计数排序的核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中。作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范围的整数。当输入的元素是 n 个 0 到 k 之间的整数时,它的运行时间是 O(n + k),计数排序不是比较排序,排序的速度快于任何比较排序算法。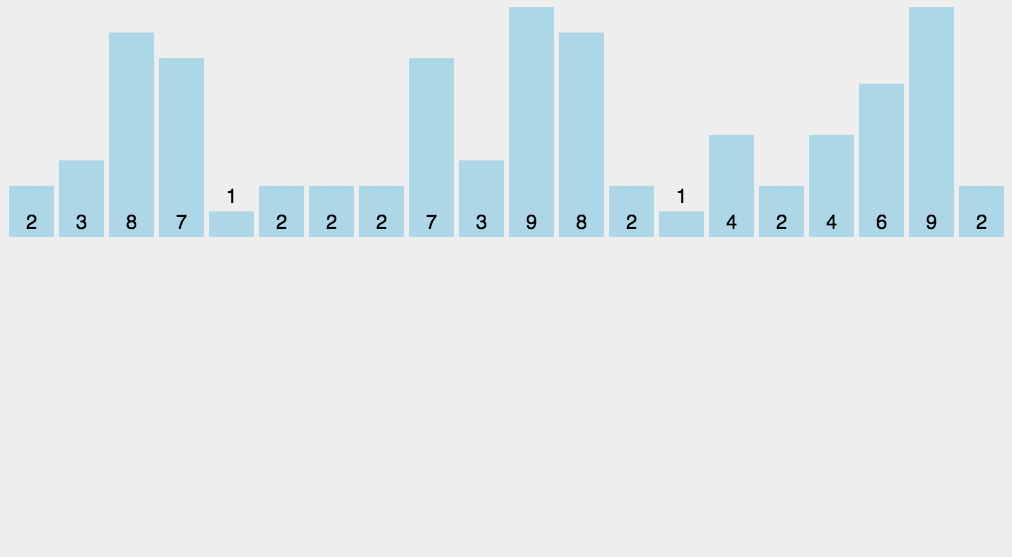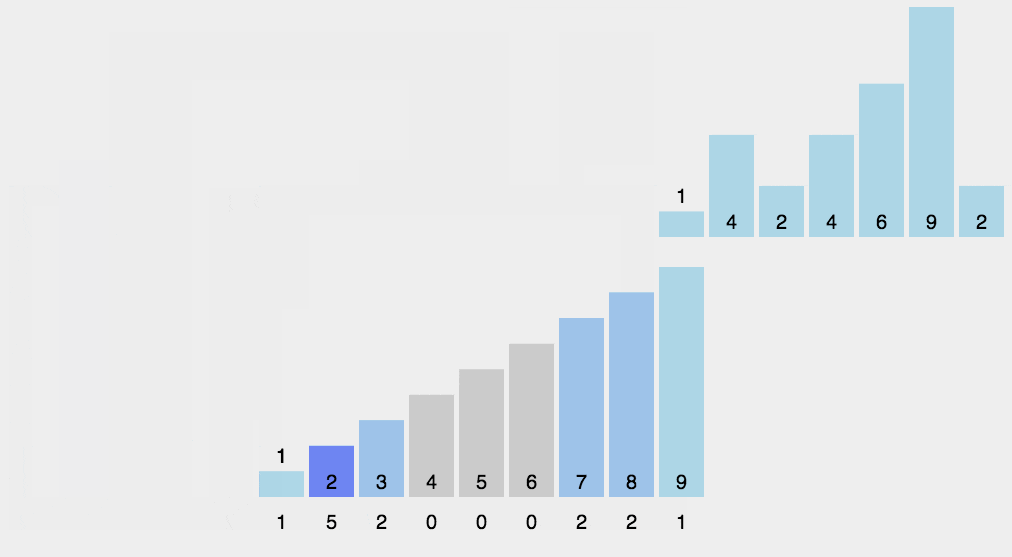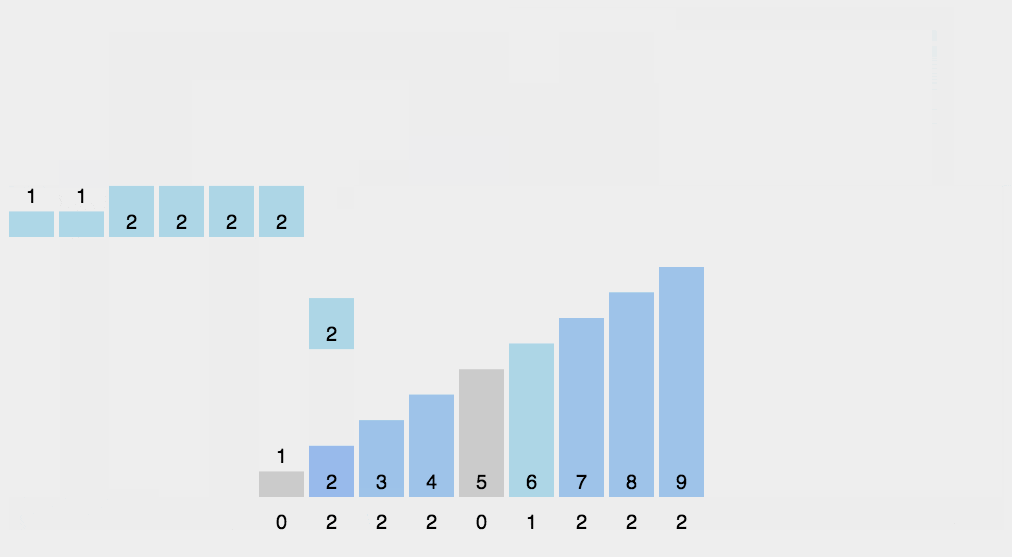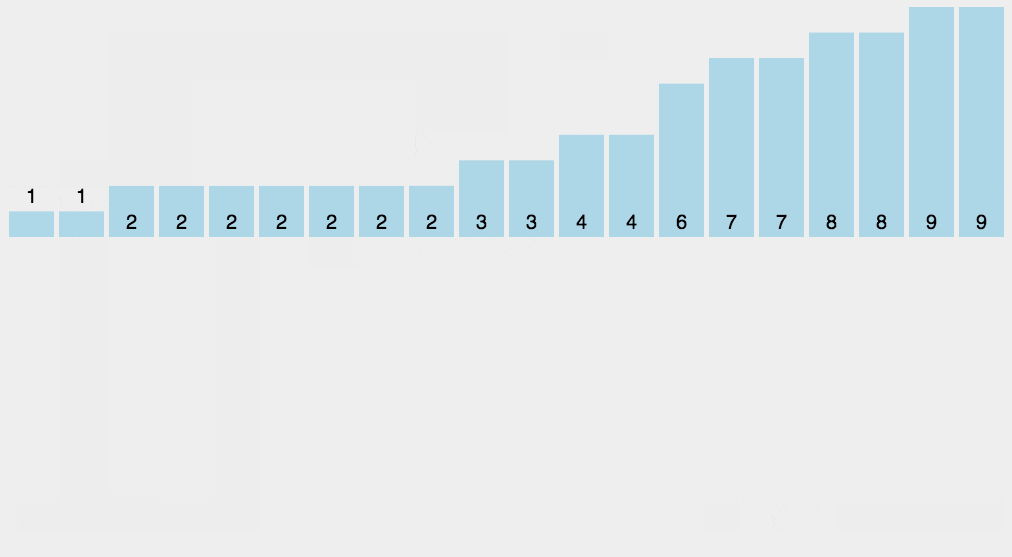
其思路是开辟一个长度为 maxValue+1(maxValue为待排序数据中最大值) 的统计数组,然后以待排序数组中的数值作为下标,对统计数组中对应位置的值进行+1操作,来统计该下标值出现的次数(即统计数组的下标为排序的值,统计数组下标位置存储的值作为该排序的值在原数组中出现的次数),然后再遍历统计数组,按照每一位出现的次数,输出到新的数组或者原数组中。
算法步骤:
- (1)找到最大值。- (2)遍历原数组,将值对应统计数组下标位置的值+1。- (3)遍历统计数组,输出到原数组或者新的数组。
一 普通实现方式
package com.sort.s08countingsort;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Arrays;public class CountingSortA {/*** (1)找到最大值。* (2)遍历原数组,将值对应统计数组下标位置的值+1。* (3)遍历统计数组,输出到原数组或者新的数组。*/public int[] sort(int[] sourceArray){// 对数组进行拷贝,不改变参数内容int[] arrToSort = Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, sourceArray.length);// (1)找到最大值int maxValue = findMaxValue(arrToSort);// 排序return countingSort(maxValue,arrToSort);}private int findMaxValue(int[] arr){int maxValue = arr[0];for(int value : arr ){maxValue=maxValue<value?value:maxValue;}return maxValue;}private int[] countingSort(int maxValue,int[] arr){// 记住,数组长度和数组统计位置是不同的,最大值为10时,要能统计10的次数,就要开辟的统计数组长度为11.int[] bucketArr = new int[maxValue+1];//(2)遍历原数组,将值对应统计数组下标位置的值+1。for(int value:arr){bucketArr[value]++;}//(3)遍历统计数组,输出到原数组或者新的数组。int sortIndex = 0;for(int bc = 0;bc<=maxValue;bc++){int count = bucketArr[bc];while(count >0){arr[sortIndex] = bc;count --;sortIndex++;}}return arr;}@Testpublic void testSort(){int[] nums = {5, 3, 4, 6, 7, 1, 2, 8, 4, 10, 100, 50, 30, 22, 34, 55, 43, 12, 31};CountingSortA countingSortA = new CountingSortA();countingSortA.println(countingSortA.sort(nums));}// 用于输出数组public void println(int [] a) {for(int x:a) {System.out.print(" "+x);}System.out.println("");}}
二 改进一下实现
找到待排序数组中最大值和最小值,统计数组的0号位置存储最小值出现的次数,因此,最大值存储的位置在maxValue-minValue,而统计数组的长度为maxValue-minValue+1。如:假如最小值为5,最大值为10,那么下标0的位置存储的是 5,最大值10存储的下标为 10 -5 =5,数组的长度为 6(统计的下标范围为0~5)。
package com.sort.s08countingsort;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Arrays;public class CountingSortB {/*** (1)找到最大值。* (2)遍历原数组,将值对应统计数组下标位置的值+1。* (3)遍历统计数组,输出到原数组或者新的数组。*/public int[] sort(int[] sourceArray){// 对数组进行拷贝,不改变参数内容int[] arrToSort = Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, sourceArray.length);// (1)找到最大值和最小值CountingRange countingRange = findMaxValue(arrToSort);// 排序return countingSort(countingRange,arrToSort);}private CountingRange findMaxValue(int[] arr){int maxValue = arr[0];int smallValue = arr[0];for(int value : arr ){maxValue=maxValue<value?value:maxValue;smallValue = smallValue>value?value:smallValue;}CountingRange countingRange = new CountingRange();countingRange.setMax(maxValue);countingRange.setSmall(smallValue);return countingRange;}private int[] countingSort(CountingRange countingRange,int[] arr){int bucketLen = countingRange.getMax() - countingRange.getSmall() +1;int[] bucketArr = new int[bucketLen];//(2)遍历原数组,将值对应统计数组下标位置的值+1。for(int value:arr){bucketArr[value-countingRange.getSmall()]++;}//(3)遍历统计数组,输出到原数组或者新的数组。int sortIndex = 0;for(int bc = 0;bc<bucketLen;bc++){int count = bucketArr[bc];while(count >0){arr[sortIndex] = bc+countingRange.getSmall();count --;sortIndex++;}}return arr;}@Testpublic void testSort(){int[] nums = {5, 3, 4, 6, 7, 1, 2, 8, 4, 10, 100, 50, 30, 22, 34, 55, 43, 12, 31};CountingSortB countingSortB = new CountingSortB();countingSortB.println(countingSortB.sort(nums));}// 用于输出数组public void println(int [] a) {for(int x:a) {System.out.print(" "+x);}System.out.println("");}class CountingRange{private int max;private int small;public int getMax() {return max;}public void setMax(int max) {this.max = max;}public int getSmall() {return small;}public void setSmall(int small) {this.small = small;}}}

