1、从 main 函数开始
我们先在在 main 函数中打一个断点,并且再添加一个 _objc_init 的符号断点,方便看调用栈状态。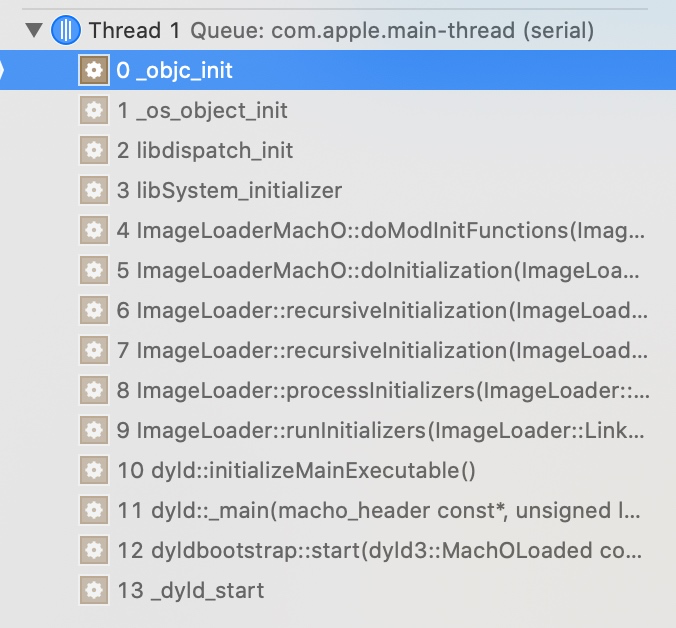
加载流程如下图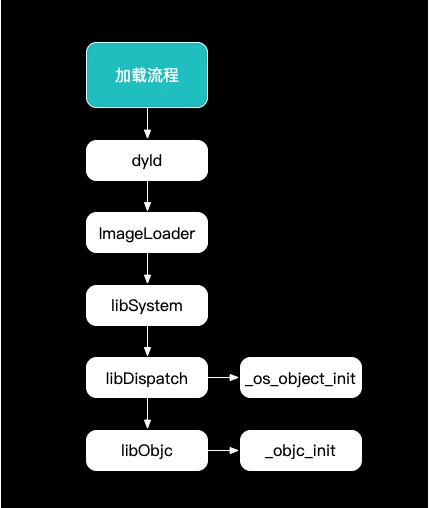
2、alloc探索
我们先在main函数里面新建一个 ZLPerson 类,然后在 alloc 处下一个断点
然后我们使用 control + in 命令进入之后可以看出
alloc 调用的其实是 objc_alloc 函数
3、探索 libObjc 源码
然后我们把源码挂载到我们项目当中,然后通过断点分析,得到以下流程: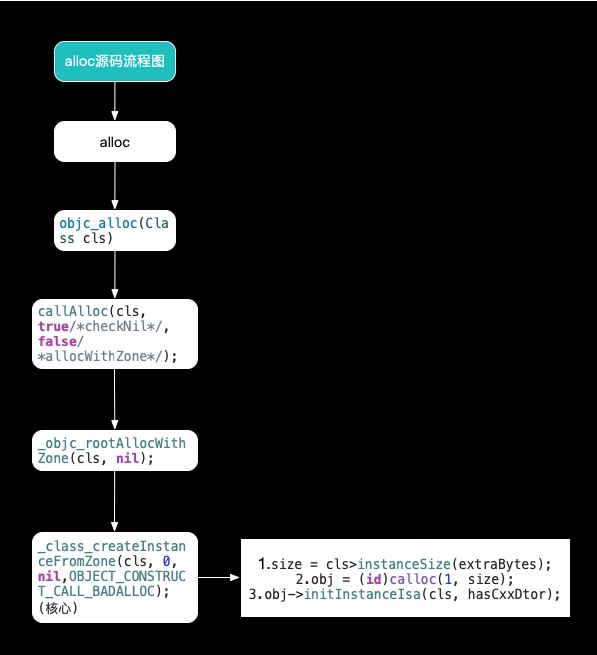
让我们配合源码信息进行分析
3.1 callAlloc源码分析
static ALWAYS_INLINE idcallAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false){#if __OBJC2__if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(cls, nil);}#endif// No shortcuts available.if (allocWithZone) {return ((id(*)(id, SEL, struct _NSZone *))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(allocWithZone:), nil);}return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(alloc));}
fastpath(x)表示x很可能不为0;slowpath(x)表示x很可能为0。——这里表示cls大概率是有值的,编译器可以不用每次都读取 return nil 指令,都是希望编译器进行优化。
3.2 核心创建实例 _class_createInstanceFromZone 分析
static ALWAYS_INLINE id_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,int construct_flags = OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_NONE,bool cxxConstruct = true,size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil){ASSERT(cls->isRealized());// Read class's info bits all at once for performancebool hasCxxCtor = cxxConstruct && cls->hasCxxCtor();bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();size_t size;// 获取cls的实例内存大小,extraBytes为0size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;id obj;if (zone) {obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);} else {// 根据实例size开辟内存obj = (id)calloc(1, size);}if (slowpath(!obj)) {if (construct_flags & OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC) {return _objc_callBadAllocHandler(cls);}return nil;}if (!zone && fast) {// 将cls和是否有c++析构器传入给initInstanceIsa,实例化isaobj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);} else {// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be// doing something weird with the zone or RR.obj->initIsa(cls);}if (fastpath(!hasCxxCtor)) {return obj;}construct_flags |= OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_FREE_ONFAILURE;return object_cxxConstructFromClass(obj, cls, construct_flags);}

