- 剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
- 剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
- 剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字">剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
- 剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树">剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
- 剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III">剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
- 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制">剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
- 剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串">剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
- 面试题 17.24. 最大子矩阵">面试题 17.24. 最大子矩阵
- 2. 两数相加">2. 两数相加
- 3.无重复字符的最长子串
- 4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数">4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
- 5. 最长回文子串">5. 最长回文子串
- 9. 回文数">9. 回文数
- 13. 罗马数字转整数">13. 罗马数字转整数
- 11.盛最多水的容器
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点">19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 20.有效的括号
- 21. 合并两个有序链表">21. 合并两个有序链表
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组">33. 搜索旋转排序数组
- 35. 搜索插入位置">35. 搜索插入位置
- 46. 全排列">46. 全排列
- 50. Pow(x, n)">50. Pow(x, n)
- 51. N 皇后">51. N 皇后
- 59. 螺旋矩阵 II">59. 螺旋矩阵 II
- 69. Sqrt(x)">69. Sqrt(x)
- 74.搜索二维矩阵
- 77. 组合">77. 组合
- 88. 合并两个有序数组">88. 合并两个有序数组
- 92. 反转链表 II">92. 反转链表 II
- 101.对称二叉树
- 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历">103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 110.平衡二叉树
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度">111. 二叉树的最小深度
- 路径总和">112.路径总和
- 路径总和 II">113.路径总和 II
- 142. 环形链表 II">142. 环形链表 II
- 155. 最小栈">155. 最小栈
- 160. 相交链表">160. 相交链表
- 189. 旋转数组">189. 旋转数组
- 191. 位1的个数">191. 位1的个数
- 206. 反转链表">206. 反转链表
- 209. 长度最小的子数组">209. 长度最小的子数组
- 213. 打家劫舍 II">213. 打家劫舍 II
- 翻转二叉树">226.翻转二叉树
- 225. 用队列实现栈">225. 用队列实现栈
- 231. 2 的幂">231. 2 的幂
- 232. 用栈实现队列">232. 用栈实现队列
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先">236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II">240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
- 283. 移动零">283. 移动零
- 404. 左叶子之和">404. 左叶子之和
- 415. 字符串相加">415. 字符串相加
- 437. 路径总和 III">437. 路径总和 III
- 485. 最大连续 1 的个数">485. 最大连续 1 的个数
- 503. 下一个更大元素 II">503. 下一个更大元素 II
- 二叉树的直径">543.二叉树的直径
- 566. 重塑矩阵">566. 重塑矩阵
- 572. 另一个树的子树">572. 另一个树的子树
- 合并二叉树">617.合并二叉树
- 687. 最长同值路径">687. 最长同值路径
- 739. 每日温度">739. 每日温度
1.String转char [] 数组char[] str=s.toCharArray();
剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
分析:题目限定数组长度n,数组中的值在 0~n-1 的范围内
方法一:
class Solution {public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {int [] tags=new int[nums.length];int res=-1;for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){tags[nums[i]]++;if(tags[nums[i]]>1){res=nums[i];break;}}return res;}}
方法二:
当条件 **nums[i]!=i**和**nums[i]==nums[nums[i]]**同时满足时说明在两个不同的索引位置 **i** 和 **nums[i]** 出现了相同的数字,nums[i]重复
class Solution {public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){if(nums[i]!=i){if(nums[i]==nums[nums[i]]){return nums[i];}/*Swap*/int temp=nums[i];nums[i]=nums[temp];nums[temp]=temp;}}return -1;}}
/*---------*/当重复数字是0时这种方法不通过测试用例:[2, 3, 1, 0, 0, 5]测试结果:-1期望结果:0/*---------*/
剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
class Solution {public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {return false;}int m=matrix.length,n=matrix[0].length; //m-行数 n-列数int i=0,j=n-1;while(i<m&&j>=0){if(target==matrix[i][j]){return true;}else if(target>matrix[i][j]){i++;}else {j--;}}return false;}}
剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
class Solution {public int minArray(int[] numbers) {int l=0,r=numbers.length-1;while(l<=r){int mid=(r-l)/2+l;if(numbers[mid]>numbers[r]) l=mid+1;else if(numbers[mid]<numbers[r]) r=mid;//需要写else if 不然第一个if和后面的if else是分开的两组条件else r--;}return numbers[l];}}
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
class Solution {public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return new int[0];Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();queue.add(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode p=queue.poll();ans.add(p.val);if(p.left!=null){queue.add(p.left);}if(p.right!=null){queue.add(p.right);}}int[] res = new int[ans.size()];for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)res[i] = ans.get(i);return res;}}
剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();if(root==null) return res;Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();q.add(root);while(!q.isEmpty()){List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();int LevelSize = q.size();for(int i=0;i<LevelSize;i++){root=q.poll();level.add(root.val);if(root.right!=null){q.add(root.right);}if(root.left!=null){q.add(root.left);}}if(res.size() % 2 == 0) Collections.reverse(level);res.add(level);}return res;}}
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if(head == null) return null;Node cur = head;Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射while(cur != null) {map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));cur = cur.next;}cur = head;// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向while(cur != null) {map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);cur = cur.next;}// 5. 返回新链表的头节点return map.get(head);}}
剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
class Solution {public int translateNum(int num) {String s = String.valueOf(num);int[] dp = new int[3];dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;dp[2] = 1; //当只有1位时,返回结果应该是1for(int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i ++){String temp = s.substring(i-2, i);if(temp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && temp.compareTo("25") <= 0)dp[2] = dp[1] + dp[0];elsedp[2] = dp[1];dp[0]=dp[1];dp[1]=dp[2];}return dp[2];}}
面试题 17.24. 最大子矩阵
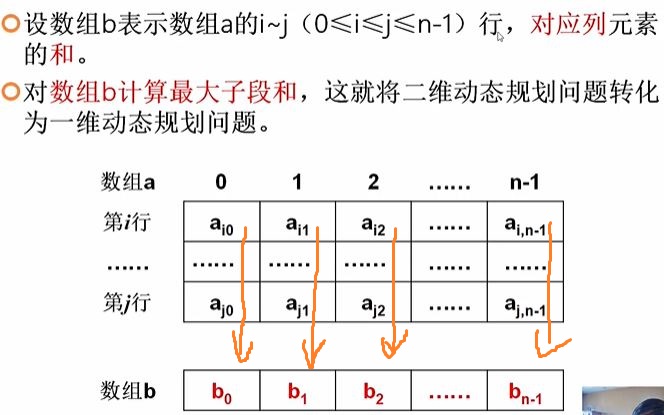
class Solution {public int[] getMaxMatrix(int[][] matrix) {int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;int dp=0,start=0;int[] ans=new int[] {-1,-1,200,200};//结果int[] sum=null;//纵向累加数组 竖线for(int i=0;i<matrix.length;i++) {sum=new int[matrix[0].length];for(int j=i;j<matrix.length;j++) {//从i到j的竖线dp=0;start=0;for(int k=0;k<sum.length;k++) {sum[k]+=matrix[j][k];dp+=sum[k];if(max<dp) {ans[0]=i;ans[1]=start;ans[2]=j;ans[3]=k;max=dp;}if(dp<0) {dp=0;start=k+1;}}}}return ans;}}
2. 两数相加
解析
数字已经是逆置的了,所以只需要保存进位即可,最后进位大于0需要多一个节点—对于类似(5+7=12)多了一位。
class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode head=null,tail=null;int carry=0;while(l1!=null||l2!=null){int n1 = l1 == null? 0:l1.val;int n2 = l2 == null? 0:l2.val;int sum = n1+n2+carry;carry = sum /10;if(head==null) head = tail = new ListNode(sum%10);else{tail.next = new ListNode(sum%10);tail = tail.next;}if(l1!=null) l1 = l1.next;if(l2!=null) l2 = l2.next;}if(carry>0) tail.next = new ListNode(carry);return head;}}
3.无重复字符的最长子串
解析:滑动窗口 —滑动窗口算法的本质是双指针法中的左右指针法,滑动窗口算法是双指针法中的左右指针法更为形象的一种表达方式。
滑动窗口算法可以用以解决数组、字符串的子元素问题。所谓滑动窗口,就像描述的那样,可以理解成是一个会滑动的窗口,每次记录下窗口的状态,再找出符合条件的适合的窗口。它可以将嵌套的循环问题,更高效的解决。
找出从l开始的最长不重复子串,res存储最大长度,r指示子串的结尾,用set存储子串中的字符,r每次移动将字符加入set
优化1,当剩余长度已经小于res,提前结束
优化2,左指针每次移动时直接移到内层循环退出时导致重复的那个字符后一位
class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {Set<Character> set=new HashSet<>();//存储从l到r的子串字符int l=0,r=0,res=0;while(l<s.length()){if(res>s.length()-l-1)//长度减1才是下标break;//提前结束while(r<s.length()&&!set.contains(s.charAt(r))){set.add(s.charAt(r));r++;}res=Math.max(res,r-l);while(r<s.length()&&set.contains(s.charAt(r))){//set.remove(s.charAt(l));l++;}}return res;}}
4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
方法一:归并排序得到数组取中位数,时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m+n)
class Solution {public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {int m=nums1.length,n=nums2.length;if(m==0){if(n%2==0){return (nums2[n/2-1]+nums2[n/2])/2.0;}else{return nums2[n/2];}}if(n==0){if(m%2==0){return (nums1[m/2-1]+nums1[m/2])/2.0;}else{return nums1[m/2];}}int [] nums=new int [m+n];int count=0;int i=0,j=0;while(count!=(m+n)){if(i==m){while(j!=n)nums[count++]=nums2[j++];break;//防止下面数组越界}if(j==n){while(i!=m)nums[count++]=nums1[i++];break;//}if(nums1[i]<nums2[j]){nums[count++]=nums1[i++];}else{nums[count++]=nums2[j++];}}if((m+n)%2==0){return (nums[(m+n)/2-1]+nums[(m+n)/2])/2.0;}else{return nums[(m+n)/2];}}}
方法二:不需要将两个数组真的合并,我们只需要找到中位数在哪里就可以了,用两个变量 left 和 right保存中间数,用 aStart 和 bStart 分别表示当前指向 A 数组和 B 数组的位置.时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {int m=nums1.length,n=nums2.length;int left=-1,right=-1;int aStart=0,bStart=0;int len=m+n;for(int i=0;i<=len/2;i++){left=right;if(aStart<m&&(bStart>=n||nums1[aStart]<nums2[bStart])){right=nums1[aStart++];}else{right=nums2[bStart++];}}if(len%2==0){return (left+right)/2.0;}else{return right;}}}
方法三:看到有序数组首先想到二分查找
5. 最长回文子串
方法一:动态规划,用dp[i][j]
public class Solution {public String longestPalindrome(String s) {int len = s.length();if (len < 2) {return s;}int maxLen = 1;int begin = 0;// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i..j] 是否是回文串boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];// 初始化:所有长度为 1 的子串都是回文串for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {dp[i][i] = true;}char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();// 递推开始// 先枚举子串长度for (int L = 2; L <= len; L++) {// 枚举左边界,左边界的上限设置可以宽松一些for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {// 由 L 和 i 可以确定右边界,即 j - i + 1 = L 得(因为左边界i=j的时候长度是1,所以len=j-i+1)int j = L + i - 1;// 如果右边界越界,就可以退出当前循环if (j >= len) {break;}if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) {dp[i][j] = false;} else {if (j - i < 3) {dp[i][j] = true;} else {dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];}}// 只要 dp[i][L] == true 成立,就表示子串 s[i..L] 是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {maxLen = j - i + 1;begin = i;}}}return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen);}}
方法二:由中心向两边扩散
class Solution {public String longestPalindrome(String s) {if (s == null || s.length() < 1) return "";int start = 0, end = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);int len = Math.max(len1, len2);if (len > end - start) {start = i - (len - 1) / 2;end = i + len / 2;//向下取整,长度为偶数时如baab end=1+4/2=3}}return s.substring(start, end + 1);}private int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {int L = left, R = right;while (L >= 0 && R < s.length() && s.charAt(L) == s.charAt(R)) {L--;R++;}return R - L - 1;}}
9. 回文数
class Solution {public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {if(x<0) return false;int cur = 0;int num = x;while(num != 0) {cur = cur * 10 + num % 10;num /= 10;}return cur == x;}}
13. 罗马数字转整数
class Solution {Map<Character, Integer> symbolValues = new HashMap<Character, Integer>() {{put('I', 1);put('V', 5);put('X', 10);put('L', 50);put('C', 100);put('D', 500);put('M', 1000);}};public int romanToInt(String s) {int res=0;int len=s.length();for(int i=0;i<len;i++){int value = symbolValues.get(s.charAt(i));if((i<len-1)&&value<symbolValues.get(s.charAt(i+1))){res-=value;}else{res+=value;}}return res;}}
11.盛最多水的容器
int l=0,r=height.length-1,res=0;while(l<r){res= height[l]<height[r] ? Math.max(res,height[l++]*(r-l)):Math.max(res,height[r--]*(r-l));//l++先执行了错误}return res;
踩的一个坑--先`height[l++]` 再 `(r-l)` 导致 `l++` 已经执行再计算的 `l-r`
解析:双指针
public int maxArea(int[] height) {int l=0,r=height.length-1,res=0;while(l<r){res= height[l]<height[r] ? Math.max(res,(r-l)*height[l++]):Math.max(res,(r-l)*height[r--]);}return res;}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode pre=new ListNode();pre.next=head;ListNode first=head;ListNode second=pre;int step=0;while(first!=null&&step<n){first=first.next;step++;}while(first!=null){first=first.next;second=second.next;}second.next=second.next.next;return pre.next;}}
20.有效的括号
public boolean isValid(String s) {Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<>();for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){if(s.charAt(i)=='('||s.charAt(i)=='['||s.charAt(i)=='{'){stack.push(s.charAt(i));}else {if(stack.empty()) return false;if(s.charAt(i)==')'){if(stack.peek()!='('){return false;}}if(s.charAt(i)==']'){if(stack.peek()!='['){return false;}}if(s.charAt(i)=='}'){if(stack.peek()!='{'){return false;}}stack.pop();}}return stack.empty();}
21. 合并两个有序链表
方法一:递归 时间 O(M+N) 空间 O(M+N) 递归调用时 mergeTwoLists 函数最多调用 n+mn+m 次,因此空间复杂度为 O(n+m)O(n+m)
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {if(l1==null) return l2;if(l2==null) return l1;if(l1.val<l2.val){l1.next=mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);return l1;}else{l2.next=mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);return l2;}}}
方法二:迭代
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode phead=new ListNode();ListNode pre=phead;while(l1!=null && l2!=null){if(l1.val<l2.val){pre.next=l1;l1=l1.next;}else{pre.next=l2;l2=l2.next;}pre=pre.next;}pre.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;return phead.next;}}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
解析 :
将数组一分为二,其中一定有一个是有序的,另一个可能是有序,也能是部分有序。此时有序部分用二分法查找。无序部分再一分为二,其中一个一定有序,另一个可能有序,可能无序。就这样循环
class Solution {public int search(int[] nums, int target) {if(nums.length==0) return -1;if(nums.length==1) return nums[0]==target ? 0 : -1 ;int l=0,r=nums.length-1;while(l <= r){int mid=(l+r)/2;if(target==nums[mid]) return mid;//假设左边有序if(nums[l] <= nums[mid]){if(nums[l] <= target && nums[mid] > target){r=mid-1;}else{l=mid+1;}}else{if(nums[mid]<target && nums[r] >= target){l=mid+1;}else{r=mid-1;}}}return -1;}}
35. 搜索插入位置
class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {int l=0,r=nums.length-1;while(l<=r){//如果查不到值,需走l=mid+1,将target插入到右边位置,如【1,3】 target=2,需将target插入到index=(0+1)/2 +1int mid=(r-l)/2+l;if(target==nums[mid]) return mid;else if(target>nums[mid]) l=mid+1;else r=mid-1;}return l;}}
46. 全排列
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums , 0 , path , used , res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int depth,List<Integer> path, boolean[] used,List<List<Integer>> res){if(depth == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<Integer> (path));return ;}// 在非叶子结点处,产生不同的分支,这一操作的语义是:在还未选择的数中依次选择一个元素作为下一个位置的元素,这显然得通过一个循环实现。for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ;i++){if(!used[i] ){path.add(nums[i]);used[i] = true;dfs(nums , depth+1 , path, used , res );// 注意:下面这两行代码发生 「回溯」,回溯发生在从 深层结点 回到 浅层结点 的过程,代码在形式上和递归之前是对称的used[i] = false;path.remove(path.size() - 1);}}}}
50. Pow(x, n)
51. N 皇后
class Solution {List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {char[][] chess = new char[n][n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)chess[i][j] = '.';dfs(res,chess,0);return res;}public void dfs(List<List<String>> res , char[][] chess ,int row){if(row==chess.length) {res.add(construct(chess));return;}for(int col=0;col<chess.length;col++){if (valid(chess, row, col)) {chess[row][col]='Q';dfs(res,chess,row+1);chess[row][col]='.';}}}public boolean valid(char[][] chess,int row,int col){//判断当前列有没有皇后,因为他是一行一行往下走的,//我们只需要检查走过的行数即可,通俗一点就是判断当前//坐标位置的上面有没有皇后for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {if (chess[i][col] == 'Q') {return false;}}//判断当前坐标的右上角有没有皇后for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < chess.length; i--, j++) {if (chess[i][j] == 'Q') {return false;}}//判断当前坐标的左上角有没有皇后for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {if (chess[i][j] == 'Q') {return false;}}return true;}//把数组转为listpublic List<String> construct(char[][] chess){List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) {path.add(new String(chess[i]));}return path;}}
59. 螺旋矩阵 II
class Solution {public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {int l = 0, r = n - 1, t = 0, b = n - 1;//左 右 上 下int [][] mat=new int [n][n];int num=1,sum=n*n;while(num<=sum){for(int i = l; i <= r; i++) mat[t][i] = num++; // left to right.t++;for(int i = t; i <= b; i++) mat[i][r] = num++;r--;for(int i = r; i >= l; i--) mat[b][i] = num++;b--;for(int i = b; i >= t; i--) mat[i][l] = num++;l++;}return mat;}}
69. Sqrt(x)
方法一:二分查找
方法二:牛顿迭代法
求 的解,过
作切线得
%2B%7BX%7B(n)%7D%7D%5E2-a#card=math&code=Y%3D2X_n%28X-X_n%29%2B%7BX%7B%28n%29%7D%7D%5E2-a&id=GMeO6)
与横轴的交点为方程%2B%7BX%7B(n)%7D%7D%5E2-a%3D0#card=math&code=2X_n%28X-X_n%29%2B%7BX%7B%28n%29%7D%7D%5E2-a%3D0&id=fDlHg)的解,即为新的迭代结果
%7D#card=math&code=X_%7B%28n%2B1%29%7D&id=wlHPY):
%7D%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B2%7D%20%20(%5Cfrac%7Ba%7D%7BXn%7D%2BX_n)%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%0A#card=math&code=X%7B%28n%2B1%29%7D%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B2%7D%20%20%28%5Cfrac%7Ba%7D%7BX_n%7D%2BX_n%29%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%0A&id=v3uuk)
注意==int*int== 会溢出 使用long存储乘积
class Solution {public int mySqrt(int x) {if (x<2) return x;long r=x;while(r*r>x){r=(r+x/r)/2;}return Long.valueOf(r).intValue();}}
74.搜索二维矩阵
行数m = matrix.length,列数n = matrix[0].length
由于矩阵每一行拼接在上一行的末尾,则会得到一个升序数组。所以基本思路还是通过将二维转化为一维数组来解决。
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {int low=0;int m=matrix.length;//行数int n=matrix[0].length;//列数int high=m*n-1;while (low<=high){int mid=(high-low)/2+low;//等同于(high+low)/2 防止溢出if(target==matrix[mid/n][mid%n]){return true;}else if(target>matrix[mid/n][mid%n]){low=mid+1;}else{high=mid-1;}}return false;}
77. 组合
回溯算法模板
void backtracking(参数) {if (终⽌条件) {存放结果;return;}for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩⼦的数量就是集合的⼤⼩)) {处理节点;backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归回溯,撤销处理结果}
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {dfs(1,n,k);return res;}public void dfs(int start , int n ,int k){if(tmp.size()==k){res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return ;}for(int j = start ; j <= n -(k-tmp.size())+1 ; j++){tmp.add(j);dfs(j+1,n,k);tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);}}}
88. 合并两个有序数组
解析:从后往前遍历,把大的排进去。
class Solution {public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {int len1=m-1,len2=n-1;int r=m+n-1;while(len1>=0&&len2>=0){if(nums1[len1]>nums2[len2]){nums1[r--]=nums1[len1--];}else{nums1[r--]=nums2[len2--];}}while(len1>=0) nums1[r--]=nums1[len1--];while(len2>=0) nums1[r--]=nums2[len2--];}}
92. 反转链表 II
class Solution {public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {//定义一个头节点ListNode preHead = new ListNode();preHead.next=head;ListNode pre=preHead;ListNode p=pre.next;//获得需要反转的节点及其前驱for(int step =0 ; step < left -1 ; step++ ){pre=pre.next;p=p.next;}ListNode last=p; //保存反转之后的最后一节点,反转完成后其next指向//最后一个反转节点的下一节点//前驱作为头节点,P作为起始节点开始头插,直到达到right-left个计数for(int i=0 ; i < right -left+1 ; i++ ){ListNode q=p.next;p.next=pre.next;pre.next=p;p=q;}last.next=p;return preHead.next;}}
101.对称二叉树
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {if(root==null) return true;return dfs(root.left,root.right);}public boolean dfs(TreeNode A,TreeNode B){if(A==null&&B==null) return true;if(A==null||B==null) return false;if(A.val!=B.val) return false;return dfs(A.left,B.right)&&dfs(A.right,B.left);}}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return res;}LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();//需先暂存queue的大小,不然后面边出队列size随之减小LinkedList<Integer> currentRes = new LinkedList<>();// 当前层一直出队.while (size > 0) {TreeNode current = queue.poll();TreeNode left = current.left;TreeNode right = current.right;if (left != null) {queue.add(left);}if (right != null) {queue.add(right);}// 奇数层,从头添加; 偶数层从尾部添加.if (depth % 2 != 0) {currentRes.add(0, current.val);} else {currentRes.add(current.val);}size--;}// 把当前层遍历的结果加入到结果中.res.add(currentRes);depth++;}return res;}}
104.二叉树的最大深度
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root==null) return 0;return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;}}
110.平衡二叉树
解析:递归求二叉树最大深度时检验是否存在不平衡。
class Solution {private boolean result = true;public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {maxDepth(root);return result;}public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int l = maxDepth(root.left);int r = maxDepth(root.right);if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) result = false;return 1 + Math.max(l, r);}}
111. 二叉树的最小深度
解析:
叶子节点的定义是左孩子和右孩子都为 null 时叫做叶子节点
- 当 root 节点左右孩子都为空时,返回 1
- 当 root 节点左右孩子有一个为空时,返回不为空的孩子节点的深度,因为这时只要有一个子节点不为空则不是叶子节点还需要往下寻找
- 当 root 节点左右孩子都不为空时,返回左右孩子较小深度的节点值
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root==null) return 0;int ldepth=minDepth(root.left);int rdepth=minDepth(root.right);if(ldepth==0||rdepth==0)return ldepth+rdepth+1;//左右孩子有一个为空时,返回不为空的孩子节点的深度return Math.min(ldepth,rdepth)+1;}}
112.路径总和
判断是否存在从根节点到叶子节点值和等于target,终止条件—叶子节点且节点值等于target遍历下来的剩余值不满足终止条件时,左右子树递归寻找。
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if(root==null) return false;if(root.left==null&&root.right==null&&root.val==targetSum) return true;return (hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val));}}
113.路径总和 II
和112.路径总和的不同在于需要把所有满足条件的路径返回,考虑把深度优先搜索,把路径依次加入结果,若不满足终止条件则剔除
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {dfs(root,0,targetSum);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode root,int pathSum,int sum){if(root==null) return ;pathSum+=root.val;path.add(root.val);if(root.left==null&&root.right==null&&pathSum==sum)res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));dfs(root.left,pathSum,sum);dfs(root.right,pathSum,sum);path.remove(path.size()-1);////恢复现场,因为targetSum是局部变量,故无须恢复现场}}
142. 环形链表 II
解析:
方法一:哈希表记录节点
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null || head.next == null) return null;Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();while(head != null){if(set.contains(head)){return head;}else{set.add(head);}head = head.next;}return null;}}
方法二:双指针快慢指针
设链表结构为

快指针 fast,慢指针slow
f=2s;
f=s+nb;
推出 s=nb ,则第一次相遇后,令f=head,f再走过a距离可以与s相遇,此时s=a+nb,意味着s又到了环的起始位置
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null || head.next == null) return null;ListNode f = head , s = head;while(true){if(f==null||f.next==null) return null;f = f.next.next;s = s.next;if(f==s) break;}f = head;while(f != s){f = f.next;s = s.next;}return f;}}
155. 最小栈
解析:辅助栈minStack 每次入栈出栈都维持当前最小值在栈顶
class MinStack {private Stack<Integer> dataStack;private Stack<Integer> minStack;private Integer min; /** initialize your data structure here. */public MinStack() {dataStack=new Stack<>();minStack=new Stack<>();min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;}public void push(int x) {dataStack.push(x);min=Math.min(min,x);minStack.push(min);}public void pop() {dataStack.pop();minStack.pop();min=minStack.isEmpty()?Integer.MAX_VALUE : minStack.peek();}public int top() {return dataStack.peek();}public int getMin() {return min;}}
160. 相交链表
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if(headA==null||headB==null){return null;}ListNode pa = headA , pb = headB;while(pa!=pb){pa = pa == null ? headB : pa.next;pb = pb == null ? headA : pb.next;}//当两个链表不相交时 总会同时变成null从而跳出循环return pa;}}
189. 旋转数组
class Solution {public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {k=k%nums.length;reverse(nums,0,nums.length-1);reverse(nums,0,k-1);reverse(nums,k,nums.length-1);}public void reverse(int[] nums,int start,int end){while(start<end){int temp=nums[start];nums[start]=nums[end];nums[end]=temp;start++;end--;}}}
191. 位1的个数
解析
方法一:
public class Solution {// you need to treat n as an unsigned valuepublic int hammingWeight(int n) {int count=0;for(int i=0;i<32;i++){if((n&1<<i)!=0){//不能写>0,因为1<<31=2147483648=(-1) Max value of System.Int32 : 2147483647count++;}}return count;}}
方法二:
public class Solution {// you need to treat n as an unsigned valuepublic int hammingWeight(int n) {int count=0;while(n!=0){n&=n-1;//每次运算会消除一个最低位1count++;}return count;}}
206. 反转链表
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode pre=new ListNode(0);//虚拟头节点ListNode p=head;//工作指针ListNode next=null;//存储工作指针下一个节点while(p!=null){next=p.next;p.next=pre.next;pre.next=p;p=next;}return pre.next;}}
209. 长度最小的子数组
class Solution {public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;int i=0;//起始位置int sum=0;// 滑动窗口数值之和int len=0;//长度for(int j=0;j<nums.length;j++){sum+=nums[j];while(sum>=target){len=j-i+1;result=Math.min(result,len);sum-=nums[i++];}}return result==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0:result;}}
不要以为for里放一个while就以为是#card=math&code=O%28n%5E2%29&id=UBytX)啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是 2 × n 也就是
#card=math&code=O%28n%29&id=c4kt9)。
213. 打家劫舍 II
由于第一个和最后一个不能同时取(可以取其中一个或者两个都不取),直接取 nums==【0,length-1】== 和 ==【1,length】==两组中大的,
class Solution {public int rob(int[] nums) {if(nums.length==1) return nums[0];return Math.max(myRob(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, nums.length - 1)),myRob(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 1, nums.length)));}public int myRob(int[] nums){int dp[] =new int [nums.length+1];dp[0]=0;dp[1]=nums[0];int max=dp[1];for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){dp[i+1]=Math.max(dp[i-1]+nums[i],dp[i]);max=Math.max(max,dp[i+1]);}return max;}}
226.翻转二叉树
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null) return null;TreeNode temp=root.right;root.right=root.left;root.left=temp;invertTree( root.left);invertTree(root.right);return root;}}
225. 用队列实现栈
class MyStack {private Queue<Integer> queue; /** Initialize your data structure here. */public MyStack() {queue = new LinkedList<>();}/** Push element x onto stack. */public void push(int x) {queue.add(x);int cnt=queue.size();while(cnt-->1){queue.add(queue.poll());}}/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */public int pop() {return queue.poll();}/** Get the top element. */public int top() {return queue.peek();}/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */public boolean empty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}
231. 2 的幂
解析
case 1: 负数、0
case 2: (n&n-1)==0
class Solution {public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {if(n<=0) return false;if((n&n-1)==0) return true;return false;}}
232. 用栈实现队列
class MyQueue {private Stack<Integer> in = new Stack<>();private Stack<Integer> out = new Stack<>();/** Initialize your data structure here. */public MyQueue() { }/** Push element x to the back of queue. */public void push(int x) {in.push(x);}/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */public int pop() {if (out.isEmpty()) {//假如out栈为空则把in栈全部送入outwhile (!in.isEmpty()) {out.push(in.pop());}}return out.pop();//若out不为空直接取栈顶}/** Get the front element. */public int peek() {if (out.isEmpty()) {//假如out栈为空则把in栈全部送入outwhile (!in.isEmpty()) {out.push(in.pop());}}return out.peek();}/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */public boolean empty() {return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();}}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
解析:结合「最近公共祖先」的定义和「后序遍历」的思路,不断向下遍历,向上返回null或者p,q或者(p,q)最近公共祖先。
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if(left == null && right == null) return null; // 1.可以合并到3.4if(left == null) return right; // 3.if(right == null) return left; // 4.return root; // 2. if(left != null and right != null)}}
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
class Solution {public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {int m=matrix.length;//行数int n=matrix[0].length;//列数int i=m-1,j=0;while (i>=0&&j<=n-1){if(target==matrix[i][j]){return true;}else if(target>matrix[i][j]){j++;}else{i--;}}return false;}}
283. 移动零
方法一:使用双指针,左指针指向当前已经处理好的序列的尾部,右指针指向待处理序列的头部。
右指针不断向右移动,每次右指针指向非零数,则将左右指针对应的数交换,同时左指针右移。
- 左指针左边均为非零数;
- 右指针左边直到左指针处均为零。
因此每次交换,都是将左指针的零与右指针的非零数交换,且非零数的相对顺序并未改变。
class Solution {public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length, left = 0, right = 0;while (right < n) {if (nums[right] != 0) {swap(nums, left, right);left++;}right++;}}public void swap(int[] nums, int left, int right) {int temp = nums[left];nums[left] = nums[right];nums[right] = temp;}}
方法二:遍历过程中把非零数字按新计数index装进nums,最后再把index之后的全部填充为0
class Solution {public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {int index=0;for(int n:nums){if(n!=0){nums[index++]=n;}}while(index<nums.length){nums[index++]=0;}}}
404. 左叶子之和
递归法三部曲
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
- 确定终止条件
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
class Solution {public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {//从左往右计算左叶子节点之和if(root==null) return 0;if(isLeaf(root.left)) return root.left.val+sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);//左叶子节点需从父节点开始判断return sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left)+sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);}public boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node){//判断叶子节点if(node==null) return false;if(node.left==null&&node.right==null)return true;return false;}}
415. 字符串相加
class Solution {public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();int len1=num1.length(),len2=num2.length();int carry=0;int i=len1-1,j=len2-1;while(i>=0||j>=0){int n1=i>=0 ? num1.charAt(i)-'0':0;int n2=j>=0 ? num2.charAt(j)-'0':0;int tempSum=n1+n2+carry;sb.insert(0,tempSum%10);carry=tempSum/10;i--;j--;}if(carry>0) sb.insert(0,carry); //进位不要漏了 类似 2.两数相加return sb.toString();}}
437. 路径总和 III
解析:首先我们的思路还是dfs,这里比较特殊的是起点不必是根节点,终点也不必是叶子节点,现在我们假设某一节点node,计算从node节点出发满足条件的路径条数 = node本身是否是一条 + dfs(node.left,tempsum)+dfs(node.right,tempsum);但是在主方法我们还需要递归计算root左右子树所有节点开始的路径条数,所以结果+pathSum(root.left,sum)+pathSum(root.right,sum).
class Solution {public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {int res=0;if(root==null) return res;res=dfs(root,sum)+pathSum(root.left,sum)+pathSum(root.right,sum);return res;}public int dfs(TreeNode node, int sum){int res=0;if(node==null) return res;if(node.val==sum)res++;res+=dfs(node.left,sum-node.val)+dfs(node.right,sum-node.val);return res;}}
485. 最大连续 1 的个数
class Solution {public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {int maxCount = 0, count = 0;int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (nums[i] == 1) {count++;} else {maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, count);count = 0;}}maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, count);return maxCount;}}
503. 下一个更大元素 II
class Solution {public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {Stack<Integer> st =new Stack<>();int[] next = new int[nums.length];Arrays.fill(next,-1);for(int i=0;i<2*nums.length-1;i++){while(!st.isEmpty()&&nums[i%nums.length]>nums[st.peek()]){next[st.pop()]=nums[i%nums.length];}st.push(i%nums.length);}return next;}}
543.二叉树的直径
解析:递归求二叉树最大深度时保存最大直径
class Solution {int max=0;public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null)return 0;MaxDepth(root);return max;}public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root){if(root==null)return 0;int leftdepth=MaxDepth(root.left);int rightdepth=MaxDepth(root.right);max=Math.max(max,leftdepth+rightdepth);return Math.max(leftdepth,rightdepth)+1;}}
566. 重塑矩阵
思路与算法
对于一个行数为 m,列数为 n,行列下标都从 00 开始编号的二维数组,我们可以通过下面的方式,将其中的每个元素 (i, j)(i,j) 映射到整数域内,并且它们按照行优先的顺序一一对应着 [0, mn)中的每一个整数。形象化地来说,我们把这个二维数组「排扁」成了一个一维数组。如果读者对机器学习有一定了解,可以知道这就是flatten 操作。
这样的映射即为:
%20%5Cto%20i%20%5Ctimes%20n%2Bj%0A(i%2Cj)%E2%86%92i%C3%97n%2Bj%0A#card=math&code=%28i%2C%20j%29%20%5Cto%20i%20%5Ctimes%20n%2Bj%0A%28i%2Cj%29%E2%86%92i%C3%97n%2Bj%0A&id=VvAo9)
同样地,我们可以将整数 x 映射回其在矩阵中的下标,
class Solution {public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {int m=nums.length,n=nums[0].length;//原矩阵的行数、列数if(m*n!=r*c)return nums;int[][] reshapedNums = new int[r][c];int index=0;for(int i=0;i<r;i++){for(int j=0;j<c;j++){reshapedNums[i][j]=nums[index/n][index%n];//index++;}}return reshapedNums;}}
572. 另一个树的子树
解析:与543.二叉树的直径 类似,对二叉树s的子树,不仅可以从root开始,也可以从子节点开始,这类都需要在主方法递归计算左右子树
class Solution {public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {if(s==null)return false;//需判断s是否为空是因为下面获取了s.left和s.right,否则会空指针异常return dfs(s,t)||isSubtree(s.left,t)||isSubtree(s.right,t);}public boolean dfs(TreeNode s, TreeNode t){if(s==null&&t==null) return true;if(s==null||t==null) return false;if(s.val!=t.val) return false;return dfs(s.left,t.left)&&(dfs(s.right,t.right));}}
617.合并二叉树
class Solution {public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if(root1==null&&root2==null) return null;if(root1==null) return root2;if(root2==null) return root1;TreeNode root=new TreeNode(root1.val+root2.val);root.left=mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);root.right=mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);return root;}}
687. 最长同值路径
解析:分析某一节点node 为根节点的子树 最长同值路径,需求出
left=node左子树的最长同值路径
right=node右子树的最长同值路径
然后有以下3种情况:
- 左右子节点val都等于node 则left+right+2
- 左节点val==node.val 右节点val不等于 或者反过来 则是 left+1||right+1
- 左、右子节点都不等于,则不需要把node连上去
class Solution {int ans=0;public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {if(root==null)return 0;dfs(root);return ans;}public int dfs(TreeNode node){if(node==null) return 0;int lpath=dfs(node.left);int rpath=dfs(node.right);int maxpath=0;//以当前node为起点的最大同值路径if(node.left!=null&&node.left.val==node.val&&node.right!=null&&node.right.val==node.val){ans=Math.max(ans,lpath+rpath+2);//左右子树都相同的情况}if(node.left!=null&&node.left.val==node.val) {//只有左子树相同的情况maxpath=lpath+1;}if(node.right!=null&&node.right.val==node.val){//只有右子树相同的情况,可能左子树的计算过,需对比大小maxpath=Math.max(maxpath,rpath+1);}ans=Math.max(ans,maxpath);//假如是左右子树相同的情况取ansreturn maxpath;}}
class Solution {int res=0;public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {if(root==null) return res;dfs(root);return res;}public int dfs(TreeNode node){if(node==null)return 0;int l=dfs(node.left);//左子节点目前的最长路径长度int r=dfs(node.right);//右子节点目前的最长路径长度int arrowLeft=0,arrowRight=0;//从节点 node 延伸出的最长箭头的长度if(node.left!=null&&node.left.val==node.val) arrowLeft=l+1;if(node.right!=null&&node.right.val==node.val) arrowRight=r+1;res=Math.max(res,arrowLeft+arrowRight);//当左右子树中存在一条与node值不一样的路径时,其arrow值为0return Math.max(arrowLeft, arrowRight);}}
739. 每日温度
解析:维护一个单调栈(元素不增,为什么是用栈而不是队列),存储元素下标,栈内元素表示尚未找到比它大的数据,一旦遇到则出栈,并计算索引差值。
class Solution {public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] T) {Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<>();int []ans=new int [T.length];for(int i=0;i<T.length;i++){while(!st.isEmpty()&&T[i]>T[st.peek()]){ans[st.peek()]=i-st.pop();}st.push(i);}return ans;}}
String length() charAt
nums[] length
stack Deque
Queue

