使用RBAC
基于角色的访问控制(RBAC)提供了简单但是非常强大的中心化访问控制。它是Yii中最强大的访问控制方法。在指导中有关于它的描述,但因为比较复杂和强大,如果不了解一些底层原理的话,比较难以理解。
在本小节中,我们将会take the roles hierarchy from the definitive guide, import it, and explain what is happening internally.
准备
- 按照官方指南http://www.yiiframework.com/doc-2.0/guide-start-installation.html的描述,使用Composer包管理器创建一个新的应用。
- 创建一个MySQL数据库并配置。
- 在
config/main.php和config/console.php中配置authManager组件:
return [// ...'components' => ['authManager' => ['class' => 'yii\rbac\DbManager',],// ...],];
- 运行migration:
yii migrate --migrationPath=@yii/rbac/migrations
如何做…
执行如下步骤:
- 创建访问规则
rbac/AuthorRule.php:
<?phpnamespace app\rbac;use yii\rbac\Rule;/*** Class AuthorRule.* @package app\rbac*/class AuthorRule extends Rule{public $name = 'isAuthor';/*** @param int|string $user* @param \yii\rbac\Item $item* @param array $params** @return bool*/public function execute($user, $item, $params){return isset($params['post']) ?$params['post']->createdBy == $user : false;}}
- 创建一个控制台命令
command/RbacController.php,initRBAC规则命令:
<?phpnamespace app\commands;use app\models\User;use Yii;use yii\console\Controller;/*** Class RbacController.* @package app\commands*/class RbacController extends Controller{public function actionInit(){$auth = Yii::$app->authManager;$createPost = $auth->createPermission('createPost');$createPost->description = 'Create a post';$updatePost = $auth->createPermission('updatePost');$updatePost->description = 'Update a post';$updatePost = $auth->createPermission('updatePost');$updatePost->description = 'Update a post';$deletePost = $auth->createPermission('deletePost');$deletePost->description = 'Delete a post';$readPost = $auth->createPermission('readPost');$readPost->description = 'Read a post';$authorRule = new \app\rbac\AuthorRule();// add permissions$auth->add($createPost);$auth->add($updatePost);$auth->add($deletePost);$auth->add($readPost);$auth->add($authorRule);// add the "updateOwnPost" permission and associate the rule with it.$updateOwnPost = $auth->createPermission('updateOwnPost');$updateOwnPost->description = 'Update own post';$updateOwnPost->ruleName = $authorRule->name;$auth->add($updateOwnPost);$auth->addChild($updateOwnPost, $updatePost);// create Author role$author = $auth->createRole('author');$auth->add($author);$auth->addChild($author, $createPost);$auth->addChild($author, $updateOwnPost);$auth->addChild($author, $readPost);// create Admin role$admin = $auth->createRole('admin');$auth->add($admin);$auth->addChild($admin, $updatePost);$auth->addChild($admin, $deletePost);$auth->addChild($admin, $author);// assign roles$auth->assign($admin, User::findByUsername('admin')->id);$auth->assign($author, User::findByUsername('demo')->id);echo "Done!\n";}}
- 在控制台中运行:
yii rbac/init
- 创建
controllers/RbacController.php:
<?phpnamespace app\controllers;use app\models\User;use stdClass;use Yii;use yii\filters\AccessControl;use yii\helpers\Html;use yii\web\Controller;/*** Class RbacController.*/class RbacController extends Controller{public function behaviors(){return ['access' => ['class' => AccessControl::className(),'rules' => [['allow' => true,'actions' => ['delete'],'roles' => ['deletePost'],],['allow' => true,'actions' => ['test'],],],],];}public function actionDelete(){return $this->renderContent(Html::tag('h1', 'Post deleted.'));}/*** @param $description* @param $rule* @param array $params** @return string*/protected function renderAccess($description, $rule, $params = []){$access = Yii::$app->user->can($rule, $params);return $description.': '.($access ? 'yes' : 'no');}public function actionTest(){$post = new stdClass();$post->createdBy = User::findByUsername('demo')->id;return $this->renderContent(Html::tag('h1', 'Current permissions').Html::ul([$this->renderAccess('Use can create post','createPost'),$this->renderAccess('Use can read post','readPost'),$this->renderAccess('Use can update post','updatePost'),$this->renderAccess('Use can own update post','updateOwnPost', ['post' => $post,]),$this->renderAccess('Use can delete post','deletePost'),]));}}
- 运行一次
rbac/test检查access to all the created permissions of the RBAC hierachy:
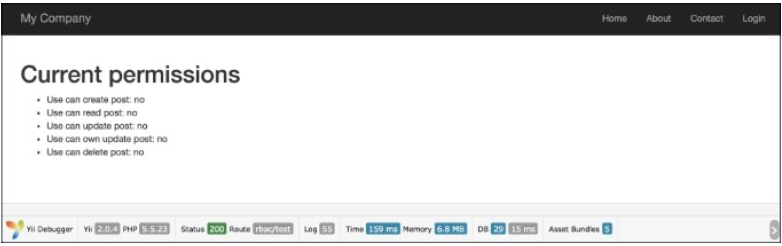
- 然后尝试使用
demo登录(密码是demo),再次运行rbac/test:
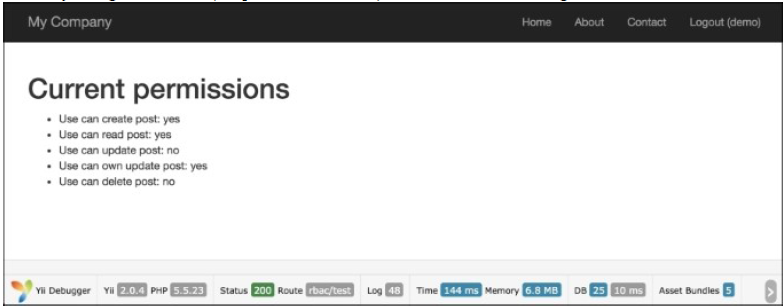
- 然后尝试使用
admin登录(密码是admin),再次运行rbac/test:
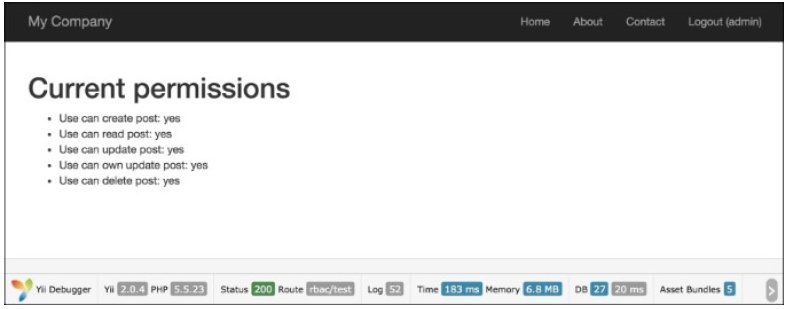
- 用
demo用户登录,运行rbac/delete:
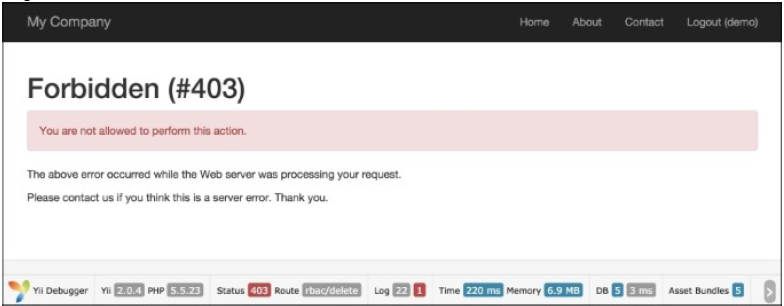
- 用
admin用户登录,运行rbac/delete:
工作原理…
Yii模仿NIST RBAC模型实现了一个一般的层次化的RBAC。它通过应用组件authManager提供了RBAC功能。
RBAC层级是一个有向无环图,也就是说,它由结点和有向连接边组成。有三种类型的结点:角色、权限和规则。
角色是权限(例如创建帖子和更新帖子)的集合。一个角色可以分配给一个或多个用户。为了检查用户是否有某个指定的权限,我们可以检查这个用户是否被赋予了拥有该权限的角色。
角色和权限都可以以等级化的方式组织。特别地,一个角色可以包含其它角色和权限,并且权限可以包含其它权限。Yii实现了一个偏序层级,它包含了特定的tree等级。当一个角色包含一个权限时,反过来说是不正确的。
为了测试权限,我们创建了两个动作。第一个动作是test,包含了创建权限和角色的检查器。第二个动作是delete,它被访问过滤器限制了访问。访问过滤的规则如下所示:
['allow' => true,'actions' => ['delete'],'roles' => ['deletePost'],],
这意味着,我们允许所有拥有deletePost权限的用户运行deletePost动作。Yii以检查deletePost权限开始。注意到访问规则元素被命名为roles,你可以指定一个RBAC等级节点,无论是角色、规则还是权限。检查updatePost是复杂的:
Yii::$app->user->can('updatePost', ['post' => $post]);
我们使用第二个参数来传递一个帖子(在我们的例子中,我们使用stdClass来模拟它)。如果用户以demo登录,然后获得了updatePost的权限。如果你很幸运,你只需要go through updatePost,updateOwnPost和作者。
因为updateOwnPost有一个定义好的规则,它会在传参给checkAccess时运行。如果结果为真,访问将会得到授权。因为Yii不知道最短的方法是什么,它会尝试检查所有可能性直至成功,或者没有剩余的备选项。
更多…
下面是一些有用的技巧,能让你更方便的使用RBAC。
保持层级简单和高效
遵守如下建议来提升性能,并降低层级复杂性:
- 避免给一个用户关联多个角色
- 不要连接相同类型的结点:例如,避免连接两个task
命名RBAC结点
一个复杂的层级如果不使用一些命名习惯的话会很难理解。能帮助我们降低复杂性的惯例是:
[group_][own_]entity_action
只有当当前用户是元素的拥有者时,才能修改这个元素的能力。这是,会使用own这个关键词。group只是一个命名空间。entity是我们工作的实体名称,action是我们执行的动作。
例如,如果我们需要创建一个规则,它决定了用户是否可以删除一个博客文章,我们把它命名为blog_post_delete。如果这个规则决定了用户是否可以编辑他自己的评论,我们将会把它命名为blog_own_comment_edit。
参考
为了了解更多关于SQL注入和使用Yii处理数据库,参考如下链接:

