将需要一个函数来复制前一个函数(使用RELU的
linear_activation_forward)次,以及复制带有SIGMOID的
linear_activation_forward。
练习:实现上述模型的正向传播。
说明:在下面的代码中,变量AL表示%20%3D%20%5Csigma(W%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%20A%5E%7B%5BL-1%5D%7D%20%2B%20b%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D)#card=math&code=A%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%20%3D%20%5Csigma%28Z%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%29%20%3D%20%5Csigma%28W%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%20A%5E%7B%5BL-1%5D%7D%20%2B%20b%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%29&id=U9sl8)(有时也称为
Yhat,即。)
提示:
- 使用你先前编写的函数
- 使用for循环复制[LINEAR-> RELU](L-1)次
- 不要忘记在“cache”列表中更新缓存。 要将新值
c添加到list中,可以使用list.append(c)。 ```pythonGRADED FUNCTION: L_model_forward
def L_model_forward(X, parameters): “”” X — data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) parameters — output of initialize_parameters_deep() AL — last post-activation value caches — list of caches containing: every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2) the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1) “””
caches = []A = XL = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.for l in range(1, L):A_prev = AA, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], activation = "relu")caches.append(linear_activation_cache)# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.AL, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation = "sigmoid")caches.append(linear_activation_cache)assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))return AL, caches
X, parameters = L_model_forward_test_case() AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters) print(X,’\n’, parameters,’\nAL = ‘, AL,’\n caches = \n’, caches)
[[ 1.62434536 -0.61175641] [-0.52817175 -1.07296862] [ 0.86540763 -2.3015387 ] [ 1.74481176 -0.7612069 ]] {‘W1’: array([[ 0.3190391 , -0.24937038, 1.46210794, -2.06014071], [-0.3224172 , -0.38405435, 1.13376944, -1.09989127], [-0.17242821, -0.87785842, 0.04221375, 0.58281521]]), ‘b1’: array([[-1.10061918], [ 1.14472371], [ 0.90159072]]), ‘W2’: array([[ 0.50249434, 0.90085595, -0.68372786]]), ‘b2’: array([[-0.12289023]])} AL = [[0.17007265 0.2524272 ]] caches = [((array([[ 1.62434536, -0.61175641], [-0.52817175, -1.07296862], [ 0.86540763, -2.3015387 ]]), array([[ 1.74481176, -0.7612069 , 0.3190391 ]]), array([[-0.24937038]])), array([[-2.77991749, -2.82513147], [-0.11407702, -0.01812665], [ 2.13860272, 1.40818979]])), ((array([[ 1.62434536, -0.61175641], [-0.52817175, -1.07296862], [ 0.86540763, -2.3015387 ]]), array([[ 1.74481176, -0.7612069 , 0.3190391 ]]), array([[-0.24937038]])), array([[-1.58511248, -1.08570881]]))]
就是加了层循环嘛,有几层网络就循环几次。<a name="7162a4e0"></a>## 3. 损失函数使用以下公式计算交叉熵损失:%7D%5Clog%5Cleft(a%5E%7B%5BL%5D%20(i)%7D%5Cright)%20%2B%20(1-y%5E%7B(i)%7D)%5Clog%5Cleft(1-%20a%5E%7B%5BL%5D(i)%7D%5Cright))%C2%A0%5Ctag%7B7%7D%0A#card=math&code=-%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7Bm%7D%20%5Csum%5Climits_%7Bi%20%3D%201%7D%5E%7Bm%7D%20%28y%5E%7B%28i%29%7D%5Clog%5Cleft%28a%5E%7B%5BL%5D%20%28i%29%7D%5Cright%29%20%2B%20%281-y%5E%7B%28i%29%7D%29%5Clog%5Cleft%281-%20a%5E%7B%5BL%5D%28i%29%7D%5Cright%29%29%C2%A0%5Ctag%7B7%7D%0A&id=JlHvV)```python# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_costdef compute_cost(AL, Y):m = Y.shape[1]# Compute loss from aL and y.cost = - 1/m * np.sum(Y * np.log(AL) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - AL), axis=1, keepdims=True)cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).assert(cost.shape == ())return cost
4. 反向传播
4.1 线性反向
请记住,反向传播用于计算损失函数相对于参数的梯度。
对于层,线性部分为:
(之后是激活)。
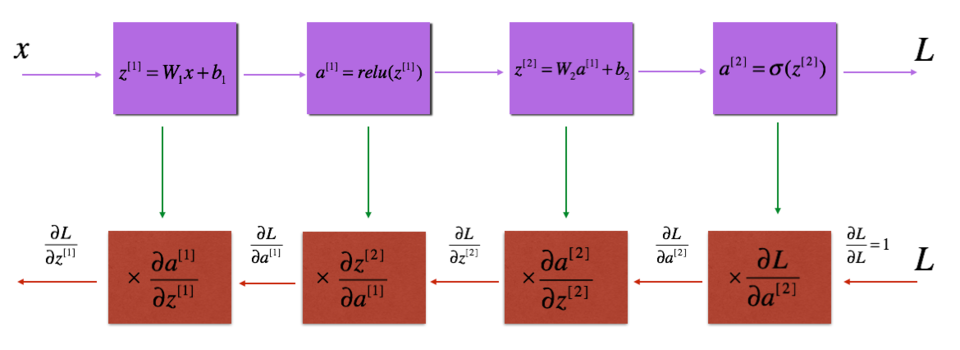
图:LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID 的正向和反向传播,紫色块代表正向传播,红色块代表反向传播。
类似于正向传播,你将分三个步骤构建反向传播:
LINEAR backward
LINEAR -> ACTIVATION backward,其中激活函数使用ReLU或sigmoid 的导数计算
[LINEAR -> RELU] × (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID backward(整个模型)
假设你已经计算出导数。 你想获得
#card=math&code=%28dW%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%2C%20db%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%20dA%5E%7B%5Bl-1%5D%7D%29&id=cb4qM)。
使用输入计算三个输出
#card=math&code=%28dW%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%2C%20db%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%2C%20dA%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%29&id=e3yMc)。以下是所需的公式:
%7D%5Ctag%7B9%7D%0A#card=math&code=db%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B%5Cpartial%20%5Cmathcal%7BL%7D%20%7D%7B%5Cpartial%20b%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%7D%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7Bm%7D%20%5Csum_%7Bi%20%3D%201%7D%5E%7Bm%7D%20dZ%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%28i%29%7D%5Ctag%7B9%7D%0A&id=UJBm6)
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_backwarddef linear_backward(dZ, cache):A_prev, W, b = cachem = A_prev.shape[1]dW = 1/m * np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T)db = 1/m * np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True)dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ)assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)assert (dW.shape == W.shape)assert (db.shape == b.shape)return dA_prev, dW, db
4.2 反向线性激活
接下来,创建一个合并两个辅助函数的函数:**linear_backward** 和反向步骤的激活 **linear_activation_backward**。
我们提供了两个反向函数:
**sigmoid_backward**:实现SIGMOID单元的反向传播。**relu_backward**:实现RELU单元的反向传播。 ```python
def relu_backward(dA, cache): Z = cache dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.dZ[Z <= 0] = 0assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)return dZ
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache): Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))dZ = dA * s * (1-s)assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)return dZ
如果#card=math&code=g%28.%29&id=qTPhr)是激活函数,<br />`sigmoid_backward`和`relu_backward`计算**练习**:实现_LINEAR->ACTIVATION_ 层的反向传播。```python# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_activation_backwarddef linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):linear_cache, activation_cache = cacheif activation == "relu":dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)elif activation == "sigmoid":dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)return dA_prev, dW, db
4.3 反向L层模型
现在,你将为整个网络实现反向传播函数。 回想一下,当你实现L_model_forward函数时,在每次迭代中,你都存储了一个包含(X,W,b和z)的缓存。 在反向传播模块中,你将使用这些变量来计算梯度。 因此,在L_model_backward函数中,你将从层开始向后遍历所有隐藏层。在每个步骤中,你都将使用
层的缓存值反向传播到层
。 图5展示了反向传播过程。
初始化反向传播:
为了使网络反向传播,我们知道输出是#card=math&code=A%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%20%3D%20%5Csigma%28Z%5E%7B%5BL%5D%7D%29&id=DUZ7d)。因此,你的代码需要计算
dAL 。
为此,请使用以下公式(不需要深入的微积分知识):
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL)) # derivative of cost with respect to AL
然后,你可以使用此激活后的梯度dAL继续反向传播。如图5所示,你现在可以将dAL输入到你实现的LINEAR-> SIGMOID反向函数中(它将使用L_model_forward函数存储的缓存值)。之后,你得通过for循环,使用LINEAR-> RELU反向函数迭代所有其他层。同时将每个dA,dW和db存储在grads词典中。为此,请使用以下公式:
%5D%20%3D%20dW%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%5Ctag%7B15%7D%20%0A#card=math&code=grads%5B%22dW%22%20%2B%20str%28l%29%5D%20%3D%20dW%5E%7B%5Bl%5D%7D%5Ctag%7B15%7D%20%0A&id=Fxzja)
例如,当时,它将在
grads["dW3"]中存储 。
练习:实现 [LINEAR->RELU] (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID 模型的反向传播。
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_backwarddef L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):grads = {}L = len(caches) # the number of layersm = AL.shape[1]Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL# Initializing the backpropagationdAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]current_cache = caches[L-1]grads["dA" + str(L)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, activation = "sigmoid")for l in reversed(range(L - 1)):# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.# Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], caches". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)]current_cache = caches[l]dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l+2)], current_cache, activation = "relu")grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] = dA_prev_tempgrads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_tempgrads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_tempreturn grads
AL, Y_assess, caches = L_model_backward_test_case()grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y_assess, caches)print(' AL = ', AL, '\n Y_assess = ',Y_assess, '\n caches = ',caches)
AL = [[1.78862847 0.43650985]]Y_assess = [[1 0]]caches = (((array([[ 0.09649747, -1.8634927 ],[-0.2773882 , -0.35475898],[-0.08274148, -0.62700068],[-0.04381817, -0.47721803]]), array([[-1.31386475, 0.88462238, 0.88131804, 1.70957306],[ 0.05003364, -0.40467741, -0.54535995, -1.54647732],[ 0.98236743, -1.10106763, -1.18504653, -0.2056499 ]]), array([[ 1.48614836],[ 0.23671627],[-1.02378514]])), array([[-0.7129932 , 0.62524497],[-0.16051336, -0.76883635],[-0.23003072, 0.74505627]])), ((array([[ 1.97611078, -1.24412333],[-0.62641691, -0.80376609],[-2.41908317, -0.92379202]]), array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796, -0.13191423]]), array([[-1.62328545]])), array([[ 0.64667545, -0.35627076]])))
5. 更新参数
使用梯度下降来更新模型的参数:
其中 是学习率。 在计算更新的参数后,将它们存储在参数字典中。
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parametersdef update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)for l in range(L):parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l + 1)]parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l + 1)]### END CODE HERE ###return parametersparameters, grads = update_parameters_test_case()parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, 0.1)
{'W1': array([[-0.59562069, -0.09991781, -2.14584584, 1.82662008],[-1.76569676, -0.80627147, 0.51115557, -1.18258802],[-1.0535704 , -0.86128581, 0.68284052, 2.20374577]]),'b1': array([[-0.04659241],[-1.28888275],[ 0.53405496]]),'W2': array([[-0.55569196, 0.0354055 , 1.32964895]]),'b2': array([[-0.84610769]])}
深度神经网络应用—图像分类
让我们首先导入在作业过程中需要的所有软件包。
- numpy是Python科学计算的基本包。
- matplotlib 是在Python中常用的绘制图形的库。
- h5py是一个常用的包,可以处理存储为H5文件格式的数据集
- 这里最后通过PIL和 scipy用你自己的图片去测试模型效果。
- dnn_app_utils提供了上一作业教程“逐步构建你的深度神经网络”中实现的函数。
- np.random.seed(1)使所有随机函数调用保持一致。 这将有助于我们评估你的作业。
import timeimport numpy as npimport h5pyimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport scipyfrom PIL import Imagefrom scipy import ndimagefrom dnn_app_utils_v2 import *%matplotlib inlineplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plotsplt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'%load_ext autoreload%autoreload 2np.random.seed(1)
数据集
你将使用与“用神经网络思想实现Logistic回归”(作业2)中相同的“cats vs non-cats”数据集。 此前你建立的模型在对猫和非猫图像进行分类时只有70%的准确率。 希望你的新模型会更好!
问题说明:你将获得一个包含以下内容的数据集(”data.h5”):
- 标记为cat(1)和非cat(0)图像的训练集m_train
- 标记为cat或non-cat图像的测试集m_test
- 每个图像的维度都为(num_px,num_px,3),其中3表示3个通道(RGB)。
让我们熟悉一下数据集吧, 首先通过运行以下代码来加载数据。
# 加载数据train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_data()# Example of a pictureindex = 7plt.imshow(train_x_orig[index])print ("y = " + str(train_y[0,index]) + ". It's a " + classes[train_y[0,index]].decode("utf-8") + " picture.")
y = 1. It's a cat picture.

# Explore your datasetm_train = train_x_orig.shape[0]num_px = train_x_orig.shape[1]m_test = test_x_orig.shape[0]print ("Number of training examples: " + str(m_train))print ("Number of testing examples: " + str(m_test))print ("Each image is of size: (" + str(num_px) + ", " + str(num_px) + ", 3)")print ("train_x_orig shape: " + str(train_x_orig.shape))print ("train_y shape: " + str(train_y.shape))print ("test_x_orig shape: " + str(test_x_orig.shape))print ("test_y shape: " + str(test_y.shape))
Number of training examples: 209Number of testing examples: 50Each image is of size: (64, 64, 3)train_x_orig shape: (209, 64, 64, 3)train_y shape: (1, 209)test_x_orig shape: (50, 64, 64, 3)test_y shape: (1, 50)
与往常一样,在将图像输入到网络之前,需要对图像进行重塑和标准化。 下面单元格给出了相关代码。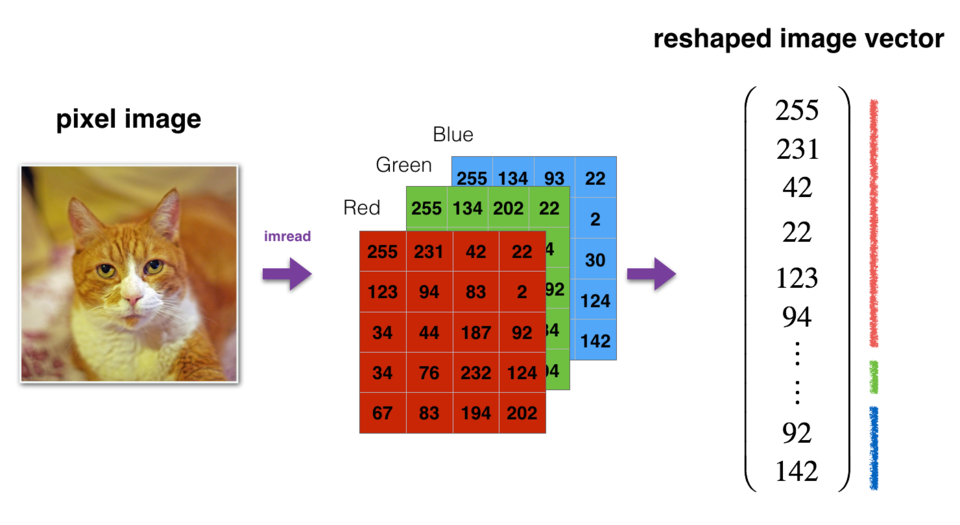
图:图像转换为向量。
# Reshape the training and test examplestrain_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T # The "-1" makes reshape flatten the remaining dimensionstest_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T# Standardize data to have feature values between 0 and 1.train_x = train_x_flatten/255.test_x = test_x_flatten/255.print ("train_x's shape: " + str(train_x.shape))print ("test_x's shape: " + str(test_x.shape))
train_x's shape: (12288, 209)test_x's shape: (12288, 50)
现在你已经熟悉了数据集,是时候建立一个深度神经网络来区分猫图像和非猫图像了。
你将建立两个不同的模型:
2层神经网络
L层深度神经网络
然后,你将比较这些模型的性能,并尝试不同的值。
通用步骤
与往常一样,你将遵循深度学习步骤来构建模型:
- 初始化参数/定义超参数
- 循环num_iterations次:
a. 正向传播
b. 计算损失函数
C. 反向传播
d. 更新参数(使用参数和反向传播的梯度) - 使用训练好的参数来预测标签
2层的神经网络
### CONSTANTS DEFINING THE MODEL ####n_x = 12288 # num_px * num_px * 3n_h = 7n_y = 1layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y)
# GRADED FUNCTION: two_layer_modeldef two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):"""Implements a two-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.Returns:parameters -- a dictionary containing W1, W2, b1, and b2"""np.random.seed(1)grads = {}costs = [] # to keep track of the costm = X.shape[1] # number of examples(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims# Initialize parameters dictionary, by calling one of the functions you'd previously implemented### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)### END CODE HERE #### Get W1, b1, W2 and b2 from the dictionary parameters.W1 = parameters["W1"]b1 = parameters["b1"]W2 = parameters["W2"]b2 = parameters["b2"]# Loop (gradient descent)for i in range(0, num_iterations):# Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.A1, cache1 =linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, activation = "relu")A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, activation = "sigmoid")# Compute costcost = compute_cost(A2, Y)# Initializing backward propagationdA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2))# Backward propagation.dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, activation = "sigmoid")dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, activation = "relu")# Set grads['dWl'] to dW1, grads['db1'] to db1, grads['dW2'] to dW2, grads['db2'] to db2grads['dW1'] = dW1grads['db1'] = db1grads['dW2'] = dW2grads['db2'] = db2# Update parameters.parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)# Retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2 from parametersW1 = parameters["W1"]b1 = parameters["b1"]W2 = parameters["W2"]b2 = parameters["b2"]# Print the cost every 100 training exampleif print_cost and i % 100 == 0:print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:costs.append(cost)# plot the costplt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))plt.ylabel('cost')plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))plt.show()return parameters
parameters = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y), num_iterations = 2500, print_cost=True)
Cost after iteration 0: 0.693049735659989Cost after iteration 100: 0.6464320953428849Cost after iteration 200: 0.6325140647912678Cost after iteration 300: 0.6015024920354665Cost after iteration 400: 0.5601966311605747Cost after iteration 500: 0.5158304772764729Cost after iteration 600: 0.4754901313943325Cost after iteration 700: 0.43391631512257495Cost after iteration 800: 0.4007977536203887Cost after iteration 900: 0.35807050113237976Cost after iteration 1000: 0.33942815383664127Cost after iteration 1100: 0.30527536361962654Cost after iteration 1200: 0.2749137728213016Cost after iteration 1300: 0.24681768210614846Cost after iteration 1400: 0.19850735037466097Cost after iteration 1500: 0.17448318112556657Cost after iteration 1600: 0.1708076297809689Cost after iteration 1700: 0.11306524562164715Cost after iteration 1800: 0.09629426845937145Cost after iteration 1900: 0.08342617959726863Cost after iteration 2000: 0.07439078704319078Cost after iteration 2100: 0.06630748132267933Cost after iteration 2200: 0.0591932950103817Cost after iteration 2300: 0.05336140348560554Cost after iteration 2400: 0.04855478562877016
L层的神经网络
layers_dims = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1] # 5-layer model# GRADED FUNCTION: L_layer_modeldef L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):#lr was 0.009np.random.seed(1)costs = [] # keep track of cost# Parameters initialization.parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)# Loop (gradient descent)for i in range(0, num_iterations):# Forward propagation: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)# Compute cost.cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)# Backward propagation.grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)# Update parameters.parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)# Print the cost every 100 training exampleif print_cost and i % 100 == 0:print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:costs.append(cost)# plot the costplt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))plt.ylabel('cost')plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))plt.show()return parameters
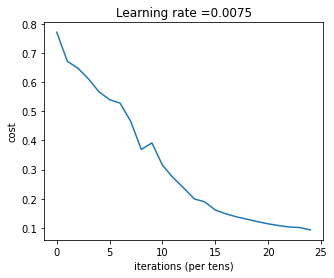
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims, num_iterations = 2500, print_cost = True)
Cost after iteration 0: 0.771749Cost after iteration 100: 0.672053Cost after iteration 200: 0.648263Cost after iteration 300: 0.611507Cost after iteration 400: 0.567047Cost after iteration 500: 0.540138Cost after iteration 600: 0.527930Cost after iteration 700: 0.465477Cost after iteration 800: 0.369126Cost after iteration 900: 0.391747Cost after iteration 1000: 0.315187Cost after iteration 1100: 0.272700Cost after iteration 1200: 0.237419Cost after iteration 1300: 0.199601Cost after iteration 1400: 0.189263Cost after iteration 1500: 0.161189Cost after iteration 1600: 0.148214Cost after iteration 1700: 0.137775Cost after iteration 1800: 0.129740Cost after iteration 1900: 0.121225Cost after iteration 2000: 0.113821Cost after iteration 2100: 0.107839Cost after iteration 2200: 0.102855Cost after iteration 2300: 0.100897Cost after iteration 2400: 0.092878
查看训练和测试集的预测结果
def predict(X, y, parameters):m = X.shape[1]n = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networkp = np.zeros((1,m))# Forward propagationprobas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)# convert probas to 0/1 predictionsfor i in range(0, probas.shape[1]):if probas[0,i] > 0.5:p[0,i] = 1else:p[0,i] = 0#print results#print ("predictions: " + str(p))#print ("true labels: " + str(y))print("Accuracy: " + str(np.sum((p == y)/m)))return p
pred_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)
Accuracy: 0.9856459330143539
pred_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)
Accuracy: 0.8
结果分析
首先,让我们看一下L层模型标记错误的一些图像。 这将显示一些分类错误的图像。
def print_mislabeled_images(classes, X, y, p):"""Plots images where predictions and truth were different.X -- datasety -- true labelsp -- predictions"""a = p + ymislabeled_indices = np.asarray(np.where(a == 1))plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (40.0, 40.0) # set default size of plotsnum_images = len(mislabeled_indices[0])for i in range(num_images):index = mislabeled_indices[1][i]plt.subplot(2, num_images, i + 1)plt.imshow(X[:,index].reshape(64,64,3), interpolation='nearest')plt.axis('off')plt.title("Prediction: " + classes[int(p[0,index])].decode("utf-8") + " \n Class: " + classes[y[0,index]].decode("utf-8"))
print_mislabeled_images(classes, test_x, test_y, pred_test)

该模型在表现效果较差的的图像包括:
- 猫身处于异常位置
- 图片背景与猫颜色类似
- 猫的种类和颜色稀有
- 相机角度
- 图片的亮度
- 比例变化(猫的图像很大或很小)