我们经常会用NFS做后端存储来做测试,因为其部署简单。但是在生产中我们并不会去选择NFS,更多的是Ceph、Glusterfs等等,今天就来带大家了解在kubernetes中使用Glusterfs。
一、安装Glusterfs
1.1、规划
| 主机名 | IP |
|---|---|
| glusterfs-master | 10.1.10.128 |
| glusterfs-node01 | 10.1.10.129 |
| glusterfs-node02 | 10.1.10.130 |
1.2、安装
我们这里采用的是YUM安装,有兴趣的也可以用其他安装方式,比如源码安装
(1)、配置hosts(/etc/hosts)
10.1.10.129 glusterfs-node0110.1.10.130 glusterfs-node0210.1.10.128 glusterfs-master
(2)、YUM安装
# yum install centos-release-gluster -y# yum install -y glusterfs glusterfs-server glusterfs-fuse glusterfs-rdma
(3)、启动并配置开机自启动
# systemctl start glusterd.service && systemctl enable glusterd.service
(4)、如果防火墙是开启的需要配置防火墙
# 如果需要可以加iptables# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 24007 -j ACCEPT# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 24008 -j ACCEPT# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 2222 -j ACCEPT# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m multiport --dports 49152:49251 -j ACCEPT
(5)、将节点加入集群
# gluster peer probe glusterfs-master# gluster peer probe glusterfs-node01# gluster peer probe glusterfs-node02
(6)、查看集群状态
# gluster peer statusNumber of Peers: 2Hostname: glusterfs-node01Uuid: bb59f0ee-1901-443c-b721-1fe3a1edebb4State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)Other names:glusterfs-node0110.1.10.129Hostname: glusterfs-node02Uuid: a0d1448a-d0f2-432a-bb45-b10650db106cState: Peer in Cluster (Connected)Other names:10.1.10.130
1.3、测试
(1)、创建volume
# 创建数据目录,节点都要操作# mkdir /data/gluster/data -p# gluster volume create glusterfs_volume replica 3 glusterfs-master:/data/gluster/data glusterfs-node01:/data/gluster/data glusterfs-node02:/data/gluster/data force
(2)、查看volume
# gluster volume infoVolume Name: glusterfs_volumeType: ReplicateVolume ID: 53bdad7b-d40f-4160-bd42-4b70c8278506Status: CreatedSnapshot Count: 0Number of Bricks: 1 x 3 = 3Transport-type: tcpBricks:Brick1: glusterfs-master:/data/gluster/dataBrick2: glusterfs-node01:/data/gluster/dataBrick3: glusterfs-node02:/data/gluster/dataOptions Reconfigured:transport.address-family: inetstorage.fips-mode-rchecksum: onnfs.disable: onperformance.client-io-threads: off
(3)、启动volume
# gluster volume start glusterfs_volume
(4)、安装client
# yum install -y glusterfs glusterfs-fuse
(5)、挂载
# mount -t glusterfs glusterfs-master:glusterfs_volume /mnt
1.4、调优
# 开启 指定 volume 的配额$ gluster volume quota k8s-volume enable# 限制 指定 volume 的配额$ gluster volume quota k8s-volume limit-usage / 1TB# 设置 cache 大小, 默认32MB$ gluster volume set k8s-volume performance.cache-size 4GB# 设置 io 线程, 太大会导致进程崩溃$ gluster volume set k8s-volume performance.io-thread-count 16# 设置 网络检测时间, 默认42s$ gluster volume set k8s-volume network.ping-timeout 10# 设置 写缓冲区的大小, 默认1M$ gluster volume set k8s-volume performance.write-behind-window-size 1024MB
二、在k8s中测试
2.1、简单测试
(1)、配置endpoints
# curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/examples/master/volumes/glusterfs/glusterfs-endpoints.json
修改glusterfs-endpoints.json,配置GlusterFS集群信息
{"kind": "Endpoints","apiVersion": "v1","metadata": {"name": "glusterfs-cluster"},"subsets": [{"addresses": [{"ip": "10.1.10.128"}],"ports": [{"port": 2020}]}]}
port可以随意写,ip为GlusterFS的IP地址
创建配置文件
# kubectl apply -f glusterfs-endpoints.json# kubectl get epNAME ENDPOINTS AGEglusterfs-cluster 10.1.10.128:2020 7m26skubernetes 10.1.10.128:6443 27d
(2)、配置service
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/examples/master/volumes/glusterfs/glusterfs-service.json
修改配置文件,我这里仅修改了端口
{"kind": "Service","apiVersion": "v1","metadata": {"name": "glusterfs-cluster"},"spec": {"ports": [{"port": 2020}]}}
创建service对象
# kubectl apply -f glusterfs-service.json# kubectl get svcNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEglusterfs-cluster ClusterIP 10.254.44.189 <none> 2020/TCP 10mkubernetes ClusterIP 10.254.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 27d
(3)、创建pod测试
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/examples/master/volumes/glusterfs/glusterfs-pod.json
修改配置文件,修改volumes下的path为我们上面创建的volume名
{"apiVersion": "v1","kind": "Pod","metadata": {"name": "glusterfs"},"spec": {"containers": [{"name": "glusterfs","image": "nginx","volumeMounts": [{"mountPath": "/mnt/glusterfs","name": "glusterfsvol"}]}],"volumes": [{"name": "glusterfsvol","glusterfs": {"endpoints": "glusterfs-cluster","path": "glusterfs_volume","readOnly": true}}]}}
创建Pod对象
# kubectl apply -f glusterfs-pod.yaml# kubectl get podNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEglusterfs 1/1 Running 0 51spod-demo 1/1 Running 8 25h# kubectl exec -it glusterfs -- df -hFilesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted onoverlay 17G 2.5G 15G 15% /tmpfs 64M 0 64M 0% /devtmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 2.5G 15G 15% /etc/hosts10.1.10.128:glusterfs_volume 17G 5.3G 12G 31% /mnt/glusterfsshm 64M 0 64M 0% /dev/shmtmpfs 910M 12K 910M 1% /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccounttmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /proc/acpitmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /proc/scsitmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/firmware
我们从磁盘挂载情况可以看到挂载成功了。
2.2、静态PV测试
(1)、创建pv(glusterfs-pv.yaml)
apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumemetadata:name: glusterfs-pvspec:capacity:storage: 5MiaccessModes:- ReadWriteManyglusterfs:endpoints: glusterfs-clusterpath: glusterfs_volume---apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: glusterfs-pvcspec:accessModes:- ReadWriteManyresources:requests:storage: 5Mi
创建pv和pvc对象
# kubectl apply -f glusterfs-pv.yaml# kubectl get pvNAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGEglusterfs-pv 5Mi RWX Retain Bound default/glusterfs-pvc 15s# kubectl get pvcNAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGEglusterfs-pvc Bound glusterfs-pv 5Mi RWX 18s
从上面可知绑定成功,可以自定写一个pod进行测试。
2.3、动态PV测试
在这里我们需要借助heketi来管理Glusterfs。
Heketi 提供了丰富的RESTful API 用来对于Glusterfs的volume进行管理。Heketi可以同时管理多个cluster,每个cluster由多个node组成,每个node都是一个物理机,准确的说是一个裸盘。然后每个裸有多个bricks,而volume就是多个bricks组成的,但是,一个volume不可以跨node组成。示意图如下所示。
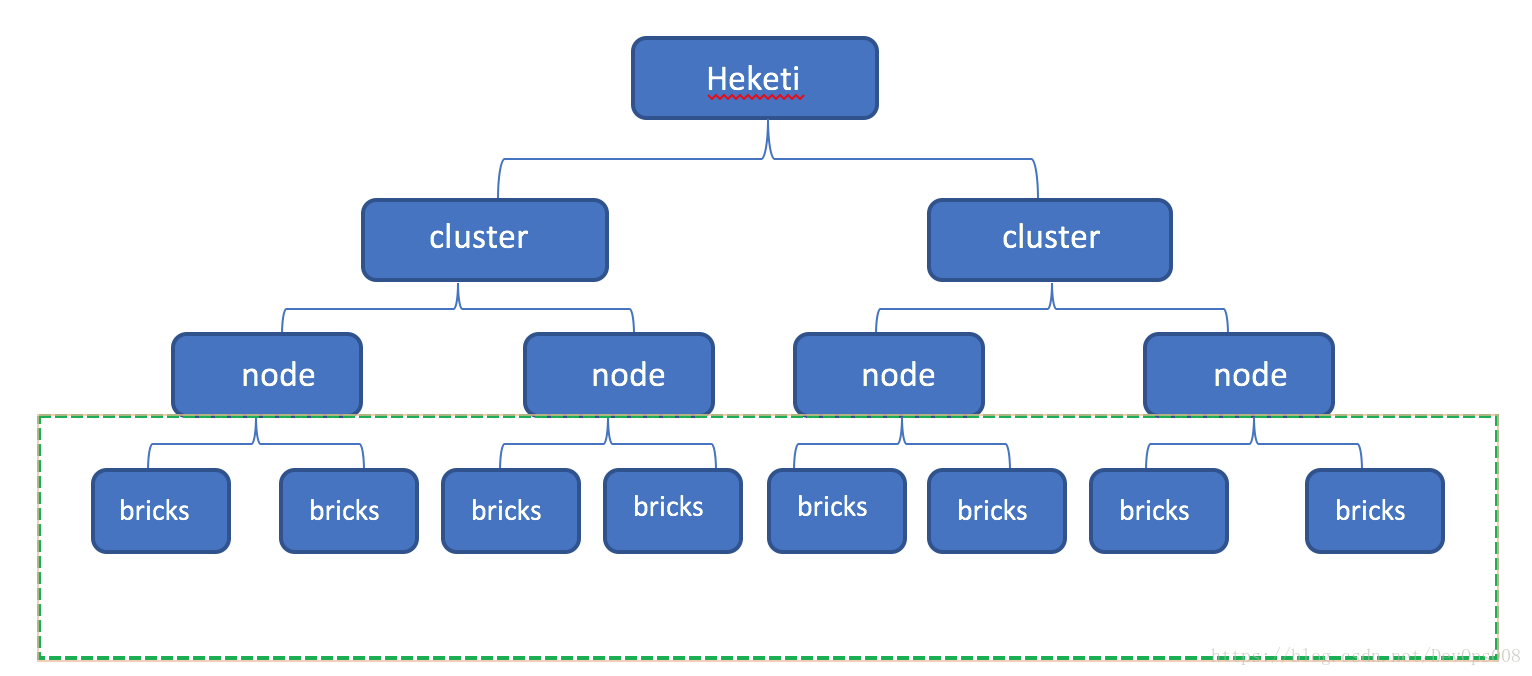
参考文档:https://blog.csdn.net/DevOps008/article/details/80757974
2.3.1、安装Heketi
(1)、安装
# yum -y install heketi heketi-client
(2)、配置heketi(/etc/heketi/heketi.json)
{"_port_comment": "Heketi Server Port Number","port": "48080", # 请求端口,默认是8080"_use_auth": "Enable JWT authorization. Please enable for deployment","use_auth": false,"_jwt": "Private keys for access","jwt": {"_admin": "Admin has access to all APIs","admin": {"key": "admin@P@ssW0rd" # 管理员密码},"_user": "User only has access to /volumes endpoint","user": {"key": "user@P@ssW0rd" # 普通用户密码}},"_glusterfs_comment": "GlusterFS Configuration","glusterfs": {"_executor_comment": ["Execute plugin. Possible choices: mock, ssh","mock: This setting is used for testing and development."," It will not send commands to any node.","ssh: This setting will notify Heketi to ssh to the nodes."," It will need the values in sshexec to be configured.","kubernetes: Communicate with GlusterFS containers over"," Kubernetes exec api."],"executor": "ssh","_sshexec_comment": "SSH username and private key file information","sshexec": {"keyfile": "/etc/heketi/private_key", # ssh私钥目录"user": "root", # ssh用户"port": "22", # ssh端口"fstab": "/etc/fstab"},"_kubeexec_comment": "Kubernetes configuration","kubeexec": {"host" :"https://kubernetes.host:8443","cert" : "/path/to/crt.file","insecure": false,"user": "kubernetes username","password": "password for kubernetes user","namespace": "OpenShift project or Kubernetes namespace","fstab": "Optional: Specify fstab file on node. Default is /etc/fstab"},"_db_comment": "Database file name","db": "/var/lib/heketi/heketi.db","_loglevel_comment": ["Set log level. Choices are:"," none, critical, error, warning, info, debug","Default is warning"],"loglevel" : "debug"}}
说明:heketi用来管理cluster的,其中配置地方在executor,其管理方式有以下三种
- mock
- ssh
- kubernetes
mock,顾名思义就是测试,在这种模式下,可以对于自己的配置文件什么的进行检验,但是处于此模式下,虽然你可以看到node添加成功,volume创建成功,但是这些volume是不可用的,无法挂载的。所以如果要在SVT或者PROD环境用的话,一定要用ssh或者kubernetes模式。我们这里是用的ssh模式。
(3)、配置免密
# ssh-keygen -t rsa -q -f /etc/heketi/private_key -N ""# ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/private_key.pub root@10.1.10.128# ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/private_key.pub root@10.1.10.129# ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/private_key.pub root@10.1.10.130
(4)、启动heketi
# 给目录授权# chown heketi.heketi /etc/heketi/ -R# systemctl enable heketi.service && systemctl start heketi.service# 测试# curl http://10.1.10.128:48080/helloHello from Heketi
(5)、配置topology
拓扑信息用于让Heketi确认可以使用的存储节点、磁盘和集群,必须自行确定节点的故障域。故障域是赋予一组节点的整数值,这组节点共享相同的交换机、电源或其他任何会导致它们同时失效的组件。必须确认哪些节点构成一个集群,Heketi使用这些信息来确保跨故障域中创建副本,从而提供数据冗余能力,Heketi支持多个Gluster存储集群。
配置Heketi拓扑注意以下几点:
- 可以通过topology.json文件定义组建的GlusterFS集群;
- topology指定了层级关系:clusters —> nodes —> node/devices —> hostnames/zone;
- node/hostnames字段的manage建议填写主机ip,指管理通道,注意当heketi服务器不能通过hostname访问GlusterFS节点时不能填写hostname;
- node/hostnames字段的storage建议填写主机ip,指存储数据通道,与manage可以不一样,生产环境管理网络和存储网络建议分离;
- node/zone字段指定了node所处的故障域,heketi通过跨故障域创建副本,提高数据高可用性质,如可以通过rack的不同区分zone值,创建跨机架的故障域;
- devices字段指定GlusterFS各节点的盘符(可以是多块盘),必须是未创建文件系统的裸设备。
以上内容来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/itzgr/p/11913342.html#_labelTop
配置文件如下(/etc/heketi/topology.json)
{"clusters": [{"nodes": [{"node": {"hostnames": {"manage": ["10.1.10.128"],"storage": ["10.1.10.128"]},"zone": 1},"devices": ["/dev/sdb1" # 必须是未创建文件系统的裸磁盘]},{"node": {"hostnames": {"manage": ["10.1.10.129"],"storage": ["10.1.10.129"]},"zone": 1},"devices": ["/dev/sdb1"]},{"node": {"hostnames": {"manage": ["10.1.10.130"],"storage": ["10.1.10.130"]},"zone": 1},"devices": ["/dev/sdb1"]}]}]}
重要说明:devices字段指定GlusterFS各节点的盘符(可以是多块盘),必须是未创建文件系统的裸设备
由于每次使用heketi-cli命令的时候都需要写用户名、密码等,我们就将其写入环境变量,方便操作。
# echo "export HEKETI_CLI_SERVER=http://10.1.10.128:48080" >> /etc/profile.d/heketi.sh# echo "alias heketi-cli='heketi-cli --user admin --secret admin@P@ssW0rd'" >> ~/.bashrc# source /etc/profile.d/heketi.sh# source ~/.bashrc# echo $HEKETI_CLI_SERVERhttp://10.1.10.128:48080
(6)、创建cluster
# heketi-cli --server $HEKETI_CLI_SERVER --user admin --secret admin@P@ssW0rd topology load --json=/etc/heketi/topology.jsonCreating cluster ... ID: cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19Allowing file volumes on cluster.Allowing block volumes on cluster.Creating node 10.1.10.128 ... ID: 5216dafba986a087d7c3b1e11fa36c05Adding device /dev/sdb1 ... OKCreating node 10.1.10.129 ... ID: e384286825957b60213cc9b2cb604744Adding device /dev/sdb1 ... OKCreating node 10.1.10.130 ... ID: 178a8c6fcfb8ccb02b1b871db01254c2Adding device /dev/sdb1 ... OK
(7)、查看集群信息
# 查看集群列表# heketi-cli cluster listClusters:Id:cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19 [file][block]# 查看集群详细信息# heketi-cli cluster info cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19# 查看节点信息# heketi-cli node list# 查看节点详细信息# heketi-cli node info 68f16b2d54acf1c18e354ec46aa736ad
2.3.2、创建volume测试
# heketi-cli volume create --size=2 --replica=2Name: vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Size: 2Volume Id: 4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Cluster Id: cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19Mount: 10.1.10.129:vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Mount Options: backup-volfile-servers=10.1.10.130,10.1.10.128Block: falseFree Size: 0Reserved Size: 0Block Hosting Restriction: (none)Block Volumes: []Durability Type: replicateDistribute Count: 1Replica Count: 2# heketi-cli volume listId:4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0 Cluster:cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19 Name:vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0# heketi-cli volume info 4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Name: vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Size: 2Volume Id: 4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Cluster Id: cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19Mount: 10.1.10.129:vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0Mount Options: backup-volfile-servers=10.1.10.130,10.1.10.128Block: falseFree Size: 0Reserved Size: 0Block Hosting Restriction: (none)Block Volumes: []Durability Type: replicateDistribute Count: 1Replica Count: 2# 挂载# mount -t glusterfs 10.1.10.129:vol_4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0 /mnt# 删除# heketi-cli volume delete 4f1a171ab06adf80460c84f2132e96e0
2.3.3、在k8s中测试
(1)、创建需要使用的secret(heketi-secret.yaml)
apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: heketi-secretdata:key: YWRtaW5AUEBzc1cwcmQ=type: kubernetes.io/glusterfs
其中key必须是base64转码后的,命令如下:
echo -n "admin@P@ssW0rd" | base64
(2)、创建storageclass(heketi-storageclass.yaml)
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: heketi-storageclassparameters:resturl: "http://10.1.10.128:48080"clusterid: "cca360f44db482f03297a151886eea19"restauthenabled: "true" # 若heketi开启认证此处也必须开启auth认证restuser: "admin"secretName: "heketi-secret" # name/namespace与secret资源中定义一致secretNamespace: "default"volumetype: "replicate:3"provisioner: kubernetes.io/glusterfsreclaimPolicy: Delete
说明:
- provisioner:表示存储分配器,需要根据后端存储的不同而变更;
- reclaimPolicy: 默认即”Delete”,删除pvc后,相应的pv及后端的volume,brick(lvm)等一起删除;设置为”Retain”时则保留数据,若需删除则需要手工处理;
- resturl:heketi API服务提供的url;
- restauthenabled:可选参数,默认值为”false”,heketi服务开启认证时必须设置为”true”;
- restuser:可选参数,开启认证时设置相应用户名;
- secretNamespace:可选参数,开启认证时可以设置为使用持久化存储的namespace;
- secretName:可选参数,开启认证时,需要将heketi服务的认证密码保存在secret资源中;
- clusterid:可选参数,指定集群id,也可以是1个clusterid列表,格式为”id1,id2”;
- volumetype:可选参数,设置卷类型及其参数,如果未分配卷类型,则有分配器决定卷类型;如”volumetype: replicate:3”表示3副本的replicate卷,”volumetype: disperse:4:2”表示disperse卷,其中‘4’是数据,’2’是冗余校验,”volumetype: none”表示distribute卷
(3)、创建pvc(heketi-pvc.yaml)
apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: heketi-pvcannotations:volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: heketi-storageclassspec:accessModes:- ReadWriteOnceresources:requests:storage: 1Gi
(4)、查看sc和pvc的信息
# kubectl get scNAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGEheketi-storageclass kubernetes.io/glusterfs Delete Immediate false 6m53s# kubectl get pvcNAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGEglusterfs-pvc Bound glusterfs-pv 5Mi RWX 26hheketi-pvc Bound pvc-0feb8666-6e7f-451d-ae6f-7f205206b225 1Gi RWO heketi-storageclass 82s
(5)、创建Pod挂载pvc(heketi-pod.yaml)
kind: PodapiVersion: v1metadata:name: heketi-podspec:containers:- name: heketi-containerimage: busyboxcommand:- sleep- "3600"volumeMounts:- name: heketi-volumemountPath: "/pv-data"readOnly: falsevolumes:- name: heketi-volumepersistentVolumeClaim:claimName: heketi-pvc
创建Pod对象并查看结果
# kubectl apply -f heketi-pod.yaml# kubectl get podNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEglusterfs 1/1 Running 0 26hheketi-pod 1/1 Running 0 2m55s
在pod中写入文件进行测试
# kubectl exec -it heketi-pod -- /bin/sh/ # cd /pv-data//pv-data # echo "text" > 1111.txt/pv-data # ls1111.txt
在存储节点查看是否有我们在pod中写入的文件
# cd /var/lib/heketi/mounts/vg_bffb11849513dded78f671f64e76750c/brick_6ff640a2d45a7f146a296473e7145ee7[root@k8s-master brick_6ff640a2d45a7f146a296473e7145ee7]# lltotal 0drwxrwsr-x 3 root 2000 40 Feb 7 14:27 brick[root@k8s-master brick_6ff640a2d45a7f146a296473e7145ee7]# cd brick/[root@k8s-master brick]# lltotal 4-rw-r--r-- 2 root 2000 5 Feb 7 14:27 1111.txt

