多线程
多线程,是对资源的利用方式,以期望使用更少的资源,做更多的事情,提升 CPU、IO等资源的利用率。
java 实现多线程的方式:runnable,thread
thread run、start、join 的几个方法的区别:
run 当前线程运行,串行,不能起到多线程的效果start 另起线程执行,并行join 等待线程执行完,阻止当前线程退出,多与 start 方法一起使用
代码
package com.xiaohui.demo.webfluxclient.thread;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** <p>* 测试多线程* </p>** @author xiaohui* @email xuxiaohuimail@163.com* @since 2021/6/22*/public class TestThread {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> start " + Thread.currentThread().getName());// run 方法,直接被当前线程调用业务代码MyThread mythead001 = new MyThread("mythead001");mythead001.run();// start 方法,另起线程执行当前业务代码MyThread mythead002 = new MyThread("mythead002");mythead002.start();// join 将当前的线程执行完成,再执行后面的业务代码(start会直接继续执行后续代码,不会等待返回),join 一般与start 一并使用MyThread mythead003 = new MyThread("mythead003");mythead003.start();mythead003.join();System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> end " + Thread.currentThread().getName());}static class MyThread extends Thread {public MyThread(String myName) {this.myName = myName;}public String getMyName() {return myName;}public void setMyName(String myName) {this.myName = myName;}private String myName;@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 进入mythread 。。。threadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",参数:" + getMyName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 退出mythread 。。。threadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",参数:" + getMyName());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {public MyRunnable(String myName) {this.myName = myName;}public String getMyName() {return myName;}public void setMyName(String myName) {this.myName = myName;}private String myName;@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 进入MyRunnable 。。。threadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",参数:" + getMyName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 退出MyRunnable 。。。threadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",参数:" + getMyName());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
线程池
有了多线程,为什么还需要线程池?
创建线程消耗时间多,资源多,线程越多,切换线程消耗时间长。线程池可以复用线程。
代码测试:
package com.xiaohui.demo.webfluxclient.thread;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Random;import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** <p>* 测试线程池* </p>** @author xiaohui* @email xuxiaohuimail@163.com* @since 2021/6/23*/public class TestThreadPool {/*** 测试非线程池下的代码** @throws InterruptedException*/@Testpublic void testNonThreadPool() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testNonThreadPool");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();final List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {list.add(new Random().nextInt());});thread.start();thread.join();}System.out.println(String.format("list size %d", list.size()));System.out.println(String.format("cost time %d", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}@Testpublic void testThreadPool() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();final List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1000);for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {/*>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPoollist size 99931cost time 5705*/// 使用 submit, 执行结果 list size 小于 100000,ArrayList 非线程安全executorService.submit(() -> {list.add(new Random().nextInt());});}executorService.shutdown();executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);System.out.println(String.format("list size %d", list.size()));System.out.println(String.format("cost time %d", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}@Testpublic void testThreadPool2() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool2");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();final List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1000);for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {/*>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool2list size 99985cost time 992*/// 使用 execute, 执行结果 list size 小于 100000,ArrayList 非线程安全executorService.execute(() -> {list.add(new Random().nextInt());});}executorService.shutdown();executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);System.out.println(String.format("list size %d", list.size()));System.out.println(String.format("cost time %d", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}@Testpublic void testThreadPool3() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool3");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// final List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();// 采用线程安全的 listCopyOnWriteArrayList<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1000);for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {/*>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool3list size 100000cost time 13683*/// 使用 execute, 执行结果 list size 等于 100000,CopyOnWriteArrayList 非线程安全executorService.execute(() -> {list.add(new Random().nextInt());});}executorService.shutdown();executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);System.out.println(String.format("list size %d", list.size()));System.out.println(String.format("cost time %d", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}/*** 采用 Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程池,不存在线程安全问题** @throws InterruptedException*/@Testpublic void testThreadPool4() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool4");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();final List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();// 采用单一线程池执行ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {/*>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> testThreadPool4list size 100000cost time 150*/// 使用 execute, 执行结果 list size 等于 100000,单一线程,不存在是否多线程的安全问题executorService.execute(() -> {list.add(new Random().nextInt());});}executorService.shutdown();executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);System.out.println(String.format("list size %d", list.size()));System.out.println(String.format("cost time %d", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}}
为什么不推荐使用 Executors 工具类创建线程池
容易导致 CPU 使用率高,比如 Executors.newCacheThreadPool(),没有缓存的线程时,一个劲儿创建线程;
容易导致 OOM 内存溢出,比如 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10)、Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(),队列过大,耗尽内存;
它的原理(源码理解)
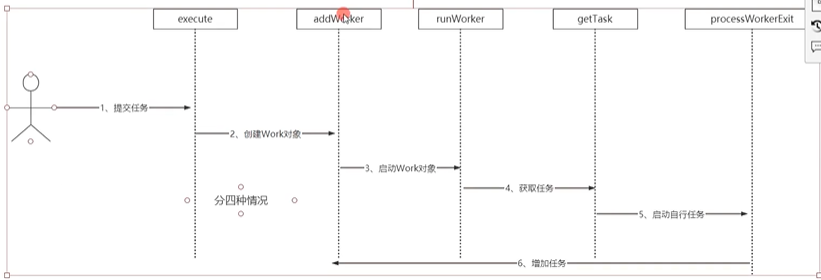
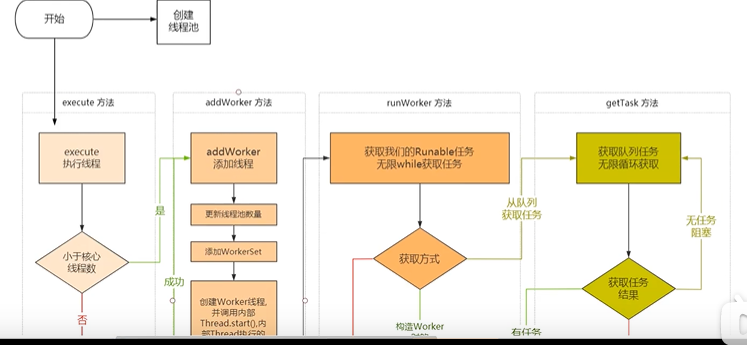

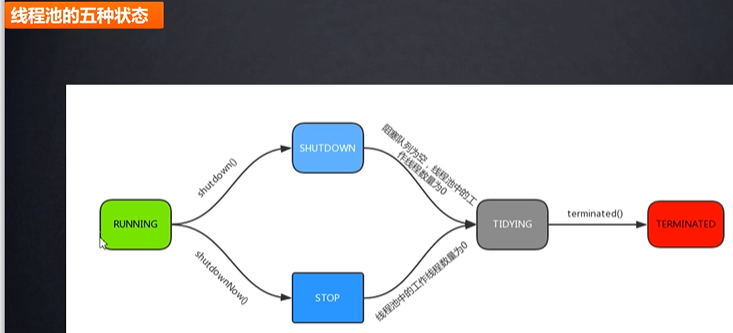

如何使用
代码。使用工具类 Executors
package com.xiaohui.demo.webfluxclient.thread;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** <p>* 测试线程池2* </p>** @author xiaohui* @email xuxiaohuimail@163.com* @since 2021/6/23*/public class TestTreadPool_2 {@Testpublic void testMultiPool() throws InterruptedException {ExecutorService executorService1 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();ExecutorService executorService2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);ExecutorService executorService3 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");System.out.println("Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() cost time:" + costTime(executorService1));System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");System.out.println("Executors.Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100) cost time:" + costTime(executorService2));System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");System.out.println("Executors.newCachedThreadPool() cost time:" + costTime(executorService3));// 結果/*>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>curr thread name: pool-1-thread-1, i 为 0curr thread name: pool-1-thread-1, i 为 1curr thread name: pool-1-thread-1, i 为 2curr thread name: pool-1-thread-1, i 为 3curr thread name: pool-1-thread-1, i 为 4Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() cost time:10021>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>curr thread name: pool-2-thread-1, i 为 0curr thread name: pool-2-thread-2, i 为 1curr thread name: pool-2-thread-3, i 为 2curr thread name: pool-2-thread-4, i 为 3curr thread name: pool-2-thread-5, i 为 4Executors.Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100) cost time:2000>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>curr thread name: pool-3-thread-1, i 为 0curr thread name: pool-3-thread-5, i 为 4curr thread name: pool-3-thread-4, i 为 3curr thread name: pool-3-thread-2, i 为 1curr thread name: pool-3-thread-3, i 为 2Executors.newCachedThreadPool() cost time:2017*/}private Long costTime(ExecutorService executorService) throws InterruptedException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {final int a = i;executorService.execute(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);System.out.println(String.format("curr thread name: %s, i 为 %d ", Thread.currentThread().getName(), a));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}executorService.shutdown();executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;}}
线程调优
术语介绍
线程与进程
进程,资源分配的最小单位;
线程,CPU 调度的最小单位;也叫轻量级进程 LWP(Light Weight Process)
一个进程拥有多个线程,一个线程属于某一个进程;
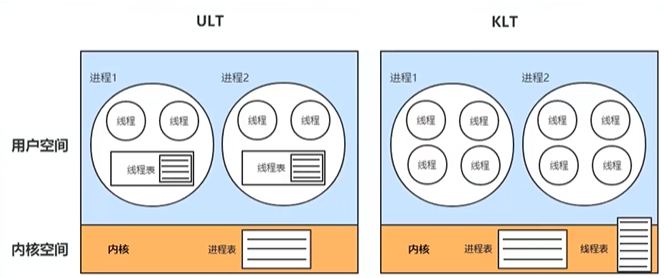
ULT 与 KLT 线程模型
用户级线程,user level thread,用户自己创建管理,操作系统(kernel)对线程的存在与否无感知。
内核级先吃,kernel level thread,依赖内核系统,与内核系统线程一对一管理
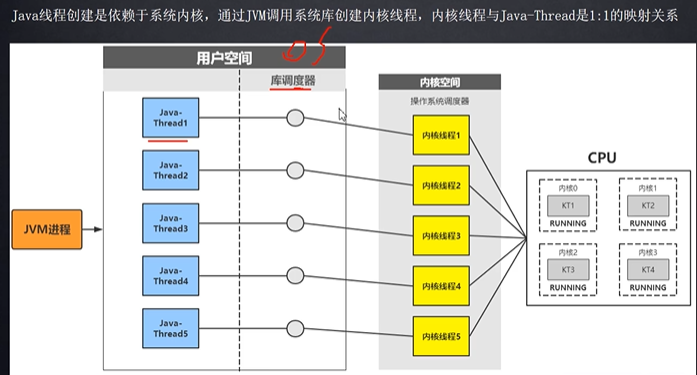
程序计数器,pc 寄存器,CPU 时间片等概念
阻塞队列
FIFO
在任意时刻(不管是否高并发),永远只有一个线程能够进行队列的入队或者出队操作!
线程安全的队列!
(实际)有界!(不管指不指定大小,最终取决于宿主操作系统);
队列满,只能进行出队操作,所有的入队操作必须等待,也就是被阻塞;
队列空,只能进行入队操作,所有的出队操作必须等待,也就是被阻塞;
提交优先级与执行优先级
线程池的提交优先级与执行优先级,都是代码实现,限定了它的表现形式。所以,查看源码吧~~~
任务提交数量:
提交优先:
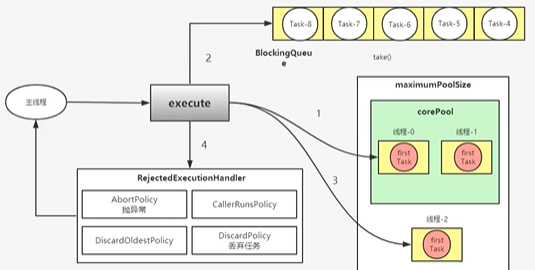
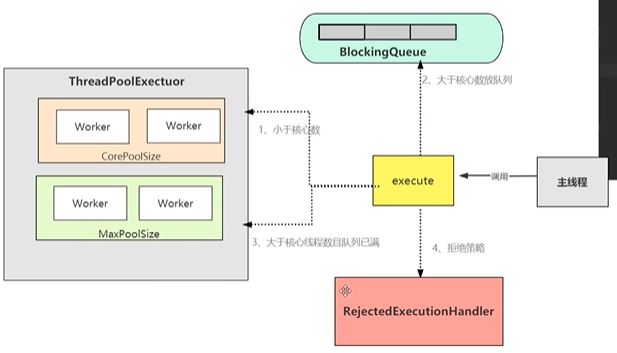
小于 coreSize 线程,创建线程,执行任务
大于 coreSize 线程,小于 blockQueue size,提交到阻塞队列中
大于 blockQueue size,小于 maxSize 线程, 创建线程,执行任务
大于 blockQueue size,大于 maxSize 线程,采用相关的策略来进行处理
执行优先级:
coreSize 的 thread 先行
maxSize 的在后(任务未能填满阻塞队列时,maxSize 的线程不会创建,即任务在会在 coreSize 线程上执行);

