HTTP首部字段
这里仅列出和跨域有关的首部字段。
HTTP 请求首部字段
请注意,这些首部字段无须手动设置。 当开发者使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象发起跨域请求时,它们已经被设置就绪。
Origin
Origin 首部字段表明预检请求或实际请求的源站。
Origin: <origin>
origin 参数的值为源站 URI。它不包含任何路径信息,只是服务器名称。
Note: 有时候将该字段的值设置为空字符串是有用的,例如,当源站是一个 data URL 时。
注意,不管是否为跨域请求,Origin 字段总是被发送。
Access-Control-Request-Method
Access-Control-Request-Method 首部字段用于预检请求。其作用是,将实际请求所使用的 HTTP 方法告诉服务器。
Access-Control-Request-Method: <method>
eg:
Access-Control-Request-Method: POST
Access-Control-Request-Headers
Access-Control-Request-Headers 首部字段用于预检请求。其作用是,将实际请求所携带的首部字段告诉服务器。
Access-Control-Request-Headers: <field-name>[, <field-name>]*
eg:
Access-Control-Request-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-Type
HTTP 响应首部字段
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
响应首部中可以携带一个 Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段,其语法如下:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: <origin> | *
*注:不存在类似 .example.com 的格式,实现正则可通过后端代码实现
其中,origin 参数的值指定了允许访问该资源的外域 URI。对于不需要携带身份凭证的请求,服务器可以指定该字段的值为通配符,表示允许来自所有域的请求。
例如,下面的字段值将允许来自 http://mozilla.com 的请求:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://mozilla.com
如果服务端指定了具体的域名而非*,那么响应首部中的 Vary 字段的值必须包含 Origin。这将告诉客户端:服务器对不同的源站返回不同的内容。
Access-Control-Expose-Headers
注:在跨域访问时,默认情况下前端只能拿到一些最基本的响应头:Cache-Control、Content-Language、Content-Type、Expires、Last-Modified、Pragma,如果要访问其他头,则需要服务器设置本响应头。
Access-Control-Expose-Headers 头让服务器把允许浏览器访问的头放入白名单,例如:
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: X-My-Custom-Header, X-Another-Custom-Header
这样浏览器就能够通过getResponseHeader访问X-My-Custom-Header和 X-Another-Custom-Header 响应头了。
Access-Control-Max-Age
Access-Control-Max-Age 头指定了preflight请求的结果能够被缓存多久。
Access-Control-Max-Age: <delta-seconds>
delta-seconds 参数表示preflight请求的结果在多少秒内有效。
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials 头指定了当浏览器的credentials设置为true时是否允许浏览器读取response的内容。当用在对preflight预检测请求的响应中时,它指定了实际的请求是否可以使用credentials。请注意:简单 GET 请求不会被预检;如果对此类请求的响应中不包含该字段,这个响应将被忽略掉,并且浏览器也不会将相应内容返回给网页。
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Allow-Methods
Access-Control-Allow-Methods 首部字段用于预检请求的响应。其指明了实际请求所允许使用的 HTTP 方法。
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: <method>[, <method>]*
eg:
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, OPTIONS
Access-Control-Allow-Headers
Access-Control-Allow-Headers 首部字段用于预检请求的响应。其指明了实际请求中允许携带的首部字段。
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: <field-name>[, <field-name>]*
eg:
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-Type
跨域
简介
注解:同一域名情况下,端口不同,协议不同均算跨域
跨域资源共享(CORS) 是一种机制,它使用额外的 HTTP 头来告诉浏览器 让运行在一个 origin (domain) 上的Web应用被准许访问来自不同源服务器上的指定的资源。当一个资源从与该资源本身所在的服务器不同的域或端口请求一个资源时,资源会发起一个跨域 HTTP 请求。
eg: 站点 http://domain-a.com 通过 JS 代码 使用 XMLHttpRequest 请求http://api.domain-b.com/data.json
出于安全原因,浏览器限制从脚本内发起的跨源HTTP请求。 例如,XMLHttpRequest和 Fetch API 遵循同源策略。 这意味着使用这些API的Web应用程序只能从加载应用程序的同一个域请求HTTP资源,除非使用CORS头文件。
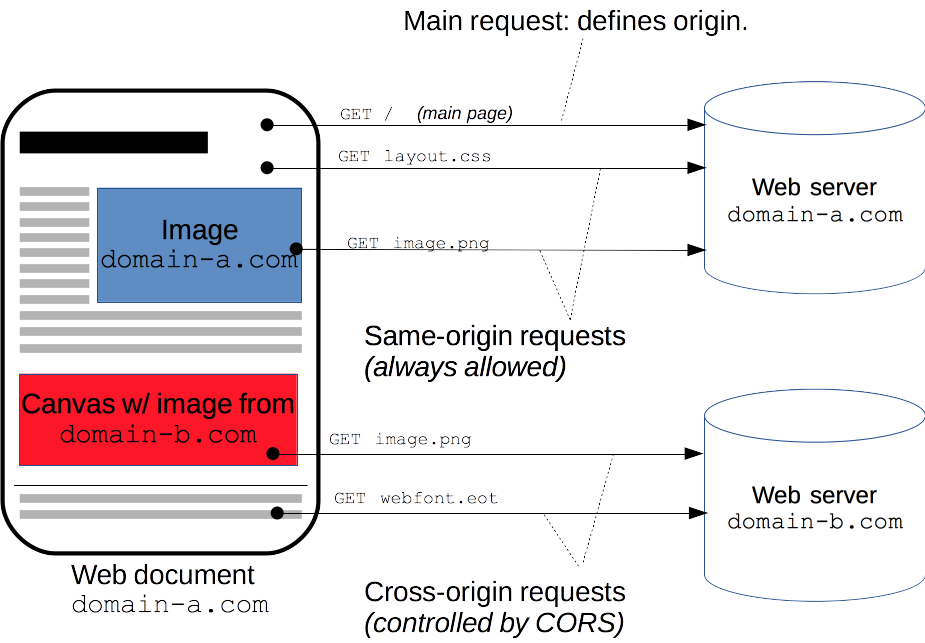
跨域资源共享( CORS )机制允许 Web 应用服务器进行跨域访问控制,从而使跨域数据传输得以安全进行。现代浏览器支持在 API 容器中(例如 XMLHttpRequest 或 Fetch )使用 CORS,以降低跨域 HTTP 请求所带来的风险。
整个CORS通信过程,都是浏览器自动完成,前端基本无感(附带身份凭证需要前端设置一个头部)。对于开发者来说,CORS通信与同源的AJAX通信没有差别,代码完全一样。浏览器一旦发现AJAX请求跨源,就会自动添加一些附加的头信息,有时还会多出一次附加的请求。因此,实现CORS通信的关键是服务端,只要服务器实现了CORS接口,就可以进行CORS通信。
CORS 场景
跨域资源共享标准 允许在下列场景中使用跨域 HTTP 请求:
- 由 XMLHttpRequest 或 Fetch 发起的跨域 HTTP 请求。
- Web 字体 (CSS 中通过
@font-face使用跨域字体资源), 因此,网站就可以发布 TrueType 字体资源,并只允许已授权网站进行跨站调用。 - WebGL 贴图
- 使用
drawImage将 Images/video 画面绘制到 canvas
三种跨域请求
注:CORS 请求失败会产生错误,在JavaScript代码层面是无法获知具体问题,只能查看浏览器的控制台查看具体错误。
- 简单请求
- 预检请求
对那些可能对服务器数据产生副作用的 HTTP 请求方法(特别是 GET 以外的 HTTP 请求,或者搭配某些 MIME 类型的 POST 请求),浏览器必须首先使用 OPTIONS 方法发起一个预检请求(preflight request),从而获知服务端是否允许该跨域请求。
- 附带身份凭证的请求
在预检请求的返回中,服务器端也可以通知客户端,是否需要携带身份凭证(包括 Cookies 和 HTTP 认证相关数据)。
简单请求
若请求满足所有下述条件,则该请求可视为简单请求:
- 使用下列方法之一:
GETHEADPOST
- HTTP的头信息不超出以下几种字段:
AcceptAccept-LanguageContent-LanguageContent-TypeDPRDownlinkSave-DataViewport-WidthWidth
Content-Type的值仅限于下列三者之一:text/plainmultipart/form-dataapplication/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 请求中的任意XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象均没有注册任何事件监听器;XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象可以使用 XMLHttpRequest.upload 属性访问。
- 请求中没有使用 ReadableStream 对象。
注:Content-Type 为 application/json 属于预检请求
eg:
站点 http://foo.example 的网页应用想要访问 http://bar.other 的资源。http://foo.example 的网页中 JavaScript 代码如下:
var invocation = new XMLHttpRequest();var url = 'http://bar.other/resources/public-data/';function callOtherDomain() {if(invocation) {invocation.open('GET', url, true);invocation.onreadystatechange = handler;invocation.send();}}
客户端和服务器之间使用 CORS 首部字段来处理跨域权限:
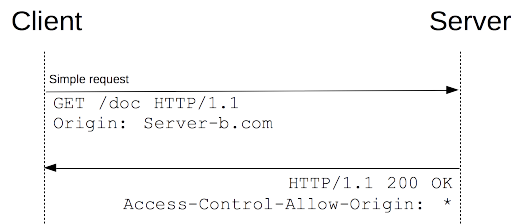
分别检视请求报文和响应报文:
GET /resources/public-data/ HTTP/1.1Host: bar.otherUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10.5; en-US; rv:1.9.1b3pre) Gecko/20081130 Minefield/3.1b3preAccept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflateAccept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7Connection: keep-aliveReferer: http://foo.example/examples/access-control/simpleXSInvocation.htmlOrigin: http://foo.exampleHTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Mon, 01 Dec 2008 00:23:53 GMTServer: Apache/2.0.61Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *Keep-Alive: timeout=2, max=100Connection: Keep-AliveTransfer-Encoding: chunkedContent-Type: application/xml[XML Data]
第 1~10 行是请求首部。第10行 的请求首部字段 Origin 表明该请求来源于 http://foo.exmaple。
第 13~22 行是来自于 http://bar.other 的服务端响应。响应中携带了响应首部字段 Access-Control-Allow-Origin(第 16 行)。使用 Origin 和 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 就能完成最简单的访问控制。本例中,服务端返回的 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * 表明,该资源可以被任意外域访问。如果服务端仅允许来自 http://foo.example 的访问,该首部字段的内容如下:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://foo.example
预检请求
需预检的请求 要求必须首先使用 OPTIONS 方法发起一个预检请求到服务器,以获知服务器是否允许该实际请求。(由浏览器自动完成,无需前端发送)
注:真正请求的控制由预检OPTIONS请求获取的服务端response控制,如:Access-Control-Allow-Headers
当请求满足下述任一条件时,即应首先发送预检请求:
- 使用了下面任一 HTTP 方法:
PUTDELETECONNECTOPTIONSTRACEPATCH
- HTTP的头信息超出以下几种字段设置:
AcceptAccept-LanguageContent-LanguageContent-TypeDPRDownlinkSave-DataViewport-WidthWidth
Content-Type的值不属于下列之一:application/x-www-form-urlencodedmultipart/form-datatext/plain
- 请求中的XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象注册了任意多个事件监听器。
- 请求中使用了ReadableStream对象。
如下是一个需要执行预检请求的 HTTP 请求:
var invocation = new XMLHttpRequest();var url = 'http://bar.other/resources/post-here/';var body = '<?xml version="1.0"?><person><name>Arun</name></person>';function callOtherDomain(){if(invocation){invocation.open('POST', url, true);invocation.setRequestHeader('X-PINGOTHER', 'pingpong');invocation.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/xml');invocation.onreadystatechange = handler;invocation.send(body);}}......
上面的代码使用 POST 请求发送一个 XML 文档,该请求包含了一个自定义的请求首部字段(X-PINGOTHER: pingpong)。另外,该请求的 Content-Type 为 application/xml。因此,该请求需要首先发起预检请求。

浏览器完成的预检请求:
OPTIONS /resources/post-here/ HTTP/1.1Host: bar.otherUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10.5; en-US; rv:1.9.1b3pre) Gecko/20081130 Minefield/3.1b3preAccept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflateAccept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7Connection: keep-aliveOrigin: http://foo.exampleAccess-Control-Request-Method: POSTAccess-Control-Request-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-TypeHTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Mon, 01 Dec 2008 01:15:39 GMTServer: Apache/2.0.61 (Unix)Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://foo.exampleAccess-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, OPTIONSAccess-Control-Allow-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-TypeAccess-Control-Max-Age: 86400Vary: Accept-Encoding, OriginContent-Encoding: gzipContent-Length: 0Keep-Alive: timeout=2, max=100Connection: Keep-AliveContent-Type: text/plain
预检请求完成之后,发送实际请求:
POST /resources/post-here/ HTTP/1.1Host: bar.otherUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10.5; en-US; rv:1.9.1b3pre) Gecko/20081130 Minefield/3.1b3preAccept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflateAccept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7Connection: keep-aliveX-PINGOTHER: pingpongContent-Type: text/xml; charset=UTF-8Referer: http://foo.example/examples/preflightInvocation.htmlContent-Length: 55Origin: http://foo.examplePragma: no-cacheCache-Control: no-cache<?xml version="1.0"?><person><name>Arun</name></person>HTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Mon, 01 Dec 2008 01:15:40 GMTServer: Apache/2.0.61 (Unix)Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://foo.exampleVary: Accept-Encoding, OriginContent-Encoding: gzipContent-Length: 235Keep-Alive: timeout=2, max=99Connection: Keep-AliveContent-Type: text/plain[Some GZIP'd payload]
浏览器检测到,从 JavaScript 中发起的请求需要被预检。从上面的报文中,我们看到,第 1~12 行发送了一个使用 OPTIONS 方法的预检请求。OPTIONS 是 HTTP/1.1 协议中定义的方法,用以从服务器获取更多信息。该方法不会对服务器资源产生影响。 预检请求中同时携带了下面两个首部字段:
Access-Control-Request-Method: POSTAccess-Control-Request-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-Type
首部字段 Access-Control-Request-Method 告知服务器,实际请求将使用 POST 方法。首部字段 Access-Control-Request-Headers 告知服务器,实际请求将携带两个自定义请求首部字段:X-PINGOTHER 与 Content-Type。服务器据此决定,该实际请求是否被允许。
第14~26 行为预检请求的响应,表明服务器将接受后续的实际请求。重点看第 17~20 行:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://foo.exampleAccess-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, OPTIONSAccess-Control-Allow-Headers: X-PINGOTHER, Content-TypeAccess-Control-Max-Age: 86400
首部字段Access-Control-Allow-Methods表明服务器允许客户端使用POST, GET和 OPTIONS 方法发起请求。
首部字段 Access-Control-Allow-Headers表明服务器允许请求中携带字段 X-PINGOTHER与Content-Type。与Access-Control-Allow-Methods一样,Access-Control-Allow-Headers 的值为逗号分割的列表。
最后,首部字段 Access-Control-Max-Age 表明该响应的有效时间为 86400 秒,也就是 24 小时。在有效时间内,浏览器无须为同一请求再次发起预检请求。请注意,浏览器自身维护了一个最大有效时间,如果该首部字段的值超过了最大有效时间,将不会生效。
预检请求与重定向
大多数浏览器不支持针对于预检请求的重定向。如果一个预检请求发生了重定向,浏览器将报告错误。
有两种方式规避上述报错行为:
- 在服务端去掉对预检请求的重定向;
- 将实际请求变成一个简单请求。
如果上面两种方式难以做到,我们仍有其他办法:
- 发出一个简单请求(使用 Response.url 或 XHR.responseURL)以判断真正的预检请求会返回什么地址。
- 发出另一个请求(真正的请求),使用在上一步通过Response.url 或 XMLHttpRequest.responseURL获得的URL。
附带身份凭证的请求
Fetch 与 CORS 的一个有趣的特性是,可以基于 HTTP cookies 和 HTTP 认证信息发送身份凭证。一般而言,对于跨域 XMLHttpRequest 或 Fetch 请求,浏览器不会发送身份凭证信息。如果要发送凭证信息,需要设置 XMLHttpRequest的某个特殊标志位。
本例中,http://foo.example 的某脚本向 http://bar.other 发起一个GET 请求,并设置 Cookies:
var invocation = new XMLHttpRequest();var url = 'http://bar.other/resources/credentialed-content/';function callOtherDomain(){if(invocation) {invocation.open('GET', url, true);invocation.withCredentials = true;invocation.onreadystatechange = handler;invocation.send();}}
第 7 行将 XMLHttpRequest的 withCredentials 标志设置为 true,从而向服务器发送 Cookies。因为这是一个简单 GET 请求,所以浏览器不会对其发起预检请求。但是,如果服务器端的响应中未携带 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true ,浏览器将不会把响应内容返回给请求的发送者。

客户端与服务器端交互示例如下:
GET /resources/access-control-with-credentials/ HTTP/1.1Host: bar.otherUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10.5; en-US; rv:1.9.1b3pre) Gecko/20081130 Minefield/3.1b3preAccept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflateAccept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7Connection: keep-aliveReferer: http://foo.example/examples/credential.htmlOrigin: http://foo.exampleCookie: pageAccess=2HTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Mon, 01 Dec 2008 01:34:52 GMTServer: Apache/2.0.61 (Unix) PHP/4.4.7 mod_ssl/2.0.61 OpenSSL/0.9.7e mod_fastcgi/2.4.2 DAV/2 SVN/1.4.2X-Powered-By: PHP/5.2.6Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://foo.exampleAccess-Control-Allow-Credentials: trueCache-Control: no-cachePragma: no-cacheSet-Cookie: pageAccess=3; expires=Wed, 31-Dec-2008 01:34:53 GMTVary: Accept-Encoding, OriginContent-Encoding: gzipContent-Length: 106Keep-Alive: timeout=2, max=100Connection: Keep-AliveContent-Type: text/plain[text/plain payload]
即使第 11 行指定了 Cookie 的相关信息,但是,如果 bar.other 的响应中缺失 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true(第 19 行),则响应内容不会返回给请求的发起者。
附带身份凭证的请求与通配符
对于附带身份凭证的请求,服务器不得设置 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 的值为“*”。
这是因为请求的首部中携带了 Cookie 信息,如果 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 的值为 *,请求将会失败。而将 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 的值设置为 http://foo.example,则请求将成功执行。
解决方案
nginx 后端配置跨域
在nginx 中配置如下配置:
location /router {add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET,POST,OPTIONS';add_header Access-Control-Expose-Headers 'Content-Length,Content-Range';add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true;add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers 'DNT,X-Mx-ReqToken,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization';if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {return 204;}if ($request_method = 'POST') {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:6541;}}
注:204 -> No Content
如需控制访问域名正则,配置如下:
location /router {if ($host !~ '.*\.(example1|example2)\.net') {return 403;}# ...}
后端代码实现
对于需要预检的请求,PHP代码示例:
<?phpif($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "GET"){header('Content-Type: text/plain');echo "This HTTP resource is designed to handle POSTed XML input from arunranga.com and not be retrieved with GET";}elseif($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "OPTIONS"){// 告诉客户端我们支持来自 arunranga.com 的请求并且预请求有效期将仅有20天if($_SERVER['HTTP_ORIGIN'] == "http://arunranga.com"){header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://arunranga.com');header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, OPTIONS');header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-PINGARUNER');header('Access-Control-Max-Age: 1728000');header("Content-Length: 0");header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true');header("Content-Type: text/plain");//exit(0);}else{header("HTTP/1.1 403 Access Forbidden");header("Content-Type: text/plain");echo "You cannot repeat this request";}}elseif($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST"){/* 通过首先获得XML传送过来的blob来处理POST请求,然后做一些处理, 最后将结果返回客户端*/if($_SERVER['HTTP_ORIGIN'] == "http://arunranga.com"){$postData = file_get_contents('php://input');$document = simplexml_load_string($postData);// 对POST过来的数据进行一些处理$ping = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_PINGARUNER'];header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://arunranga.com');header('Content-Type: text/plain');header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true');echo // 处理之后的一些响应}elsedie("POSTing Only Allowed from arunranga.com");}elsedie("No Other Methods Allowed");?>
通过 jsonp 跨域
缺点:只能实现get一种请求
vue 示例如下:
this.$http.jsonp('http://www.domain.com/login', {params: {},jsonp: 'onBack'}).then((res) => {console.log(res);})
常见报错
重定向
The request was redirected to 'https://example.com/foo', which is disallowed for cross-origin requests that require preflight
头部错误
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource
添加了跨域服务器不允许的自定义头
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://www.example.com/cors. Request header field custom_heaer is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response.
未设置允许某种复杂请求
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://www.example.com/cors. Method PUT is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Methods in preflight response.
预处理请求没常处理
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://www.example.com/cors?allow_method=PUT. Response for preflight has invalid HTTP status code 405
来源地址不是服务器所允许的来源地址
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://example.com/cors?allow_method=PUT. Response to preflight request doesn't pass access control check: The 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header has a value 'http://www.movesun.com' that is not equal to the supplied origin. Origin 'http://movesun.com' is therefore not allowed access.
前端设置了携带身份凭证标志,但是跨域服务器不允许携带,没有设置 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials:true
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://example.com/cors?allow_method=PUT. Credentials flag is 'true', but the 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' header is ''. It must be 'true' to allow credentials. Origin 'http://movesun.com' is therefore not allowed access.
前端尝试在真实请求中携带身份凭证Cookie,跨域服务器允许携带Cookie
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://example.com/cors?allow_method=PUT. A wildcard '*' cannot be used in the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header when the credentials flag is true. Origin 'http://movesun.com' is therefore not allowed access. The credentials mode of an XMLHttpRequest is controlled by the withCredentials attribute.
参考文章:
阮一峰【跨域资源共享 CORS 详解】
MDN web docs【CORS】
跨域资源共享标准
MDN web docs【HTTP访问控制(CORS)】
CORS wiki

