内容可见注释
#simple note in learning pytorchimport torchimport numpy'''# create tensorx = torch.empty(5,3)y = torch.rand(5,3)z = torch.zeros(5,3)print(y)print(x)print(z)print (x.dtype)print(z.dtype)a=torch.tensor([5,5,3])print(a)b=torch.tensor([6,6,8])print(b)#basic operationb=a+bprint(b)b=torch.add(a,b)print(b)#special in placeb.add_(a)print(b)#resizetest=torch.rand(4,2)print(test)test=test.view(8)print(test)test=torch.rand(1)print(test)test2=test.item()print(test2)# transition between torch and numpy# they share the dataa=torch.ones(5)print (a)b=a.numpy()print(b)b[1]=2print(a)print(b)a =numpy.ones(5)b=torch.from_numpy(a)print(a)print(b)# if you have a GPU you can .....if torch.cuda.is_available():device=torch.device("cuda")print("yes I have")y=torch.ones_like(b,device=device)b=b.to(device)#warming up# try to build a simple two layer neural net (using numpy)N,D_in,H,D_out = 64,1000,100,10x=numpy.random.randn(N,D_in)y=numpy.random.randn(N,D_out)w1=numpy.random.randn(D_in,H)w2=numpy.random.randn(H,D_out)learning_rate=1e-6for t in range(500):# forward passh=x.dot(w1)h_Relu=numpy.maximum(h,0)y_pred=h_Relu.dot(w2)#compute loss and use square lossloss = numpy.square(y_pred-y).sum()print(t,loss)#backward pass# 1. compute gradiendgrad_y_pred=2.0*(y_pred-y)grad_w2 =h_Relu.T.dot(grad_y_pred)grad_h_relu=grad_y_pred.dot(w2.T)grad_h = grad_h_relu.copy()grad_h[h<0]=0grad_w1 = x.T.dot(grad_h)# Update weightsw1 -= learning_rate * grad_w1w2 -= learning_rate * grad_w2#now try to use torch to do the jobN,D_in,H,D_out = 64,1000,100,10x=torch.randn(N,D_in)y=torch.randn(N,D_out)w1=torch.randn(D_in,H)w2=torch.randn(H,D_out)learning_rate=1e-6for t in range(500):# forward passh=x.mm(w1)h_Relu=h.clamp(min=0)y_pred=h_Relu.mm(w2)#compute loss and use square lossloss = (y_pred-y).pow(2).sum().item()print(t,loss)#backward pass# 1. compute gradiendgrad_y_pred=2.0*(y_pred-y)grad_w2 =h_Relu.t().mm(grad_y_pred)grad_h_relu=grad_y_pred.mm(w2.t())grad_h = grad_h_relu.clone()grad_h[h<0]=0grad_w1 = x.T.mm(grad_h)# Update weightsw1 -= learning_rate * grad_w1w2 -= learning_rate * grad_w2#final version by using auto_backwardN,D_in,H,D_out = 64,1000,100,10x=torch.randn(N,D_in,requires_grad=True)#default is Falsey=torch.randn(N,D_out,requires_grad=True)w1=torch.randn(D_in,H,requires_grad=True)w2=torch.randn(H,D_out,requires_grad=True)learning_rate=1e-6for t in range(500):# forward passy_pred =x.mm(w1).clamp(min=0).mm(w2)#compute loss and use square lossloss = (y_pred-y).pow(2).sum()#loss_num=loss.item()print(t, loss_num)#backward pass# compute gradiendloss.backward()# Update weightswith torch.no_grad():w1 -= learning_rate * w1.gradw2 -= learning_rate * w2.gradw1.grad.zero_()w2.grad.zero_()'''import torch.nn as nnimport timetime_start=time.time()N,D_in,H,D_out = 64,1000,100,10x=torch.randn(N,D_in,requires_grad=True)#default is Falsey=torch.randn(N,D_out,requires_grad=True)model=torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(D_in,H),torch.nn.ReLU(),torch.nn.Linear(H,D_out),)if torch.cuda.is_available():model=model.cuda()x=x.cuda()y=y.cuda()loss_func=nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')learning_rate=1e-6for t in range(20000):# forward passy_pred =model(x)#compute loss and use square lossloss = loss_func(y_pred , y)#loss_num=loss.item()print(t)#backward pass# compute gradiendloss.backward()with torch.no_grad():for param in model.parameters():param-=learning_rate*param.gradmodel.zero_grad()# Update weightstime_end=time.time()print('totally cost',time_end-time_start)
最后分别使用GPU和CPU运行尝试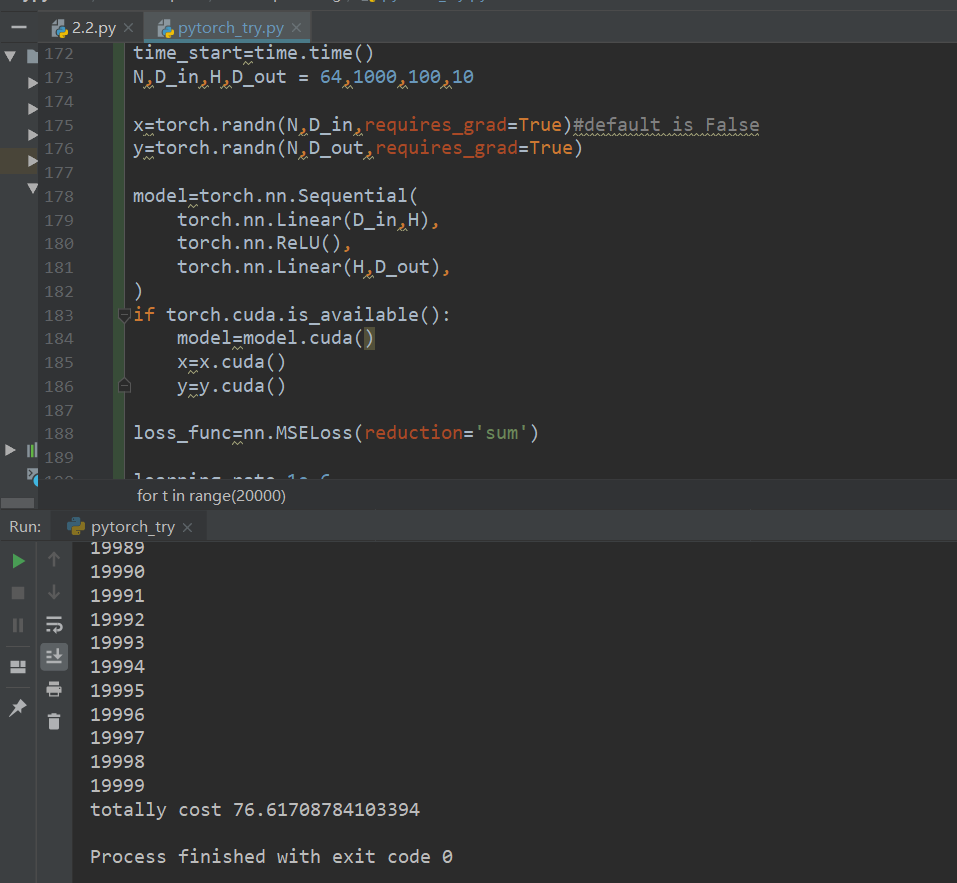
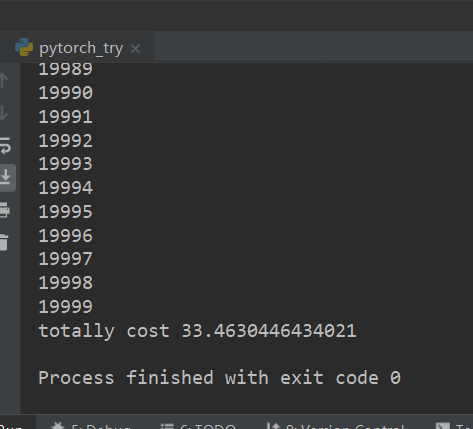
从而有了若干问题
- 使用CPU运行时间只有GPU一半,,反而更快
- 使用了模型进行统一化之后,反而收敛效果更差,loss值降不下来

