在空对象模式(Null Object Pattern)中,一个空对象取代 NULL 对象实例的检查。Null 对象不是检查空值,而是反应一个不做任何动作的关系。这样的 Null 对象也可以在数据不可用的时候提供默认的行为。
在空对象模式中,我们创建一个指定各种要执行的操作的抽象类和扩展该类的实体类,还创建一个未对该类做任何实现的空对象类,该空对象类将无缝地使用在需要检查空值的地方。
意图
通过对缺失对象的封装,以提供默认无任何行为的对象替代品
适用场景
满足下列条件时可以使用空对象模式
- 一个对象需要一个协作对象,但并无具体的协作对象
- 协作对象不需要做任何事情
优点
1.对于对象交互更加统一
2.解决部分语言不支持返回nil的问题
缺点
会增加空对象的开发量
示例
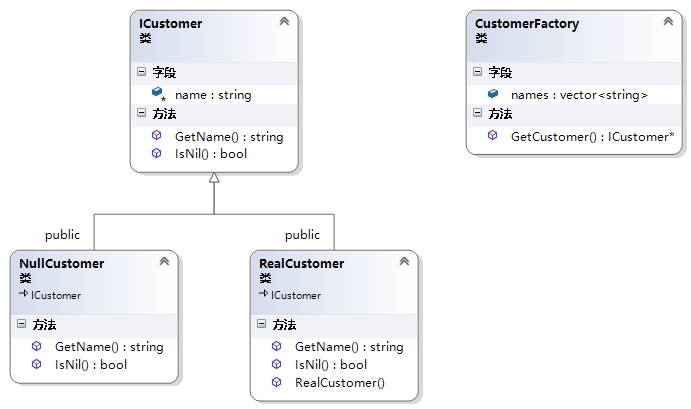
#include "stdafx.h"#include <iostream>#include <vector>class ICustomer{public:virtual bool IsNil()=0;virtual std::string GetName()=0;protected:std::string name;};class RealCustomer : public ICustomer{public:RealCustomer(std::string name){this->name = name;}virtual std::string GetName(){return name;}virtual bool IsNil(){return false;}};class NullCustomer : public ICustomer{public:virtual std::string GetName(){return "Invalid Customer";}virtual bool IsNil(){return true;}};class CustomerFactory{public:static std::vector<std::string> names;static ICustomer* GetCustomer(std::string name){for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++) {if (names[i] == name){return new RealCustomer(name);}}return new NullCustomer();}};std::vector<std::string> CustomerFactory::names = { "Rob", "Bob", "Laura" };int main(){ICustomer* customer1 = CustomerFactory::GetCustomer("Rob");ICustomer* customer2 = CustomerFactory::GetCustomer("Bob");ICustomer* customer3 = CustomerFactory::GetCustomer("Julie");ICustomer* customer4 = CustomerFactory::GetCustomer("Laura");std::cout << "Customers:" << std::endl;std::cout << customer1->GetName().c_str() << std::endl;std::cout << customer2->GetName().c_str() << std::endl;std::cout << customer3->GetName().c_str() << std::endl;std::cout << customer4->GetName().c_str() << std::endl;}
Customers:RobBobInvalid CustomerLaura

