一、栈
1. 运用场景


2. 代码实现
package com.atguigu.stack;public class Calculator {public static void main(String[] args) {// 完成表达式的运算String expression = "3+2*6-2";// 创建2个栈,数栈和符号栈ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);// 定义需要的相关变量int index = 0; // 用于扫描int num1 = 0;int num2 = 0;int oper = 0;int result = 0;String keepNum = null;char ch = ' '; //将每次扫描得到的char保存到ch中// 开始用while语句扫描expressionwhile (true) {// 依次得到expression中的每一个字符ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);// 判断是数字还是符号if (operStack.isOper(ch)) {// 如果是运算符,则需要判断当前的符号栈是否为空if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {// 对符号进行优先级比较if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.pop();oper = operStack.pop();result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, (char) oper);// 把运算的结果入数栈numStack.push(result);// 把当前的运算符入符号栈operStack.push(ch);} else {// 如果为空则直接入栈operStack.push(ch);}}} else {// 如果是数,则直接入数栈// 当是多位数时,不能发现是数就入数栈。需要向expression后再看一位,如果是数就继续扫描,如果是符号就入栈// 因此需要定义一个字符串变量keepNum += ch;if (index == expression.length() - 1) {numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum)); // 根据ASK码将字符转为数字} else {// 注意:只是往后看一位,不是index++if (!operStack.isOper(expression.substring(index + 1, index + 2).charAt(0))) {numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum)); // 根据ASK码将字符转为数字// 注意:keepNum需要清空keepNum = "";}// 让index+1并判断是否扫描到expression最后了index++;if (index >= expression.length()) {break;}}}// 当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序的从数栈和符号栈中pop出相应的数和符号,并运行while (true) {// 如果符号栈为空,则计算到了最后,数栈中只有一个数字(即结果)if (operStack.isEmpty()) {break;}num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.cal(num1, num2, (char) oper);numStack.push(result);}System.out.printf("表达式%s=%d", expression, numStack.pop());}}// 数字栈static class ArrayStack2 {// 定义栈的大小private int maxSize;private int[] stack; // 数组模拟栈,int类型的元素private int top = -1; //栈底,初始化没有数据// 构造器public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {this.maxSize = maxSize;}public boolean inFull() {return top == maxSize - 1;}public boolean isEmpty() {return top == -1;}// 入栈public void push(int value) {// 先判断栈满没满if (inFull()) {System.out.println("栈满!");return;}top++;stack[top] = value;}// 出栈public int pop() {// 实质:将栈顶的数据返回if (isEmpty()) {// 抛出异常throw new RuntimeException("空栈,没有数据");}int value = stack[top];return value;}// 遍历栈,从栈顶往下遍历public void list() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("空栈,没有数据");return;}for (int i = top; i > 0; i--) {System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d出栈\n!", i, stack[i]);}}// 返回运算符的优先级,优先级是程序员来定的。优先级使用数字来表示,数值越大,优先级越高public int priority(int oper) {if (oper == '*' || oper == '/') {return 1; // 乘法和除法的优先级高} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {return 0; // 加法和减法的优先级底} else {return -1; // 假设当前的计算式中只有加减乘除}}// 判断是不是一个运算符public boolean isOper(char val) {return val == '*' || val == '/' || val == '+' || val == '-';}// 计算方法public int cal(int num1, int num2, char oper) {int res = 0; // res用于存放计算的结果switch (oper) {case '+':res = num1 + num2;break;case '-':res = num2 - num1;break;case '*':res = num1 * num2;break;case '/':res = num2 / num1;break;}return res;}// 栈满public int peek() {return stack[top];}}}
3. 栈的前缀、中缀和后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
3.1 前缀:波兰表达式
3.2 后缀:逆波兰表达式
package com.atguigu.stack;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Stack;public class PolandNotationDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 先定义一个逆波兰表达式// (3+4)*5-6 ==> 3 4 + 5 * 6 -String suffixExpresson = "3 4 + 5 * 6 -";List<String> rpnList = getListString(suffixExpresson);}/*** 从最开始的方法--扫描字符串,改为将suffixExpression放入一个ArrayList中* step2: 通过配合栈的形式,完成运算*/// 将逆波兰表达式依次放入一个ArrayList中public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpresson) {// 将suffixExpressopm进行分割String[] splits = suffixExpresson.split(" ");List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (String item : splits) {list.add(item);}return list;}// 完成计算public static int cal(List<String> ls) {// 创建一个栈Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();for (String item : ls) {// 使用正则表达式取数if (item.matches("\\d+")) {// 匹配的是多位数stack.push(item);} else {// pop出2个数并运算,然后入栈int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());int res = 0;if (item.equals("+")) {res = num1 + num2;} else if (item.equals("-")) {res = num2 - num1;} else if (item.equals("*")) {res = num1 * num2;} else if (item.equals("/")) {res = num2 / num1;} else{throw new RuntimeException("运算符有问题!");}// 把res入栈stack.push(""+res);}}return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());}}
4. 如何将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
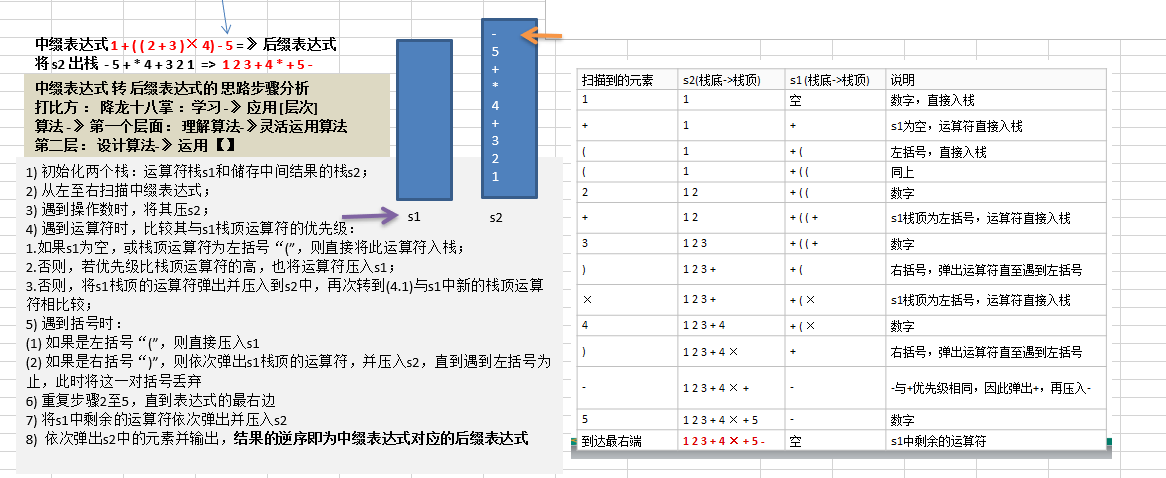
// 将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
public List<String> parseSuffixExpressionList(List<String> ls){
// 定义2个栈
Stack<String> s1= new Stack<String>(); // 符号栈
// 说明:因为s2 这个栈,在这个转换过程中,没有pop操作,而且后面我们还需要逆序输出,因此比较麻烦
// 这里我们不用栈的结构,直接使用List
// Stack<String> s2= new Stack<String>();
List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<String>();
// 遍历ls
for (String item : ls) {
// 如果是一个数,就加入到s2
if(item.matches("\\d+")){
s2.add(item);
}else if(item.equals("(")){
s1.push(item);
}else if(item.equals("(")){
// 如果是右括号,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃
while(!s1.peek().equals(")")){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop(); // 消除左括号
}else{
// 当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到s2中,再次转到(4.1)与s1中新的栈顶运算符进行比较
// 优先级比较高低的方法
while(s1.size()!=0 && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item)){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
// 还需要将item压入栈
s1.push(item);
}
// 将s1的元素加入到s2中
while (s1.size()!=0){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
return s2; //因为是存放到List,因此按顺序存入就是逆波兰表达式
}
return s2;
}
`比较运算符优先级的类:
// 编写比较运算符高低的类
class Operation{
// 加减乘除的优先级
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 2;
private static int DIV = 2;
// 写一个方法返回对应优先级的数字
public static int getValue(String operation){
int result = 0;
switch (operation) {
case "+":
result=ADD;
break;
case "-":
result=SUB;
break;
case "*":
result=MUL;
break;
case "/":
result=DIV;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符!");
break;
}
return result;
}
}

