前言
在 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 中介绍了创建 Bean 的流程大概流程,这里进入单例 Bean 的创建过程。
这里主要分为三个部分创建单例 Bean
- getSingleton
- createBean
- getObjectForBeanInstance
getSingleton
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");// 加锁synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {// 检查 singletonObjects 缓存中是否有Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);if (singletonObject == null) {// 检查是否在执行销毁if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");}if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");}// 将 Bean 添加到 singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 集合中, 表示正在创建beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);boolean newSingleton = false;boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();}try {// 调用工厂方法// 也就是调用 createBean(beanName, mbd, args)singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();newSingleton = true;}catch (IllegalStateException ex) {// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);if (singletonObject == null) {throw ex;}}catch (BeanCreationException ex) {if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);}}throw ex;}finally {if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {this.suppressedExceptions = null;}// 创建成功, 从 singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 移除afterSingletonCreation(beanName);}if (newSingleton) {// 将给定的单例对象添加到该工厂的单例缓存中// this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);// this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);// this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);// this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);}}return singletonObject;}}
返回以给定名称注册的(原始)单例对象,如果尚未注册,则创建并注册一个新对象。
这一块一共可以拆成三部分来理解: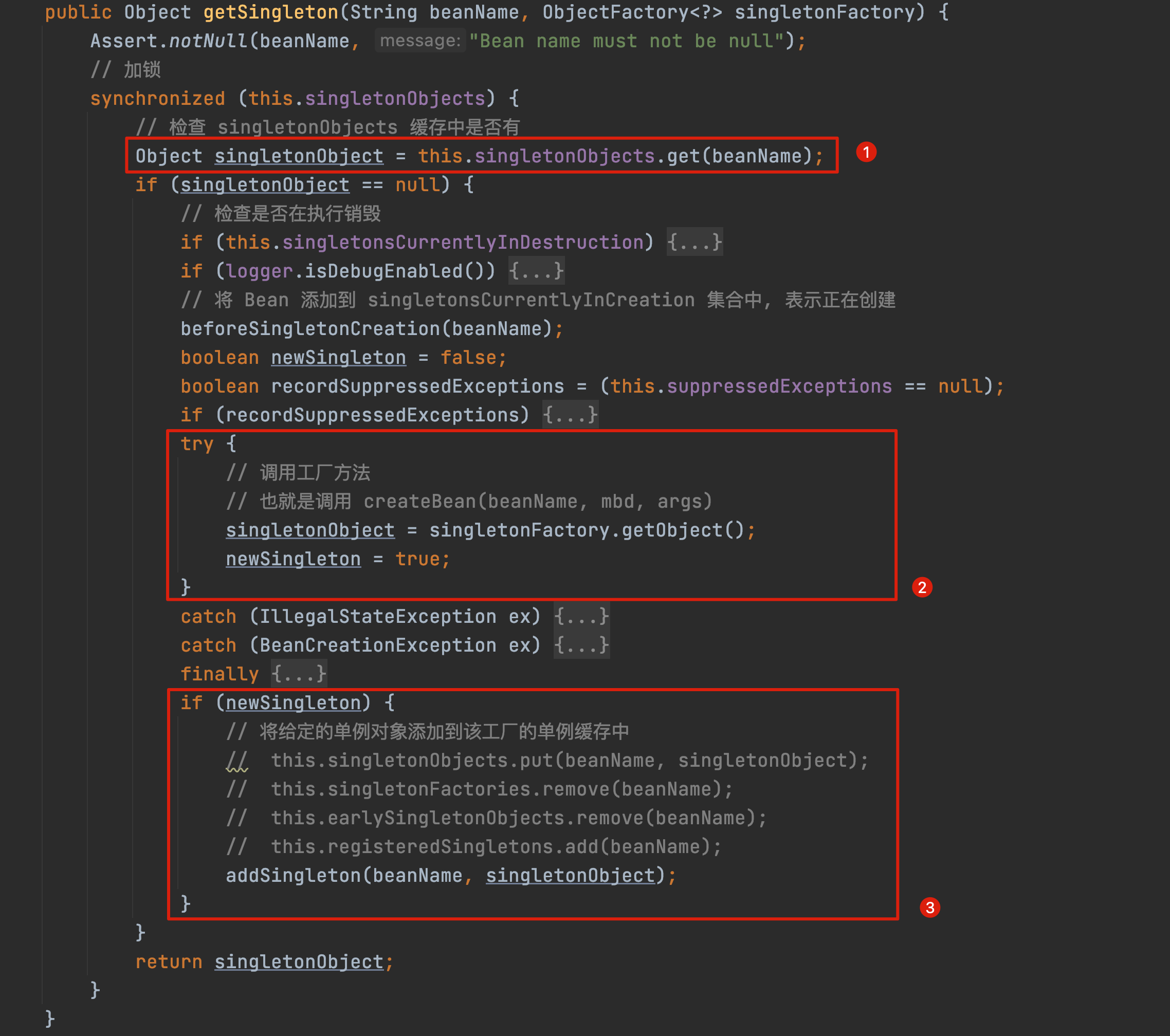
1. 从缓存中获取 singletonObjects
singletonObject 是什么?
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
singletonObjects 是一个 ConcurrentHashMap, 用来缓存单例对象的实例。
2. 创建 singletonObject
在从缓存中没有获取到 singletonObject ,创建新的对象singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
这一步其实就是调用外边的 createBean(beanName, mbd, args) 方法,这是一个工厂方法。 通过 createBean 方法,会创建一个新的 singletonObject。
3. 将创建的 singletonObject 添加到缓存中
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);// 已经成功创建的单例this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);}}
这一步涉及到三个缓存,以及一个成功创建的单例列表。
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. *//** 缓存单例对象, K-V -> BeanName - Bean 实例 */private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. *//** 缓存 Bean 工厂 */private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. *//** 缓存早期单例对象 */private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);/** Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order. *//** 已注册的单例列表,按注册顺序保存 BeanName。 */private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(256);
将创建的单例对象,添加到单例缓存中,同时将工厂缓存以及早期单例对象缓存中的对应对象删除。
createBean
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");}RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.// 获取真实的类型Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {// 创建新的 mbd 防止 其他线程修改mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);}// Prepare method overrides.try {// 验证并准备为此bean定义的方法替代。 检查是否存在具有指定名称的方法。mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();}catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);}try {// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.// 应用实例化之前的后处理器,以解决指定的bean是否存在实例化快捷方式。// InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 后置处理器// postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法可能会已经实例化 BeanObject bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);if (bean != null) {return bean;}}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);}try {// 实例化 BeanObject beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");}return beanInstance;}catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);}}
这个方法中涉及到:创建 Bean 实例 , 填充 Bean , 应用 PostProcessor。
其中实例化 Bean 是在 doCreateBean 中。现在重点看一下 doCreateBean 方法。
doCreateBean
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {// Instantiate the bean.// Bean 的 对象包装BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;if (mbd.isSingleton()) {// 从缓存中获取instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);}if (instanceWrapper == null) {// 缓存中获取不到则直接创建, 这里创建的 BeanInstance !!!instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);}// 获取 Bean 实例以及类型Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();if (beanType != NullBean.class) {mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;}// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {if (!mbd.postProcessed) {try {// 如果允许修改 mbd// 调用 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 后置处理器的// postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);}mbd.postProcessed = true;}}// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.// mbd 是单例 且 允许循环引用, (默认 true) 且在创建boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));if (earlySingletonExposure) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");}// 先获取 之前的 Bean 的引用, 从 beanPostProcessorCache 中 获取 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor// 然后从 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#getEarlyBeanReference 获取之前的引用addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));}// Initialize the bean instance.Object exposedObject = bean;try {// 属性赋值populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);// 执行 init 方法exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);}catch (Throwable ex) {if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {throw (BeanCreationException) ex;}else {throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);}}// 这里允许循环依赖if (earlySingletonExposure) {// 获取早期的 Bean, 如果没有循环依赖 则获取不到Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);// 有循环依赖if (earlySingletonReference != null) {// 创建的是不是同一个,可能会有代理对象if (exposedObject == bean) {exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;}else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {// 获取依赖的 Bean 并 循环放入到 actualDependentBeansString[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);}}if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");}}}}// Register bean as disposable.try {// 注册销毁方法registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);}catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);}return exposedObject;}
同样是代码很长很长!
分步骤阅读:
如果这个 Bean 是单例 Bean 且允许循环引用且在创建中,则说明在有循环引用。则调用:addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
这一行代码涉及到两个方法,分别是 getEarlyBeanReference 和 addSingletonFactory
- getEarlyBeanReference
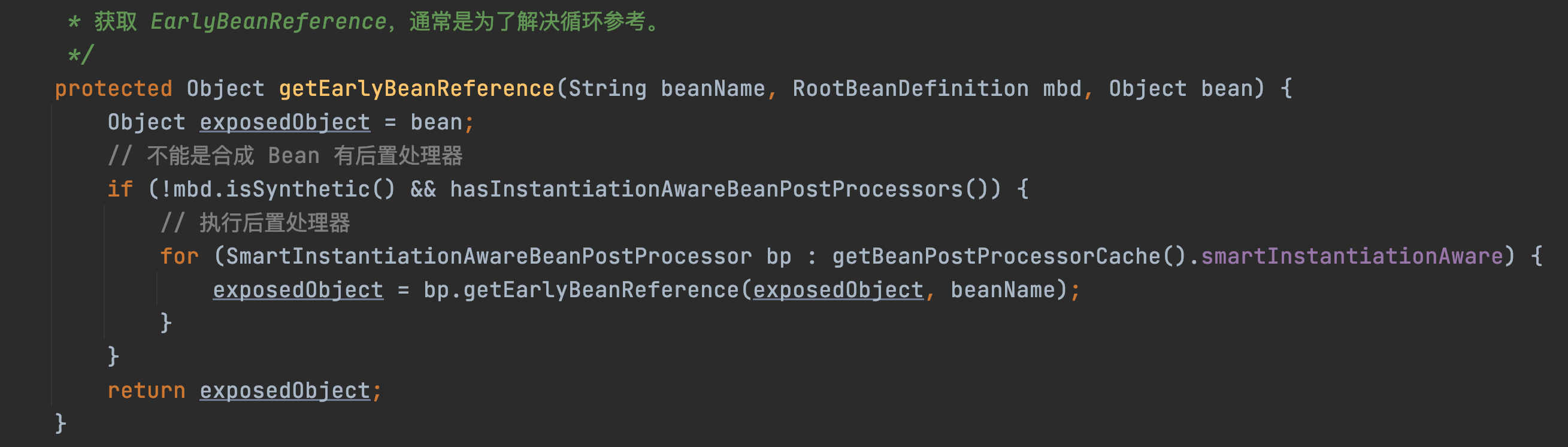
- addSingletonFactory

这一块可以看到将创建的一个单例对象的 singletonFactory 添加到了 singletonFactories 缓存中。
同时将 earlySingletonObjects 缓存中的单例对象移除。
那什么时候添加到 earlySingletonObjects 缓存中的呢?
这块可以参考 Spring 源码学习 15:finishBeanFactoryInitialization 在 getSingleton 方法中 put 进去的。
为了方便,我把这一小块代码也贴出来: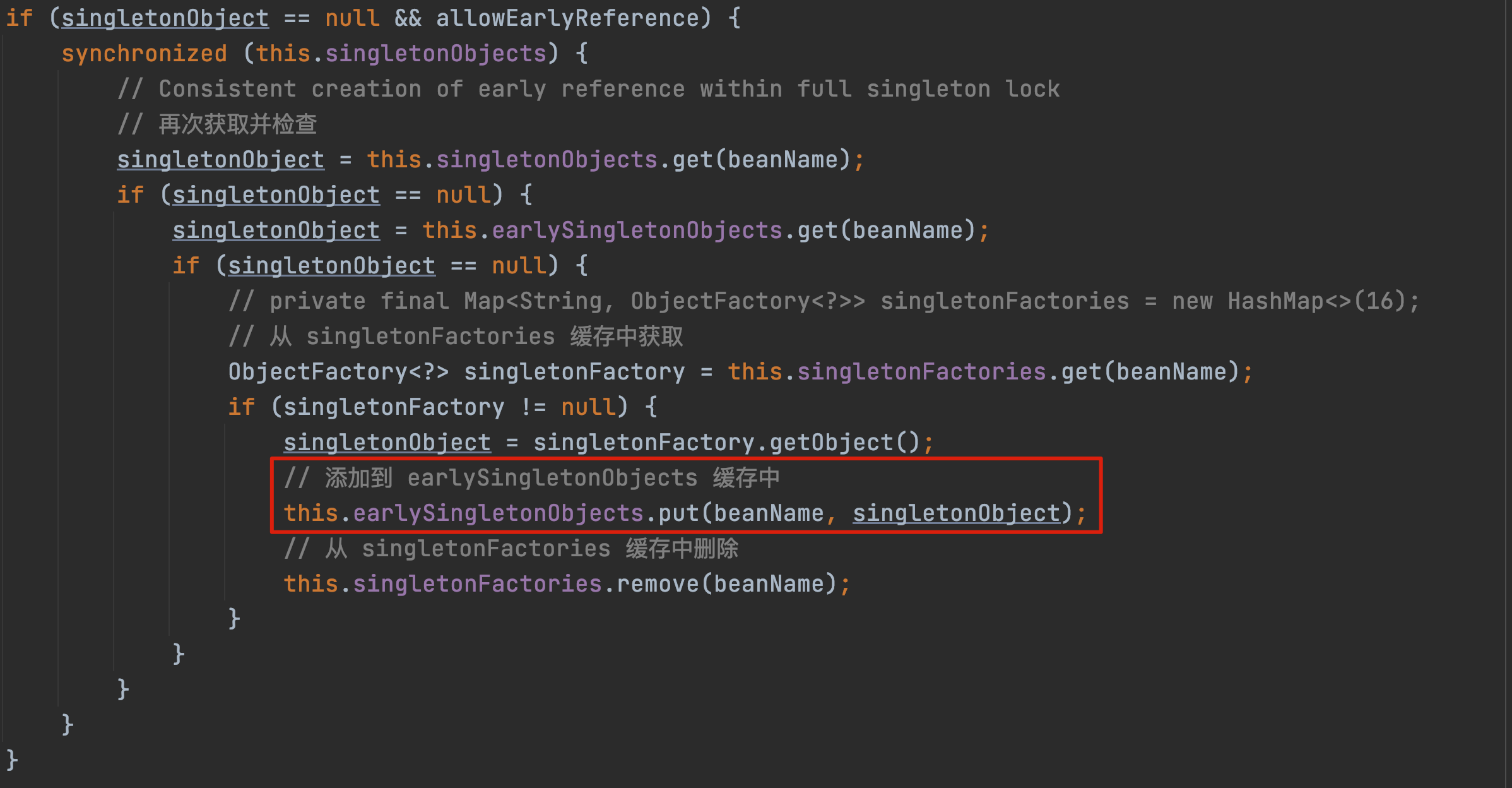
在这里将缓存从 singletonFactories 移到了 earlySingletonObjects。
Spring 的 Bean 实例化的时候用到的三级缓存其实是:
singletonObjects: 一级缓存,存储单例对象,Bean 已经实例化,初始化完成。
earlySingletonObjects: 二级缓存,存储 singletonObject,这个 Bean 实例化了,还没有初始化。
singletonFactories: 三级缓存,存储 singletonFactory
下面会初始化 Bean
这里关注重点关注下面一部分: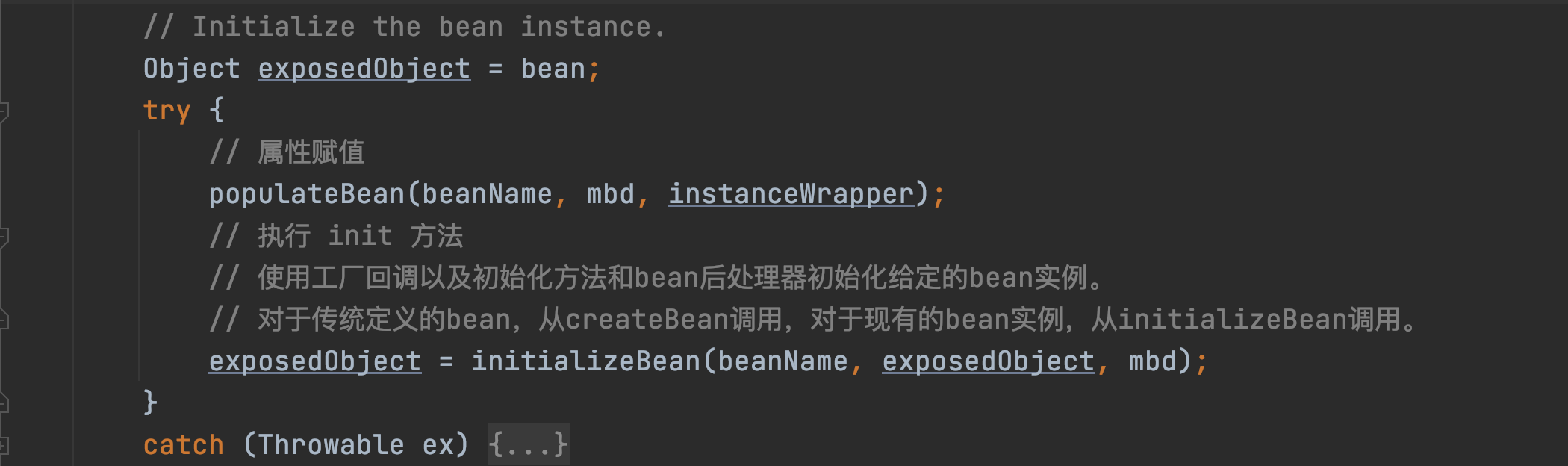
- populateBean
对 Bean 的属性进行赋值。
这块需要注意的是,在对属性进行赋值时,发现依赖了其他 Bean,就会去先创建其他 Bean。
我这边使用的注解 _@_Autowired 就会执行下面一部分: 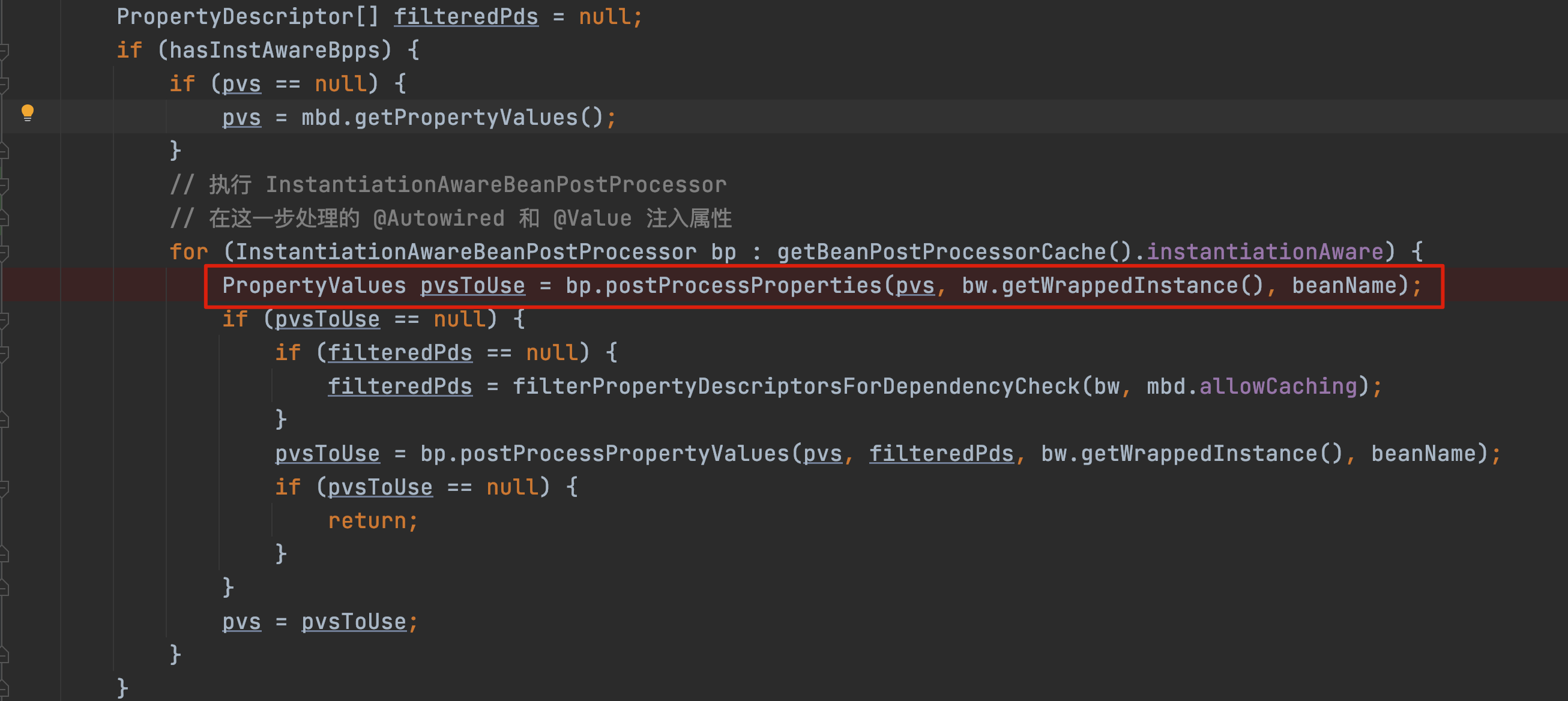
在这里解析属性的时候,就会去创建内部依赖的 Bean。
-
getObjectForBeanInstance
获取给定bean实例的对象,如果是FactoryBean,则为bean实例本身或其创建的对象。
这一块逻辑相对比较简单,就是根据前面你创建的 beanInstance , 判断其类型,从而创建 Bean 实例。总结
本文主要介绍了一个 单例 Bean 的创建,当然都是大块大块的源码,需要耐心的啃。
阅读完源码,基本上对循环依赖能有个详细的了解,知道 Spring 在初始化 Bean 的时候是使用三级缓存来处理循环依赖的额,而后面则会单独准备一篇文章对循环依赖做介绍。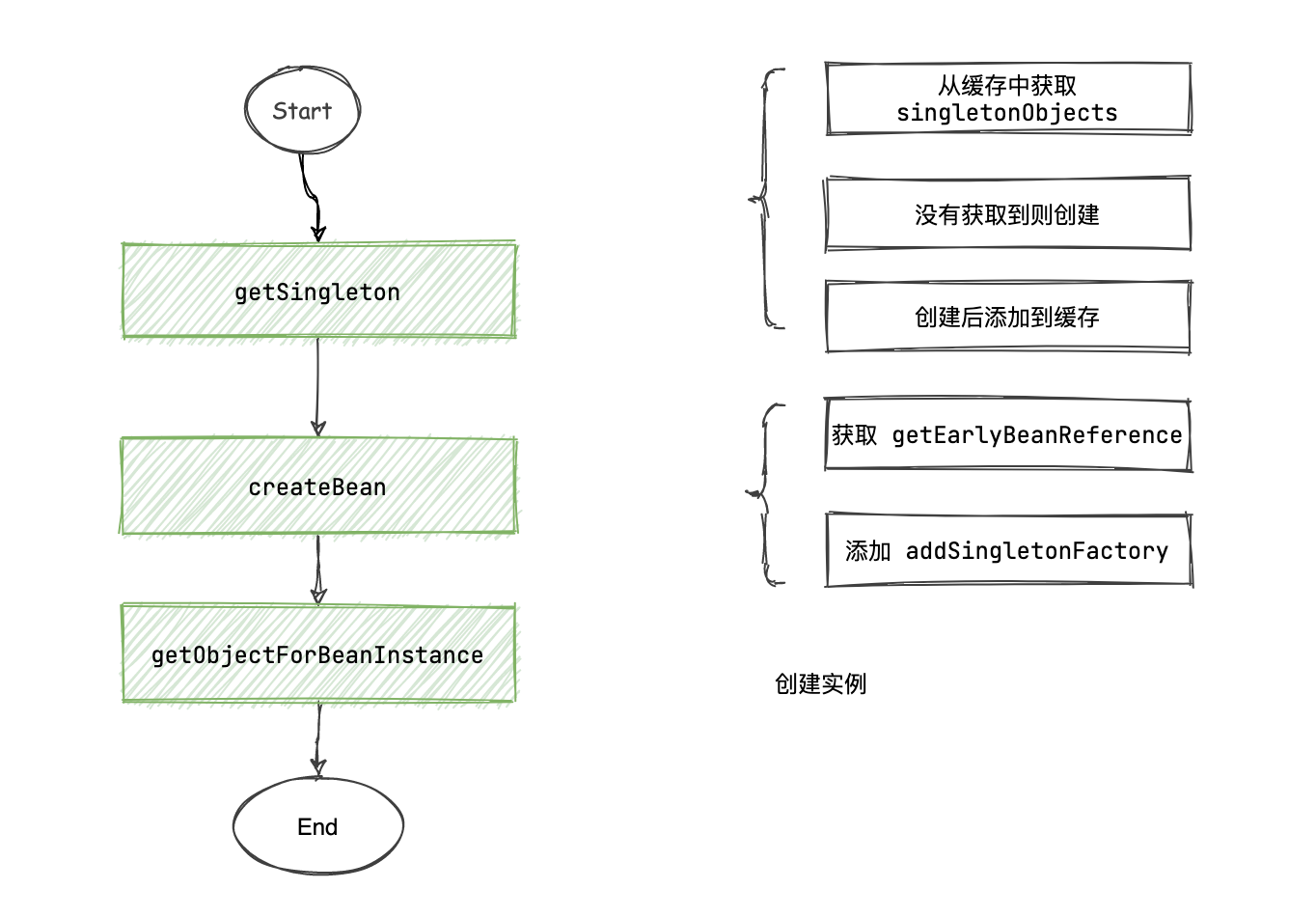
相关推荐
- Spring 源码学习 14:initApplicationEventMulticaster
- Spring 源码学习 13:initMessageSource

