使用缓存依赖和chains
Yii支持需要缓存后端,但是使Yii缓存灵活的是依赖和依赖chaining支持。有一些情况,你不能简单的只缓存1个小时的数据,因为信息随时可能会边。
在这个小节中,我们将会学习如何缓存整个页面,并能在有更新时获取最新的数据。这个页面是一个仪表盘类型的,将会展示5个最新添加的文章,以及总数。
注意:注意一个操作不能被编辑 as it is added,但是一个文章可以。
准备
按照官方指南http://www.yiiframework.com/doc-2.0/guide-start-installation.html的描述,使用Composer包管理器创建一个新的yii2-app-basic应用。
- 在
config/web.php中激活缓存组件:
return [// ...'components' => ['cache' => ['class' => 'yii\caching\FileCache',],],];
- 设置一个新的数据库,并将它配置到
config/db.php中: - 运行如下migration:
<?phpuse yii\db\Schema;use yii\db\Migration;class m160308_093233_create_example_tables extends Migration{public function up(){$tableOptions = null;if ($this->db->driverName === 'mysql') {$tableOptions = 'CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci ENGINE=InnoDB';}$this->createTable('{{%account}}', ['id' => Schema::TYPE_PK,'amount' => Schema::TYPE_DECIMAL . '(10,2) NOT NULL',], $tableOptions);$this->createTable('{{%article}}', ['id' => Schema::TYPE_PK,'title' => Schema::TYPE_STRING . ' NOT NULL','text' => Schema::TYPE_TEXT . ' NOT NULL',], $tableOptions);}public function down(){$this->dropTable('{{%article}}');$this->dropTable('{{%account}}');}}
- 使用Yii为account和article表生成模型。
- 创建
protected/controllers/DashboardController.php:
<?phpnamespace app\controllers;use app\models\Account;use app\models\Article;use yii\web\Controller;class DashboardController extends Controller{public function actionIndex(){$total = Account::find()->sum('amount');$articles = Article::find()->orderBy('id DESC')->limit(5)->all();return $this->render('index', array('total' => $total,'articles' => $articles,));}public function actionRandomOperation(){$rec = new Account();$rec->amount = rand(-1000, 1000);$rec->save();echo 'OK';}public function actionRandomArticle(){$n = rand(0, 1000);$article = new Article();$article->title = "Title #".$n;$article->text = "Text #".$n;$article->save();echo 'OK';}}
- 创建
views/dashboard/index.php:
<?phpuse yii\helpers\Html;/* @var $this yii\web\View *//* @var $total int *//* @var $articles app\models\Article[] */?><h1>Total: <?= $total ?></h1><h2>5 latest articles:</h2><?php foreach($articles as $article): ?><h3><?= Html::encode($article->title) ?></h3><div><?= Html::encode($article->text) ?></div><?php endforeach ?>
- 运行
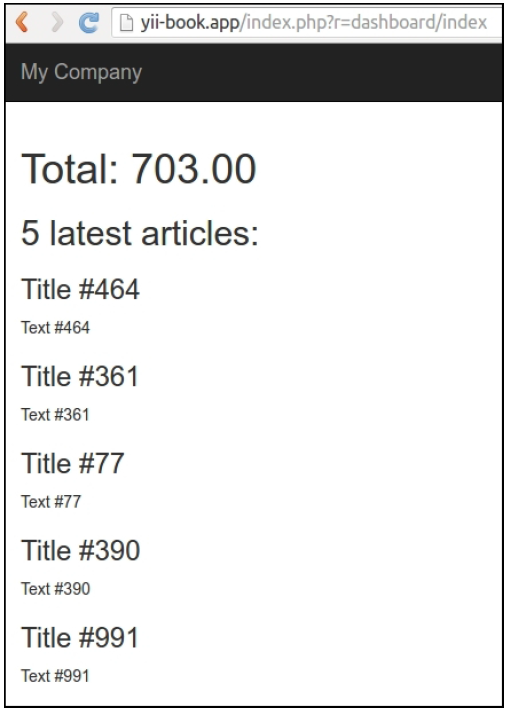
dashboard/random-operation和dashboard/random-article几次,然后,运行dashboard/index你将会看到如下所示的截图:
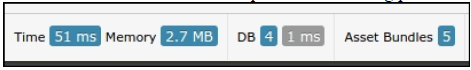
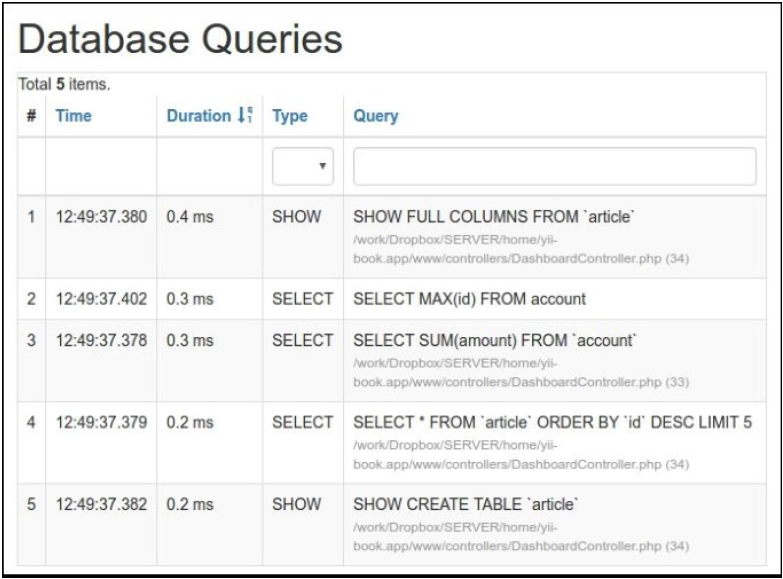
- 在页面的底部,点击调试面板上数据库查询的数量:
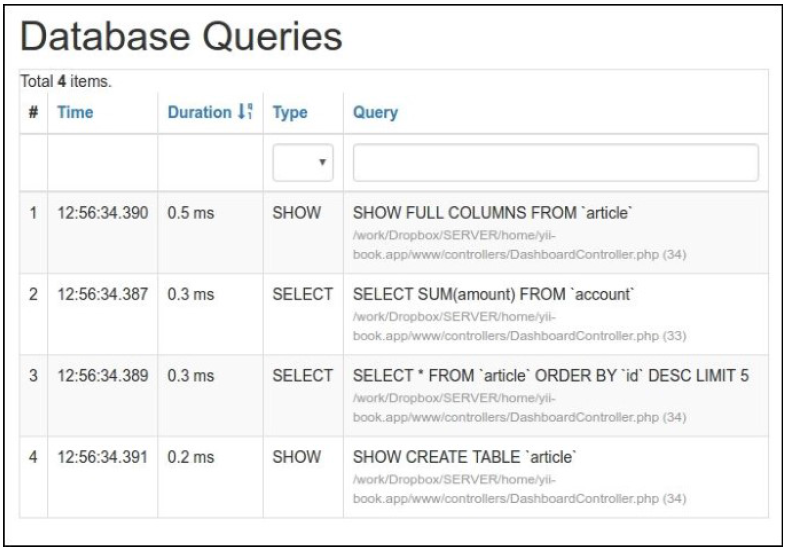
看到一个查询列表:
如何做…
执行如下步骤:
- 我们需要修改控制器的代码:
<?phpnamespace app\controllers;use app\models\Account;use app\models\Article;use yii\caching\DbDependency;use yii\caching\TagDependency;use yii\web\Controller;class DashboardController extends Controller{public function behaviors(){return ['pageCache' => ['class' => 'yii\filters\PageCache','only' => ['index'],'duration' => 24 * 3600 * 365, // 1 year'dependency' => ['class' => 'yii\caching\ChainedDependency','dependencies' => [new TagDependency(['tags' =>['articles']]),new DbDependency(['sql' => 'SELECT MAX(id) FROM ' . Account::tableName()])]],],];}public function actionIndex(){$total = Account::find()->sum('amount');$articles = Article::find()->orderBy('id DESC')->limit(5)->all();return $this->render('index', array('total' => $total,'articles' => $articles,));}public function actionRandomOperation(){$rec = new Account();$rec->amount = rand(-1000, 1000);$rec->save();echo 'OK';}public function actionRandomArticle(){$n = rand(0, 1000);$article = new Article();$article->title = "Title #".$n;$article->text = "Text #".$n;$article->save();TagDependency::invalidate(\Yii::$app->cache,'articles');echo 'OK';}}
- 完成了。现在,在加载
dashboard/index几次以后,你将会看到只有1个查询,如下所示:
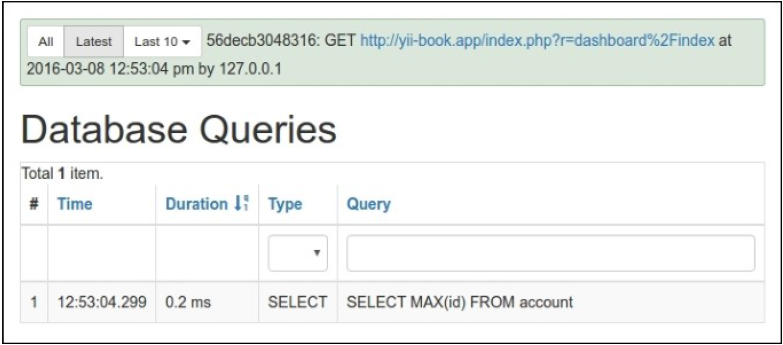
此外,尝试运行dashboard/random-operation或者dashboard/randomarticle,并刷新dashboard/index。数据将会改变:
工作原理…
为了修改最少的代码,并达到最高的性能,我们使用一个过滤器来作全页缓存:
public function behaviors(){return ['pageCache' => ['class' => 'yii\filters\PageCache','only' => ['index'],'duration' => 24 * 3600 * 365, // 1 year'dependency' => ['class' => 'yii\caching\ChainedDependency','dependencies' => [new TagDependency(['tags' => ['articles']]),new DbDependency(['sql' => 'SELECT MAX(id) FROM account'])]],],];}
先前的代码意味着我们在index动作中应用一个全页缓存。这个页面将会缓存1年,并且如果数据改变了,这个缓存将会刷新。因此,一般情况下,依赖工作如下:
- 按依赖中的描述,第一次运行会获取最新的数据,保存以备之后调用,并更新缓存
- 按依赖中的描述,获取最新的数据,获取保存的数据,然后比较两者
- 如果相等,使用缓存的数据
- 如果不相等,更新缓存,使用最新的数据,并保存最新依赖数据,以备以后调用
在我们的例子中,使用了两个类型的依赖——标签和DB。一个标签依赖使用自定义字符串标签标记数据,并检查它,来决定缓存是否无效,一个DB依赖使用SQL查询结果来达到相同的目的。
现在你可能有的问题是,“为什么有时候使用DB而有时候使用标签?”这是一个好问题。
使用DB依赖的目的是,替换重的计算,并选择一个轻的查询,尽可能获取少的数据。关于这种依赖最好的事情是,我们不需要在已有的代码中嵌入任何额外的逻辑。在我们的例子中,我们可以使用这种类型的依赖用于账户操作,但是不能用于文章,因为文章的内容会改变。因此,对于文章,我们设置一个全局标签,名叫文章,它表示我们可以手动调用来刷新文章缓存:
TagDependency::invalidate(\Yii::$app->cache, 'articles');
参考
欲了解更多关于缓存的信息,并使用缓存依赖,参考http://www.yiiframework.com/doc-2.0/guide-caching-overview.html。

