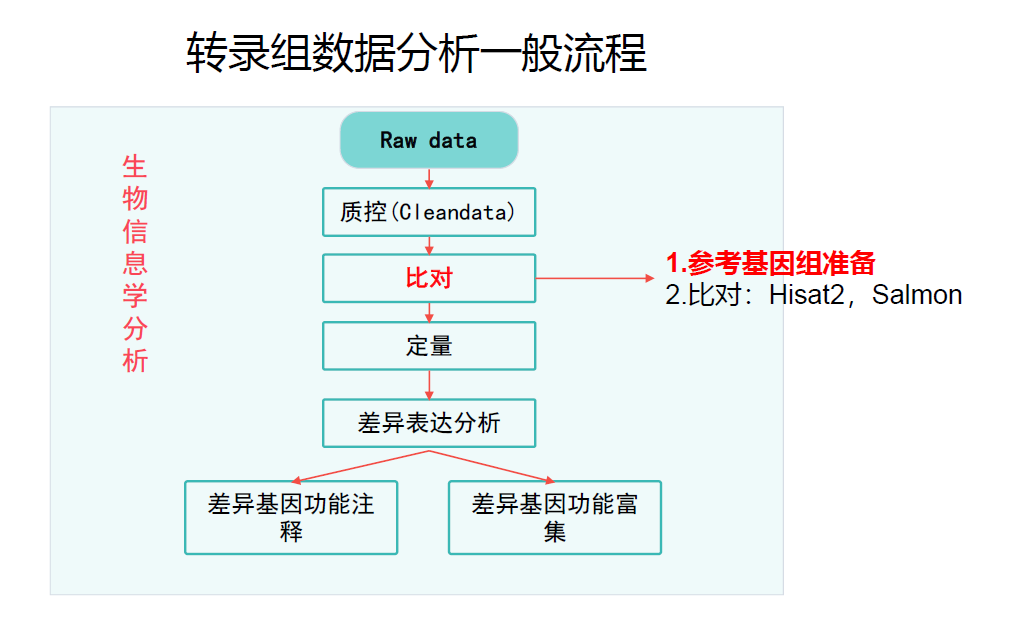
准备
参考基因组 4大常用数据库
Ensembl: www.ensembl.org (主要)
NCBI:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/genome/guide/human/index.shtml
UCSC:http://www.genome.ucsc.edu/
gencode: https://www.gencodegenes.org/
Ensembl
 物种数据表 http://asia.ensembl.org/info/about/species.html
物种数据表 http://asia.ensembl.org/info/about/species.html
用ctrl + F 浏览 注意 物种名, Taxon ID, 和 组装版本 和 NCBI ID 对应关系
http://asia.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Info/Annotation
人的基因注释统计信息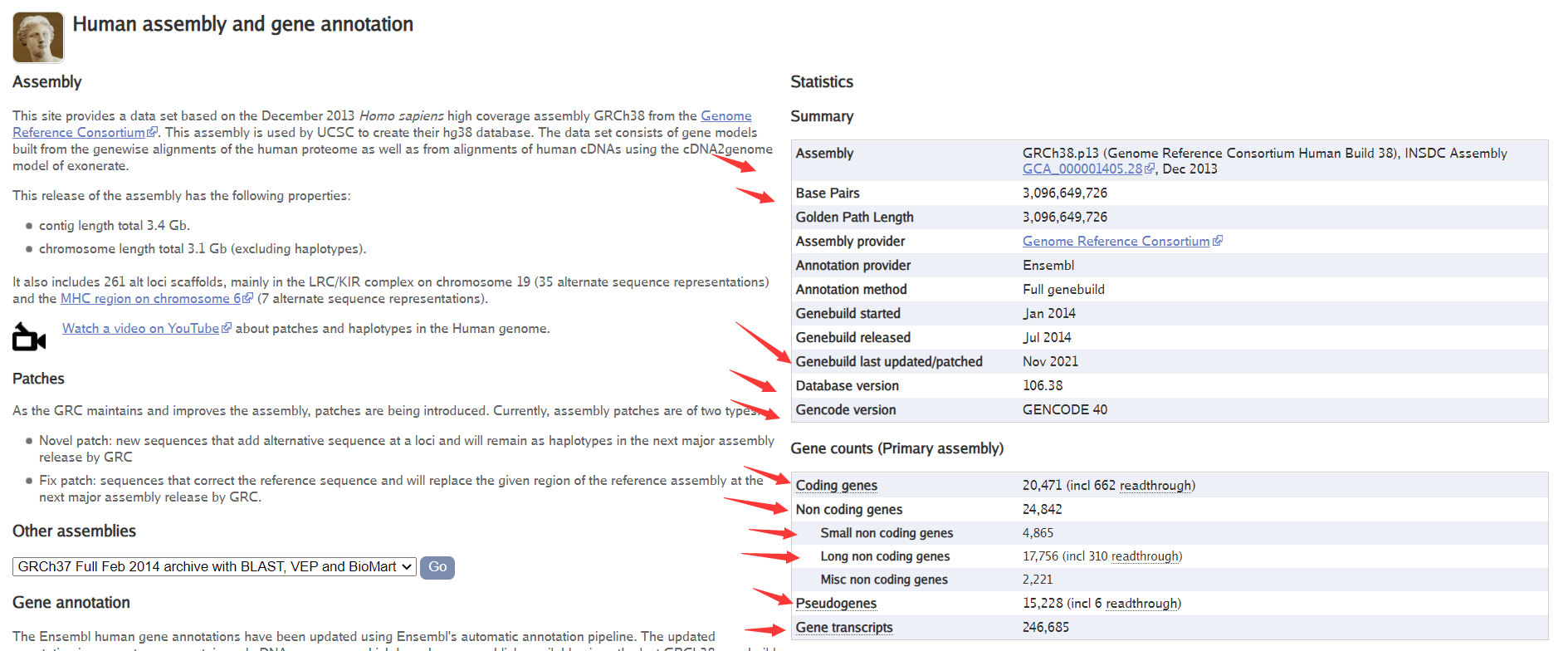
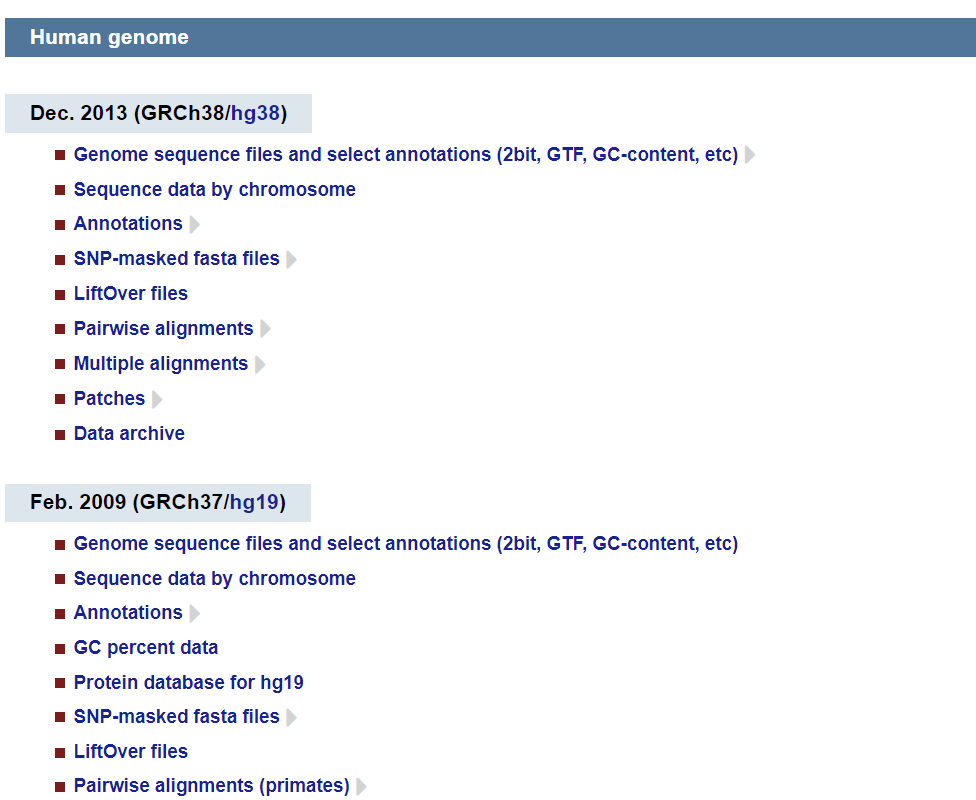
ucsc
https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/downloads.html
gencode
https://www.gencodegenes.org/human/stats.html
可查询统计信息 和 ensembl有差别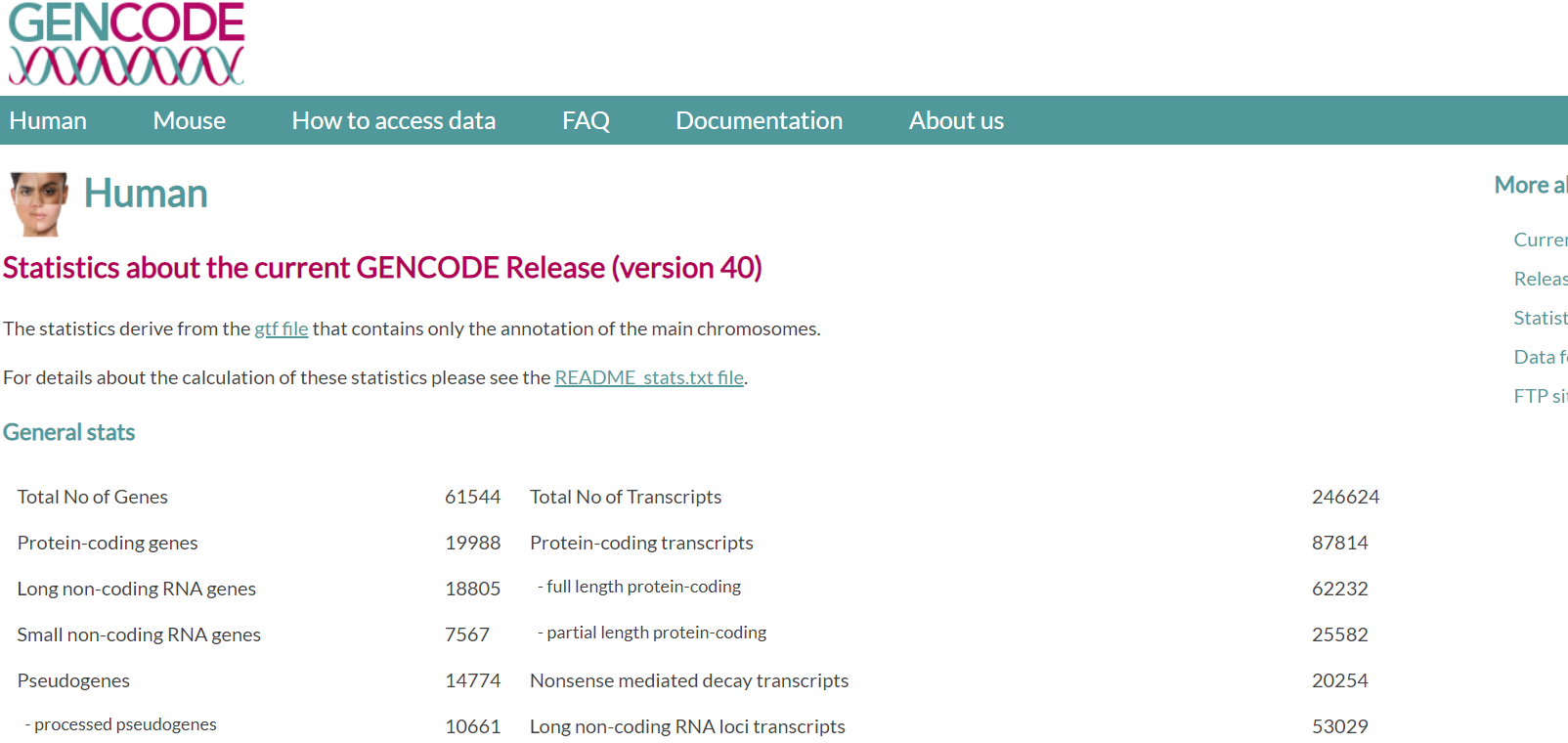
参考数据下载




http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/fasta/homo_sapiens/dna/
http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/fasta/homo_sapiens/cdna/
http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/gtf/
http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/gff3/
shell下载数据
###最好最新release 版本 ##### 4个文件# 下载基因组序列axel curl 文件较大 458Mnohup wget -c http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-105/fasta/homo_sapiens/dna/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gz >dna.log &tail dna.log # 查看# 下载转录组cDNA参考序列 72Mnohup wget -c http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-105/fasta/homo_sapiens/cdna/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.cdna.all.fa.gz >rna.log &tail rna.log # 查看# 下载基因组注释文件nohup wget -c http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-105/gtf/homo_sapiens/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.105.chr.gtf.gz >gtf.log &nohup wget -c http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-105/gff3/homo_sapiens/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.105.chr.gff3.gz >gff.log&
解压
# 再次强调,一定要在文件下载完后再进行解压!!!nohup gunzip Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gz Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.cdna.all.fa.gz >unzip.log &
fasta 介绍
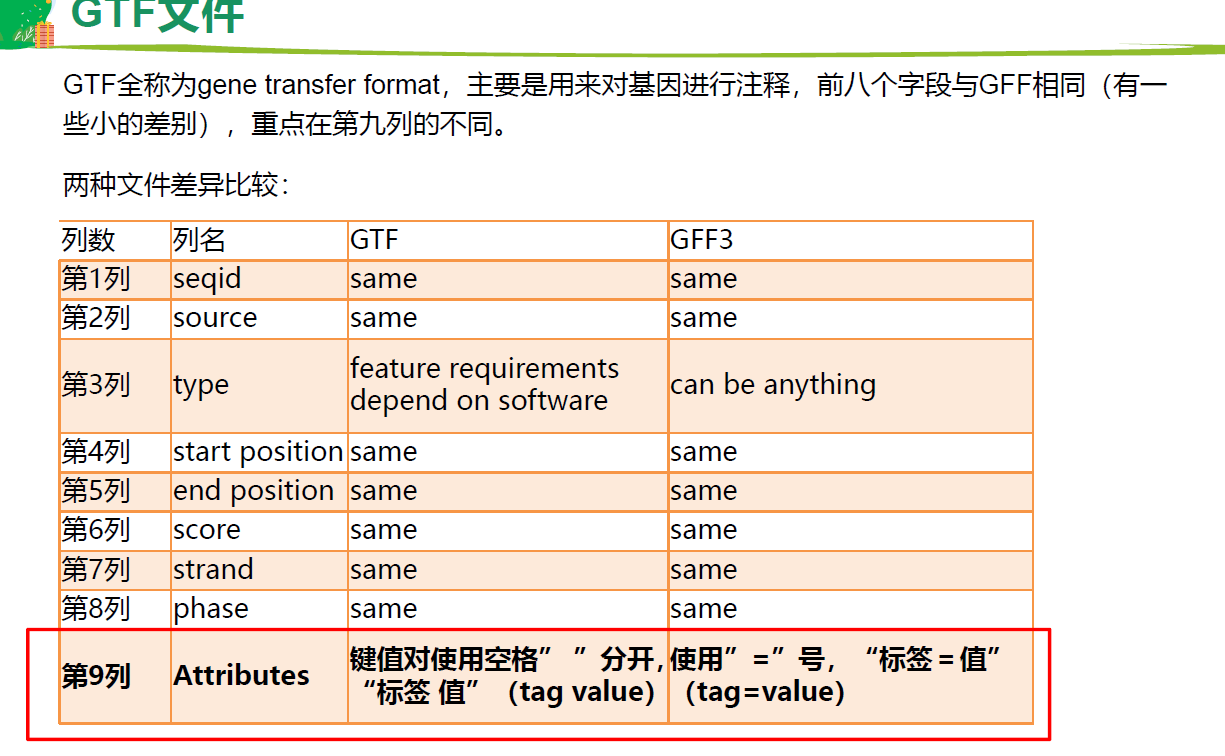
基因注释文件 GTF, GFF3
GFF3 基因组注释
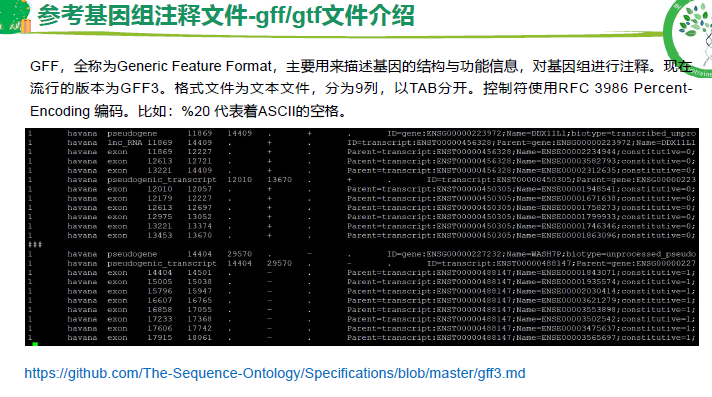
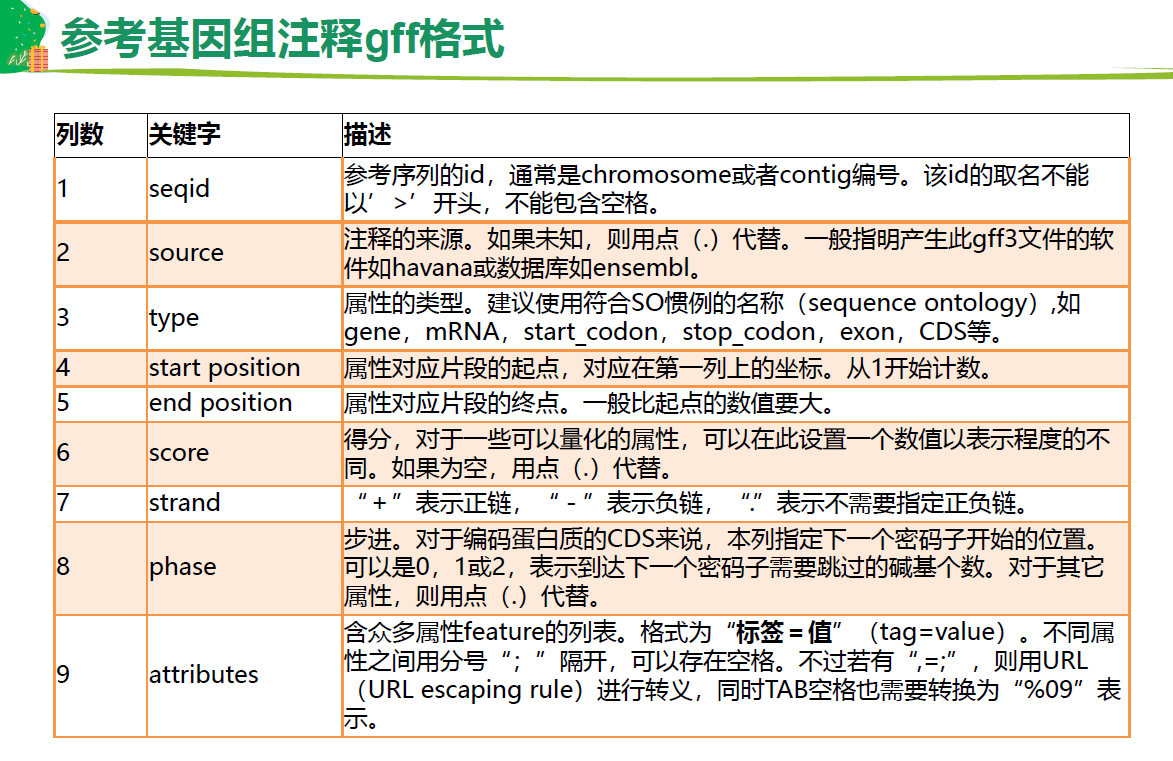
第3列 重要,基因的属性,
zless -S XXX |grep -v '#'| cut -f 3 | sort | uniq -c
GTF文件 注释基因
基因ID解析
思考题
fasta官方参考 https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastDocs&DOC_TYPE=BlastHelp
参考基因N的问题
N是正常的,’N’表示gap或者未注释区域,常见于端粒和着丝点区域,GRCH37共有234350281个‘N’,而GRCH38中有150630719个,减少了83719562个,占比35.7%。每次版本更新,N都会越少,所以尽量选择较新版的参考数据,结果会更加准确。可能以后长度长测序技术会慢慢克服N的问题。
参考基因的大小写区别
官方允许小写字母,并会被转作大写字母,有些程序对大小写有明确要求。
参考基因数据库的readme
包括对每个文件的描述,表头注释,举例说明,例外情况
#### README ####IMPORTANT: Please note you can download subsets of data via theBioMart data mining tool.See https://www.ensembl.org/info/data/biomart/ for more information.The genome assembly represented here corresponds to GenBank Assembly IDGCA_000001405.28#######################Fasta DNA dumps#######################-----------FILE NAMES------------The files are consistently named following this pattern:<species>.<assembly>.<sequence type>.<id type>.<id>.fa.gz<species>: The systematic name of the species.<assembly>: The assembly build name.<sequence type>:* 'dna' - unmasked genomic DNA sequences.* 'dna_rm' - masked genomic DNA. Interspersed repeats and lowcomplexity regions are detected with the RepeatMasker tool and maskedby replacing repeats with 'N's.* 'dna_sm' - soft-masked genomic DNA. All repeats and low complexity regionshave been replaced with lowercased versions of their nucleic base<id type> One of the following:* 'chromosome' - The top-level coordinate system in most species in Ensembl* 'nonchromosomal' - Contains DNA that has not been assigned a chromosome* 'seqlevel' - This is usually sequence scaffolds, chunks or clones.-- 'scaffold' - Larger sequence contigs from the assembly of shortersequencing reads (often from whole genome shotgun, WGS) which couldnot yet be assembled into chromosomes. Often more genome sequencingis needed to narrow gaps and establish a tiling path.-- 'chunk' - While contig sequences can be assembled into large entities,they sometimes have to be artificially broken down into smaller entitiescalled 'chunks'. This is due to limitations in the annotationpipeline and the finite record size imposed by MySQL which stores thesequence and annotation information.-- 'clone' - In general this is the smallest sequence entity. It is oftenidentical to the sequence of one BAC clone, or sequence regionof one BAC clone which forms the tiling path.<id>: The actual sequence identifier. Depending on the <id type> the <id>could represent the name of a chromosome, a scaffold, a contig, a clone ..Field is empty for seqlevel filesfa: All files in these directories represent FASTA database filesgz: All files are compacted with GNU Zip for storage efficiency.EXAMPLESThe genomic sequence of human chromosome 1:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna.chromosome.1.fa.gzThe masked version of the genome sequence on human chromosome 1(contains '_rm' or '_sm' in the name):Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.chromosome.1.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_sm.chromosome.1.fa.gzNon-chromosomal assembly sequences:e.g. mitochondrial genome, sequence contigs not yet mapped on chromosomesHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna.nonchromosomal.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.nonchromosomal.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_sm.nonchromosomal.fa.gz---------TOPLEVEL---------These files contains all sequence regions flagged as toplevel in an Ensemblschema. This includes chromsomes, regions not assembled into chromosomes andN padded haplotype/patch regions.EXAMPLESToplevel sequences unmasked:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna.toplevel.fa.gzToplevel soft/hard masked sequences:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_sm.toplevel.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.toplevel.fa.gz-----------------PRIMARY ASSEMBLY-----------------Primary assembly contains all toplevel sequence regions excluding haplotypesand patches. This file is best used for performing sequence similarity searcheswhere patch and haplotype sequences would confuse analysis. If the primaryassembly file is not present, that indicates that there are no haplotype/patchregions, and the 'toplevel' file is equivalent.EXAMPLESPrimary assembly sequences unmasked:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gzPrimary assembly soft/hard masked sequences:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_sm.primary_assembly.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.primary_assembly.fa.gz--------------SPECIAL CASES--------------Some chromosomes have alternate haplotypes which are presented in files withthe haplotype sequence only:Homo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.chromosome.HSCHR6_MHC_QBL.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh37.dna_rm.chromosome.HSCHR17_1.fa.gzAll alternative assembly and patch regions have their sequence paddedwith N's to ensure alignment programs can report the correct indexregionse.g. A patch region with a start position of 1,000,001 will have 1e6 N's addedits start so an alignment program will report coordinates with respect to thewhole chromosome.Human has sequenced Y chromosomes and the pseudoautosomal region (PAR)on the Y is annotated. By definition the PAR region is identical on theX and Y chromosome. The Y chromosome file contains the Y chromsomeminus these repeated PAR regions i.e. the unique portion of Y.
练习
1fastq->fasta
zless -S SRR1039511_1_val_1.fq.gz |awk '{ if(NR%4==1){print">" substr($0,2)} if(NR%4==2){print} }' | less -S
2.从gff或者gft文件中获取基因的ID与symbol对应关系,以及biotype类型
免包map
zless -S gtf.gz |awk -F'\t' '{if($3=="gene"){print$9}}' |\
awk -F';' '{print$1,$3,$5}' |awk '{if($6!=""){print$2"\t"$4"\t"$6}}' |\
sed 's/"//g' > ID_symbol_biotype.txt
数据比对
概述
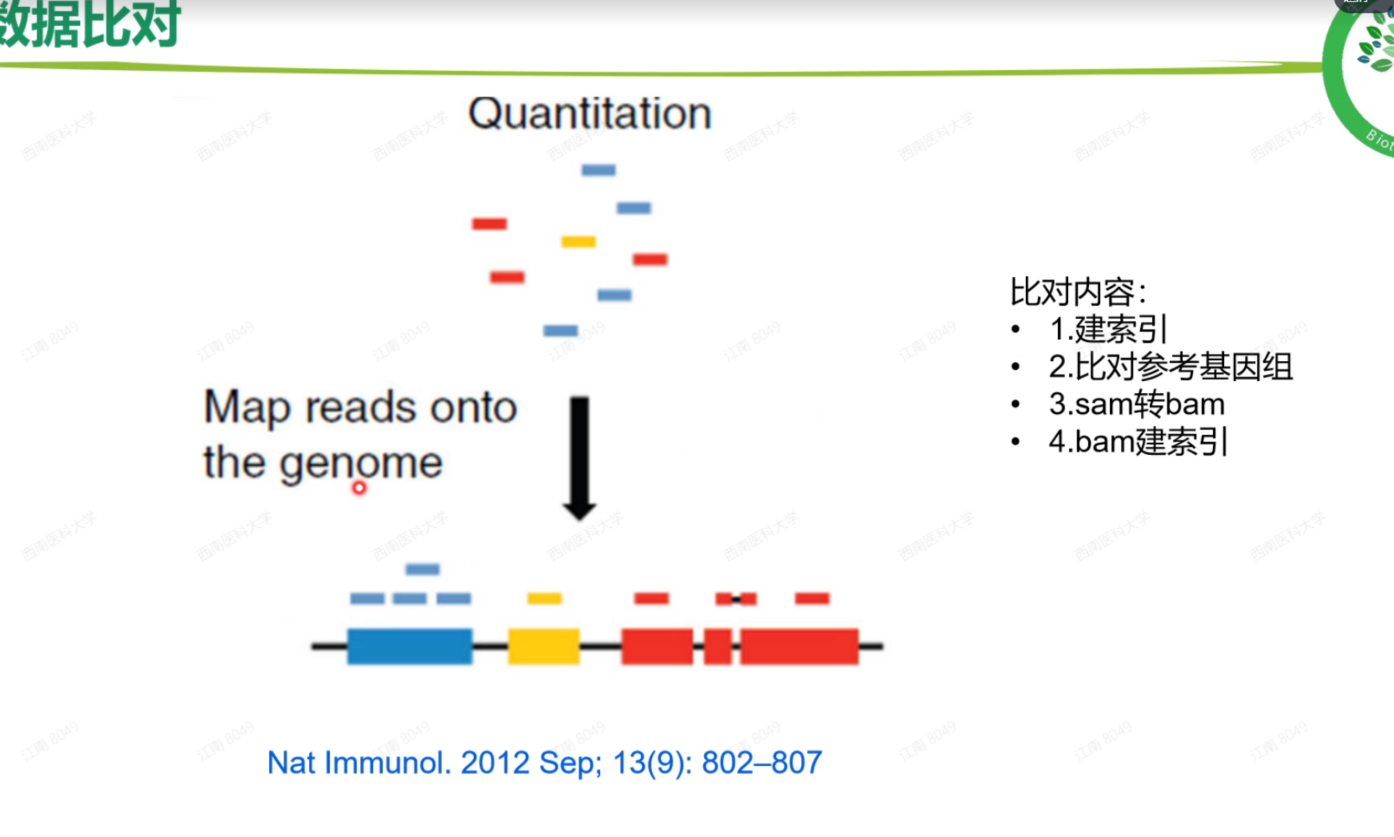
- 跨越内含子
- 不止一个片段比对到一个基因上
- 碱基序列匹配
- 需要索引
Hisat2 比对软件

索引构建

## ----构建索引 # 进入参考基因组目录 cd $HOME/database/GRCh38.105 # Hisat2构建索引,构建索引时间比较长,建议提交后台运行,一般会运行20多分钟左右 # vim Hisat2Index.sh mkdir Hisat2Index fa=Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa fa_baseName=GRCh38.dna hisat2-build -p 12 -f ${fa} Hisat2Index/${fa_baseName} # -p 可以设大一点,cpu多核的话 # 运行 nohup sh Hisat2Index.sh >Hisat2Index.sh.log &
sa文件是临时文件 不能删除单样本比对,sam->bam, bam建索引
```shell——比对
进入比对文件夹
cd $HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/Mapping/Hisat2
单个样本比对,步骤分解
index=/home/t_rna/database/GRCh38.104/Hisat2Index/GRCh38.dna # 索引 inputdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/data/cleandata/trim_galore/ # 清洗后数据 outdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/Mapping/Hisat2 # 比对结果
hisat2 -p 10 -x ${index} \ -1 ${inputdir}/SRR1039510_1_val_1.fq.gz \ -2 ${inputdir}/SRR1039510_2_val_2.fq.gz \ -S ${outdir}/SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sam
sam转bam
samtools sort -@ 15 -o SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sam
对bam建索引
samtools index SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam.bai
<a name="Ic9vu"></a>
### 批量 比对+sam->bam + bam建索引
&& 串联任务<br />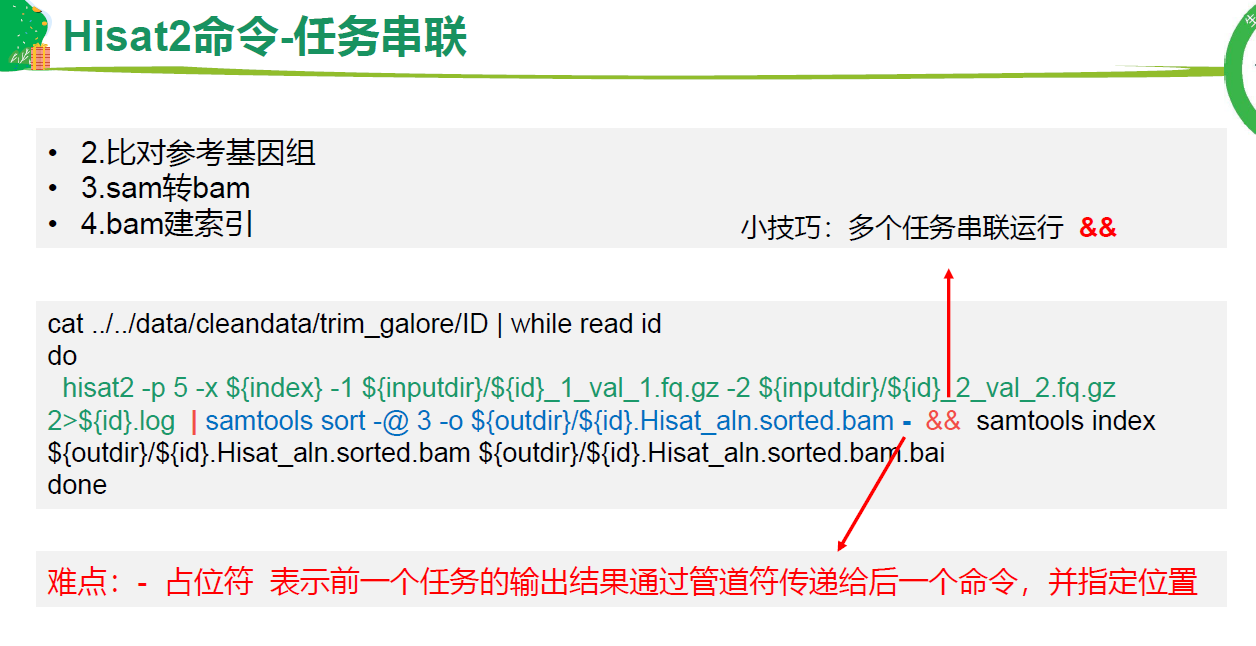<br />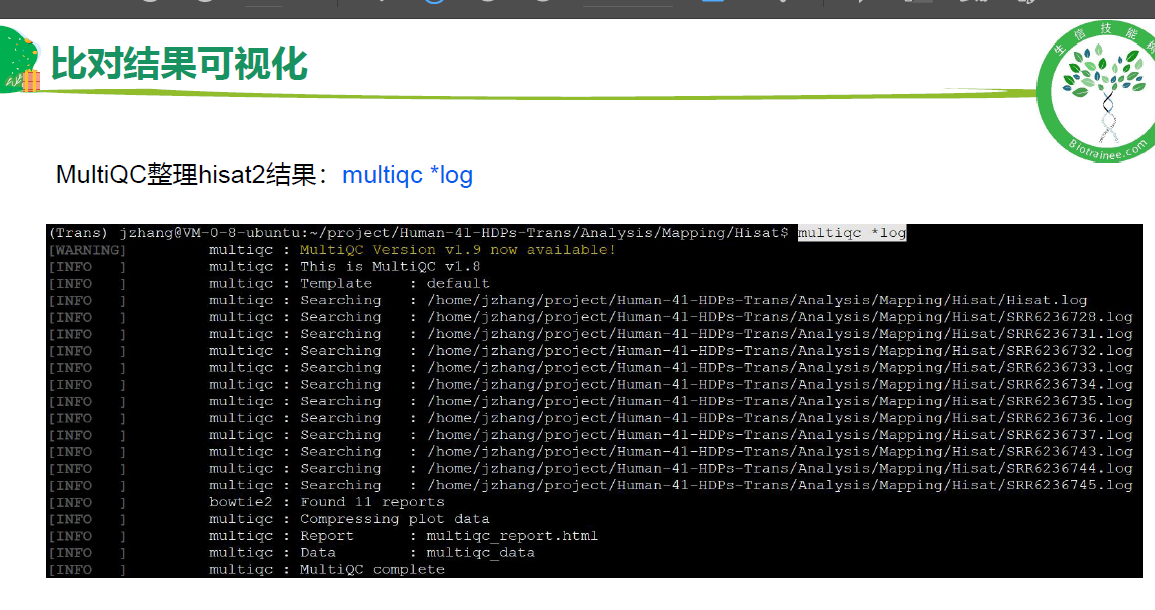
```python
# 多个样本批量进行比对,排序,建索引
# Hisat.sh内容: 注意命令中的-,表示占位符,表示|管道符前面的输出。
## 此处索引直接使用服务器上已经构建好的进行练习
# vim Hisat.sh
index=/home/t_rna/database/GRCh38.104/Hisat2Index/GRCh38.dna # 索引
inputdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/data/cleandata/trim_galore/ # 洗后数据文件夹
outdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/Mapping/Hisat2 # 结果目录
cat ../../data/cleandata/trim_galore/ID | while read id
do
hisat2 -p 10 -x ${index} -1 ${inputdir}/${id}_1_val_1.fq.gz -2 ${inputdir}/${id}_2_val_2.fq.gz 2>${id}.log | samtools sort -@ 3 -o ${outdir}/${id}.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam - && samtools index ${outdir}/${id}.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam ${outdir}/${id}.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam.bai
done
# 提交后台运行
nohup sh Hisat.sh >Hisat.log &
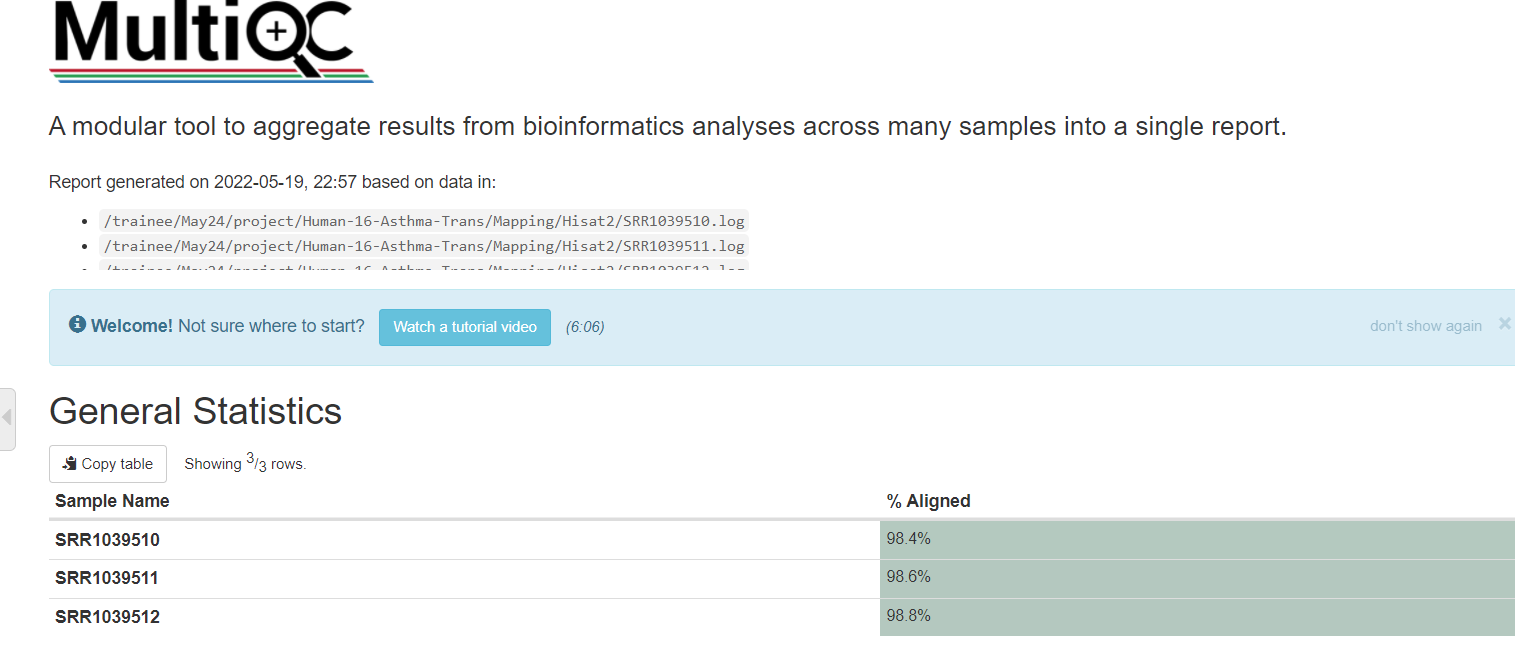
# 统计比对情况
multiqc -o ./ SRR*log
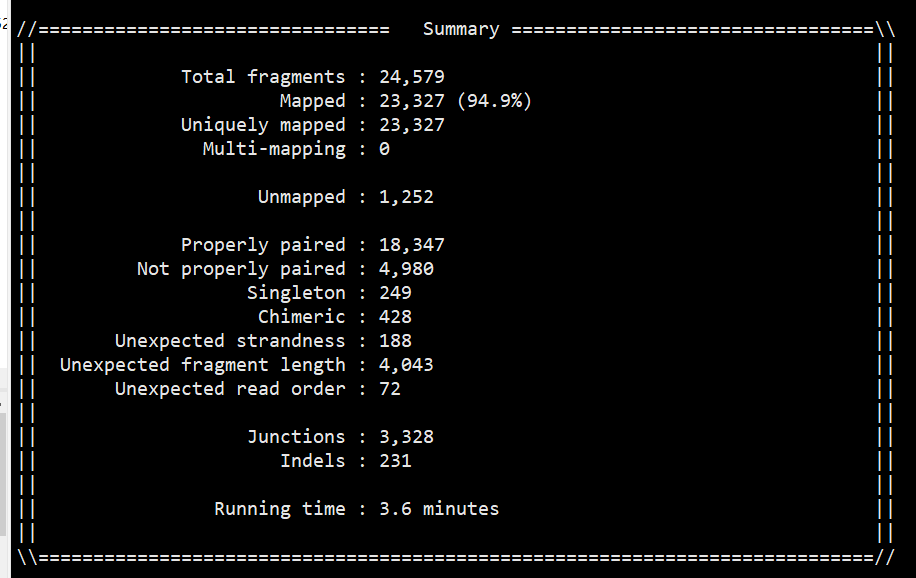
结果质量关注点
练习:
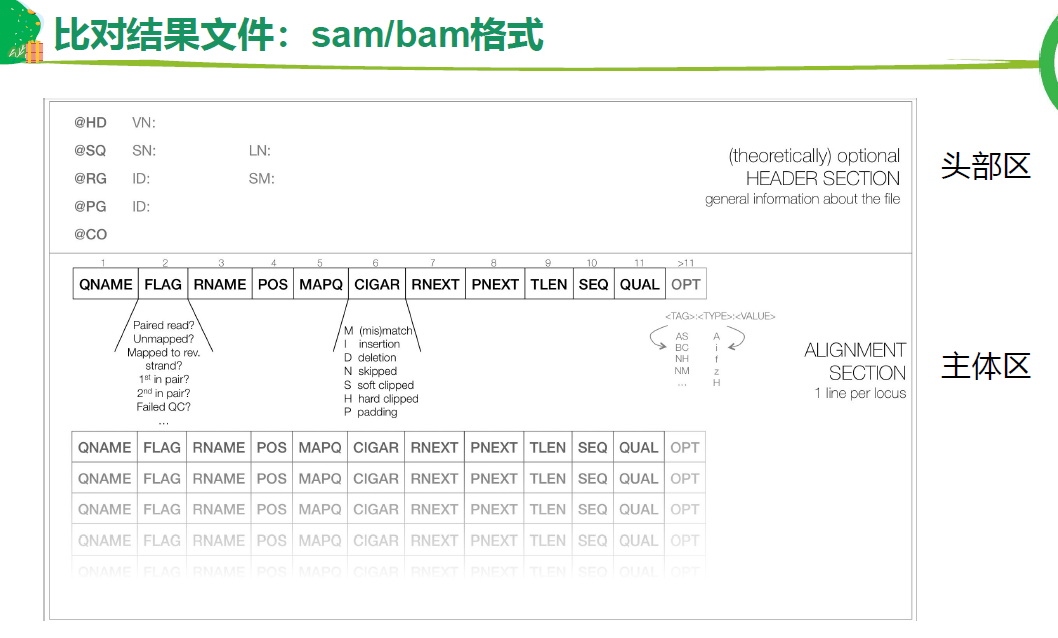
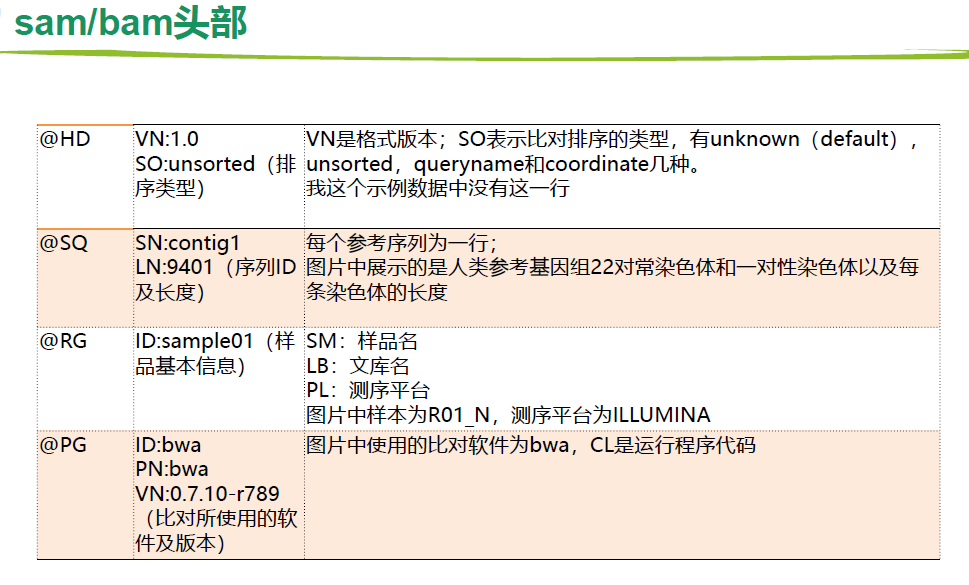
比对结果 sam/bam
Flag 是重要字段
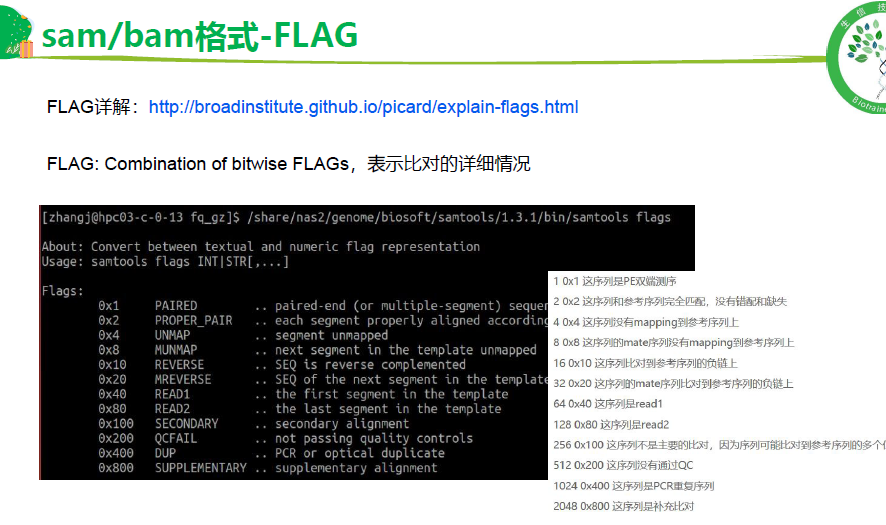
flag: http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/explain-flags.html
samtools flags 99
CIGAR

samtools查看 sam /bam
##----view查看bam文件
samtools view SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam |less
samtools view -H SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam #只看头部
samtools view -h SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam # 都看
##----index对bam文件建索引
samtools index SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam.bai
##----flagstat统计比对结果
samtools flagstat -@ 3 SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam #-@ 线程
##----sort排序 sam转bam并排序
samtools sort -@ 3 -o SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sam
##----depth统计测序深度
# 得到的结果中,一共有3列以指标分隔符分隔的数据,第一列为染色体名称,第二列为位点,第三列为覆盖深度
samtools depth SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam >SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam.depth.txt
1 14729 1
1 14730 1
1 14731 1
1 14732 1
##----计算某一个基因的测序深度
# 找到基因的坐标
zless -S /home/t_rna/database/GRCh38.104/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.104.chr.gff3.gz |awk '{if($3=="gene")print}' |grep 'ID=gene:ENSG00000186092' |awk '{print $1"\t"$4"\t"$5}' >ENSG00000186092.bed
$ cat ENSG00000186092.bed
1 65419 71585
samtools depth -b ENSG00000186092.bed SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sorted.bam >ENSG00000186092.bed.depth
# 如何找到多比对的reads,flag值的理解
# (0x100) 代表着多比对情况,所以直接用samtools view -f 0x100可以提取 multiple比对的 情况
samtools view -f 0x100 SRR1039510.Hisat_aln.sam |head -n 2
###例:比对到 7号染色体 的 104669496 下一片段在104669431 序列边长到125 因为考虑两个片段信息
# flag = 339 read paired (0x1) + read mapped in proper pair (0x2)+ read reverse strand (0x10)+ first in pair (0x40)+ not primary alignment (0x100)
SRR1039510.8 339 7 104669496 1 60M = 104669431 -125 AAGTTCAGTTCTGCAAGCAAGTATGCTGCTCTCTCTGTTGATGGTGAAGATGAAAATGAG JGIGGIJJJJJJIJJJJJIIIIJJGIGIIIIIIHJIJJJJIIGIJIJIIIIIJJJJIIIH AS:i:0 ZS:i:0 XN:i:0 XM:i:0 XO:i:0 XG:i:0 NM:i:0 MD:Z:60 YS:i:0 YT:Z:CP NH:i:3
SRR1039510.8 419 7 104669431 1 63M = 104669496 125 GCAAAAAGGATCAAGACTCCAGATCTGCACCTGAGCCAAAGAAACCTGAGGAAAATCCAGCTT
GJJJJJJJIJJIJJJJIJJJJJGHIIJJIJJJJJJJIGHIJIJJJJJJJIJJJJHHHFHHFFE AS:i:0 ZS:i:0 XN:i:0 XM:i:0 XO:i:0 XG:i:0 NM:i:0 MD:Z:63 YS:i:0 YT:Z:CP NH:i:3
subjunc

## ----构建索引
# 进入参考基因组目录
cd $HOME/database/GRCh38.105
# subjunc构建索引,构建索引时间比较长大约40分钟左右,建议携程sh脚本提交后台运行
## 后续索引可直接使用服务器上已经构建好的进行练习
# vim SubjuncIndex.sh
mkdir SubjuncIndex
fa=Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa
fa_baseName=GRCh38.dna
subread-buildindex -o SubjuncIndex/${fa_baseName} ${fa}
# 运行
nohup sh SubjuncIndex.sh >SubjuncIndex.sh.log &
## ----比对
# 进入文件夹
cd $HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/Mapping/Subjunc
# vim subjunc.sh
index=/home/t_rna/database/GRCh38.104/SubjuncIndex/GRCh38.dna
inputdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/data/cleandata/trim_galore
outdir=$HOME/project/Human-16-Asthma-Trans/Mapping/Subjunc
cat ../../data/cleandata/trim_galore/ID | while read id
do
subjunc -T 10 -i ${index} -r ${inputdir}/${id}_1_val_1.fq.gz -R ${inputdir}/${id}_2_val_2.fq.gz -o ${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.bam 1>${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.log 2>&1 && samtools sort -@ 6 -o ${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.sorted.bam ${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.bam && samtools index ${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.sorted.bam ${outdir}/${id}.Subjunc.sorted.bam.bai
done
## 三任务串联
# 运行
nohup sh subjunc.sh >subjunc.log &
log: 主要看mapped 率