Serilog是一个很棒的 3rd 方库,用于在我们的 ASP.NET 核心应用程序中进行结构化日志记录。结构化日志记录是生成易于阅读和过滤的日志的关键。
使用 SQL Server 作为日志目的地,允许我们利用 SQL 查询的强大功能进行日志过滤。如果我们的应用程序已经在使用 SQL Server,它可能是一个不错的选择。
那么,我们如何在 ASP.NET Core 2.0 中实现 Serilog SQL 日志……
首先我们需要引入以下nuget包:
- Serilog.AspNetCore
- Serilog.Settings.Configuration
- Serilog.Sinks.MSSqlServer
接下来,我们需要更改在Program.cs. 开头的 3 行Main()告诉程序使用 Serilog 作为记录器并从appsettings.json.
public class Program{public static IConfiguration Configuration { get; } = new ConfigurationBuilder().SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true).AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT") ?? "Production"}.json", optional: true).Build();public static void Main(string[] args){Log.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration().ReadFrom.Configuration(Configuration).CreateLogger();try{Log.Information("Getting the motors running...");BuildWebHost(args).Run();}catch (Exception ex){Log.Fatal(ex, "Host terminated unexpectedly");}finally{Log.CloseAndFlush();}}public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args).UseStartup<Startup>().UseConfiguration(Configuration).UseSerilog().Build();}
然后可以将 Serilog 配置为使用 SQL Server 作为 中的目标appSettings.json,以及最低日志记录级别。我们需要指定日志数据库的连接字符串和将数据记录到的表名。
{..."Serilog": {"MinimumLevel": "Information","WriteTo": [{"Name": "MSSqlServer","Args": {"connectionString": "<our connection string>","tableName": "Log"}}]},...}
我们可以让 SerilogLog自动创建我们的表,但让我们自己做,这样我们就可以控制我们的模式。例如,我们希望Properties列基于xml数据类型,以便我们可以查询它(serilog 将其创建为nvarchar)。
下面是创建Log表的TSQL 脚本:
CREATE TABLE [Log] ([Id] int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,[Message] nvarchar(max) NULL,[MessageTemplate] nvarchar(max) NULL,[Level] nvarchar(128) NULL,[TimeStamp] datetimeoffset(7) NOT NULL,[Exception] nvarchar(max) NULL,[Properties] xml NULL,[LogEvent] nvarchar(max) NULLCONSTRAINT [PK_Log]PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([Id] ASC))
然后我们可以在我们的代码中写入日志,记录{@object}在消息模板中使用的结构化对象。下面是用于获取和返回记录(在本例中为联系人)的 Web API 操作方法。我们记录何时从缓存/数据库中获取联系人以及何时在缓存中设置联系人。
[HttpGet("{contactId}")]public async Task GetById(Guid contactId){// Initialise the contact that is going to be returnedContact contact = null;// Get the requested ETagstring requestETag = "";if (Request.Headers.ContainsKey("If-None-Match")){requestETag = Request.Headers["If-None-Match"].First();if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestETag)){// The client has supplied an ETag, so, get this version of the contact from our cache// Construct the key for the cache which includes the entity type (i.e. "contact"), the contact id and the version of the contact record (i.e. the ETag value)string oldCacheKey = $"contact-{contactId}-{requestETag}";// Get the cached itemstring cachedContactJson = await cache.GetStringAsync(oldCacheKey);// If there was a cached item then deserialise this into our contact objectif (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(cachedContactJson)){contact = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(cachedContactJson);Log.Information("Contact {@contact} retrieved from cache", contact);}}}// We have no cached contact, then get the contact from the databaseif (contact == null){contact = await dataRepository.GetContactByIdAsync(contactId);Log.Information("Contact {@contact} retrieved from database", contact);}// If no contact was found in the cache or the database, then return a 404if (contact == null){Log.Information("Contact {@contactId} not found", contactId);return NotFound();}// Construct the new ETagstring responseETag = Convert.ToBase64String(contact.RowVersion);// Return a 304 if the ETag of the current record matches the ETag in the "If-None-Match" HTTP headerif (Request.Headers.ContainsKey("If-None-Match") && responseETag == requestETag){return StatusCode((int)HttpStatusCode.NotModified);}// Add the contact to the cache for 30 minsstring cacheKey = $"contact-{contactId}-{responseETag}";await cache.SetStringAsync(cacheKey, JsonConvert.SerializeObject(contact), new DistributedCacheEntryOptions() { AbsoluteExpiration = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(30) });Log.Information("Contact {@contact} added to cache with key {@cacheKey}", contact, cacheKey);// Add the current ETag to the HTTP headerResponse.Headers.Add("ETag", responseETag);return Ok(contact);}
现在 Serilog 和 SQL Server 已设置、连接在一起并且我们有一些日志记录代码,我们应该将日志输出到我们的 SQL Server 表。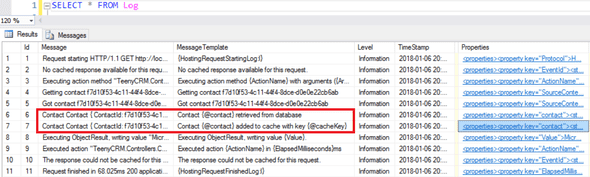
请注意,如果我们在将日志写入 SQL Server 时遇到问题,我们可以使用Serilog.Debugging.SelfLog.Enable()inProgram.Main()从 Serilog 中显示错误。
public class Program{public static int Main(string[] args){Log.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration().ReadFrom.Configuration(Configuration).CreateLogger();Serilog.Debugging.SelfLog.Enable(msg =>{Debug.Print(msg);Debugger.Break();});...}...}
该Properties列包含有用的附加信息,包括我们在将联系人添加到缓存后在结构化日志中指定的内容: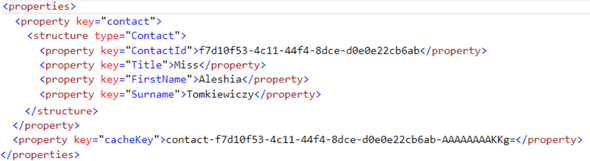
我们可以Properties使用XQuery语法提取列中的特定数据。我们甚至可以过滤Properties列中的值。
例如,如果我们想查找特定联系人何时添加到缓存中,我们可以使用类似的方法:
SELECTProperties.value('(/properties/property[@key="contact"]/structure[@type="Contact"]/property[@key="ContactId"])[1]', 'nvarchar(max)') AS ContactId,Properties.value('(/properties/property[@key="contact"]/structure[@type="Contact"]/property[@key="FirstName"])[1]', 'nvarchar(50)') AS FirstName,Properties.value('(/properties/property[@key="contact"]/structure[@type="Contact"]/property[@key="Surname"])[1]', 'nvarchar(100)') AS Surname,Properties.value('(/properties/property[@key="cacheKey"])[1]', 'nvarchar(100)') AS CacheKey,*FROM LogWHERE MessageTemplate = 'Contact {@contact} added to cache with key {@cacheKey}'AND Properties.value('(/properties/property[@key="contact"]/structure[@type="Contact"]/property[@key="ContactId"])[1]', 'nvarchar(max)') = 'f7d10f53-4c11-44f4-8dce-d0e0e22cb6ab'


