https://blog.csdn.net/bit452/article/details/109677086
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44841652/article/details/105068509
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?p=5
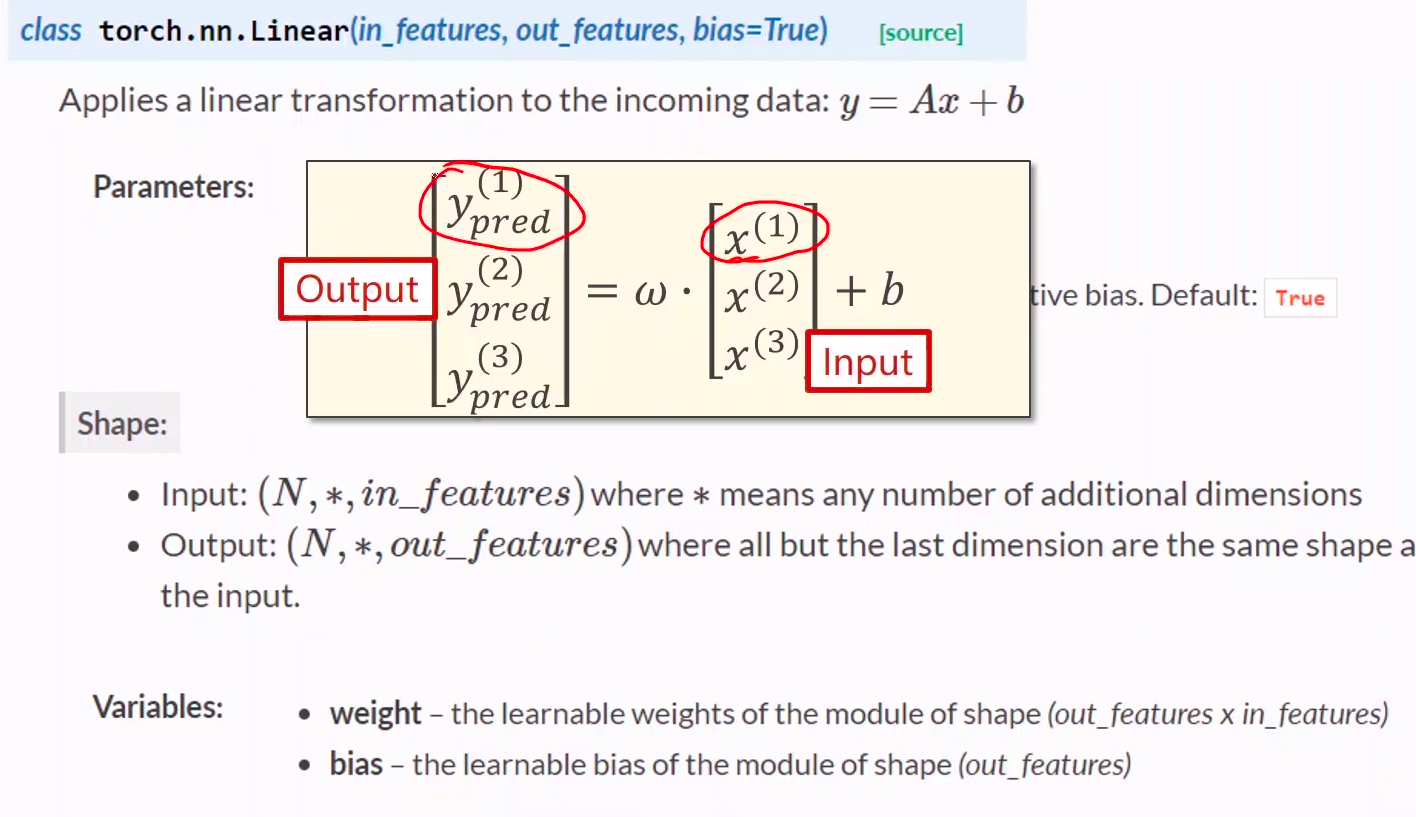
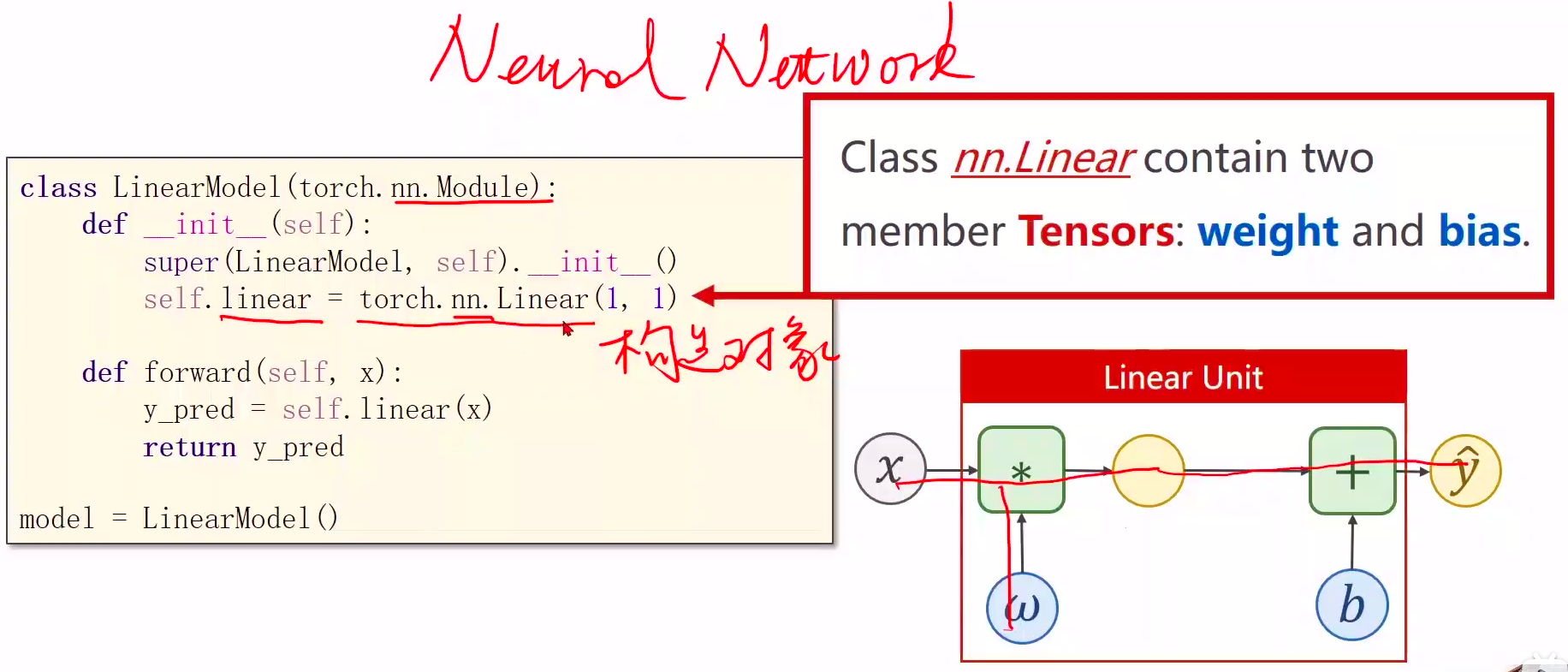
官方文档 torch.nn.Linear的pytorch文档
代码说明:必看
- 损失函数计算必须是标量值
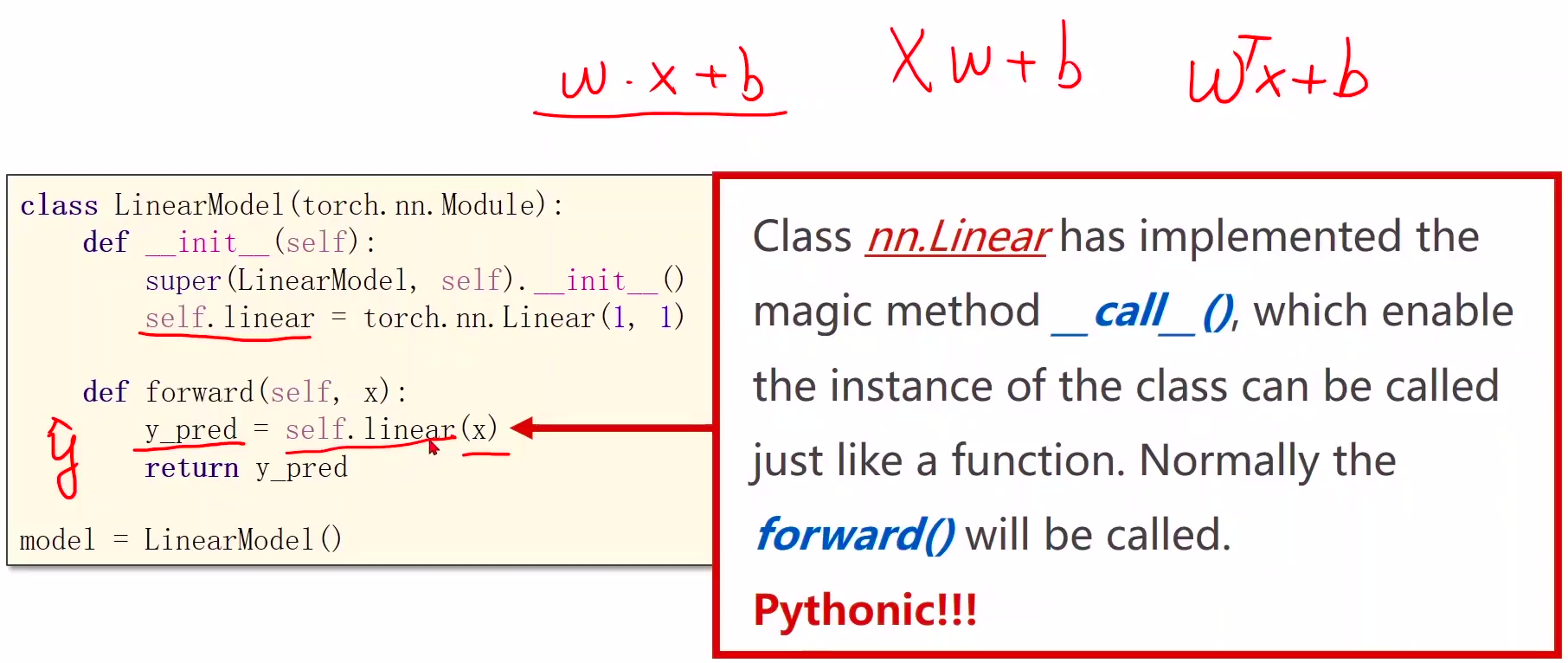
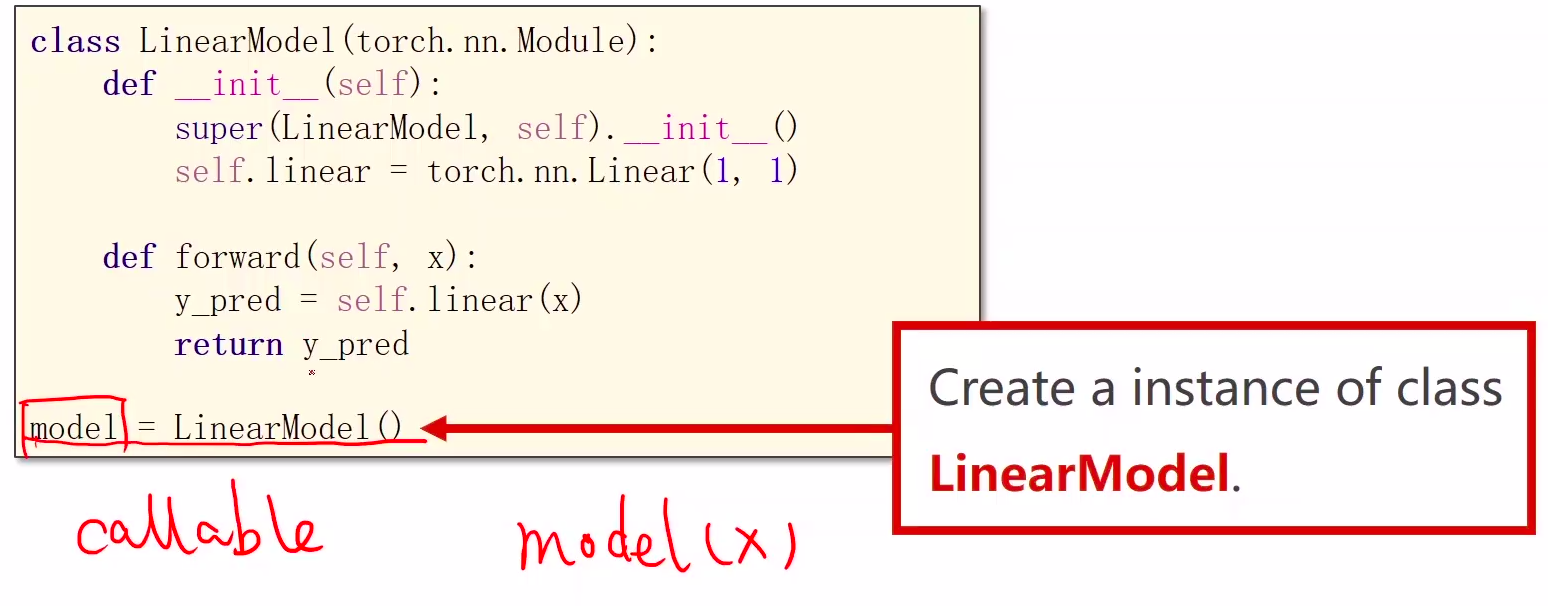
1、Module实现了魔法函数call(),call()里面有一条语句是要调用forward()。因此新写的类中需要重写forward()覆盖掉父类中的forward()
2、call函数的另一个作用是可以直接在对象后面加(),例如实例化的model对象,和实例化的linear对象
3、本算法的forward体现是通过以下语句实现的:
y_pred = model(x_data)
由于魔法函数call的实现,model(x_data)将会调用model.forward(x_data)函数,model.forward(x_data)函数中的
y_pred = self.linear(x)
将会调用torch.nn.Linear类中的forward,至此完成封装,也就是说forward最终是在torch.nn.Linear类中实现的,具体怎么实现,可以不用关心,大概就是y= wx + b。
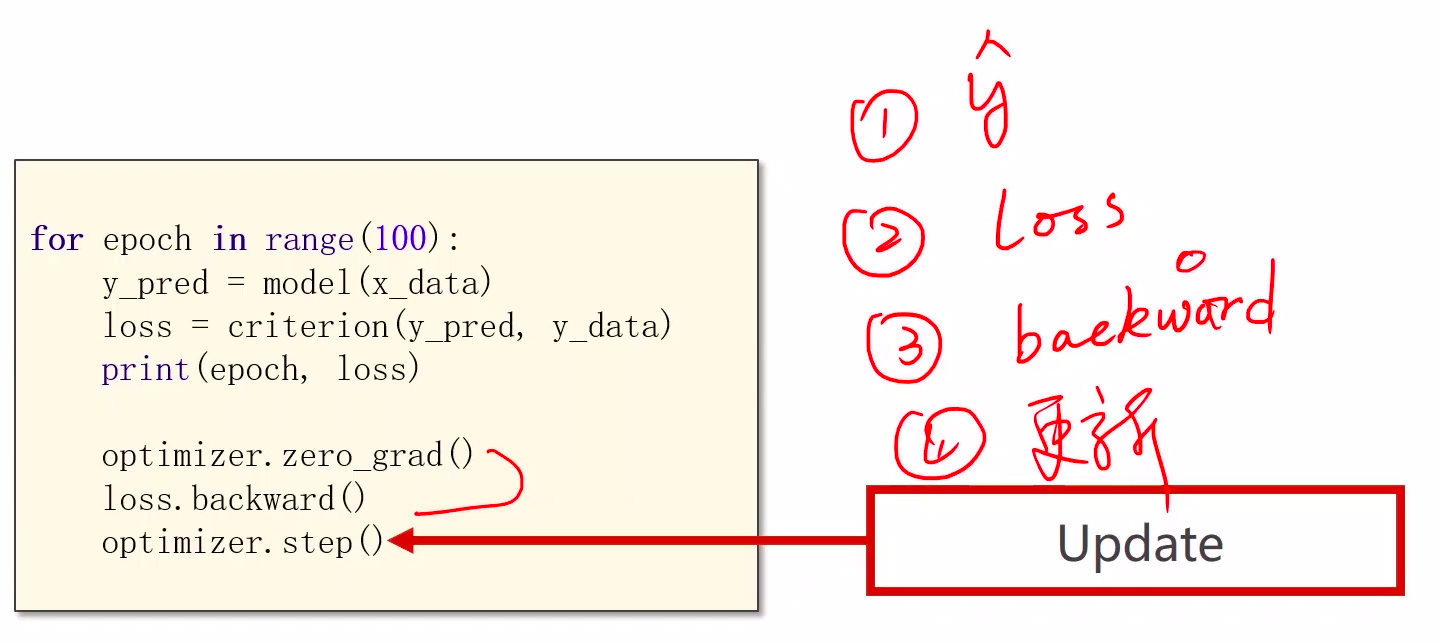
4、训练的循环也是4步
①求y hat (输入的预测值)
②计算loss
③反向传播 backward (计算梯度)
④ 更新参数
5、官方文档 torch.nn.Linear的pytorch文档
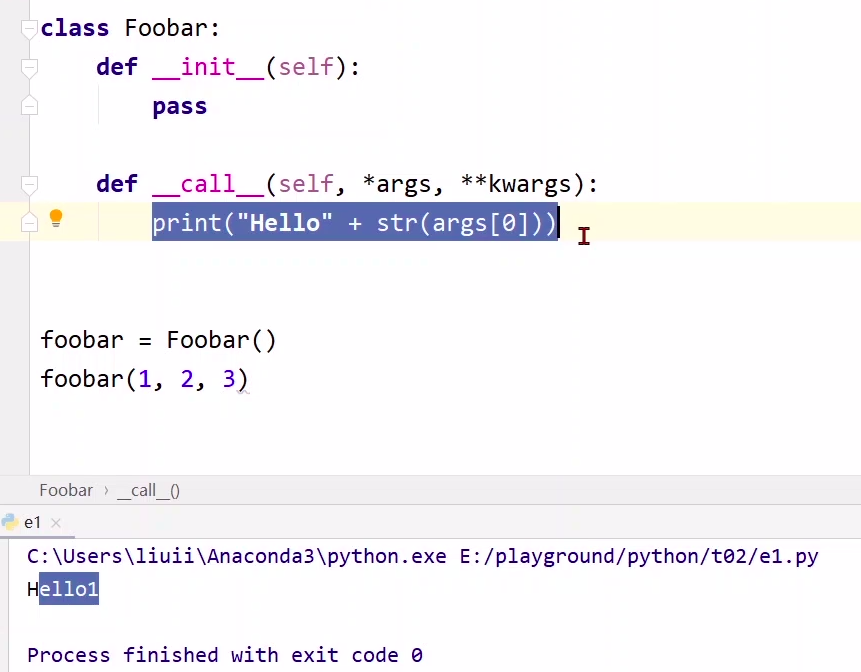
小知识点:可调用对象
如果要使用一个可调用对象,那么在类的声明的时候要定义一个 call()函数就OK了,就像这样
class Foobar:
def __init__(self):
pass
def __call__(self,*args,**kwargs):
pass
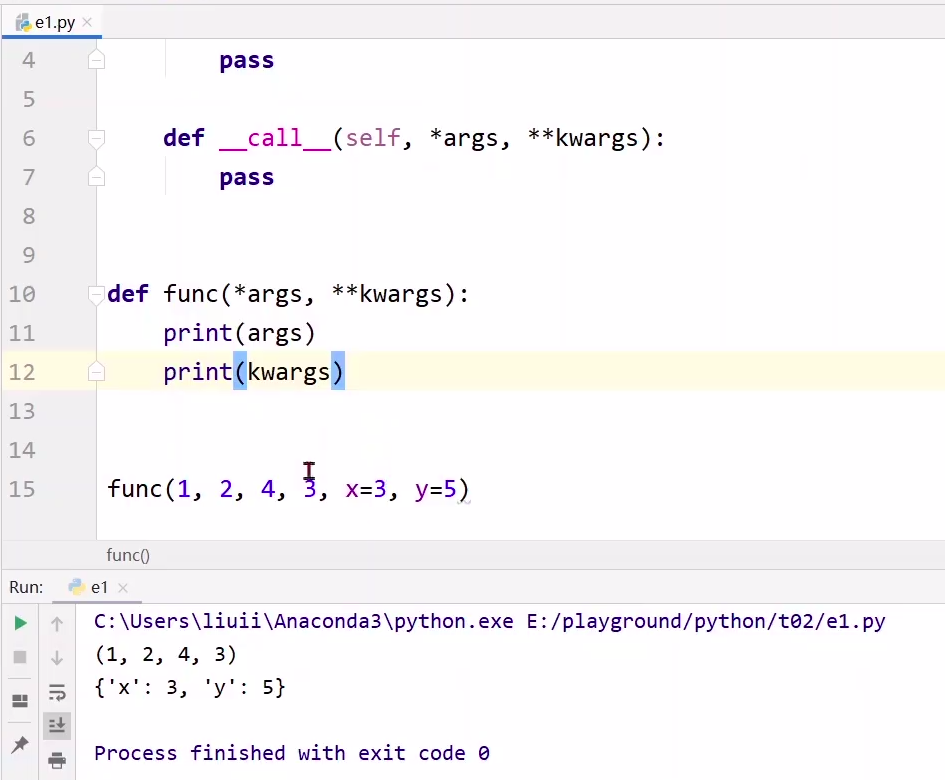
其中参数*args代表把前面n个参数变成n元组,kwargsd会把参数变成一个词典,举个例子:**
def func(*args,**kwargs):
print(args)
print(kwargs)
#调用一下
func(1,2,3,4,x=3,y=5)
过程
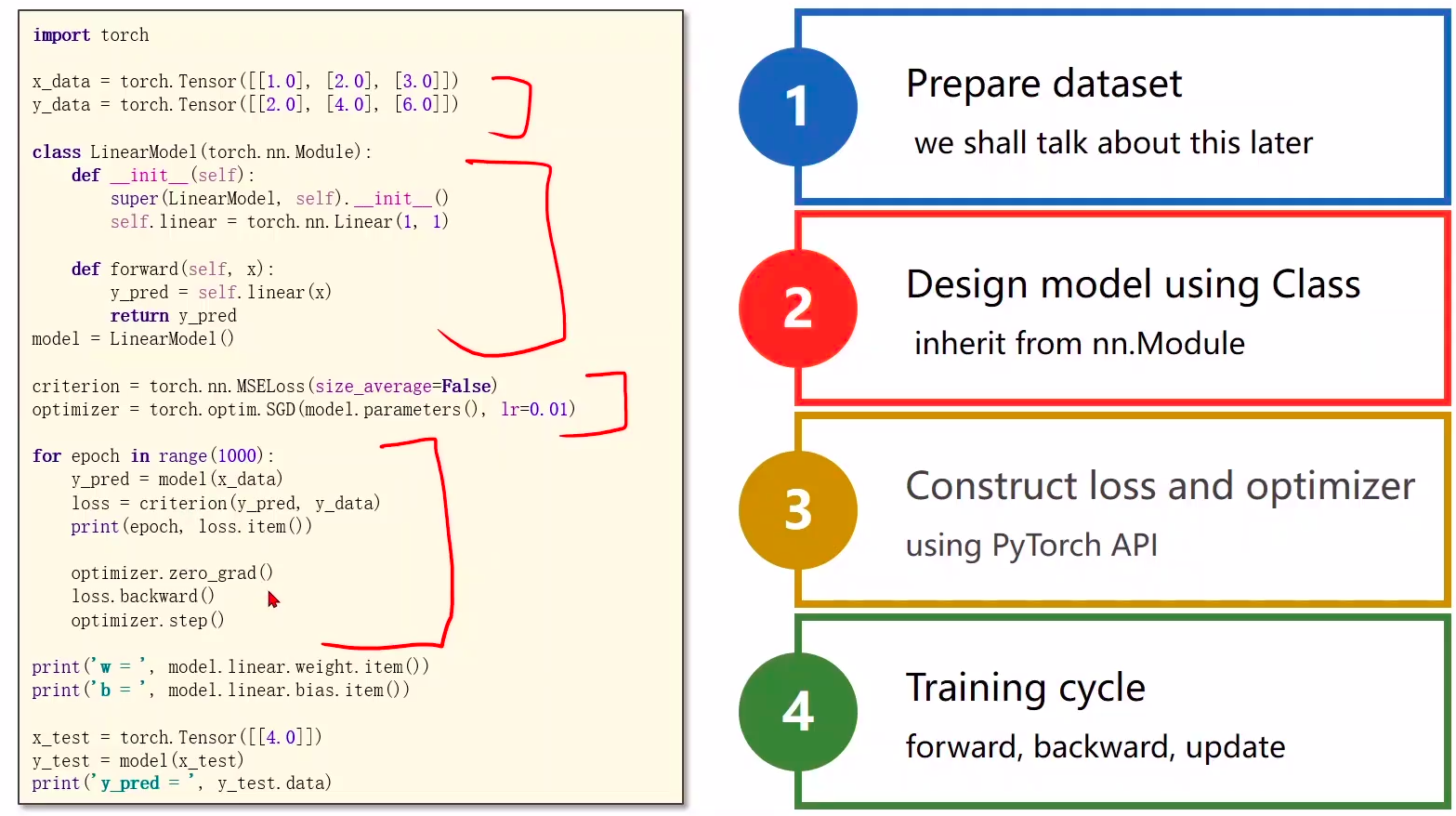
1 Prepare dataset
2 Design model using Class
- inherit from nn.Module 计算y^hat
3 Construct loss and optimizer
- using PyTorch API 计算loss和optimizer
4 Training cycle
- forward, backward, update 前馈,反馈,更新
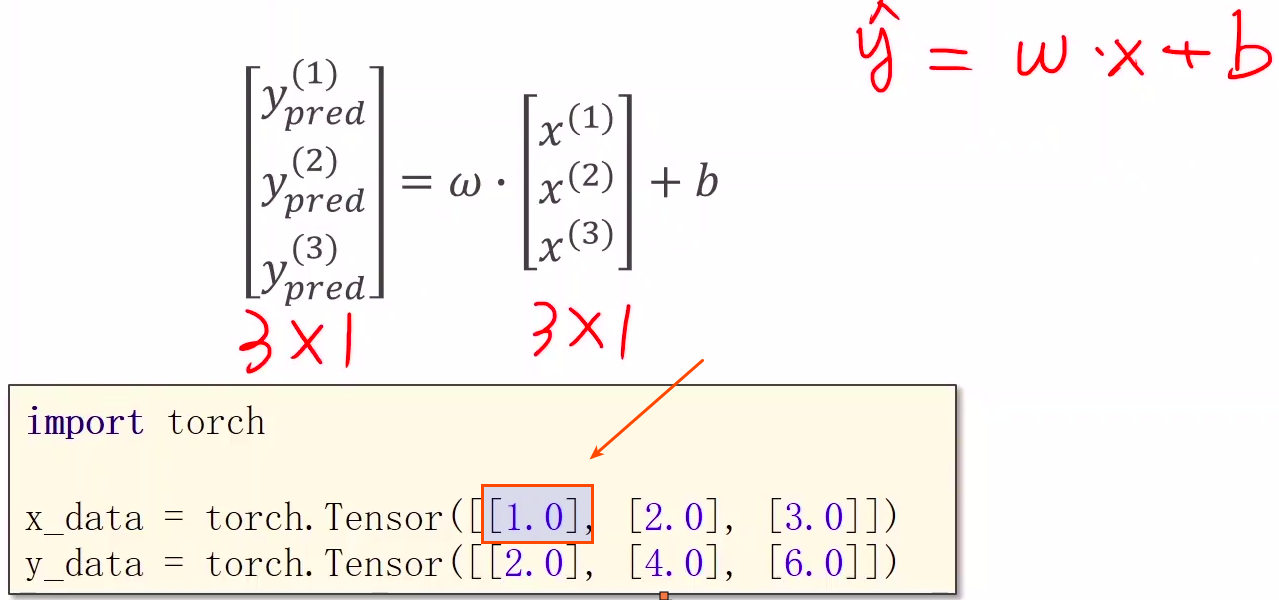
1 Prepare dataset
广播机制,注意x,y的值必须是3行矩阵,里面每个数都要加[]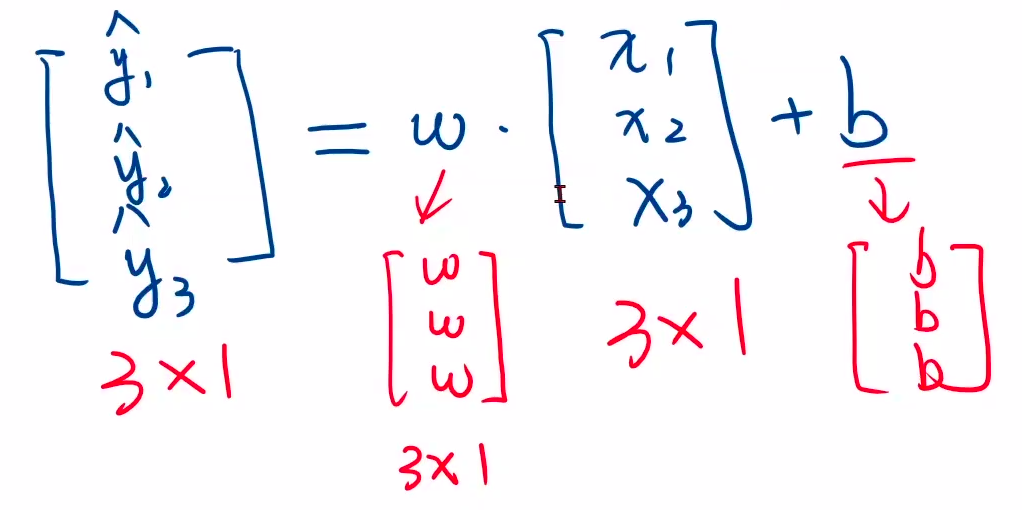
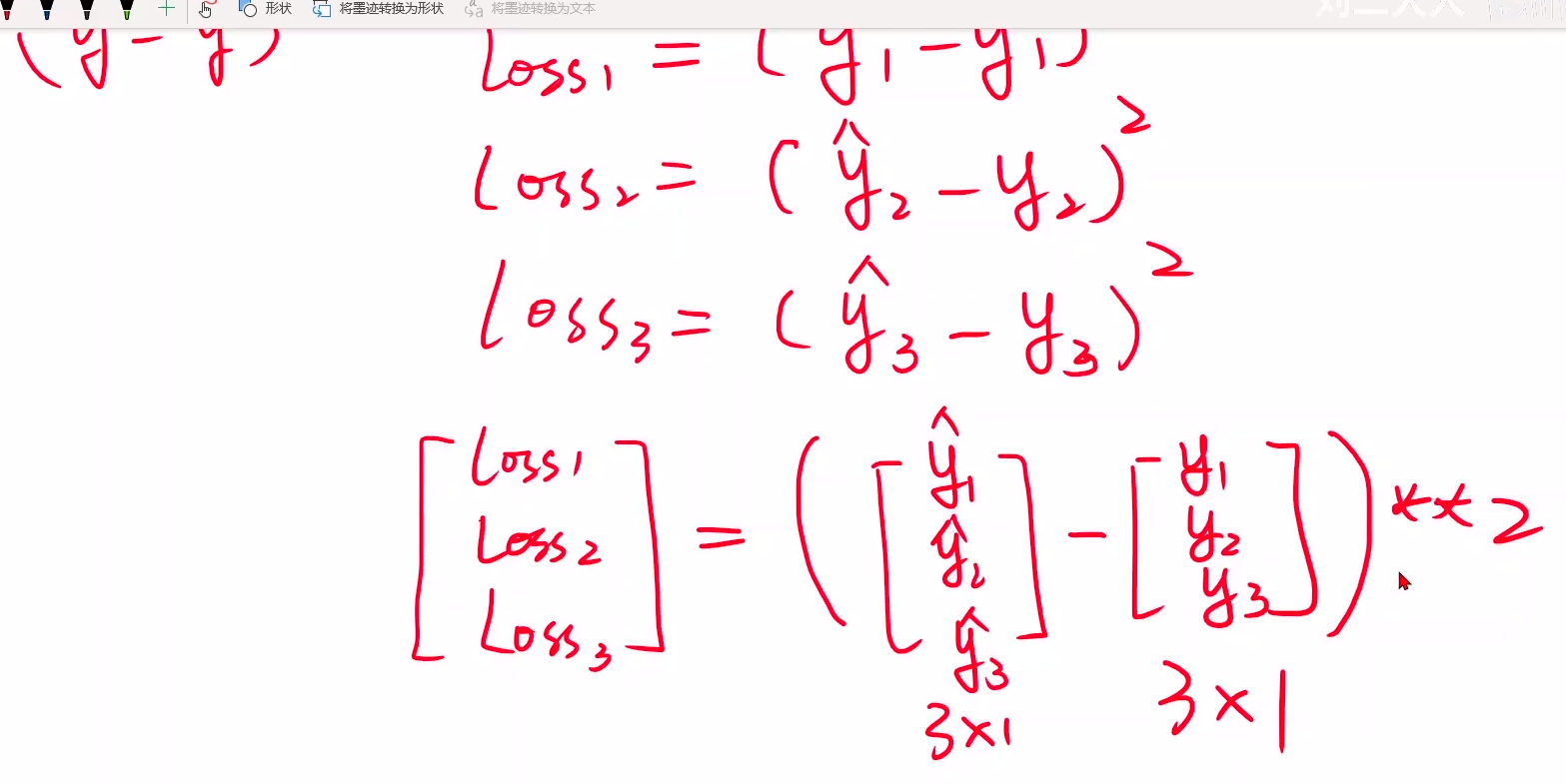
2 Design model using Class
- inherit from nn.Module 计算y^hat
线性单元:构造计算图,注意维度
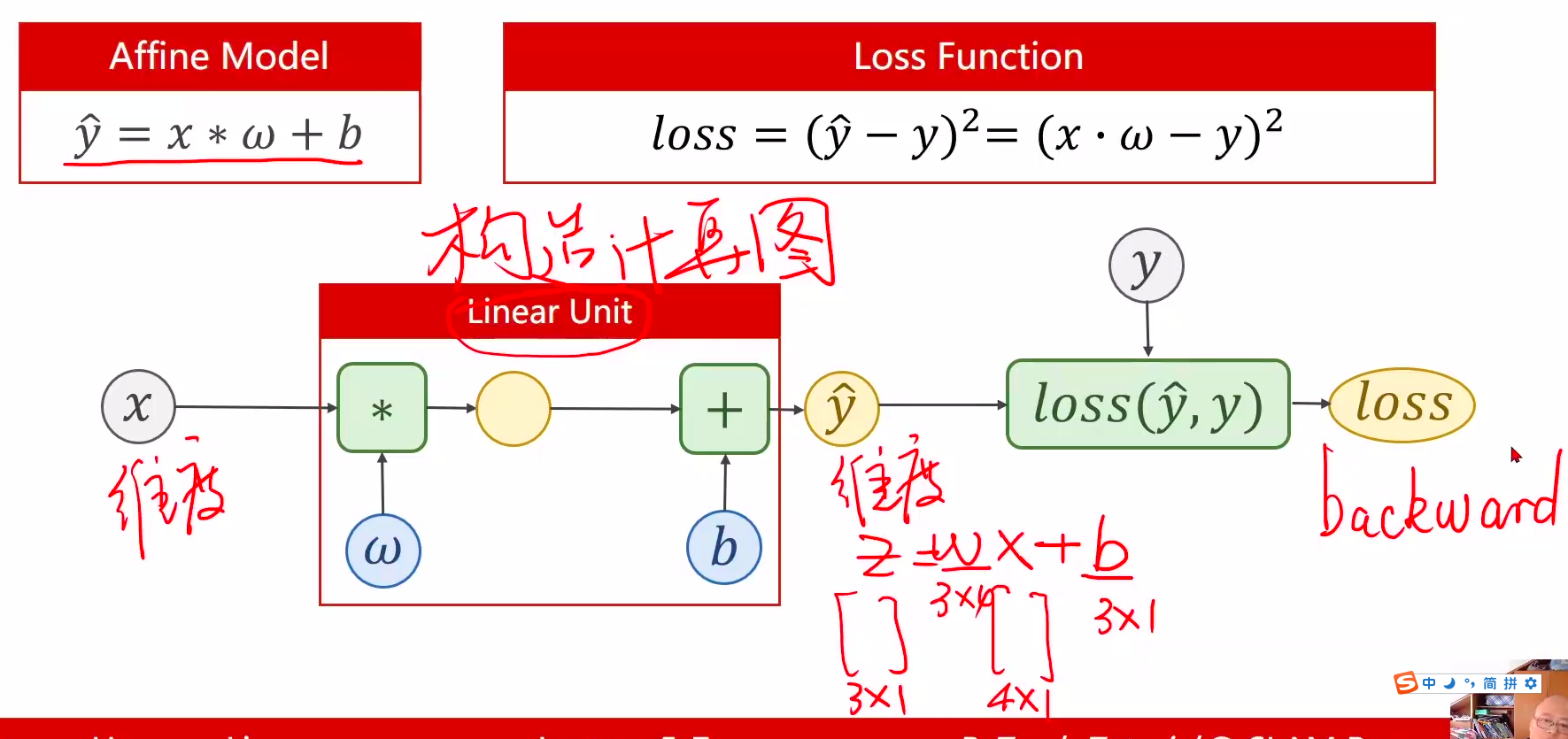
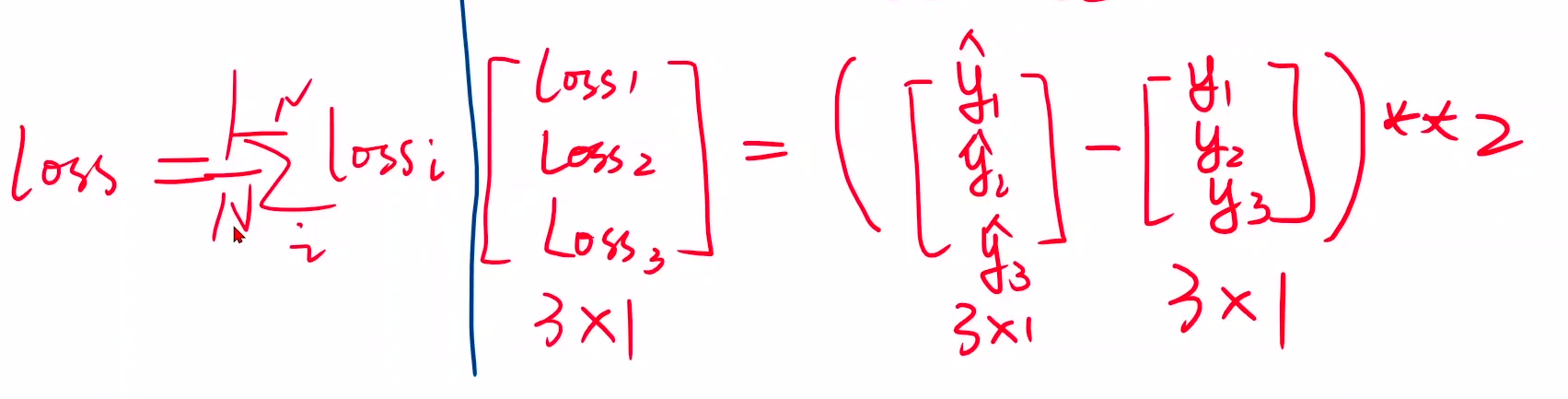
torch.nn.``Linear(in_features: int, out_features: int, bias: bool = True)
torch.nn.``Linear(in_features: int, out_features: int, bias: bool = True)
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) # 构造对象,执行wx+b的操作
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) # 构造对象,执行wx+b的操作
- 行表示样本
- 列表示feature
- 注意w维数
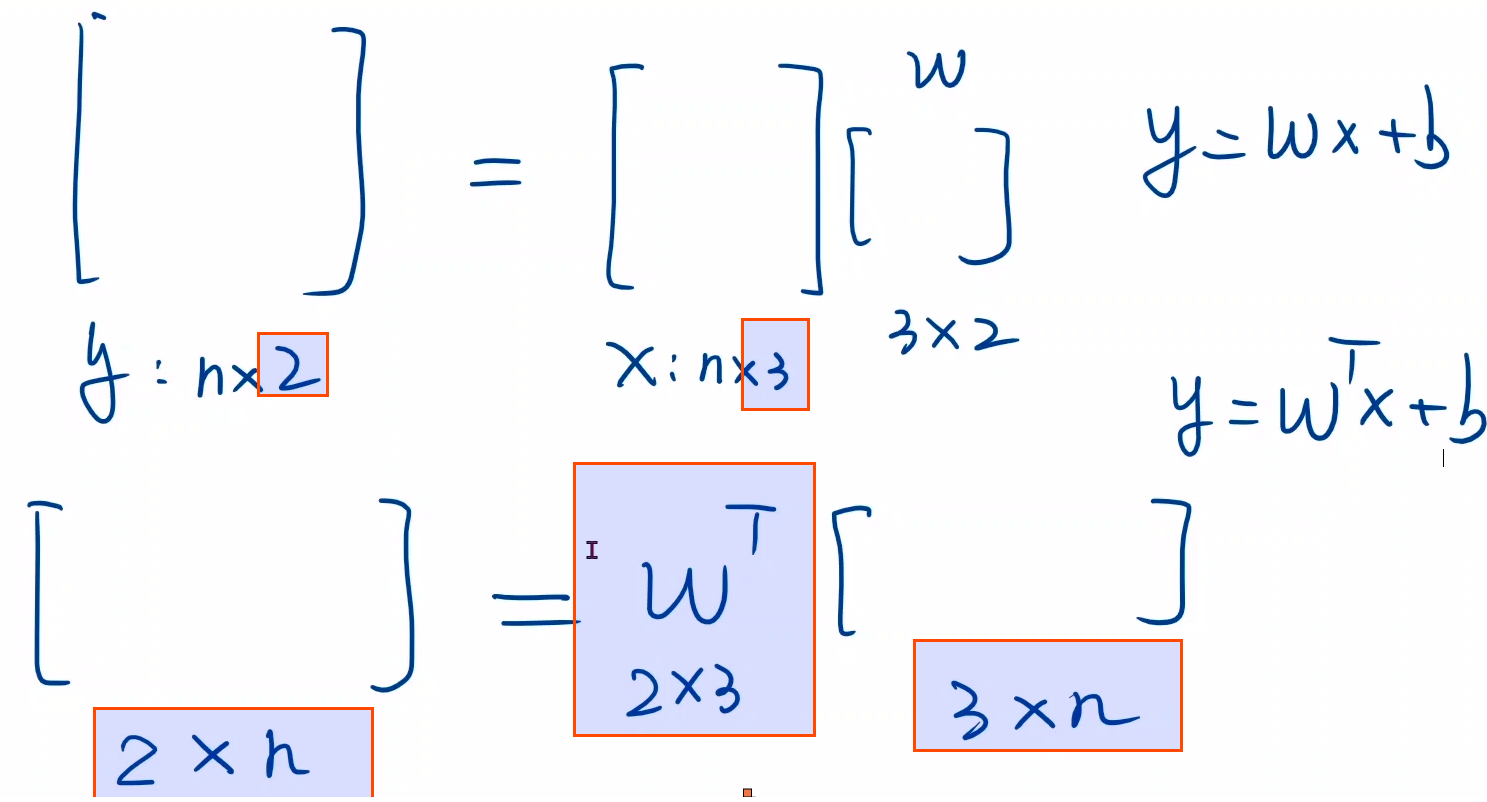
y_pred = self.linear(x) #可调用对象(对象括号里面加参数x),计算y=wx+b
小知识点:可调用对象
如果要使用一个可调用对象,那么在类的声明的时候要定义一个 call()函数就OK了,就像这样
class Foobar:
def __init__(self):
pass
def __call__(self,*args,**kwargs):
pass
其中参数*args代表把前面n个参数变成n元组,kwargsd会把参数变成一个词典,举个例子:**
def func(*args,**kwargs):
print(args)
print(kwargs)
#调用一下
func(1,2,3,4,x=3,y=5)
结果:
(1,2,3,4)
{‘x’:3,‘y’:5}
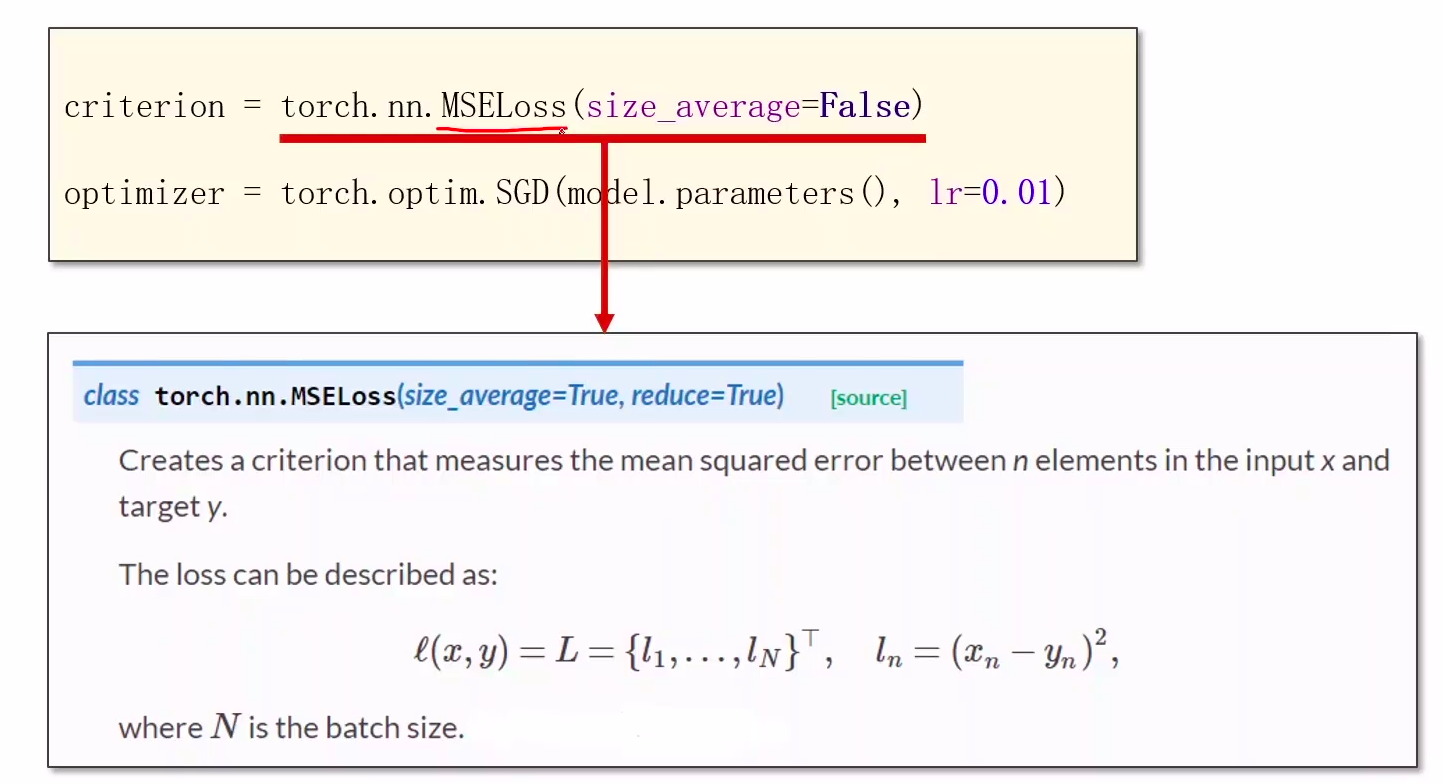
3 Construct loss and optimizer
- using PyTorch API 计算loss和optimizer
API:
- LOSS: https://pytorch.org/docs/1.7.0/nn.html#loss-functions
- optimals:https://pytorch.org/docs/1.7.0/optim.html
4 Training cycle
- forward, backward, update 前馈,反馈,更新
5 test

完整代码
'''
Description: 用Pytorch实现线性回归
https://blog.csdn.net/bit452/article/details/109677086
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44841652/article/details/105068509
Author: HCQ
Company(School): UCAS
Email: 1756260160@qq.com
Date: 2020-12-05 12:20:13
LastEditTime: 2021-06-08 21:23:22
FilePath: /pytorch/PyTorch深度学习实践/05用Pytorch实现线性回归.py
'''
import torch
# prepare dataset
# x,y是矩阵,3行1列 也就是说总共有3个数据,每个数据只有1个特征
x_data = torch.Tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.Tensor([[2.0], [4.0], [6.0]])
#design model using class
"""
our model class should be inherit from nn.Module, which is base class for all neural network modules.
member methods __init__() and forward() have to be implemented
class nn.linear contain two member Tensors: weight and bias
class nn.Linear has implemented the magic method __call__(),which enable the instance of the class can
be called just like a function.Normally the forward() will be called
"""
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module): # torch.nn.Module是父类
def __init__(self): # 构造函数(初始化)
super(LinearModel, self).__init__() # 调用父类的init super(LinearModel, self) == torch.nn.Module
# (1,1)是指输入x和输出y的特征维度,这里数据集中的x和y的特征都是1维的
# 该线性层需要学习的参数是w和b 获取w/b的方式分别是~linear.weight/linear.bias
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) # 构造对象,执行wx+b的操作,Linear也是继承自Model,并说明输入输出的维数,第三个参数默认为true,表示用到b
def forward(self, x):
y_pred = self.linear(x) #可调用对象(对象括号里面加参数x),计算y=wx+b
return y_pred
model = LinearModel() # 自动构建计算图,实现反向(自带的,不用写)
# construct loss and optimizer
# criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average = False)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction = 'sum')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01) # model.parameters()自动完成所有设计权重参数的初始化操作
# training cycle forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(100):
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward:predict 等同于self.linear(x_data)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # forward: loss
print(epoch, loss.item())
# print(epoch, loss) # loss是个对象,Tensor格式
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归零the grad computer by .backward() will be accumulated. so before backward, remember set the grad to zero
loss.backward() # 反向传播backward: autograd
optimizer.step() # update 参数,即更新w和b的值
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item())
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.Tensor([[4.0]])
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)